Содержание
- 2. Learning Objectives Basics of EKG Establish Consistent Approach to Interpreting ECGs Rate, rhythm, axis, identifying ischemia
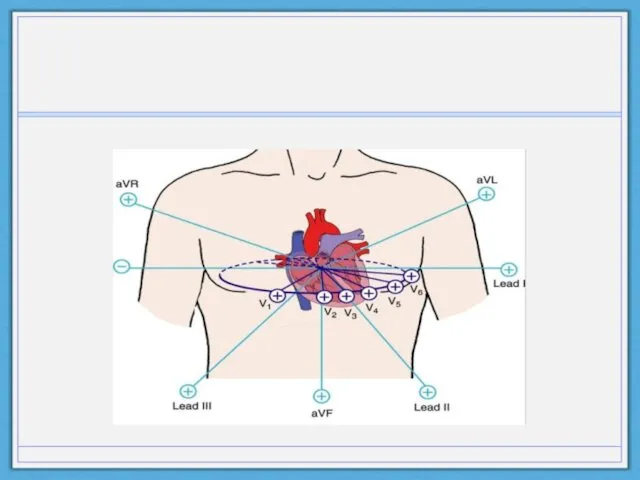
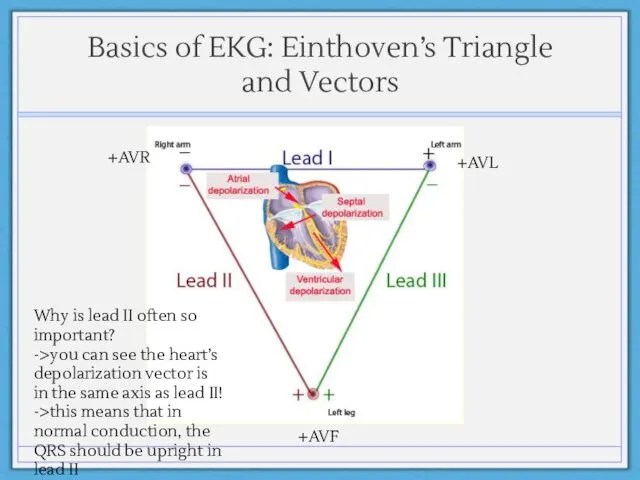
- 4. Basics of EKG: Einthoven’s Triangle and Vectors +AVR +AVL +AVF Why is lead II often so
- 5. ECG Interpretation What is your approach to reading an ECG? Rate Rhythm Axis Hypertrophy Intervals P
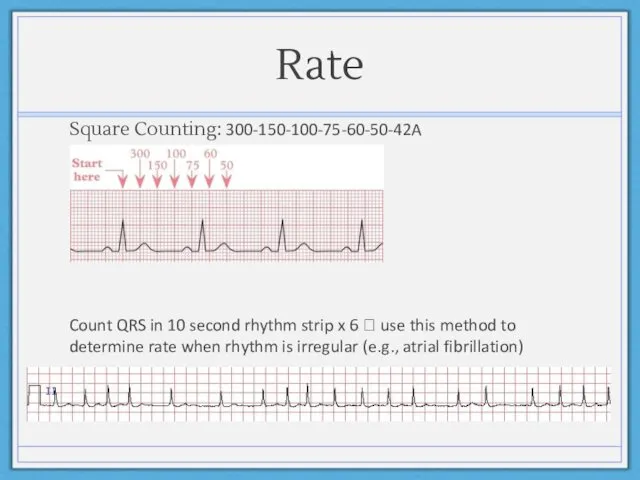
- 6. Rate Square Counting: 300-150-100-75-60-50-42A Count QRS in 10 second rhythm strip x 6 ? use this
- 7. Rhythm Look at the rhythm strip below and answer the questions Are P waves present? yes
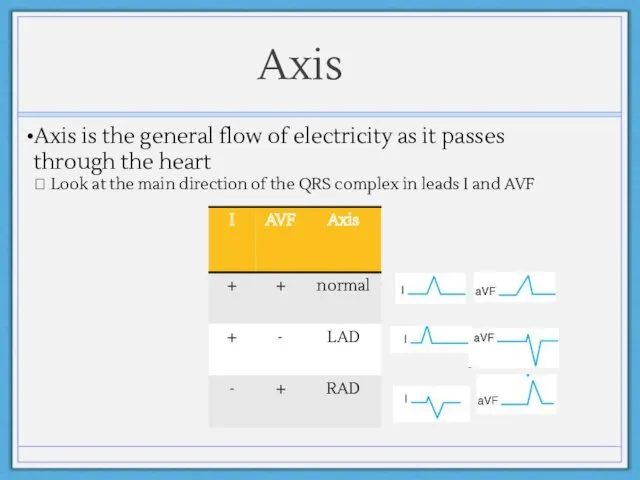
- 8. Axis Axis is the general flow of electricity as it passes through the heart ? Look
- 9. QRS Duration Normal QRS is Prolonged QRS duration (>120ms) is seen in bundle branch blocks (BBB).
