Содержание
- 2. Plan What is the bronchitis? The types of bronchitis Anatomy of the bronchioles Who can get
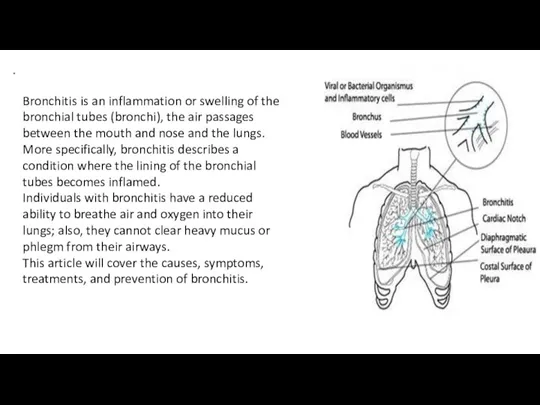
- 3. . Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes (bronchi), the air passages between
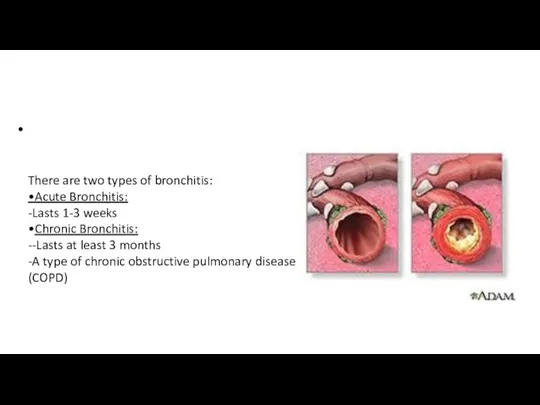
- 4. • There are two types of bronchitis: •Acute Bronchitis: -Lasts 1-3 weeks •Chronic Bronchitis: --Lasts at
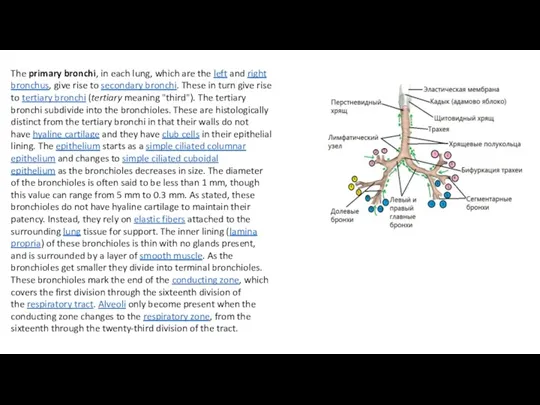
- 5. The primary bronchi, in each lung, which are the left and right bronchus, give rise to
- 6. Who can get bronchitis? •People of all ages and ethnicity can get chronic bronchitis but it’s
- 7. Causes Bronchitis is caused by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes. Acute bronchitis is usually caused
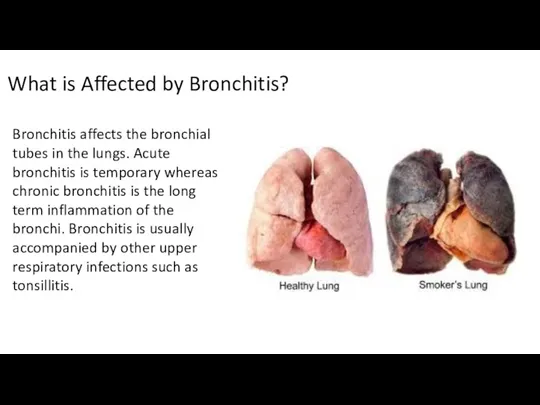
- 8. What is Affected by Bronchitis? Bronchitis affects the bronchial tubes in the lungs. Acute bronchitis is
- 9. What are symptoms of bronchitis? For both types of bronchitis the symptoms are: •Coughing •Production of
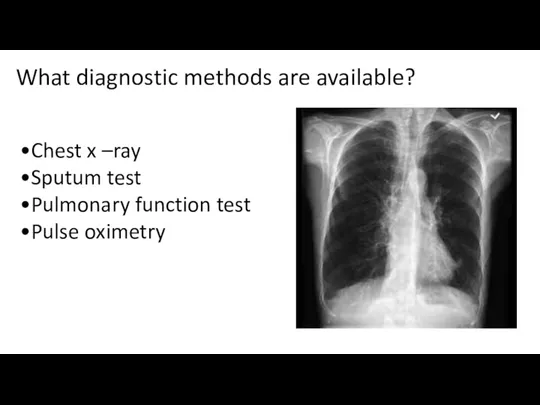
- 10. What diagnostic methods are available? •Chest x –ray •Sputum test •Pulmonary function test •Pulse oximetry
- 11. What treatments are available? •For acute bronchitis, most cases are resolved without medical treatment in 2
- 12. Side effects of treatment : Different types of antibiotics have different side effects. Common side effects
- 13. Is the bronchitis curable? What is the probable outcome after treatment? Bronchitis is a curable disease.
