Содержание
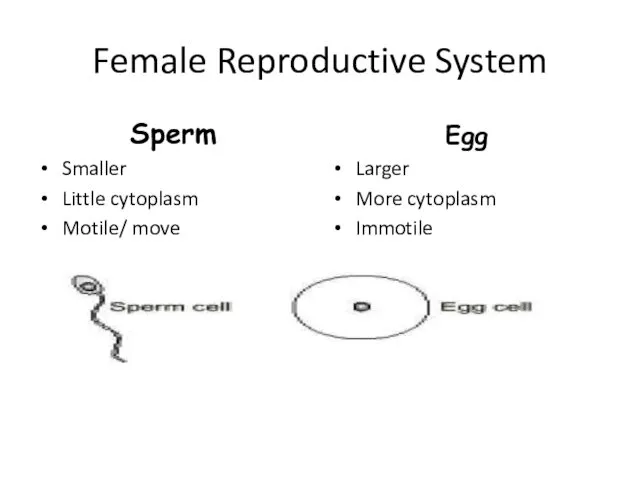
- 2. Female Reproductive System Sperm Smaller Little cytoplasm Motile/ move Egg Larger More cytoplasm Immotile
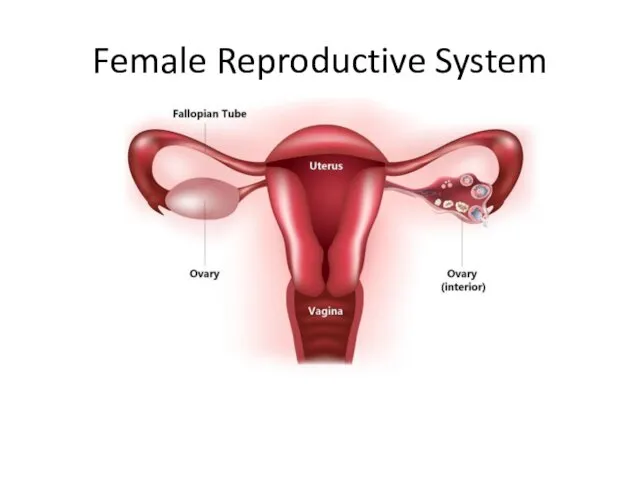
- 3. Female Reproductive System
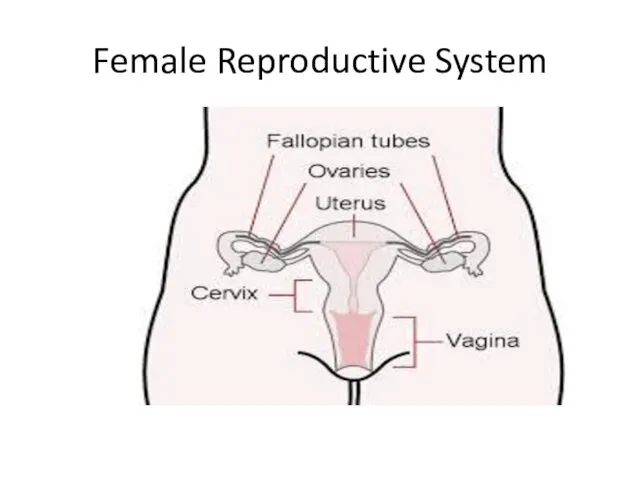
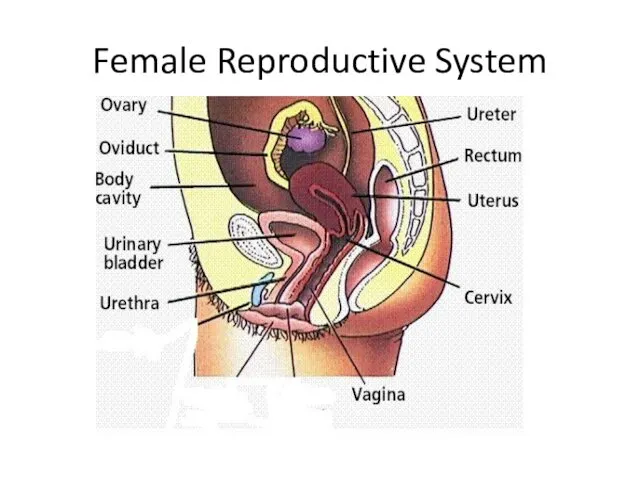
- 4. Female Reproductive System
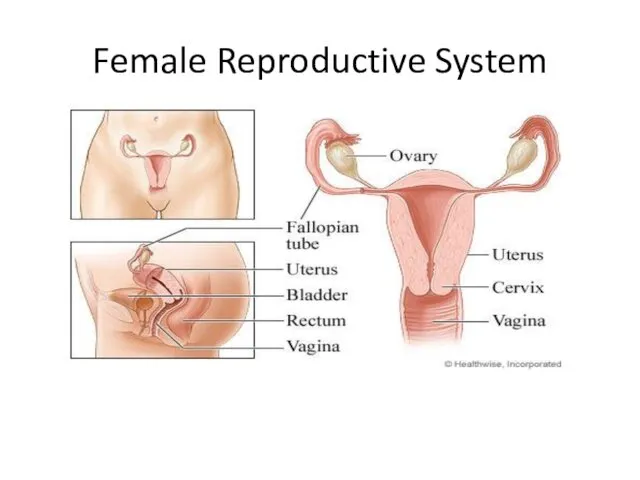
