Содержание
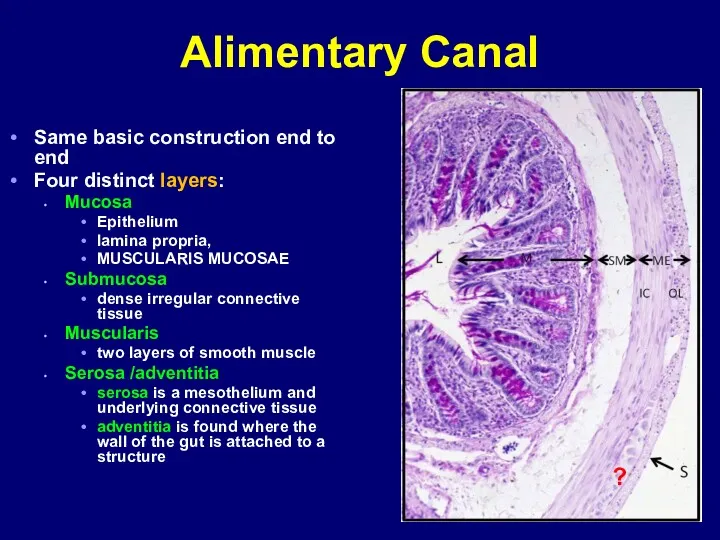
- 2. Alimentary Canal Same basic construction end to end Four distinct layers: Mucosa Epithelium lamina propria, MUSCULARIS
- 3. Mucosa Mucosa has three functions: Barrier separates the lumen (which is in contact with the environment)
- 4. Mucosa: Epithelium Epithelium secretes: Digestive enzymes into lumen onto apical plasma membrane Hormones Mucous Antibodies which
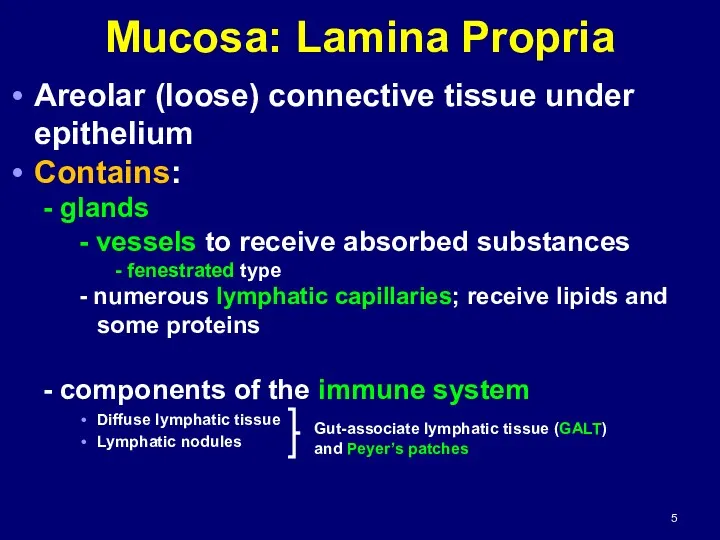
- 5. Mucosa: Lamina Propria Areolar (loose) connective tissue under epithelium Contains: - glands - vessels to receive
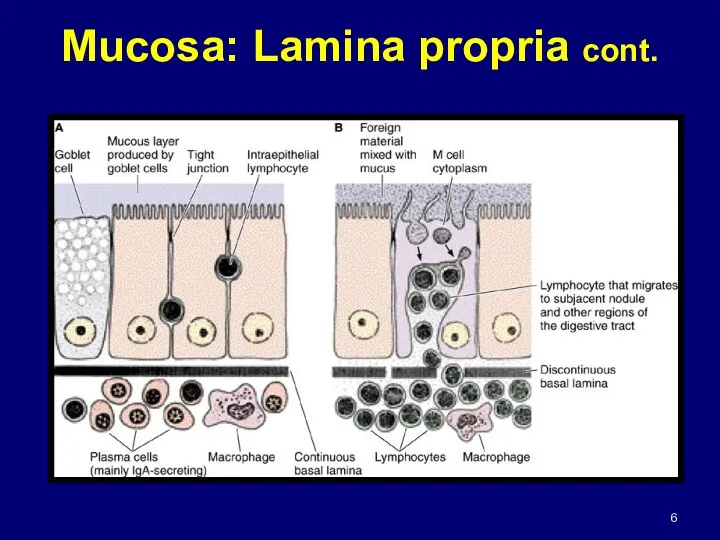
- 6. Mucosa: Lamina propria cont.
