Содержание
- 2. is the higher form of reflection of the objective reality, a process of a generalized and
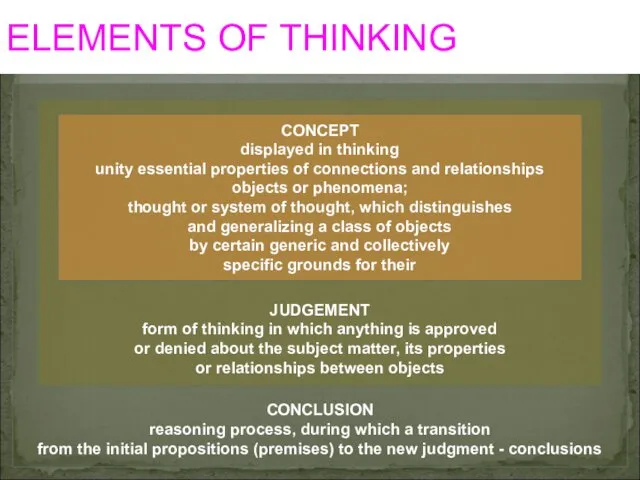
- 3. ELEMENTS OF THINKING CONCLUSION reasoning process, during which a transition from the initial propositions (premises) to
- 4. analysis synthesis generalization concentration abstraction classification inclusion exclusion conception thinking. Thinking is determined by operations
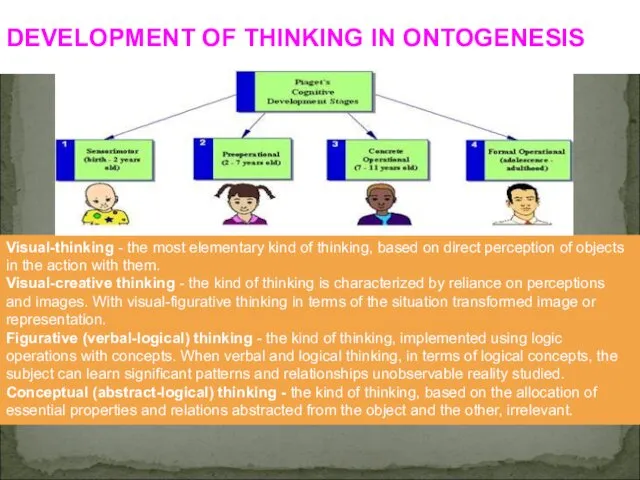
- 5. DEVELOPMENT OF THINKING IN ONTOGENESIS Visual-thinking - the most elementary kind of thinking, based on direct
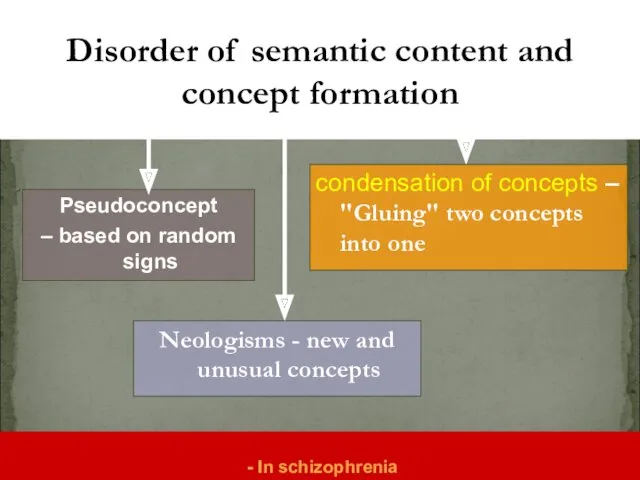
- 6. 1. A disturbance in the formation of concepts: a) pseudoconcepts, b) condensation of concepts, c) neologisms.