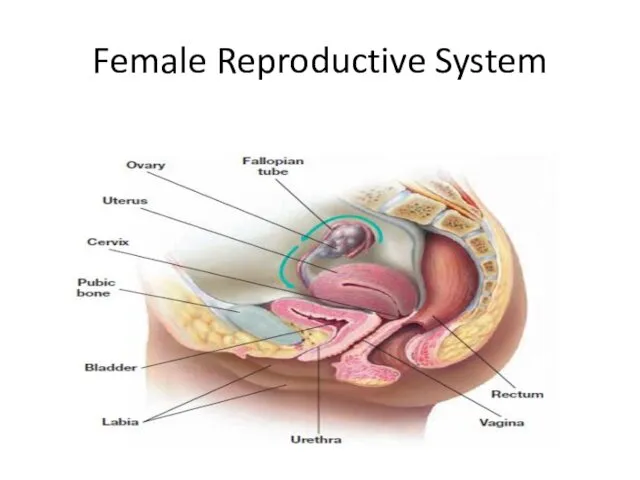
- 5. Female Reproductive System
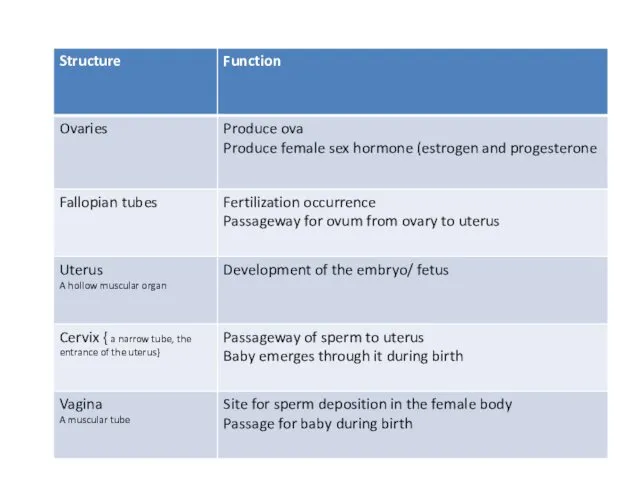
- 6. Female Reproductive System
- 7. Female Reproductive System
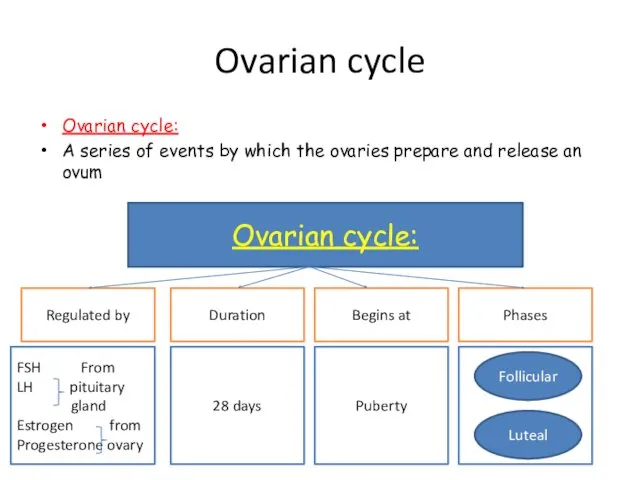
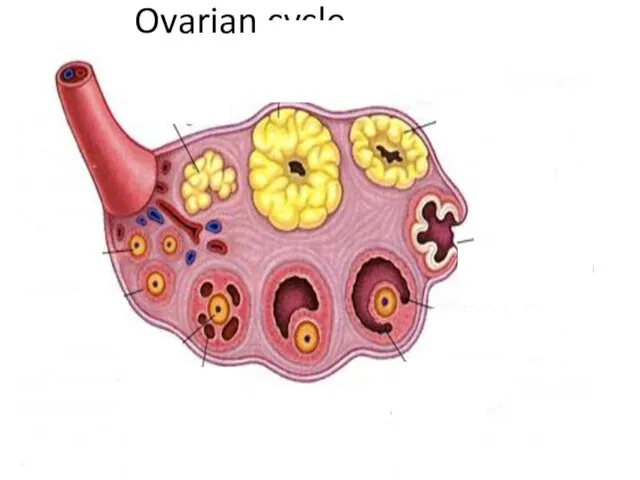
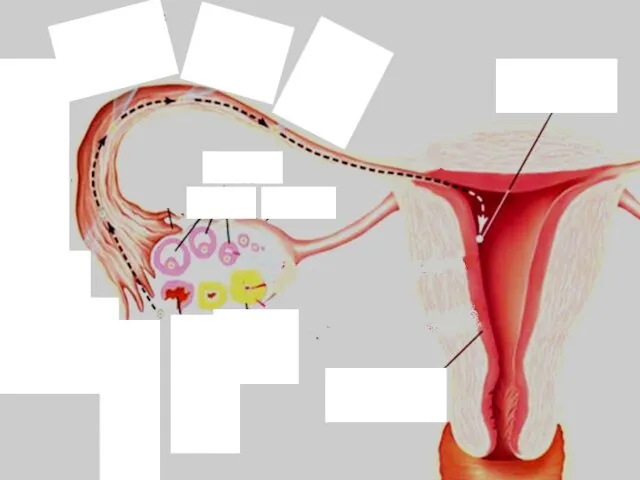
- 9. Ovarian cycle Ovarian cycle: A series of events by which the ovaries prepare and release an