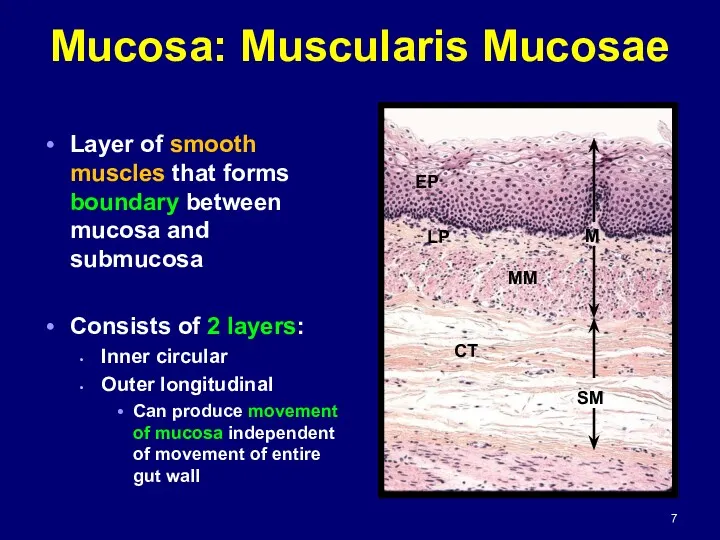
- 7. Mucosa: Muscularis Mucosae Layer of smooth muscles that forms boundary between mucosa and submucosa Consists of
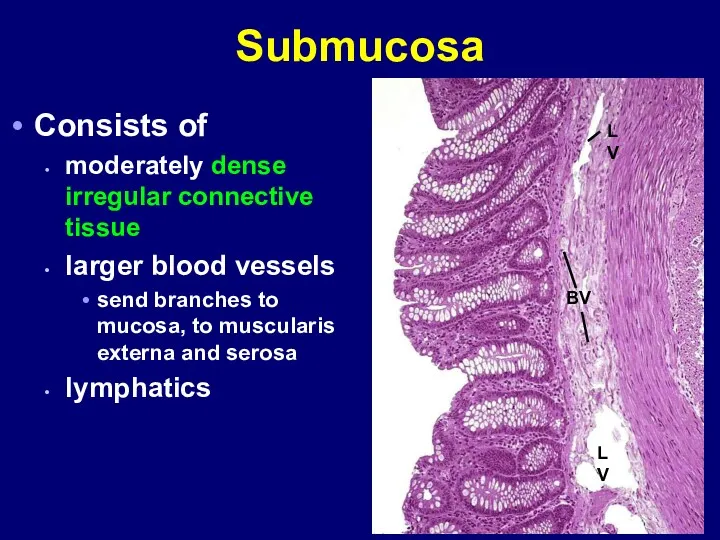
- 8. Submucosa Consists of moderately dense irregular connective tissue larger blood vessels send branches to mucosa, to
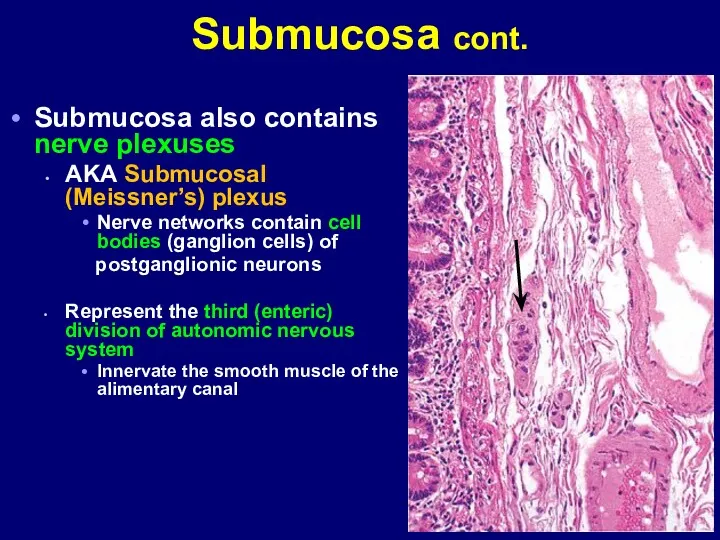
- 9. Submucosa cont. Submucosa also contains nerve plexuses AKA Submucosal (Meissner’s) plexus Nerve networks contain cell bodies
- 10. Neurons of the enteric division show the same pathologic changes that can occur in neurons of
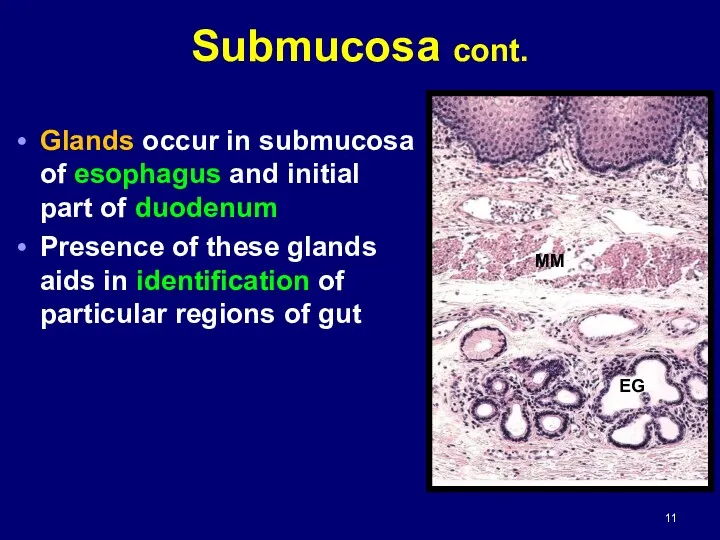
- 11. Glands occur in submucosa of esophagus and initial part of duodenum Presence of these glands aids
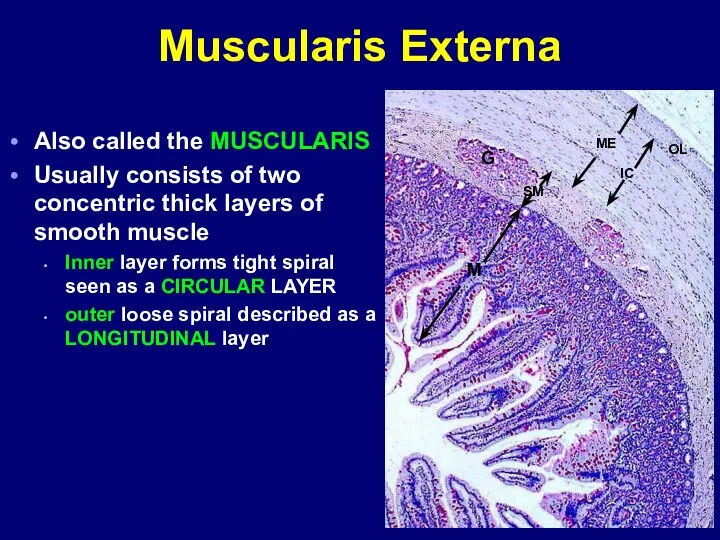
- 12. Muscularis Externa Also called the MUSCULARIS Usually consists of two concentric thick layers of smooth muscle
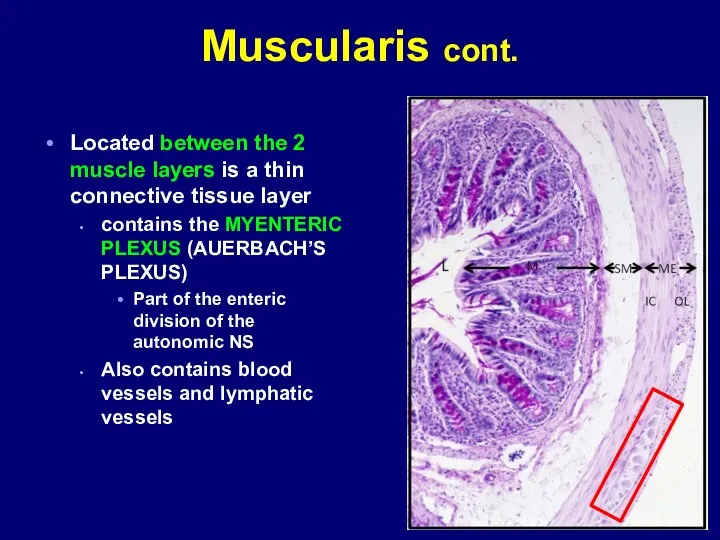
