Содержание
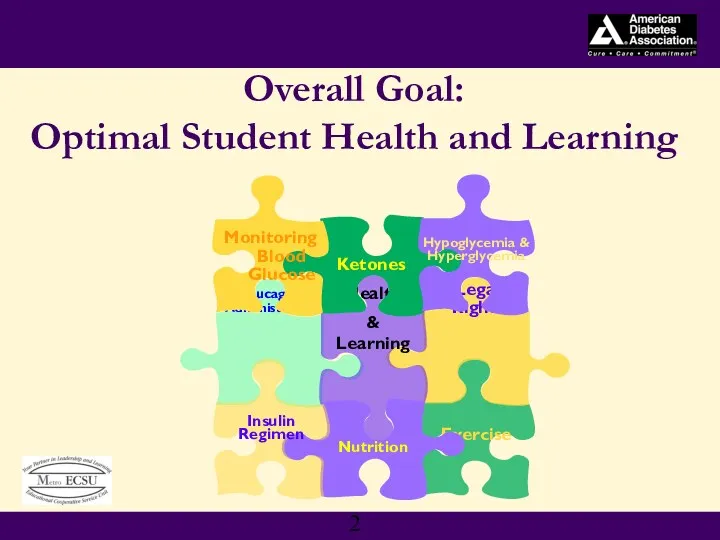
- 2. Overall Goal: Optimal Student Health and Learning Exercise Legal Rights Glucagon Administration Health & Learning Nutrition
- 3. Learning Objectives Participants will learn: What is diabetes? Why care at school is required Basic components
- 4. What is Diabetes? Body does not make or properly use insulin: no insulin production insufficient insulin
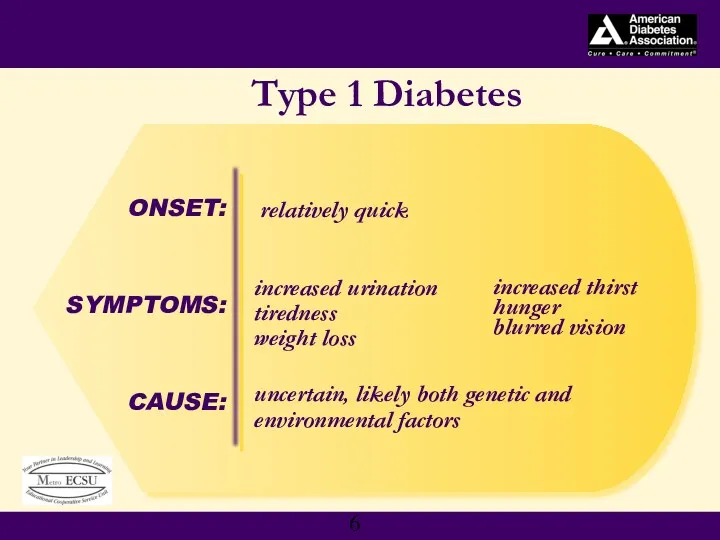
- 5. Type 1 Diabetes auto immune disorder insulin-producing cells destroyed age of onset: usually childhood, young adulthood
- 6. SYMPTOMS: Type 1 Diabetes increased urination tiredness weight loss CAUSE: uncertain, likely both genetic and environmental
- 7. Type 2 Diabetes Insulin resistance – first step Age at onset: Most common in adults Increasingly
- 8. SYMPTOMS: ONSET: Type 2 Diabetes some children show no symptoms at diagnosis in children variable timeframe
- 9. Diabetes is Managed, But it Does Not Go Away. GOAL: To maintain target blood glucose
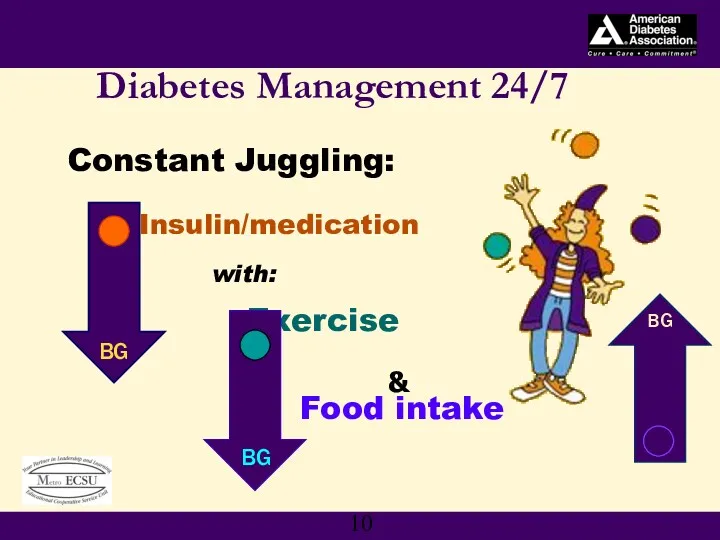
- 10. Constant Juggling: Insulin/medication with: Exercise Food intake Diabetes Management 24/7 BG BG BG &
- 11. Diabetes Management Proactive a response is indicated corrective actions for highs or low emergency intervention keep
- 12. Assistance in Diabetes Management Routine Care: Many students will be able to handle all or almost
- 13. Care in the Schools: School Nurses and Others Nurse most appropriate to: Supervise diabetes care Provide
- 14. Diabetes Medical Management Plan A Diabetes Medical Management Plan (DMMP) should be implemented for every student
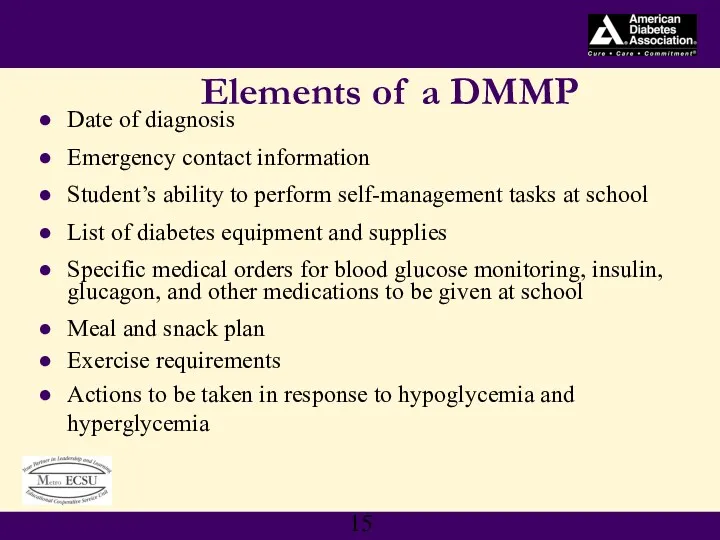
- 15. Elements of a DMMP Date of diagnosis Emergency contact information Student’s ability to perform self-management tasks
- 16. Quick Reference Plan Development based on information from students DMMP Summarizes how to recognize and treat
- 18. Скачать презентацию











 Задержка психического развития
Задержка психического развития Healthy lifestyle
Healthy lifestyle Анестезиология и реаниматология. Введение в дисциплину
Анестезиология и реаниматология. Введение в дисциплину Сlinical anatomy of the chest and mammary gland
Сlinical anatomy of the chest and mammary gland Методы обследования пациентов с патологией органов сердечно-сосудистой системы: пальпация, перкуссия, аускультация
Методы обследования пациентов с патологией органов сердечно-сосудистой системы: пальпация, перкуссия, аускультация Использование эмбриональных стволовых клеток (ЭСК) в медицинской практике. Проблемы и последствия