- 10. Ovarian cycle
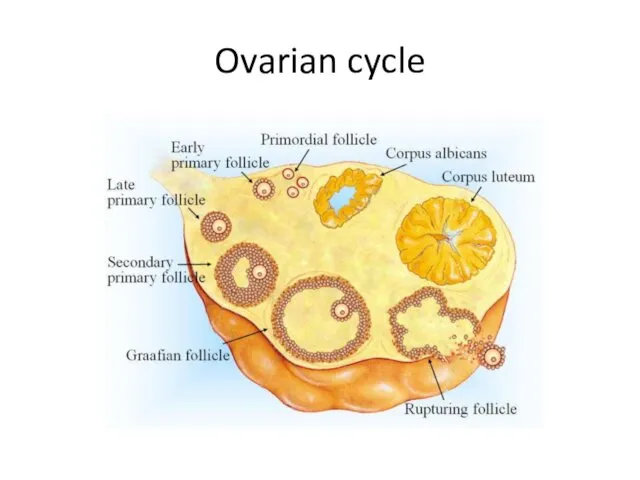
- 12. Ovarian cycle
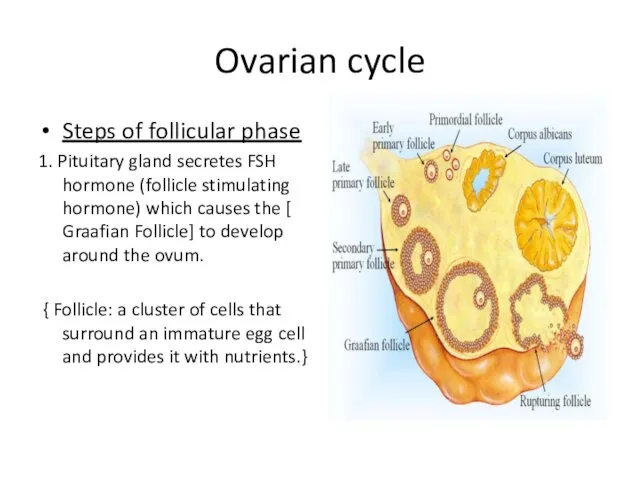
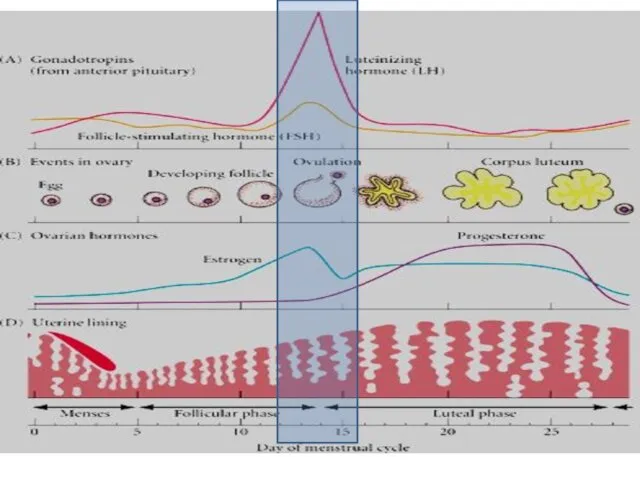
- 13. Ovarian cycle Steps of follicular phase 1. Pituitary gland secretes FSH hormone (follicle stimulating hormone) which
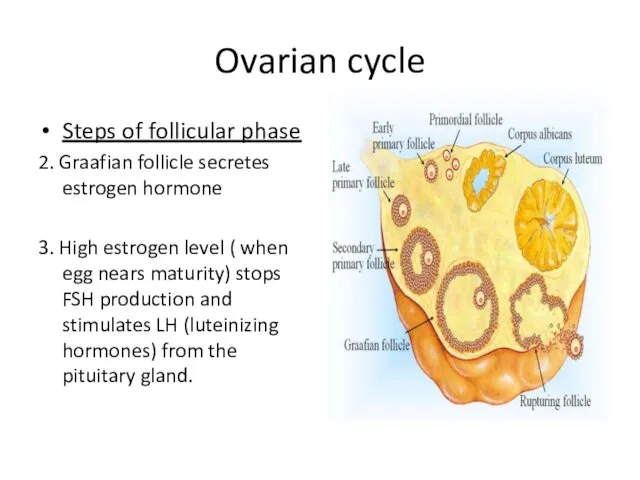
- 14. Ovarian cycle Steps of follicular phase 2. Graafian follicle secretes estrogen hormone 3. High estrogen level
