Содержание
- 2. Emotions - are responses in the form of subjectively tinctured feelings of an individual which reflect
- 3. FUNCTION OF EMOTIONS Reflective function target function Information function Enabling function regulatory function reinforces the function
- 4. FUNCTION OF EMOTIONS Switching function Adaptive function Communicative function Protective function
- 5. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS Stage 1 - the newborn - the predominance of the instincts
- 6. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS 2 stage - the stage of the organic feeling - processing
- 7. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS Stage 3 – 3 - 4 years to 12 - 14
- 8. STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT OF EMOTIONS 4 STAGE – from 10 - 12 years old to 22
- 9. COMPONENTS emotional functioning INTENSITY (Strength, depth) THE BASIC BACKGROUND positive negative
- 10. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS STHENIC - Increase the functioning of the organism ASTHENIC - Reducing the vital
- 11. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS EMOTIONAL STATE (mood) EMOTIONAL RELATIONS (feelings) EMOTIONAL REACTIONS (affect)
- 12. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS AFFECT - a special emotional state, which is a very strong short-term excitement,
- 13. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS At physiological affect arisen state is the intense emotion that dominates the mind
- 14. CLASSIFICATION OF EMOTIONS Pathological affect is characterized by full dimming of consciousness and uncontrollable impulsive action,
