Содержание
- 2. Caries Prevention By Professor Nagwa Khattab Professor of Pediatric and Community Dentistry Ain Shams University
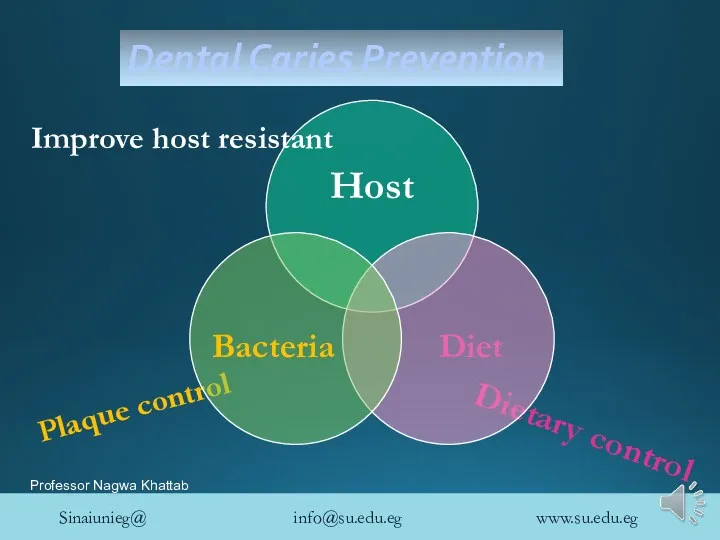
- 3. Plaque control Dietary control Dental Caries Prevention Improve host resistant
- 4. Strategies for caries prevention Modifying caries promoting ingredients of the diet: Reduction of carbohydrate Sucrose substitutes
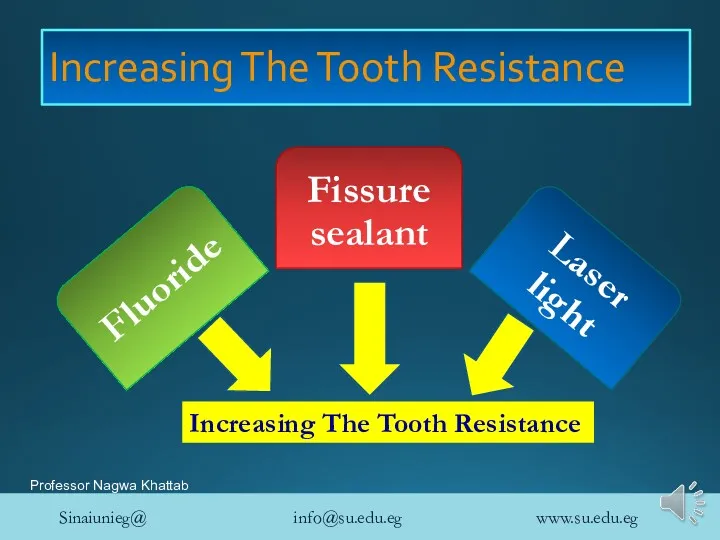
- 5. Caries prevention by Increasing the tooth resistance
- 6. Increasing The Tooth Resistance
- 7. FLUORIDE
- 8. What is fluoride? Halogen. Electronegative (F-) Most active element. Not present in the free form. Possess
- 9. Sources of fluoride
- 10. Sources of fluoride Soil: Rocks, soil, and volcanic rocks Water: Sea water (1.2-1.4 mg/kg) Rivers (
- 11. Food: Meat and poultry contain little fluoride Sea foods may contain 2.5ppm Most of beverages &
- 12. Metabolism
- 13. Metabolism Absorption : Over than 85% of the ingested fluoride is absorbed through the GIT &
- 14. Soft tissue: The kidney , heart and lunges accumulate the maximum amount of fluoride Brain and
- 15. Excretion of fluoride: Kidney: 30% within 3 hrs and 40-60% within 24 hrs. Gut :10% is
- 16. Fluoride and dental health
- 17. Uptake of fluoride by the teeth Before eruption: During calcification and further amounts of fluoride are
- 18. Fluoride and dental health Affinity between fluoride ions and hydroxyapetite of teeth and bone. Inverse relationship
- 19. Mode of action of fluoride Ionic exchange. Bacterial inhibition Enzymatic inhibition (inhibits glycolysis) Aids in remineralization
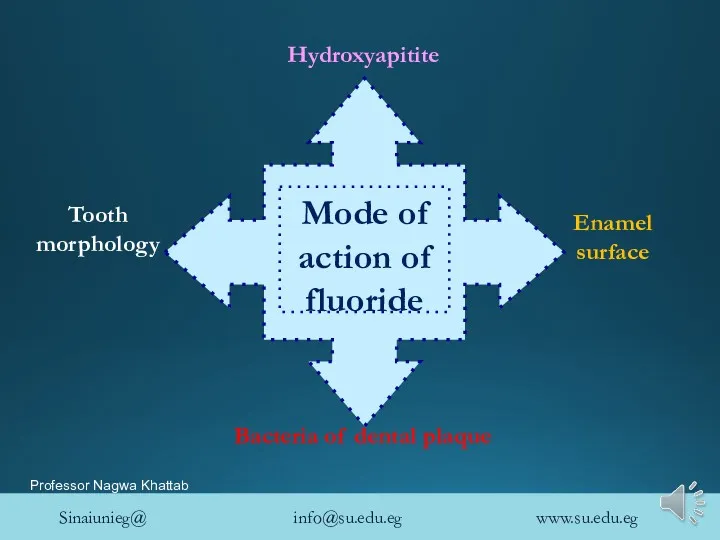
- 20. Hydroxyapitite Enamel surface Tooth morphology Bacteria of dental plaque
- 21. Mode of action of fluoride Action on hydroxyapitite Decreasing its solubility Improving its crystalinity Remineralization Action
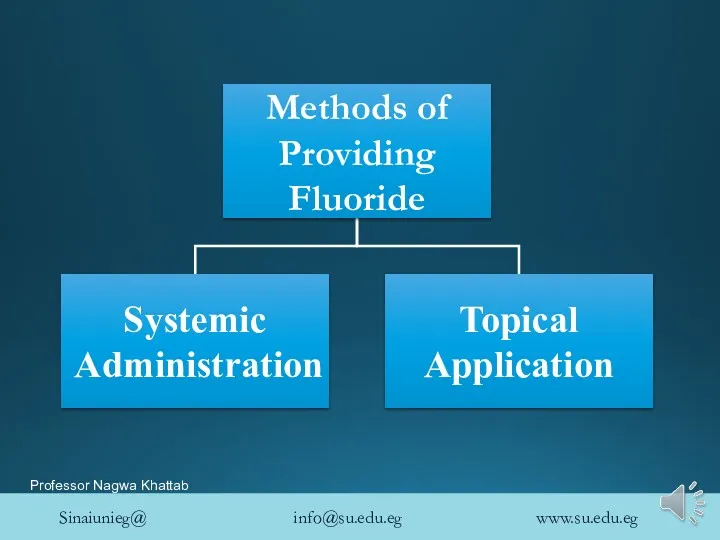
- 22. Methods of Providing Fluoride