- 13. Muscularis cont. Located between the 2 muscle layers is a thin connective tissue layer contains the
- 15. Serosa & Adventitia Serosa is a membrane containing simple squamous epithelium the MESOTHELIUM and a small
- 16. Serosa & Adventitia cont. Large amounts of fat can accumulate in serosa Where gut has no
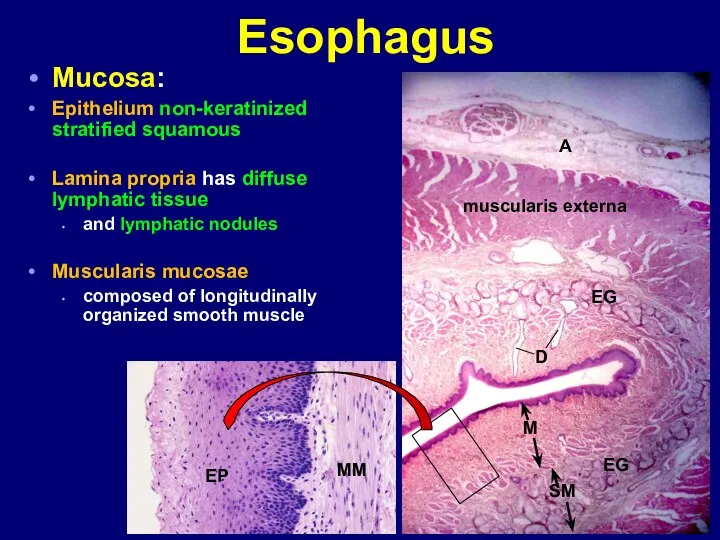
- 17. Esophagus Mucosa: Epithelium non-keratinized stratified squamous Lamina propria has diffuse lymphatic tissue and lymphatic nodules Muscularis
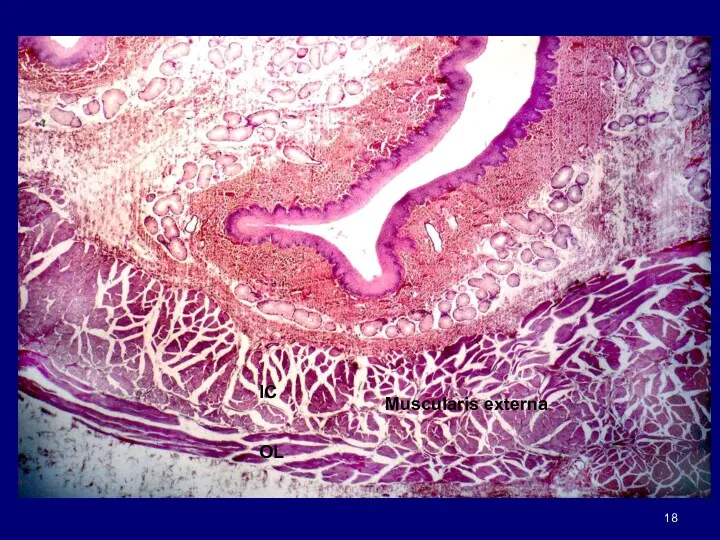
- 18. Muscularis externa IC OL
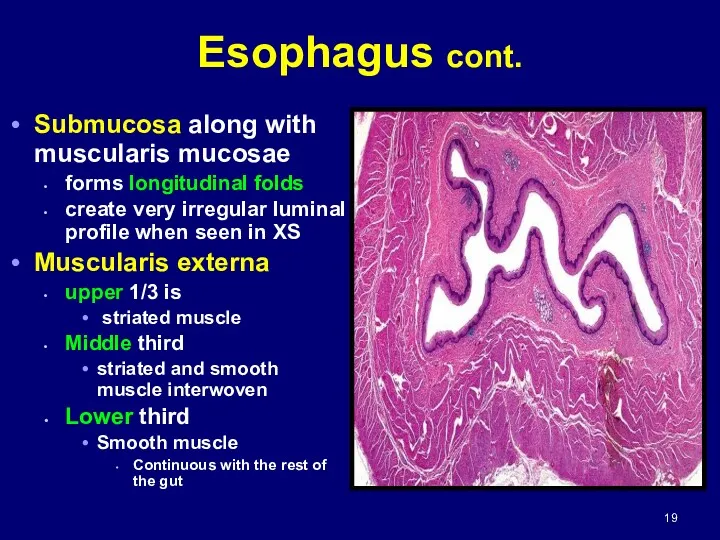
- 19. Esophagus cont. Submucosa along with muscularis mucosae forms longitudinal folds create very irregular luminal profile when
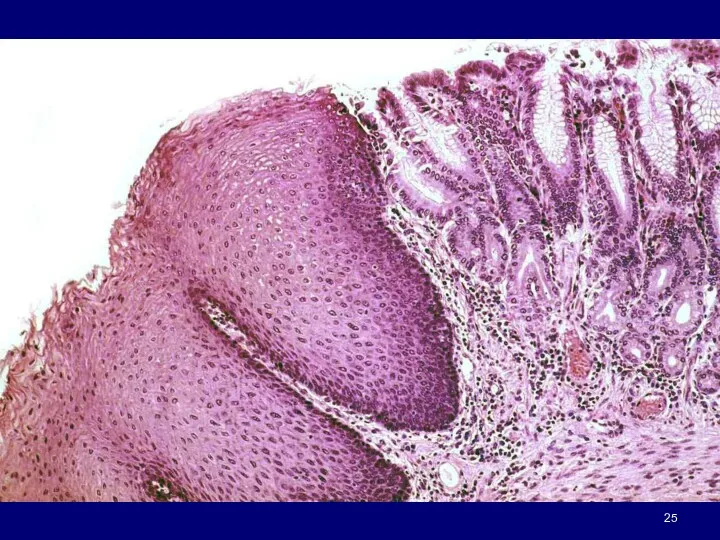
- 21. Esophagus has adventitia until it enters abdominal cavity where it is covered by SEROSA Esophagus cont.