Использование эмбриональных стволовых клеток (ЭСК) в медицинской практике. Проблемы и последствия Особенности питания при фармакотерапии
Особенности питания при фармакотерапии Туберкулез органов мочевой системы
Туберкулез органов мочевой системы Гломерулонефриты. Этиология. Лечение
Гломерулонефриты. Этиология. Лечение Медициналық заттарды стерилизациялау. Медициналық құралжабдықтарды стерилизация алды өңдеу
Медициналық заттарды стерилизациялау. Медициналық құралжабдықтарды стерилизация алды өңдеу Лабараторные технологии диагностики и мониторинга сахарного диабета и его осложнений
Лабараторные технологии диагностики и мониторинга сахарного диабета и его осложнений Топографическая анатомия передней брюшной стенки. Хирургия грыж. (Лекция 4)
Топографическая анатомия передней брюшной стенки. Хирургия грыж. (Лекция 4) Химизм имплантантов. (Лекция 1)
Химизм имплантантов. (Лекция 1) Одножелудочковая коррекция
Одножелудочковая коррекция Оздоровительно профилактическая гимнастика при нарушении осанки и плоскостопия
Оздоровительно профилактическая гимнастика при нарушении осанки и плоскостопия Терминалды жағдай
Терминалды жағдай Режим дня младшего школьника
Режим дня младшего школьника Советская медицина в годы Великой Отечественной войны
Советская медицина в годы Великой Отечественной войны Организация работы лечебного отделения. (Лекция 3)
Организация работы лечебного отделения. (Лекция 3) Врожденная кишечная непроходимость
Врожденная кишечная непроходимость Нерв талшықтары мен басқа да қозған ұлпалардың әрекет потенциалы. Молекулалық механизмдері. (Дәріс 5)
Нерв талшықтары мен басқа да қозған ұлпалардың әрекет потенциалы. Молекулалық механизмдері. (Дәріс 5) Церебральные инсульты у детей
Церебральные инсульты у детей Жіночий таз і тазове дно
Жіночий таз і тазове дно Лекарственные средства, производные конденсированных гетероциклических систем. (Тема 5)
Лекарственные средства, производные конденсированных гетероциклических систем. (Тема 5) Клиническая анатомия носа. Септопластика. Ринопластика
Клиническая анатомия носа. Септопластика. Ринопластика Антисептики и дезинфицирующие средства
Антисептики и дезинфицирующие средства Проведение профилактических медицинских осмотров и диспансеризации: нормативно-правовые и прикладные аспекты
Проведение профилактических медицинских осмотров и диспансеризации: нормативно-правовые и прикладные аспекты Науково-теоретичні засади вивчення дизартрій
Науково-теоретичні засади вивчення дизартрій