- 7. 3. A disturbance in the form of thinking: a) pathologically circumstantial thinking, b) philosophizing, c) non-continuous
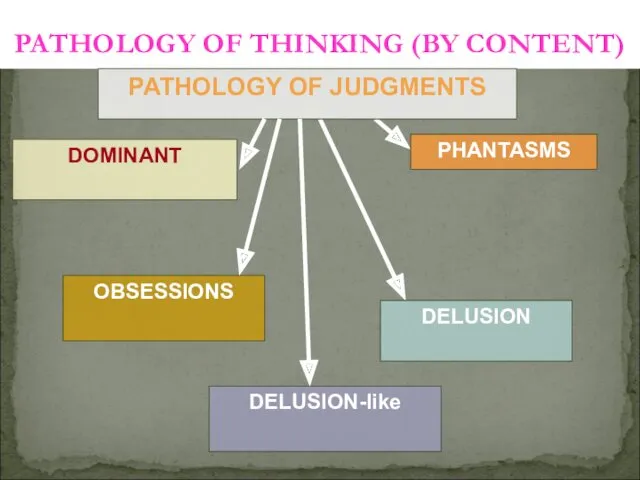
- 8. 4. A disturbance in the contents of thinking: a) Obsessive ideas, b) dominant ideas, c) supervaluable
- 9. Pseudoconcept – based on random signs condensation of concepts – "Gluing" two concepts into one Disorder
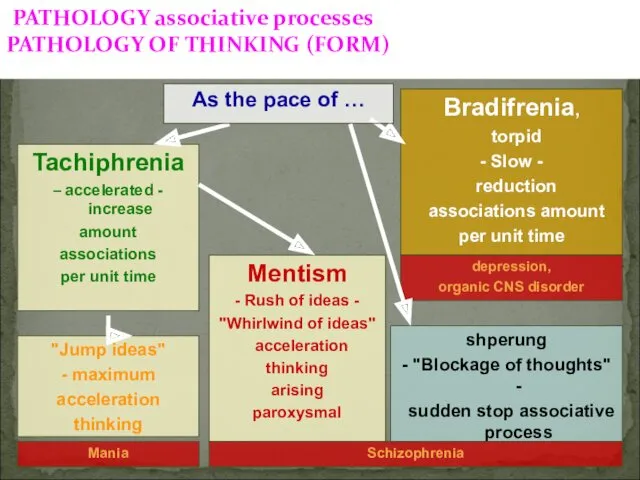
- 10. PATHOLOGY associative processes PATHOLOGY OF THINKING (FORM) Tachiphrenia – accelerated - increase amount associations per unit
- 11. Reasoner Using the technical tools of logic in an unhelpful and pedantic manner by focusing on
- 12. Symbolic thinking: the patient supplies various concepts with some allegorical meaning which is absolutely unclear for
- 13. Shperrung Delay of thinking (Shperrung) manifests itself by a sudden arrest in the flow of thoughts.
- 14. Mentism Flow of thoughts (mentism) is an automatic flow of thoughts which is painfully feel by
- 15. Autistic – utterly introverted thinking. Autistic thinking based upon the patient’s inner feelings, his subjective aims,
- 16. Incoherent thinking is characterized by inability to form associations; separate perceptions, images, concepts are not connected
- 17. Perseveration - is the uncontrollable repetition of a particular response, such as a word, usually caused
- 18. Detailed (pathologically circumstantial thinking) speech contains big amount of useless smallest details. Verbigeration is a senseless
- 19. Concrete thinking characterized by actual things, events, and immediate experience, rather than by abstractions; seen in
- 20. OBSESSIONS DELUSION-like PATHOLOGY OF THINKING (BY CONTENT) PATHOLOGY OF JUDGMENTS DELUSION DOMINANT PHANTASMS
- 21. Obsessive thinking - stereotype repeated ideas, representations, memories, rituals, which arise against the will (switched gas,
- 22. phobia Persistent, pathological, unrealistic, intense fear of an object or situation; the phobic person may realize
- 23. - develop at special stenic persons, dominate in the mental life, superseding all other motives, criticism
- 24. Delusion ideas - false conclusion, arising on the painful basis (change of mood, perception, or formation
- 25. false conclusions arising on the painful basis (changes of mood, perception or development of specific logic)
- 26. Stages of formation of delusion ideas (acc. to K. Conrad) Delusional mood Delusional perception Delusional interpretation