- 24. Systemic Fluoride Administration Fluoridation of water supply Fluoridation of School water supplies Fluoride supplements Fluoride incorporation
- 25. Fluoridation of water supply Definition: The adjustment of the natural fluoride concentration of fluoride deficient water
- 26. Fluoridation of water supply Fluoridation of the public water supply at 1 ppm has been shown
- 27. Fluoridation of water supply The optimal dose of fluoride ingested daily in children from 0.5 to
- 28. The recommended optimal fluoride doses 0.7 to 1.2 ppm In Egypt the fluoride concentration of Nile
- 29. Fluoridation of School water supplies Fluoridation of school water supply is the best approach if fluoridation
- 30. Fluoride supplements Supplements can be in the form of tablets, drops or syrups. The usual dose
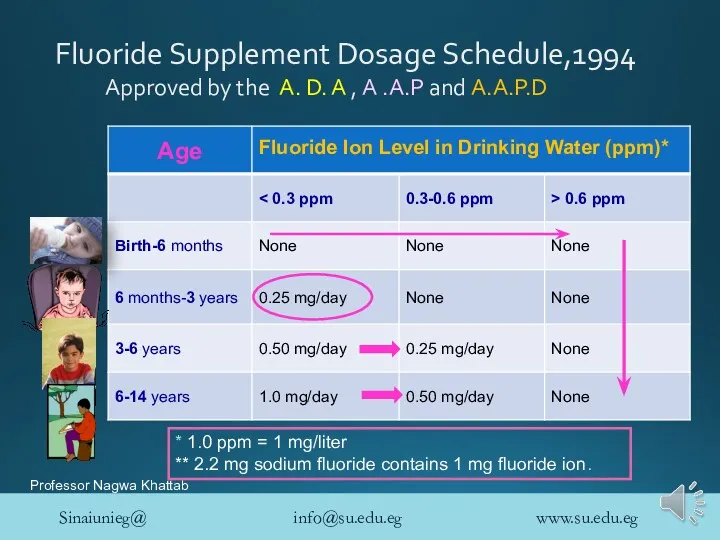
- 31. Fluoride Supplement Dosage Schedule,1994 Approved by the A. D. A , A .A.P and A.A.P.D Fluoride
- 32. Fluoride incorporation in various foods Personal choice Fluoride incorporated in certain foods of common use such
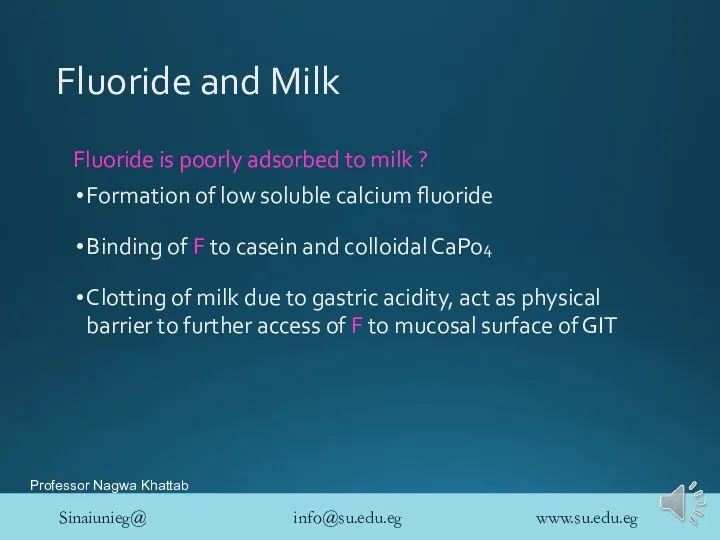
- 33. Fluoride and Milk Fluoride is poorly adsorbed to milk ? Formation of low soluble calcium fluoride
- 35. Скачать презентацию
























 Диагностика болезней сердечно - сосудистой системы
Диагностика болезней сердечно - сосудистой системы Инфекциялық емес патологиядағы менингеальды синдром. Туберкулезді менингитпен екшеу диагностикасы
Инфекциялық емес патологиядағы менингеальды синдром. Туберкулезді менингитпен екшеу диагностикасы Стерилизация и ее роль в профилактике ВБИ
Стерилизация и ее роль в профилактике ВБИ Клиническая симптоматология ревматоидного артрита, остеоартроза
Клиническая симптоматология ревматоидного артрита, остеоартроза Жылу терапиясы. Күн терапиясы. Электротерапия
Жылу терапиясы. Күн терапиясы. Электротерапия Интенсивная терапия при гиповолемическом и геморрагическом шоке у детей