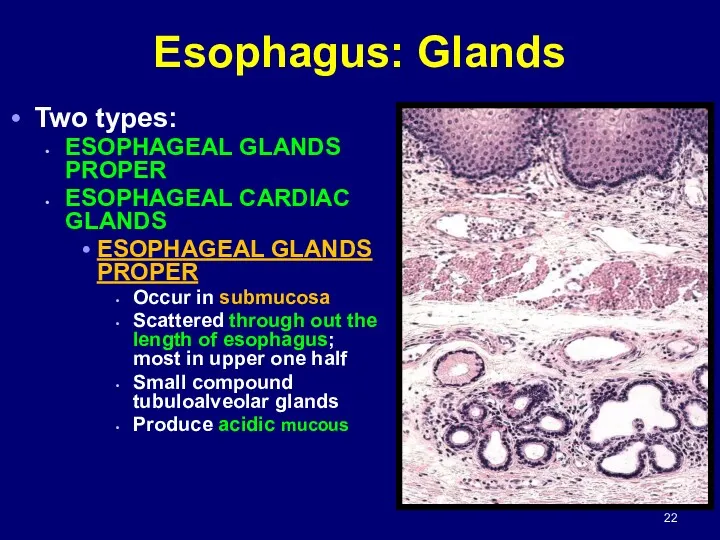
- 22. Esophagus: Glands Two types: ESOPHAGEAL GLANDS PROPER ESOPHAGEAL CARDIAC GLANDS ESOPHAGEAL GLANDS PROPER Occur in submucosa
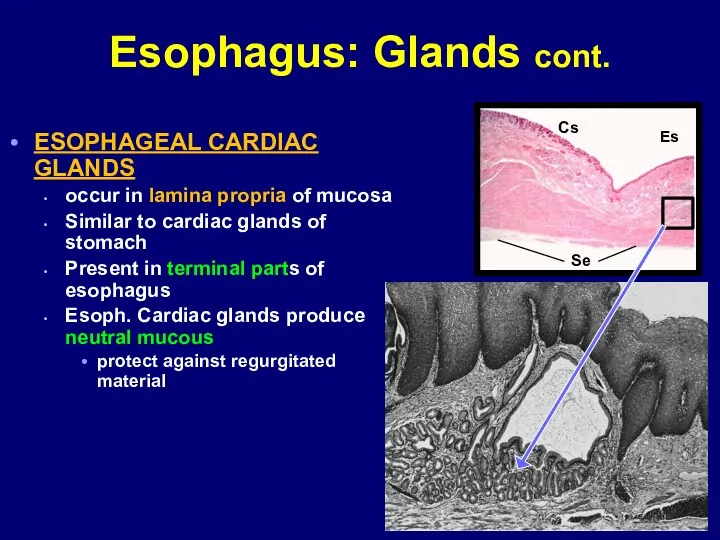
- 24. Esophagus: Glands cont. ESOPHAGEAL CARDIAC GLANDS occur in lamina propria of mucosa Similar to cardiac glands
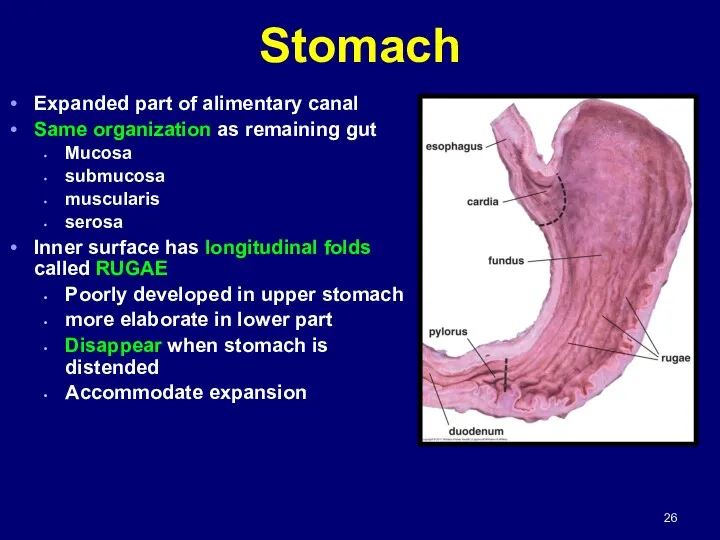
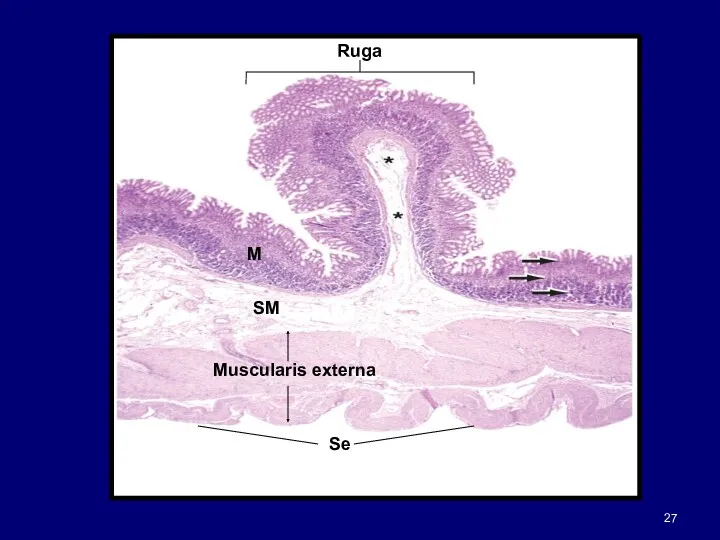
- 26. Stomach Expanded part of alimentary canal Same organization as remaining gut Mucosa submucosa muscularis serosa Inner
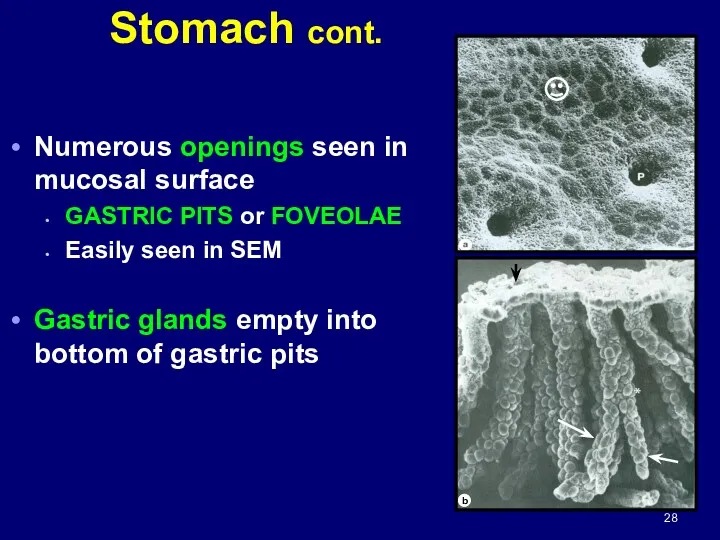
- 28. Stomach cont. Numerous openings seen in mucosal surface GASTRIC PITS or FOVEOLAE Easily seen in SEM
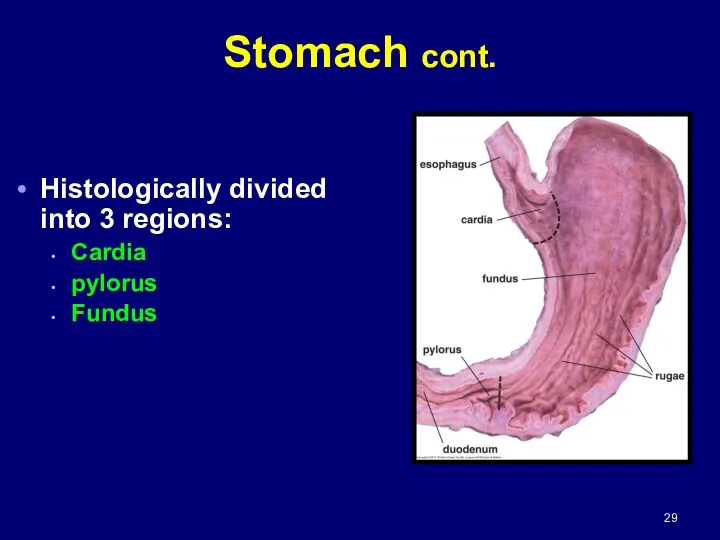
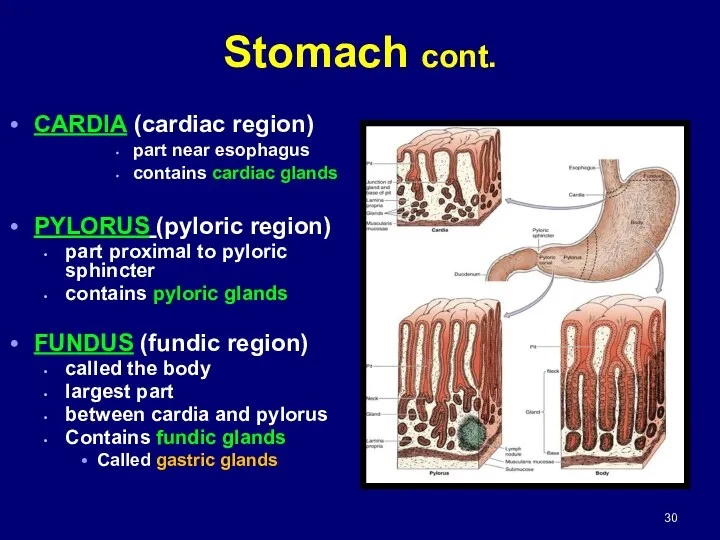
- 29. Histologically divided into 3 regions: Cardia pylorus Fundus Stomach cont.
- 30. CARDIA (cardiac region) part near esophagus contains cardiac glands PYLORUS (pyloric region) part proximal to pyloric
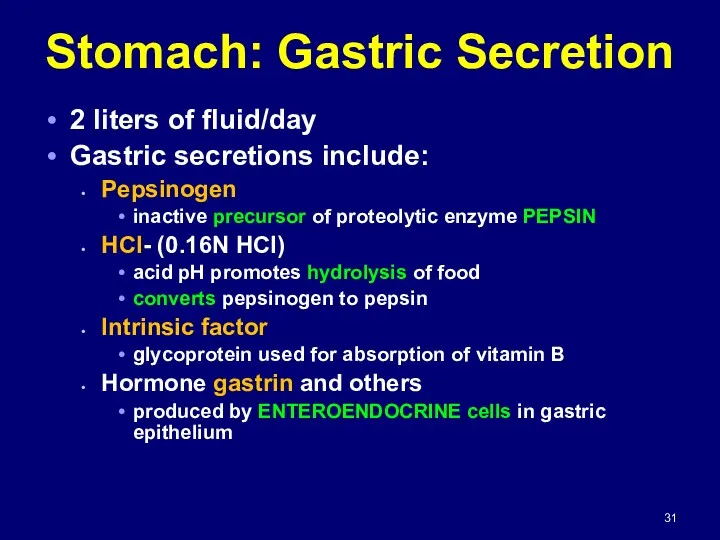
- 31. Stomach: Gastric Secretion 2 liters of fluid/day Gastric secretions include: Pepsinogen inactive precursor of proteolytic enzyme