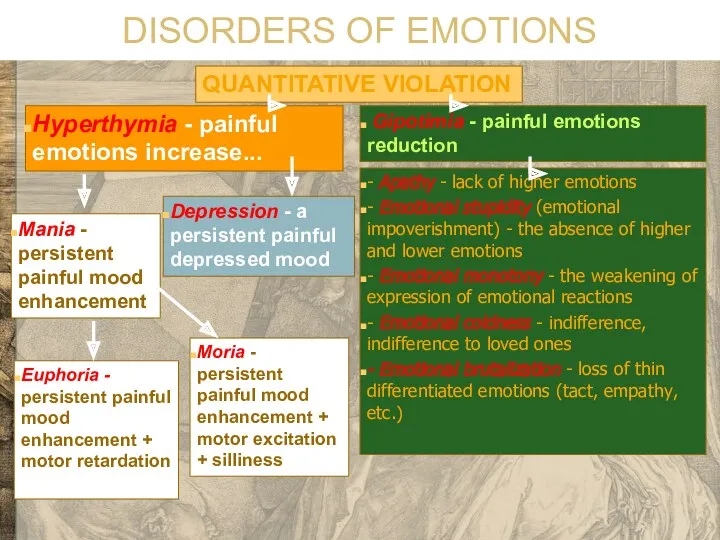
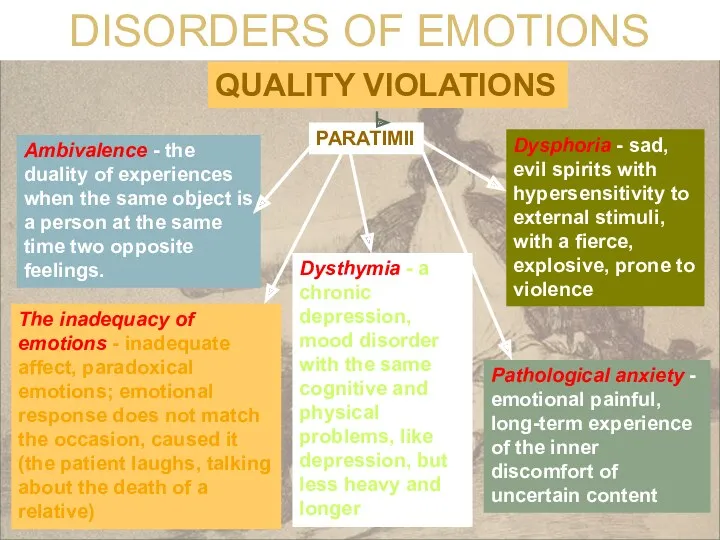
- 15. DISORDERS OF EMOTIONS QUANTITATIVE VIOLATION Hyperthymia - painful emotions increase... - Apathy - lack of higher
- 16. РАССТРОЙСТВА ЭМОЦИЙ КОЛИЧЕСТВЕННЫЕ НАРУШЕНИЕ ГИПЕРТИМИЯ – болезненное увеличение эмоций – апатия – отсутствие высших эмоций –
- 17. РАССТРОЙСТВА ЭМОЦИЙ КОЛИЧЕСТВЕННЫЕ НАРУШЕНИЕ ГИПЕРТИМИЯ – болезненное увеличение эмоций – апатия – отсутствие высших эмоций –
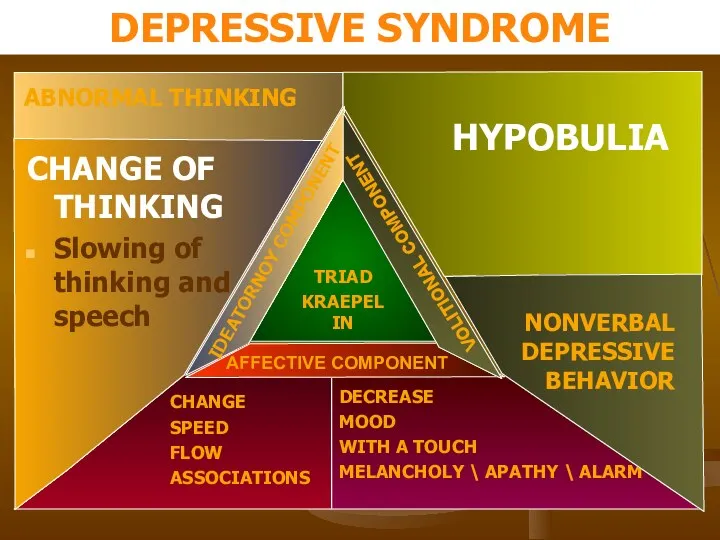
- 18. TRIAD KRAEPELIN DEPRESSIVE SYNDROME
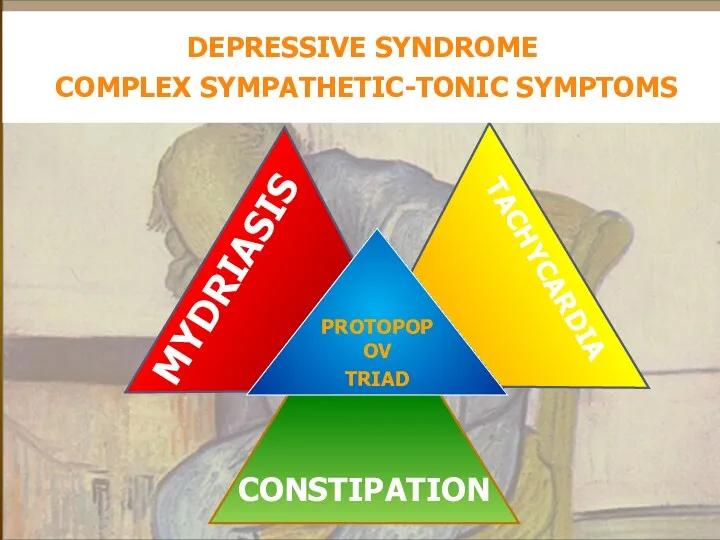
- 19. PROTOPOPOV TRIAD DEPRESSIVE SYNDROME COMPLEX SYMPATHETIC-TONIC SYMPTOMS
- 20. Depressive syndrome Clinical variants of depression : - anaesthetic - with phobias - with anxiety -
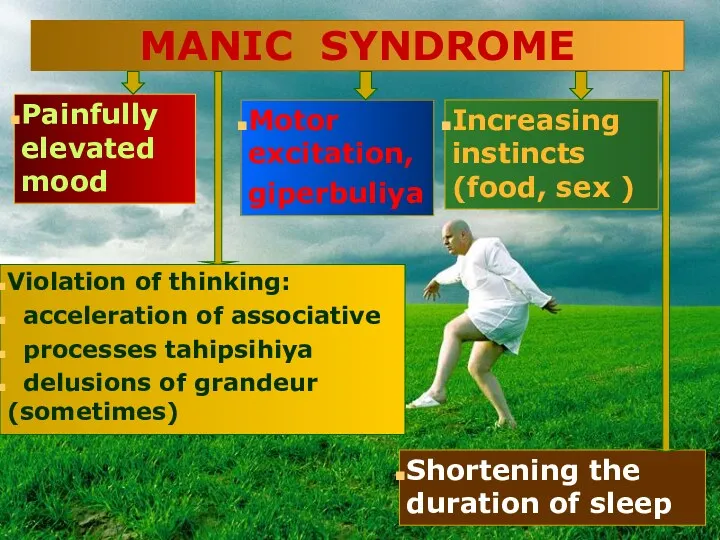
- 21. Painfully elevated mood Violation of thinking: acceleration of associative processes tahipsihiya delusions of grandeur (sometimes) Motor
- 22. MANIC SYNDROME Clinical variants : - with euphoria - with moria - with irritability - unproductive
- 23. DYSPHORIA - irritability, maliciousness, dissatisfaction accompanied by aggression and destructive actions 1) dysphoric reaction 2) dysphoric
- 24. Will - the mental process of deliberate and targeted regulation of human activities and their behavior
- 25. Stages of volitional process and his violation Attraction - primary, instinctive, emotional manifestation of human needs,
- 26. Stages of volitional process and his violation origin of motive - incentive to action; psycho-physiological process