- 15. Ovarian cycle Steps of follicular phase 4. LH causes the egg cell to mature and the
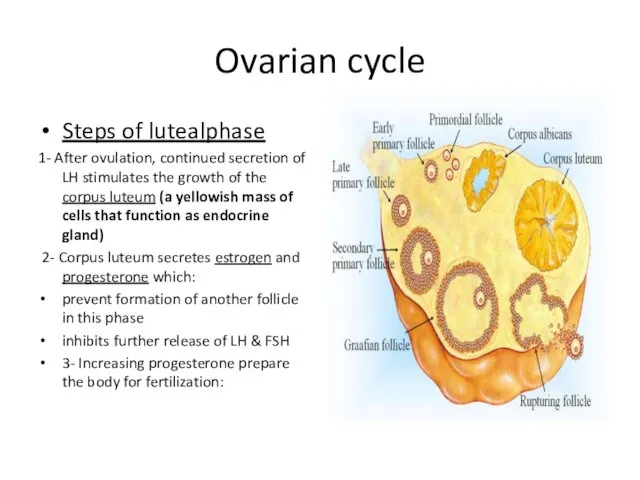
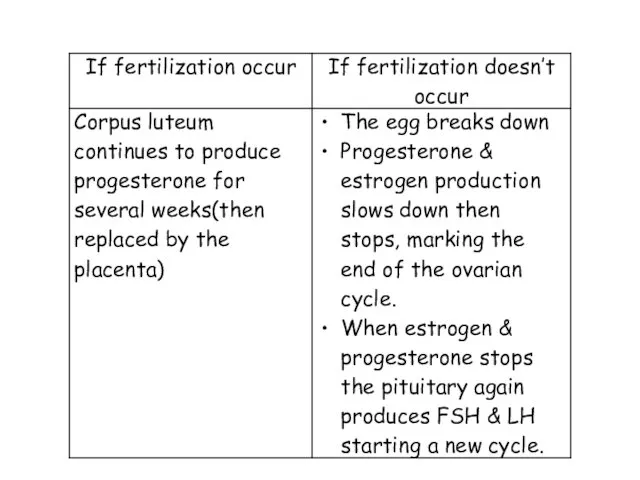
- 16. Ovarian cycle Steps of lutealphase 1- After ovulation, continued secretion of LH stimulates the growth of
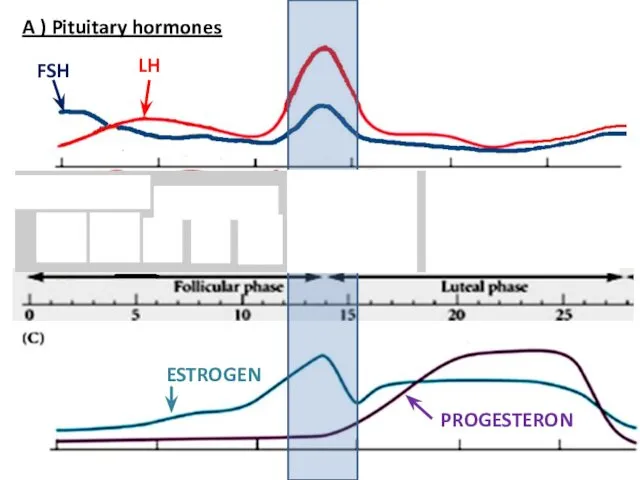
- 18. A ) Pituitary hormones