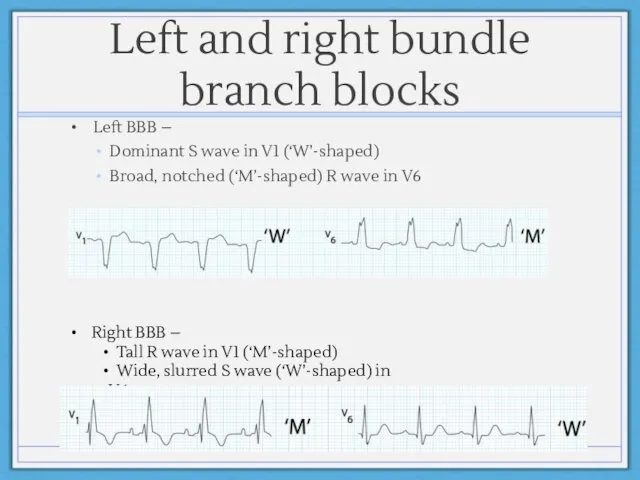
- 10. Left and right bundle branch blocks Left BBB – Dominant S wave in V1 (‘W’-shaped) Broad,
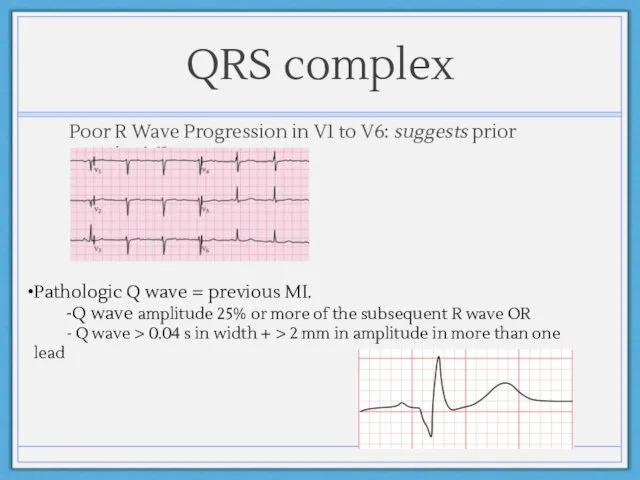
- 11. QRS complex Poor R Wave Progression in V1 to V6: suggests prior anterior MI Pathologic Q
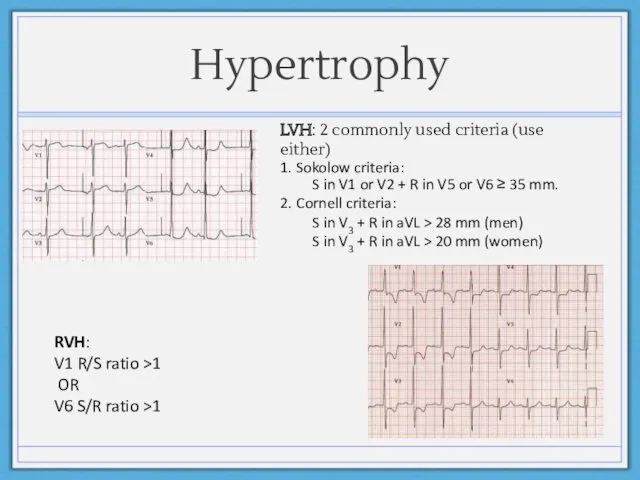
- 12. Hypertrophy RVH: V1 R/S ratio >1 OR V6 S/R ratio >1 LVH: 2 commonly used criteria
- 13. Intervals What is the normal PR interval? 0.12 to 0.20 s (3 - 5 small squares).
