Содержание
- 2. What is it & what does it do? Every morsel of food we eat has to
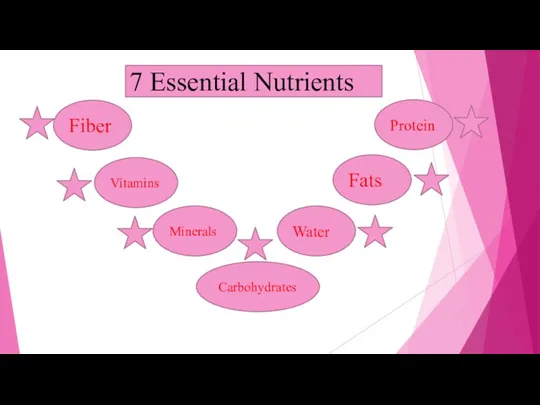
- 3. 7 Essential Nutrients Fiber Carbohydrates Vitamins Minerals Water Fats Protein
- 4. In humans, protein must be broken down into amino acids, starches into simple sugars, and fats
- 5. What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal (also called the digestive tract) is the long
- 6. Parts of the digestive system 1. Teeth-The strongest stuff in the body! Their purpose is to
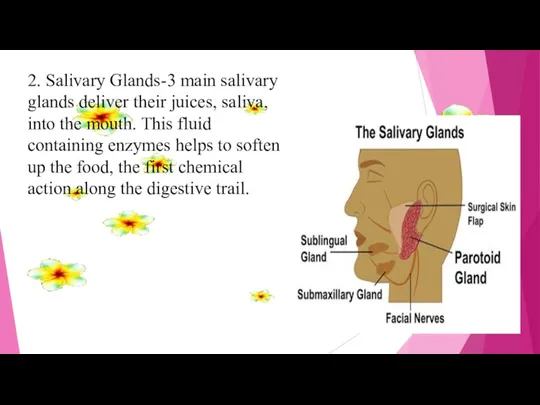
- 7. 2. Salivary Glands-3 main salivary glands deliver their juices, saliva, into the mouth. This fluid containing
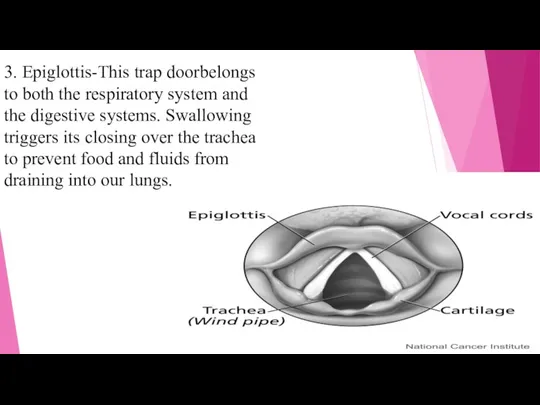
- 8. 3. Epiglottis-This trap doorbelongs to both the respiratory system and the digestive systems. Swallowing triggers its
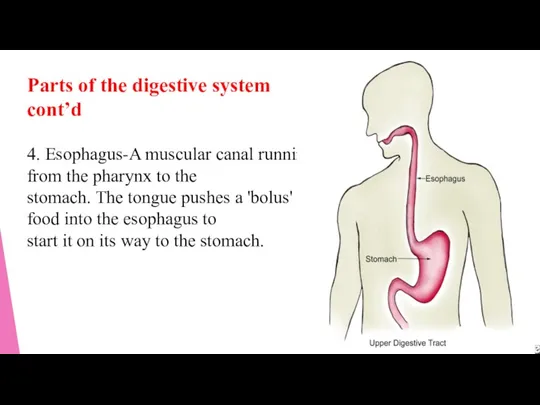
- 9. Parts of the digestive system cont’d 4. Esophagus-A muscular canal running from the pharynx to the
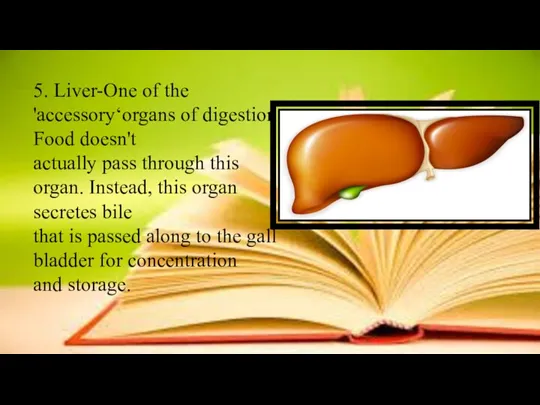
- 10. 5. Liver-One of the 'accessory‘organs of digestion. Food doesn't actually pass through this organ. Instead, this
- 11. 6. Gall Bladder-Another accessory organ. Food doesn't touch this one, either. It is a pear-shaped sac
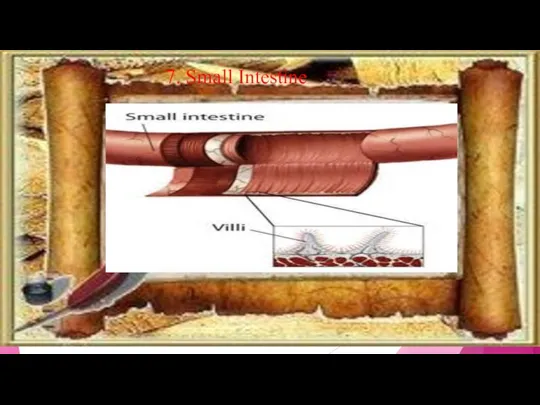
- 12. 7. Small Intestine-The small bowel has 3 main sections: the duodenum, jejunum and ileum. The duodenum
- 13. 7. Small Intestine
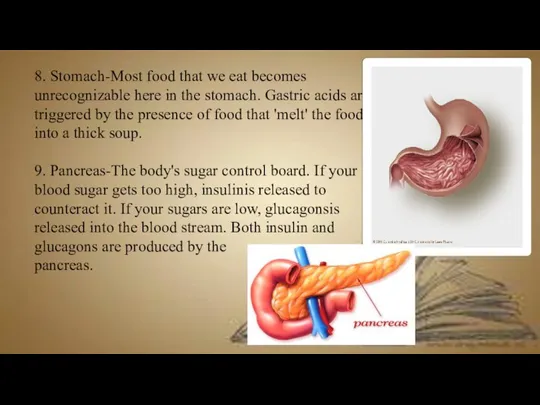
- 14. 8. Stomach-Most food that we eat becomes unrecognizable here in the stomach. Gastric acids are triggered