- 14. References : Retrieved from http://www.emedicinehealth.com/ Bronchitis - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis - Flu (Seasonal) - C-Health.
- 16. Скачать презентацию








 Формирование культурно-гигиенических навыков у детей дошкольного возраста
Формирование культурно-гигиенических навыков у детей дошкольного возраста Опухоли. Теории развития опухоли
Опухоли. Теории развития опухоли Коленный сустав. Функциональная анатомия, биомеханика, виды коррекции и лечения патологии КС
Коленный сустав. Функциональная анатомия, биомеханика, виды коррекции и лечения патологии КС Инфекция мочевой системы у детей
Инфекция мочевой системы у детей Геморрагический инсульт. Внутримозговое кровоизлияние. Субарахноидальное кровоизлияние
Геморрагический инсульт. Внутримозговое кровоизлияние. Субарахноидальное кровоизлияние Физиология крови
Физиология крови Изучение мнения пациентов об имидже врача
Изучение мнения пациентов об имидже врача Жүре пайда болған (ЖИТС, СПИД ағылш. AIDS) иммундық дефицитiнiң синдромы - Вич
Жүре пайда болған (ЖИТС, СПИД ағылш. AIDS) иммундық дефицитiнiң синдромы - Вич Внутриутробная задержка роста плода. Этиология. Классификация, формы, степени
Внутриутробная задержка роста плода. Этиология. Классификация, формы, степени Вчення про м'язи
Вчення про м'язи Противомикробные и противопаразитные средства
Противомикробные и противопаразитные средства Пневмоторакс. Классификация пневмоторакса
Пневмоторакс. Классификация пневмоторакса Современные репродуктивные технологии в лечении женского бесплодия
Современные репродуктивные технологии в лечении женского бесплодия Cоматикалық аурулар кезіндегі психикалық бұзылыстар
Cоматикалық аурулар кезіндегі психикалық бұзылыстар Постстрептококковый гломерулонефрит. Острый гломерулонефрит. Этиология и патогенез. Клинические варианты. Клиника и диагностика
Постстрептококковый гломерулонефрит. Острый гломерулонефрит. Этиология и патогенез. Клинические варианты. Клиника и диагностика Алергічні реакції
Алергічні реакції Основные средства повышения работоспособности и восстановления организма спортсменов после физических нагрузок
Основные средства повышения работоспособности и восстановления организма спортсменов после физических нагрузок Функциональные методы диагностики в кардиологии
Функциональные методы диагностики в кардиологии Рентген сәулелер
Рентген сәулелер ЛЕКЦИЯ ВГ_
ЛЕКЦИЯ ВГ_ Программа реабилитации пожилых лиц с сосудистой деменцией
Программа реабилитации пожилых лиц с сосудистой деменцией Оценка тяжести состояния пациентов с циррозом печени
Оценка тяжести состояния пациентов с циррозом печени Методы отбора проб воздуха для контроля его загрязнения и методика измерения концентрации твердых аэрозолей (пыли) в воздухе
Методы отбора проб воздуха для контроля его загрязнения и методика измерения концентрации твердых аэрозолей (пыли) в воздухе Подготовка пациента к наркозу, разговор с владельцем
Подготовка пациента к наркозу, разговор с владельцем Системная красная волчанка
Системная красная волчанка Интересные факты о людях
Интересные факты о людях Терапиялық стоматология. Тісжегіні емдеу қағидалары. Қателіктері және асқынулары, оларды жою жолдары, алдын алу
Терапиялық стоматология. Тісжегіні емдеу қағидалары. Қателіктері және асқынулары, оларды жою жолдары, алдын алу Цукровий діабет
Цукровий діабет