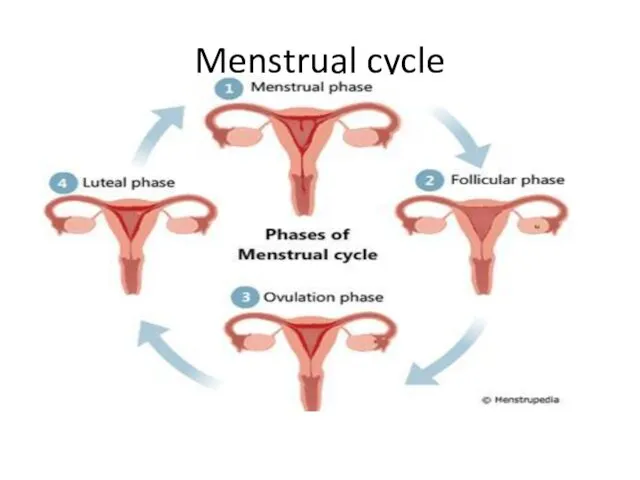
- 20. Menstrual cycle Menstrual Cycle: changes occur in the uterus preparing it for pregnancy each month It
- 21. Menstrual cycle Events of the cycle: 1. before ovulation when estrogen increases the lining of the
- 22. Menstrual cycle
- 23. Menstrual cycle Menstruation: A process when blood and discarded tissue leave the body through the vagina.