Интенсивная терапия при гиповолемическом и геморрагическом шоке у детей Принципы профилактического консультирования
Принципы профилактического консультирования Фізіологія кровоносних судин. Артеріальний тиск у людини. Функціональна характеристика судин, роль судинного русла в кровообігу
Фізіологія кровоносних судин. Артеріальний тиск у людини. Функціональна характеристика судин, роль судинного русла в кровообігу Механизм возникновения МПП и МПД
Механизм возникновения МПП и МПД Morphine
Morphine Острые лекарственные токсидермии
Острые лекарственные токсидермии Қаңқалық тіндердің жасқа байланысты өзгерістері
Қаңқалық тіндердің жасқа байланысты өзгерістері Общая вирусология
Общая вирусология Заболевания мочевой системы. Занятие 6
Заболевания мочевой системы. Занятие 6 Сердечно-сосудистая система
Сердечно-сосудистая система Злоупотребление алкоголем и алкоголизм: социальная и медицинская проблема
Злоупотребление алкоголем и алкоголизм: социальная и медицинская проблема Медико-социальная помощь лицам пожилого возраста и инвалидам
Медико-социальная помощь лицам пожилого возраста и инвалидам Микозы
Микозы Туберкулез. Возбудители туберкулеза у человека
Туберкулез. Возбудители туберкулеза у человека Алергічні реакції
Алергічні реакції Нарушения кровообращения
Нарушения кровообращения Организация стоматологического терапевтического кабинета
Организация стоматологического терапевтического кабинета Анатомо-топографические особенности челюстно-лицевой области у детей
Анатомо-топографические особенности челюстно-лицевой области у детей Инфекция туралы ілім
Инфекция туралы ілім Патанатомия СРС. Бауыр аурулары алуан түрлі
Патанатомия СРС. Бауыр аурулары алуан түрлі Аудиологический скрининг новорождëнных
Аудиологический скрининг новорождëнных Жатыр түтігінің және аналық безінің ісіктері. Емдеу әдістері мен негіздері. Алдын-алу
Жатыр түтігінің және аналық безінің ісіктері. Емдеу әдістері мен негіздері. Алдын-алу Соматизированная депрессия
Соматизированная депрессия