- 27. Stages of volitional process and his violation fight of reasons The process of analyzing the ways
- 28. Stages of volitional process and his violation decision-choice making - a route and method of satisfying
- 29. Stages of volitional process and his violation choice of ways of realization
- 30. Stages of volitional process and his violation execution of decision
- 31. Violation of volitional process Quantitative : - hypobulia - hyperbulia - abulia High-quality : - parabulias
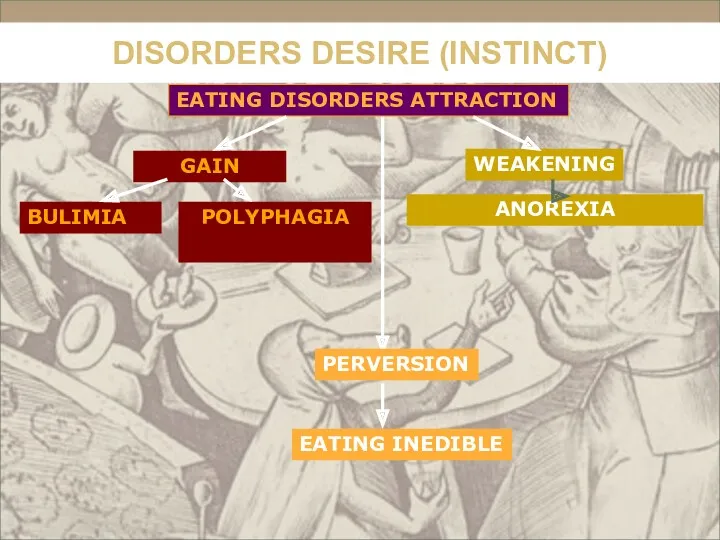
- 32. Sickly strengthening of food instinct Bulimia -uncontrolled food intake in a large amount Polyphagia - increased
- 33. Sickly weakening of food instinct Anorexia – a syndrome consisting in the complete absence of appetite
- 34. Sickly weakening of food instinct Anorexia – a syndrome consisting in the complete absence of appetite
- 35. Violation of volitional process Quantitative : - hypobulia - hyperbulia - abulia High-quality : - parabulias
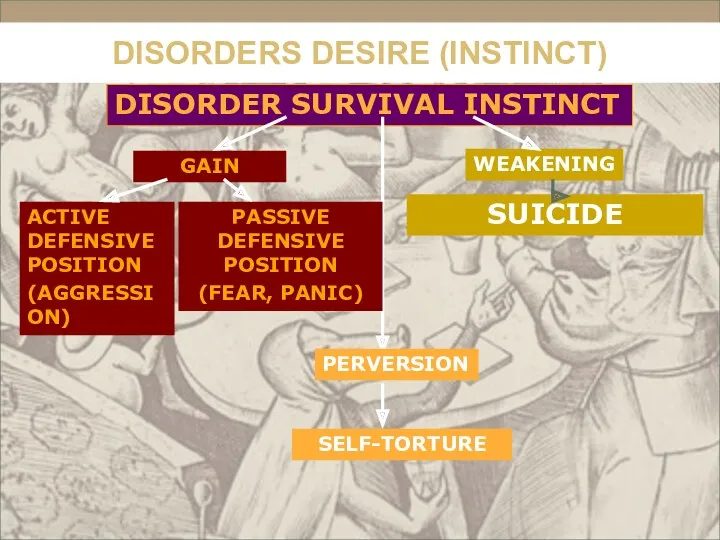
- 36. Sickly strengthening of self-preservation instinct Aggression - motivated destructive behavior that is contrary to the norms
- 37. Sickly weakening self-preservation instinct Suicide -deliberate deprivation of life itself independent and voluntary
- 38. Perversion of instincts Auto aggression -intentional infliction of physical damage itself
- 39. Violation of volitional process Quantitative : - hypobulia - hyperbulia - abulia High-quality : - parabulias
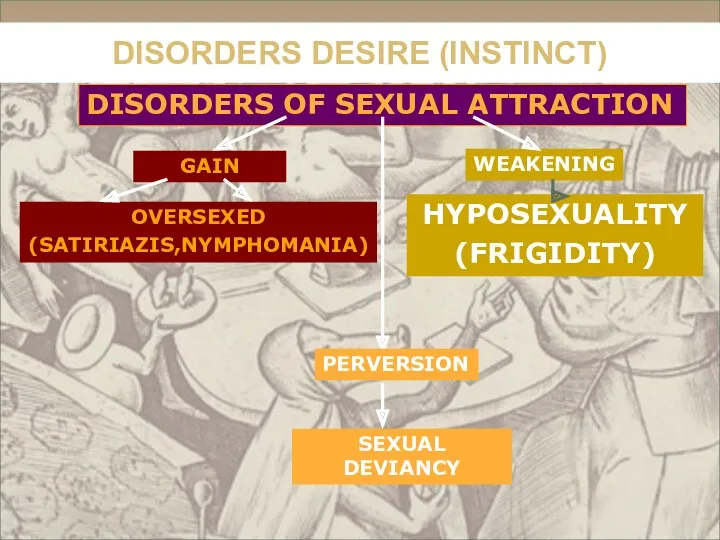
- 40. Sickly weakening of sexual instinct impotence frigidity