- 32. Stomach: Absorption Stomach lining absorbs some water salts lipid-soluble drugs certain drugs Asprin enters by damaging
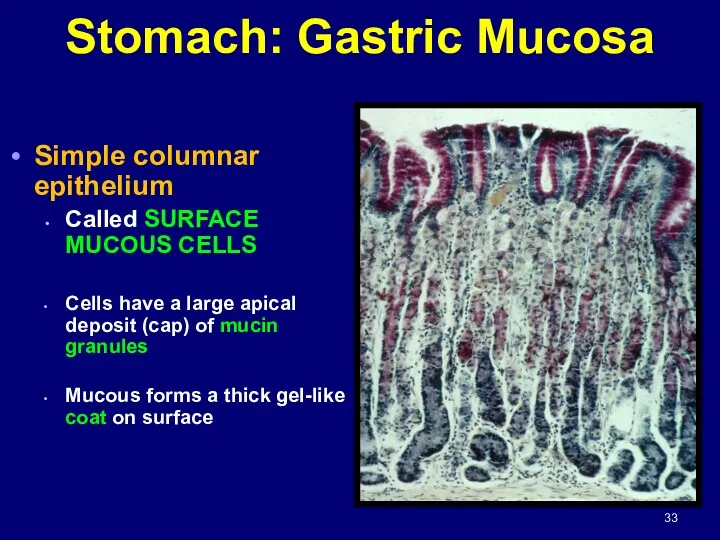
- 33. Stomach: Gastric Mucosa Simple columnar epithelium Called SURFACE MUCOUS CELLS Cells have a large apical deposit
- 34. Fundic Glands Fundic glands; also called gastric glands Produce digestive juice of stomach Present throughout gastric
- 35. Fundic Glands cont. Several glands open into one gastric pit Each gland has long NECK SEGMENT
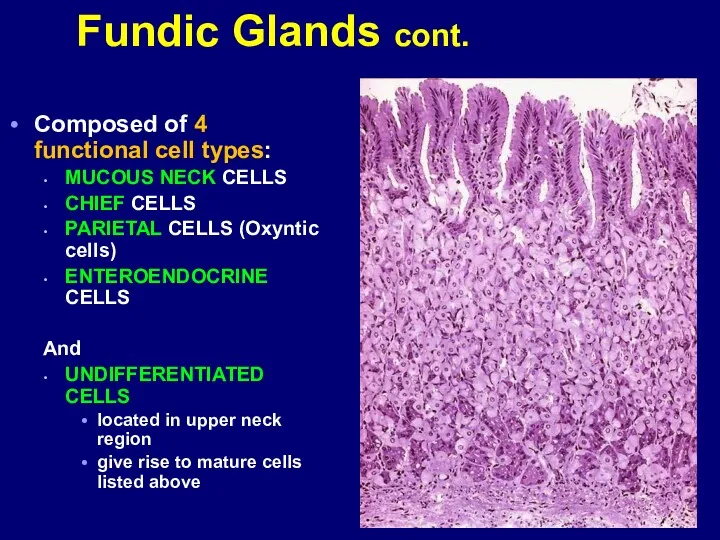
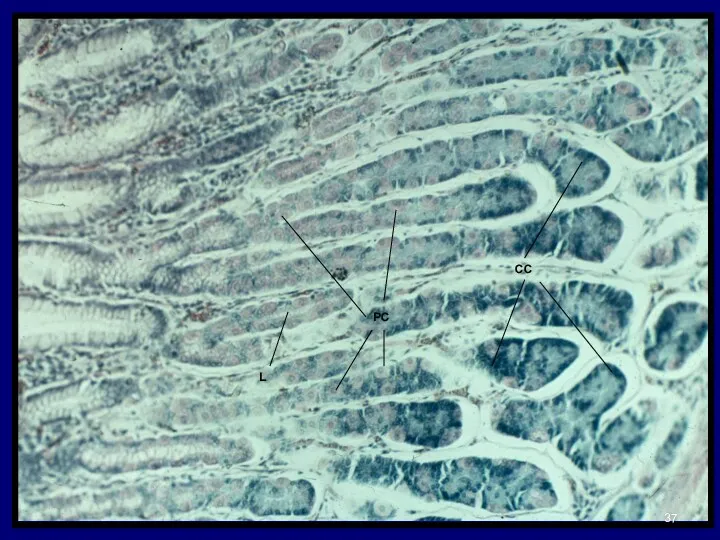
- 36. Composed of 4 functional cell types: MUCOUS NECK CELLS CHIEF CELLS PARIETAL CELLS (Oxyntic cells) ENTEROENDOCRINE
- 37. PC CC L
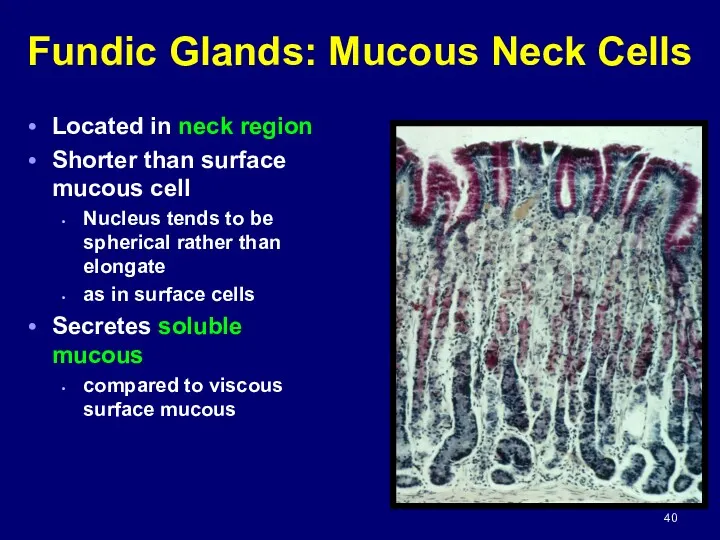
- 40. Fundic Glands: Mucous Neck Cells Located in neck region Shorter than surface mucous cell Nucleus tends
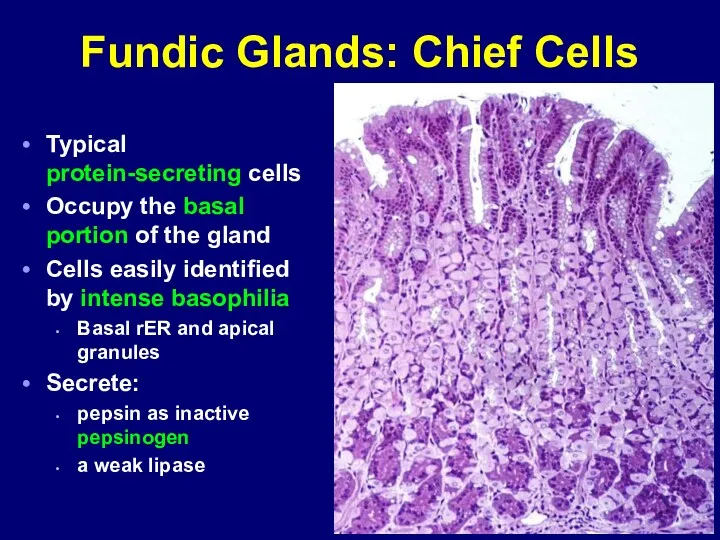
- 41. Fundic Glands: Chief Cells Typical protein-secreting cells Occupy the basal portion of the gland Cells easily
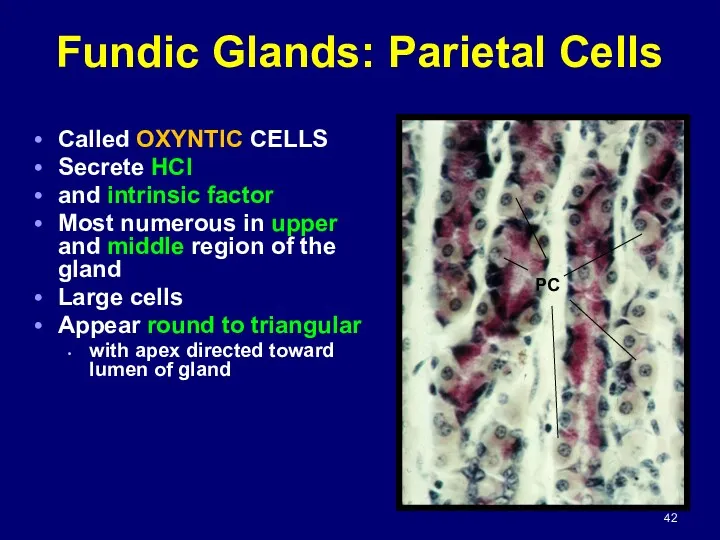
- 42. Fundic Glands: Parietal Cells Called OXYNTIC CELLS Secrete HCl and intrinsic factor Most numerous in upper