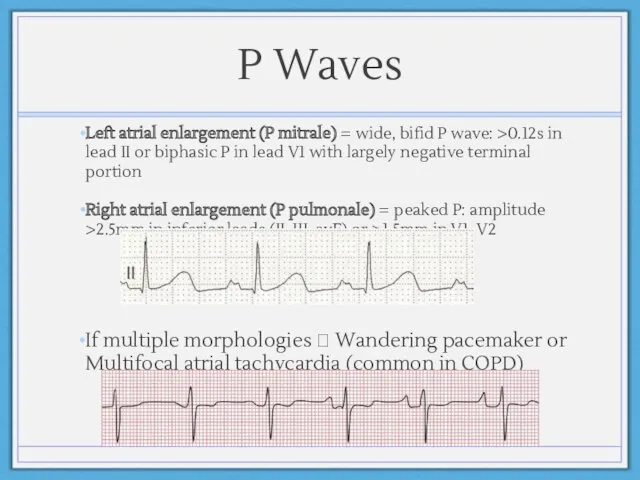
- 14. P Waves Left atrial enlargement (P mitrale) = wide, bifid P wave: >0.12s in lead II
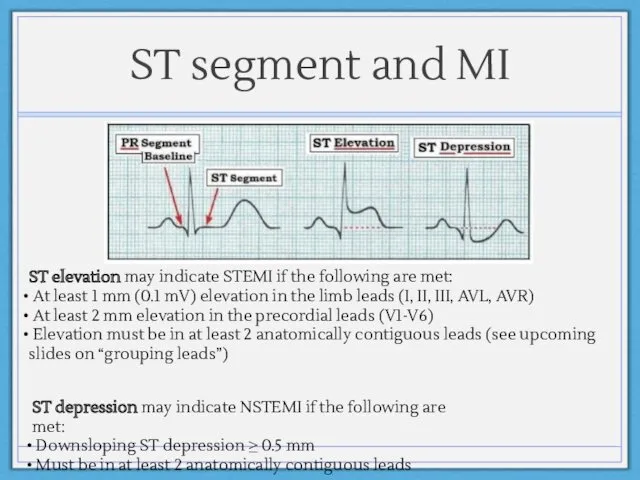
- 15. ST segment and MI ST elevation may indicate STEMI if the following are met: At least
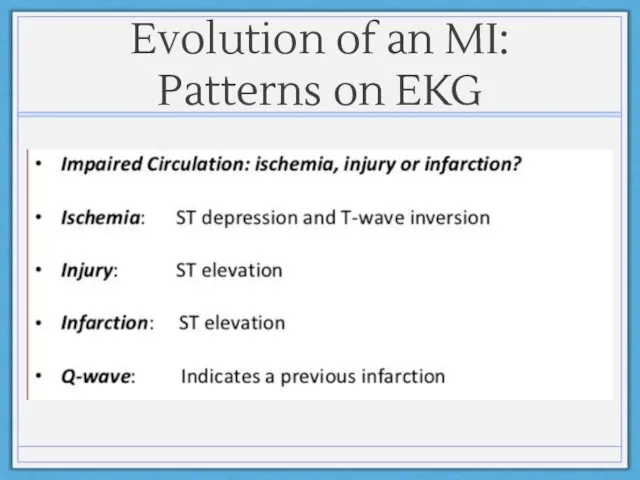
- 16. Evolution of an MI: Patterns on EKG
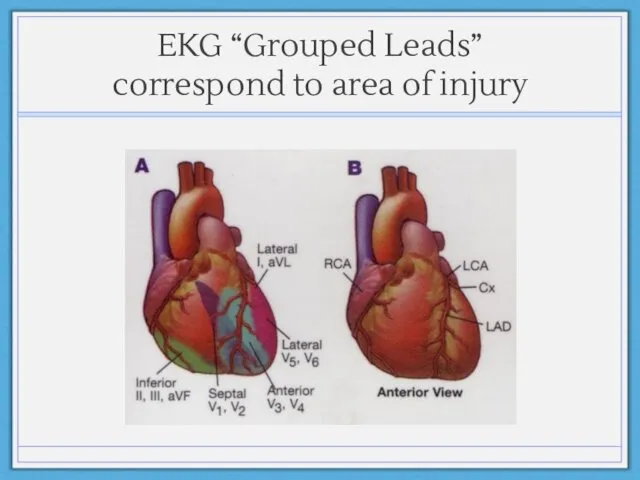
- 17. First thing you should do when looking for ischemia: Group leads by region!