- 41. Sickly strengthening of sexual instinct Satyriasis Nymphomania
- 42. Classification of instinctive drives Self-preservation
- 43. Perversion of instincts Sexual narcissism sadism masochism exhibitionism voyeurism
- 44. PARABULIAS ambitendenc the existence of antagonistic emotions, ideas or desires in relation to one and the
- 46. Скачать презентацию

































 Эндовидеолапароскопические вмешательства при опухолях женской мочеполовой системы
Эндовидеолапароскопические вмешательства при опухолях женской мочеполовой системы Профилактика зубочелюстных аномалий у детей
Профилактика зубочелюстных аномалий у детей Жүрек-қантамыр аурулары кезіндегі медициналық-әлеуметтік реабилитация
Жүрек-қантамыр аурулары кезіндегі медициналық-әлеуметтік реабилитация Аутизм
Аутизм Инвазивные методы диагностики ишемической болезни сердца
Инвазивные методы диагностики ишемической болезни сердца Безопасность применения ЛС у беременных
Безопасность применения ЛС у беременных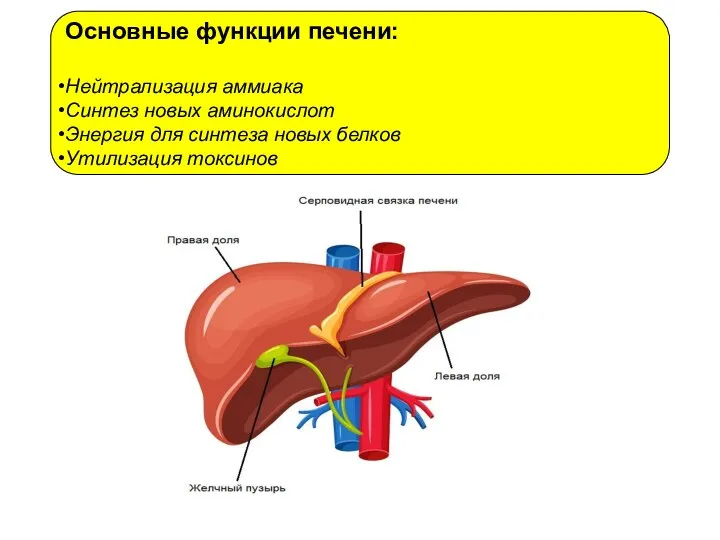 Основные функции печени
Основные функции печени Алгоритм диагностики и оказания скорой помощи при отравлениях и укусах
Алгоритм диагностики и оказания скорой помощи при отравлениях и укусах Cardiology
Cardiology Фізіологія, гігієна праці та виробнича санітарія. Виробничий травматизм
Фізіологія, гігієна праці та виробнича санітарія. Виробничий травматизм Дені сау балаларды диспансерлік бақылау
Дені сау балаларды диспансерлік бақылау Захворювання щитовидної залози у дітей
Захворювання щитовидної залози у дітей Жан тазалығы, тән тазалығы