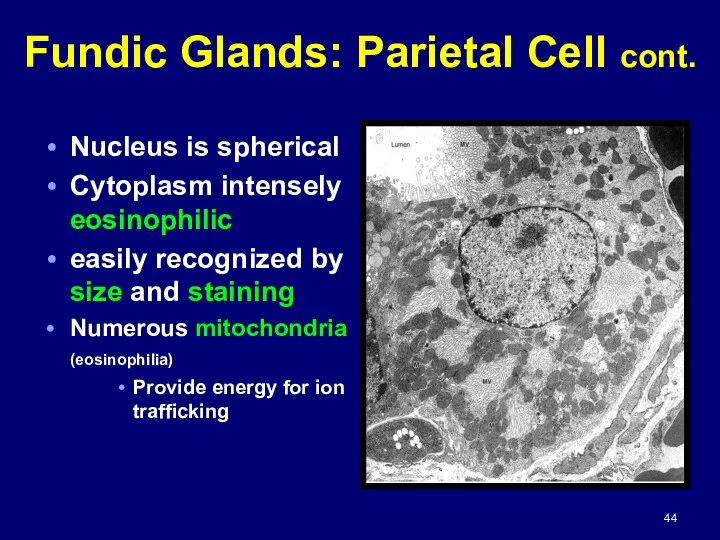
- 44. Fundic Glands: Parietal Cell cont. Nucleus is spherical Cytoplasm intensely eosinophilic easily recognized by size and
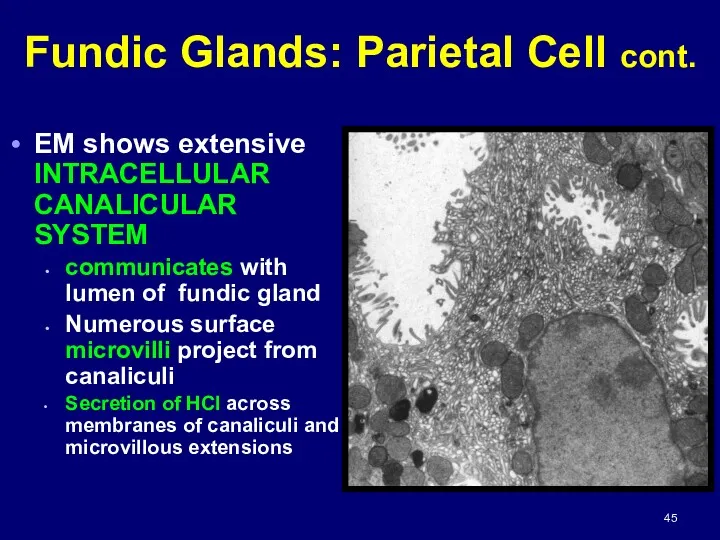
- 45. EM shows extensive INTRACELLULAR CANALICULAR SYSTEM communicates with lumen of fundic gland Numerous surface microvilli project
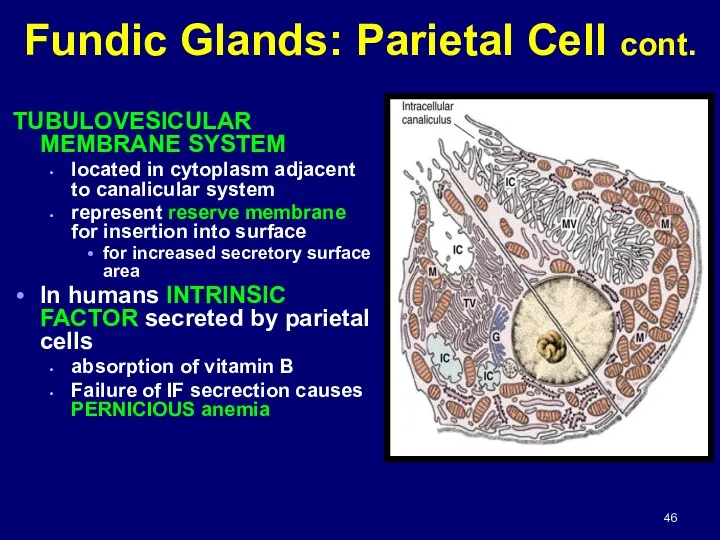
- 46. TUBULOVESICULAR MEMBRANE SYSTEM located in cytoplasm adjacent to canalicular system represent reserve membrane for insertion into
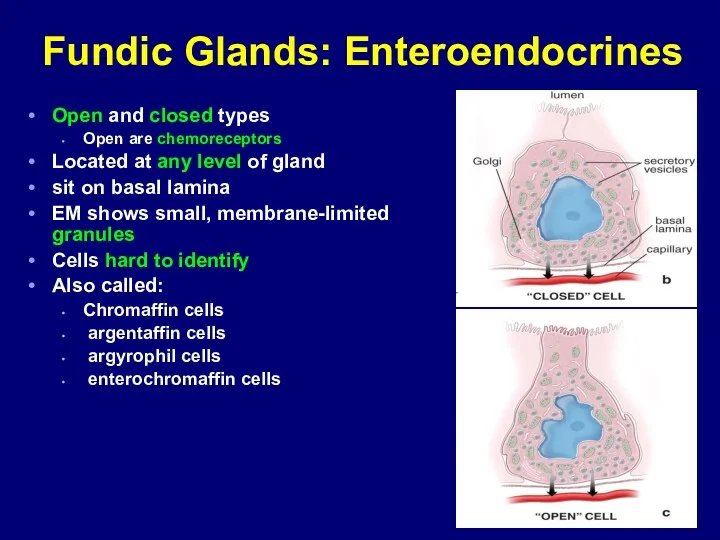
- 47. Fundic Glands: Enteroendocrines Open and closed types Open are chemoreceptors Located at any level of gland
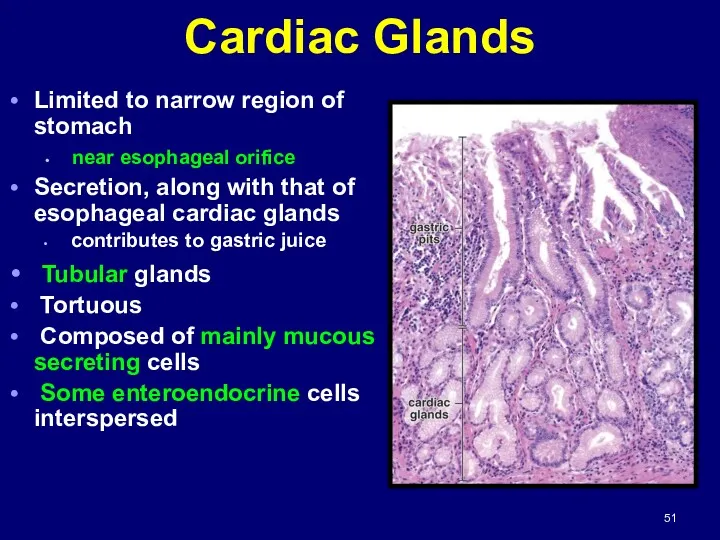
- 51. Cardiac Glands Limited to narrow region of stomach near esophageal orifice Secretion, along with that of
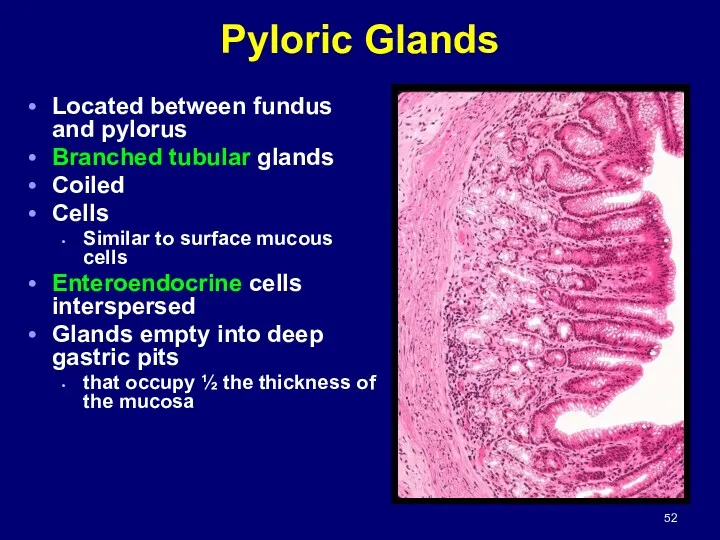
- 52. Pyloric Glands Located between fundus and pylorus Branched tubular glands Coiled Cells Similar to surface mucous
- 55. Скачать презентацию


















 Державна санітарно-епідеміологічна експертиза, як елемент соціально-гігієнічного моніторингу. Основні положення та організація