- 18. EKG “Grouped Leads” correspond to area of injury
- 19. LET’S DO SOME PRACTICE CASES
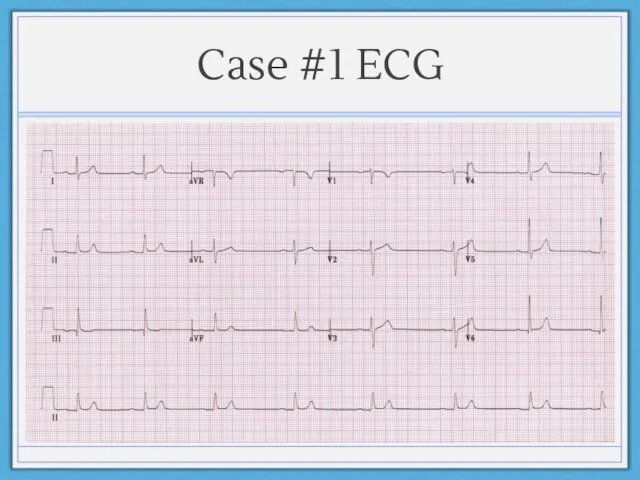
- 20. Case #1 70 year old male with history of diabetes mellitus and hypertension occasionally feels lightheaded.
- 21. Case #1 ECG
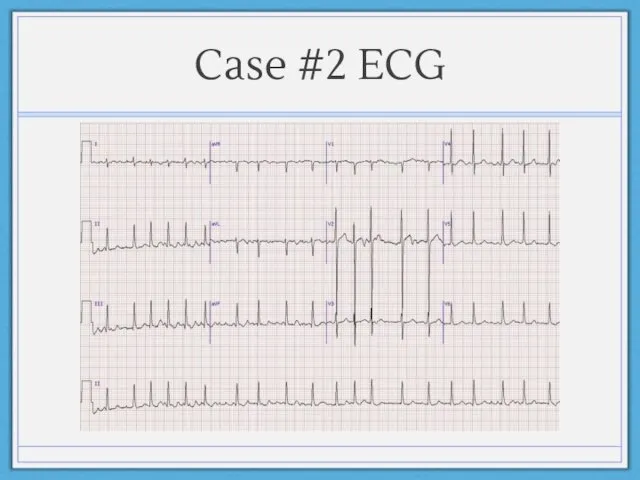
- 22. Case #2 58 year old female with no significant past medical history presents with fatigue, lightheadedness
- 23. Case #2 ECG
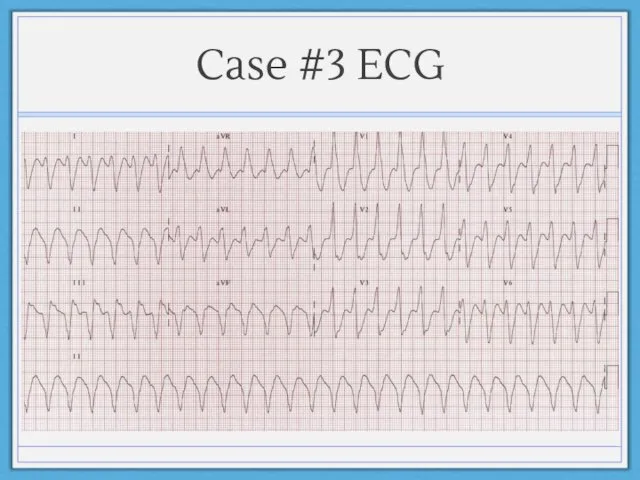
- 24. Case #3 78 year old female with history of HTN, DM, HL, CAD admitted for syncope
- 25. Case #3 ECG
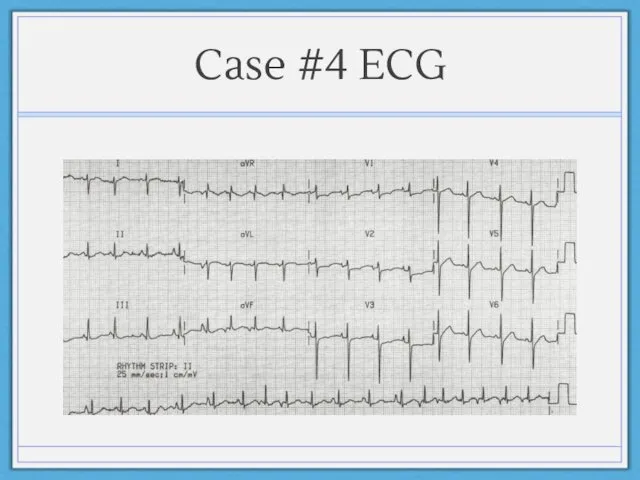
- 26. Case #4 67 year old male with history of diabetes, hypertension, COPD presents with chest pain.