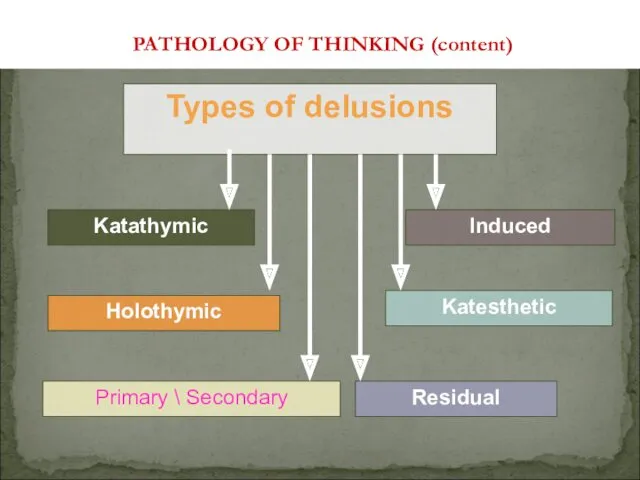
- 27. Holothymic Residual Katathymic PATHOLOGY OF THINKING (content) Types of delusions Katesthetic Primary \ Secondary Induced
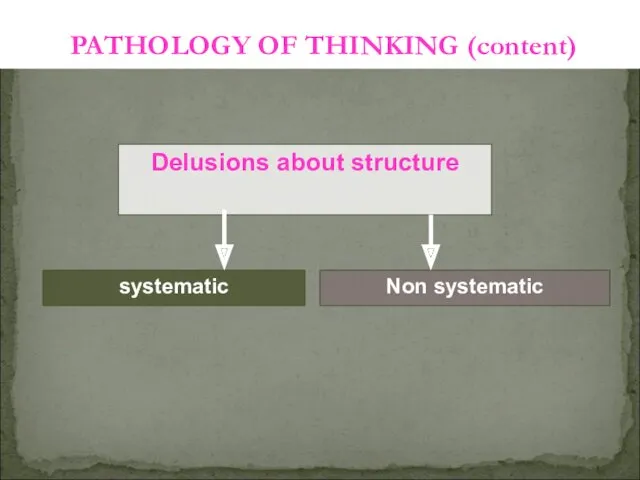
- 28. systematic PATHOLOGY OF THINKING (content) Delusions about structure Non systematic
- 29. Mechanism of formation The paranoiс syndrome - Systematized (primary) interpretation, constructing of stage-by-stage logic The paranoid
- 30. Delusion ideas (of depressive character) I of guilt and self accusation, hypochondria (incurable diseases), nihilistic (internal
- 31. richness, highbred of origin, powerfulness Delusion ideas (of manic character)
- 32. poisoning, damage, influence, relations, prejudice, harassment, jealousy Delusion ideas (of persecution character)
- 33. is a variety of the paranoid syndrome and characterized by phenomena of psychic automatism manifested in
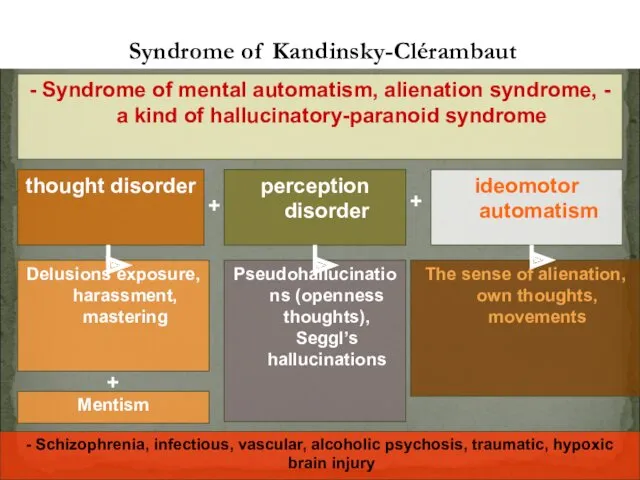
- 34. thought disorder Syndrome of Kandinsky-Clérambaut - Syndrome of mental automatism, alienation syndrome, - a kind of
- 35. Trying to protect against the imposition of other people's thoughts and their openness the syndrome of
- 36. Cotar`s sdm The patients develop delusions of damage, death, destruction of the world, self-condemnation for perpetration
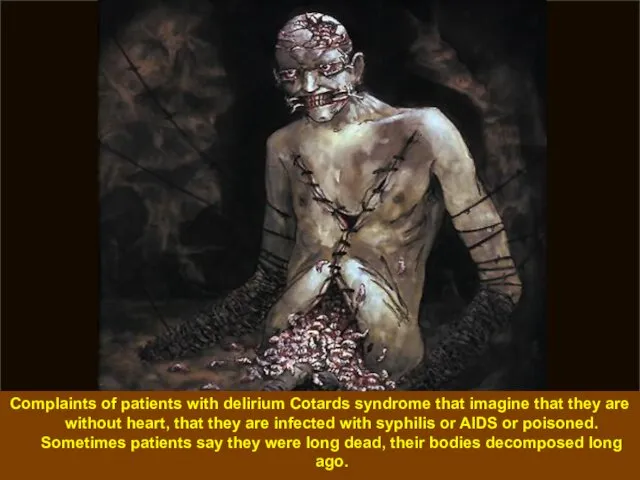
- 37. Complaints of patients with delirium Cotards syndrome that imagine that they are without heart, that they
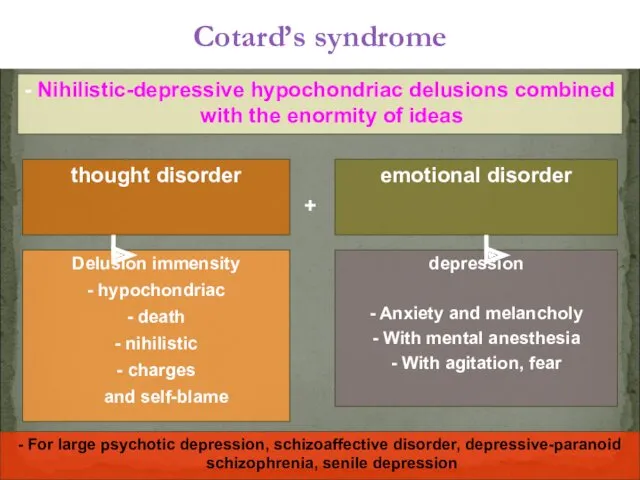
- 38. thought disorder Cotard’s syndrome - Nihilistic-depressive hypochondriac delusions combined with the enormity of ideas depression -
- 39. Figure of Cotard’s syndrome patient with delirium: "I have seen my heart, lungs, covered with pus,
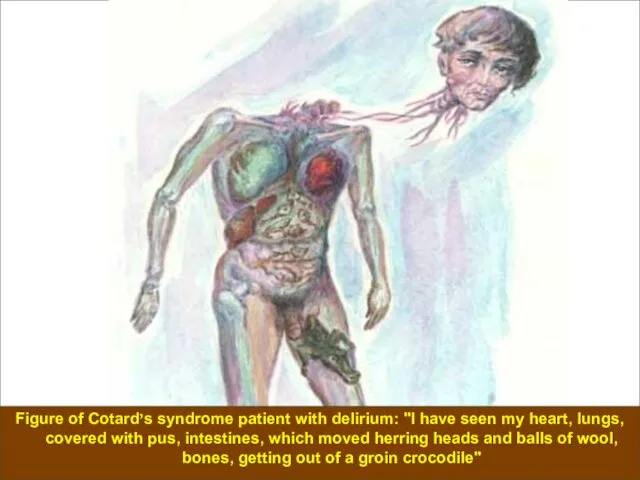
- 40. Ideas denial of the external world in delirium Cotards. Patients say that everything was lost, desolate
- 41. Fregoli`s sdm Fregoli syndrome is the delusional belief that one or more familiar persons, usually persecutors
- 42. Capgra`s sdm Capgras’ syndrome (named after J.M. Capgras) manifests itself by a disturbance in recognizing people.
- 44. Скачать презентацию






























 Философия сестринского дела. Модели сестринского дела
Философия сестринского дела. Модели сестринского дела Экономический анализ деятельности лечебно-профилактических учреждений