Жан тазалығы, тән тазалығы Жеңіл, ауыр және өте ауыр пневмонияны емдеудің негізгі
Жеңіл, ауыр және өте ауыр пневмонияны емдеудің негізгі Школа здоровья для больных с артериальной гипертензией
Школа здоровья для больных с артериальной гипертензией Проявления соматических заболеваний в полости рта
Проявления соматических заболеваний в полости рта влияние комплексных физических упражнений на коррекцию нарушений осанки у детей школьного возраста
влияние комплексных физических упражнений на коррекцию нарушений осанки у детей школьного возраста Сучасні проблеми молекулярної біології. Генна терапія. (Лекція 8)
Сучасні проблеми молекулярної біології. Генна терапія. (Лекція 8) Врожденная дисфункция коры надпочечников
Врожденная дисфункция коры надпочечников Пропаганда здорового образа жизни, как средство профилактики наркомании среди подрастающего поколения
Пропаганда здорового образа жизни, как средство профилактики наркомании среди подрастающего поколения Опухоли почек, мочеточников, мочевого пузыря
Опухоли почек, мочеточников, мочевого пузыря Пищеварение в ротовой области
Пищеварение в ротовой области Мүмкіндіктері шектеулі науқастармен қарым-қатынас
Мүмкіндіктері шектеулі науқастармен қарым-қатынас Неизлечимые болезни разных времен
Неизлечимые болезни разных времен Тоны сердца
Тоны сердца Усік. Куйік. Электрожарақат
Усік. Куйік. Электрожарақат Кюреты. Методика работы универсальной кюретой
Кюреты. Методика работы универсальной кюретой Біофармація – теоретична основа виробництва лікарських засобів
Біофармація – теоретична основа виробництва лікарських засобів