- 27. Case #4 ECG
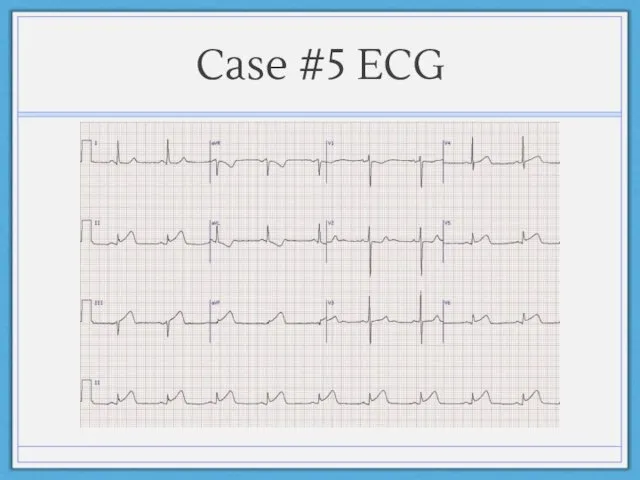
- 28. Case #5 60 year-old man with history of HTN, HL, CAD presents with nausea, shortness of
- 29. Case #5 ECG
- 30. Additional Resources Websites: http://en.ecgpedia.org/ http://ecg.utah.edu http://ecg.bidmc.harvard.edu/maven/ Apps: ECG Guide by QxMD (iPad and iPhone) ECG Interpret
- 32. Скачать презентацию













 Паразитарные заболевания кожи
Паразитарные заболевания кожи Приобретенные (вторичные) иммунодефициты
Приобретенные (вторичные) иммунодефициты Этиология дизартрии
Этиология дизартрии Зарядка для глаз
Зарядка для глаз Вирусные кишечные инфекции
Вирусные кишечные инфекции Клиническая фармакология препаратов для лечения ЖКТ
Клиническая фармакология препаратов для лечения ЖКТ Помощь при обструкции дыхательных путей. Приём Хеймлиха
Помощь при обструкции дыхательных путей. Приём Хеймлиха Дискинезии желчевыводящих путей у детей
Дискинезии желчевыводящих путей у детей Алергозы. Этиология и патогенез
Алергозы. Этиология и патогенез Современный алгоритм диспансерного регламента для детей с врожденной патологией челюстно-лицевой области
Современный алгоритм диспансерного регламента для детей с врожденной патологией челюстно-лицевой области Наследственность. Генетика человека. Часть 2
Наследственность. Генетика человека. Часть 2 Психическое расстройство депрессия
Психическое расстройство депрессия Клиническая биохимия щитовидной железы
Клиническая биохимия щитовидной железы Инфузионная терапия в детской инфекционной патологии
Инфузионная терапия в детской инфекционной патологии Хирургическое лечение портальной гипертензии и её осложнений
Хирургическое лечение портальной гипертензии и её осложнений Повреждения наружных половых органов
Повреждения наружных половых органов Сухожильный шов
Сухожильный шов Бронхобструктивті синдром
Бронхобструктивті синдром Репродуктивное здоровье и профилактика репродуктивных нарушений
Репродуктивное здоровье и профилактика репродуктивных нарушений Aberration of normal development and involution (andi) of thebreast
Aberration of normal development and involution (andi) of thebreast Спектроскопия и оптическая биопсия в медицине. Аутофлуоресценция клеток
Спектроскопия и оптическая биопсия в медицине. Аутофлуоресценция клеток Сульфаниламидные средства
Сульфаниламидные средства Гепатит С
Гепатит С 7 советов о здоровом питании
7 советов о здоровом питании Вегетарианство
Вегетарианство Особенности работы медицинской сестры офтальмологического отделения
Особенности работы медицинской сестры офтальмологического отделения Пероральные лекарственные формы с модифицированным высвобождением
Пероральные лекарственные формы с модифицированным высвобождением Методы индивидуальной и коммунальной профилактики стом заболеваний у детей и взрослых
Методы индивидуальной и коммунальной профилактики стом заболеваний у детей и взрослых