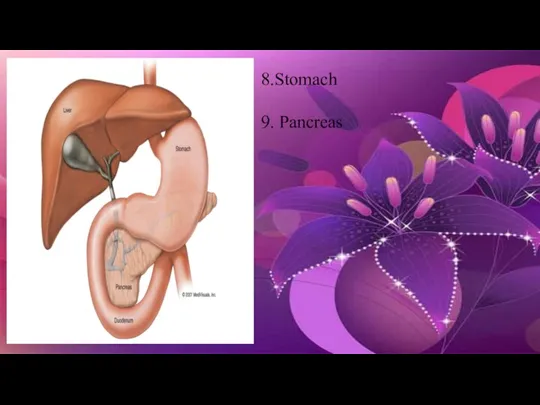
- 15. 8.Stomach 9. Pancreas
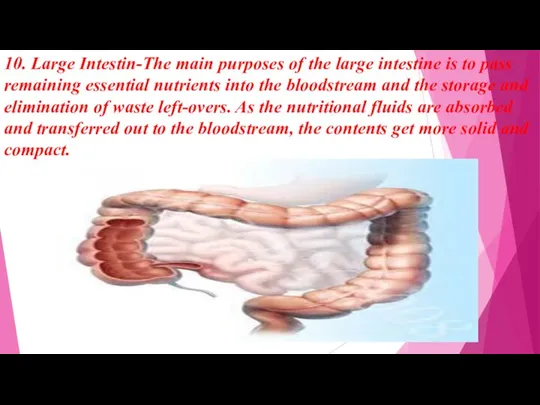
- 16. 10. Large Intestin-The main purposes of the large intestine is to pass remaining essential nutrients into
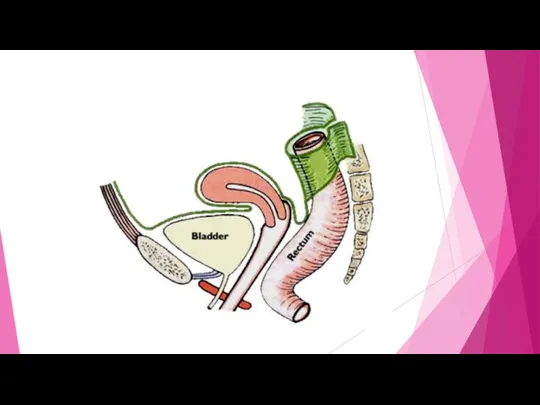
- 17. 11. Rectum-The last portion of the large intestine used for storageof stool ready for disposal. When
- 19. TERMINOLOGY: Esophagus-the long tube between the mouth and the stomach. It uses rhythmic muscle movements to
- 21. Скачать презентацию








 Балалар стоматологиялық клиникасында баладан анамнез жинау
Балалар стоматологиялық клиникасында баладан анамнез жинау Псориаз. Красный плоский лишай
Псориаз. Красный плоский лишай Межличностного общения и консультирования пациентов врачом общей практики особенности видения больных
Межличностного общения и консультирования пациентов врачом общей практики особенности видения больных Хронический панкреатит. Консервативное лечение
Хронический панкреатит. Консервативное лечение Обращение с медицинскими отходами
Обращение с медицинскими отходами Муковисцидоз. Патогенезі
Муковисцидоз. Патогенезі Питание беременных и кормящих. Основы вскармливания детей 1 года жизни
Питание беременных и кормящих. Основы вскармливания детей 1 года жизни Холера
Холера Этиология и эпидемиология туберкулеза
Этиология и эпидемиология туберкулеза Как сохранить и преумножить женское здоровье с Витамакс
Как сохранить и преумножить женское здоровье с Витамакс Вегетарианство – за или против
Вегетарианство – за или против Простатспецифический антиген