Экономический анализ деятельности лечебно-профилактических учреждений Наследственные гипо- и апластические анемии
Наследственные гипо- и апластические анемии Хроническая сердечная недостаточность у пожилых пациентов
Хроническая сердечная недостаточность у пожилых пациентов Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания
Сердечно-сосудистые заболевания Товароведческий анализ резиновых и полимерных изделий
Товароведческий анализ резиновых и полимерных изделий Повреждения голени
Повреждения голени Основы клинической физиологии сердца
Основы клинической физиологии сердца Перкуссия легких
Перкуссия легких Наркотические и ненаркотические анальгетики
Наркотические и ненаркотические анальгетики Балалардағы дермо-респираторлық синдром
Балалардағы дермо-респираторлық синдром Эндокринология. Несахарный диабет. (Лекция 10)
Эндокринология. Несахарный диабет. (Лекция 10) История российского красного креста
История российского красного креста Аускультация сердца
Аускультация сердца Жедел холецистит. Жіктемесі, диагностикасы, саралау диагностикасы. Аурудың асқынулары,асқынуларды диагностикалау
Жедел холецистит. Жіктемесі, диагностикасы, саралау диагностикасы. Аурудың асқынулары,асқынуларды диагностикалау Заболевания почек. Пиелонефрит и гломерулонефрит
Заболевания почек. Пиелонефрит и гломерулонефрит Наиболее распространенные онкозаболевания. Рак толстой кишки
Наиболее распространенные онкозаболевания. Рак толстой кишки Гельминтозы
Гельминтозы Программа государственных гарантий оказания гражданам РФ бесплатной медицинской помощи. (Лекция 2)
Программа государственных гарантий оказания гражданам РФ бесплатной медицинской помощи. (Лекция 2) Характеристика адреностимуляторов, механизм действия, бронхосиндром
Характеристика адреностимуляторов, механизм действия, бронхосиндром Краснуха. Этиология
Краснуха. Этиология Хронический гломерулонефрит. Гематурический гломерулонефрит
Хронический гломерулонефрит. Гематурический гломерулонефрит Спирометрия. Кіріспе бөлім. Спирография туралы түсінік
Спирометрия. Кіріспе бөлім. Спирография туралы түсінік Туберкулез және АИВ
Туберкулез және АИВ Мигрень: патогенез, диагностика, лечение
Мигрень: патогенез, диагностика, лечение Нарушение осанки и плоскостопие
Нарушение осанки и плоскостопие Бұлшықет ұлпасы
Бұлшықет ұлпасы Этико-правовые проблемы трансплантации органов и тканей. (Лекция 9)
Этико-правовые проблемы трансплантации органов и тканей. (Лекция 9)