Державна санітарно-епідеміологічна експертиза, як елемент соціально-гігієнічного моніторингу. Основні положення та організація Операции на органах шеи
Операции на органах шеи Физиология паращитовидных желёз
Физиология паращитовидных желёз Повреждения и заболевания мочеполовых органов
Повреждения и заболевания мочеполовых органов Хирург Н.Н. Бурденко
Хирург Н.Н. Бурденко Арбовирусты инфекциялар. Кенелік энцефалит вирусы
Арбовирусты инфекциялар. Кенелік энцефалит вирусы Венозный возврат (ВВ) – приток венозной крови к сердцу
Венозный возврат (ВВ) – приток венозной крови к сердцу Шум и вибрация
Шум и вибрация Алкогольный цирроз
Алкогольный цирроз Возрастные особенности системы крови и иммунитета
Возрастные особенности системы крови и иммунитета Неврозы
Неврозы Противоаритмические лекарственные средства
Противоаритмические лекарственные средства Здоровье на работе. Что должен знать о ВИЧ/СПИДе каждый?
Здоровье на работе. Что должен знать о ВИЧ/СПИДе каждый? Гигиена аптечных заведений
Гигиена аптечных заведений Гиперчувствительность. Иммунодефициты. Аутоиммунные процессы
Гиперчувствительность. Иммунодефициты. Аутоиммунные процессы Послеродовые депрессии
Послеродовые депрессии Аллергия. Стоматология
Аллергия. Стоматология 84-я Всероссийская научная конференция студентов и молодых ученых. Отчет. Секция: Общая хирургия
84-я Всероссийская научная конференция студентов и молодых ученых. Отчет. Секция: Общая хирургия Клинико-экономические исследования
Клинико-экономические исследования Химиотерапевтические лекарственные препараты, макролиды и азалиды
Химиотерапевтические лекарственные препараты, макролиды и азалиды Пороки сердца
Пороки сердца Асқорыту жолдарының қатерлі және қатерсіз ісіктері
Асқорыту жолдарының қатерлі және қатерсіз ісіктері Мировые демографические показатели рождаемость, смертность в развитых и развивающихся странах. Демографическая ситуация в Росси
Мировые демографические показатели рождаемость, смертность в развитых и развивающихся странах. Демографическая ситуация в Росси Классификация геморрагического васкулита
Классификация геморрагического васкулита Белки
Белки ЦМК СД в акушерстве и гинекологии ,
ЦМК СД в акушерстве и гинекологии , Medical Education in Japan
Medical Education in Japan Заболевания органов пищеварения у пожилых людей
Заболевания органов пищеварения у пожилых людей