Простатспецифический антиген Лекарственные растения
Лекарственные растения Врачи без границ
Врачи без границ Венерические болезни
Венерические болезни Аскаридоз у человека
Аскаридоз у человека Доношена і недоношена новонароджена дитина
Доношена і недоношена новонароджена дитина Роль правильного питания в нашей жизни
Роль правильного питания в нашей жизни Дефицитное состояние у детей. Биоэнергетическая недостаточность
Дефицитное состояние у детей. Биоэнергетическая недостаточность Синдром обструктивного апное сна
Синдром обструктивного апное сна Реанимация и интенсивная терапия при экстремальных состояниях на догоспитальном этапе
Реанимация и интенсивная терапия при экстремальных состояниях на догоспитальном этапе Особенности медико-социального сопровождения потребителей наркотических средств и психотропных веществ, живущих с ВИЧ
Особенности медико-социального сопровождения потребителей наркотических средств и психотропных веществ, живущих с ВИЧ Philosophy and medicine
Philosophy and medicine Гигиенические требования и нормы на занятиях физической культурой
Гигиенические требования и нормы на занятиях физической культурой Методы иммунодиагностики и иммунопрофилактики инфекционных болезней
Методы иммунодиагностики и иммунопрофилактики инфекционных болезней Современный взгляд на терапию гиперфосфатемии при ХБП. Гиперкалиемия, профилактика и коррекция
Современный взгляд на терапию гиперфосфатемии при ХБП. Гиперкалиемия, профилактика и коррекция Дисплазия позвоночника
Дисплазия позвоночника Экзамен по гистологии
Экзамен по гистологии