- 24. Menopause: It is when women stop menstruation (or the shutdown of ovarian & menstrual cycles) It
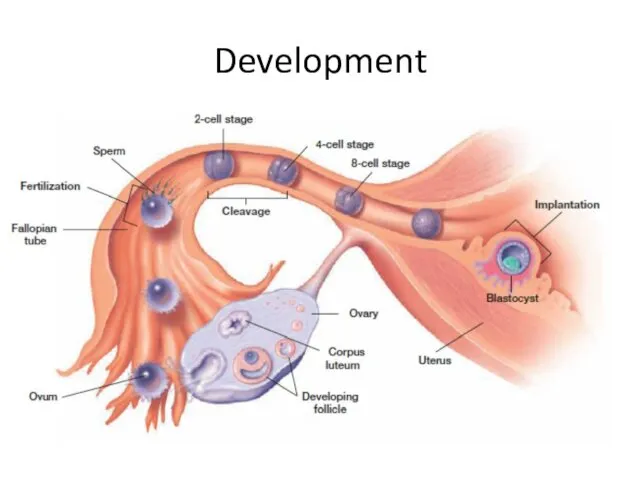
- 25. Development Fertilization: Ovulation occurs About the same time, sperm enter the vagina. Sperm swim up through
- 26. Development The zygote is produced. zygote is the fertilized egg or the cell that is produced
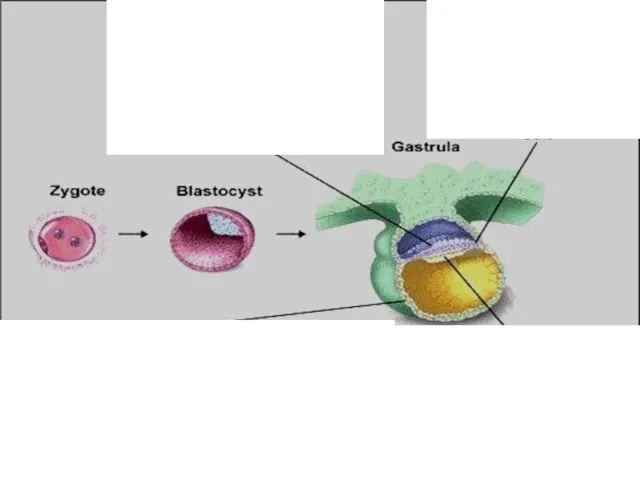
- 28. Cleavage Cleavage
- 29. Development
- 31. Development - it produces many smaller cells within the zygote (1,2,4,8.16….) - it continues as the
- 32. PREGNANCY
- 33. Pregnancy: Gestation: the period of about 9 months (about 40 weeks) of humans developments inside the
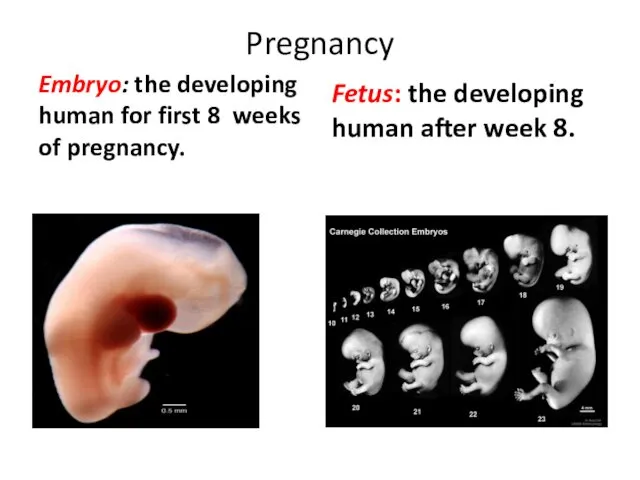
- 34. Pregnancy Fetus: the developing human after week 8. Embryo: the developing human for first 8 weeks
- 35. pregnancy The 9 months of pregnancy are often divided into three trimesters, or 3-month periods. Gestation
- 39. Pregnancy First Trimester: the most important events of development occur. 1. The embryo grows rapidly 2.
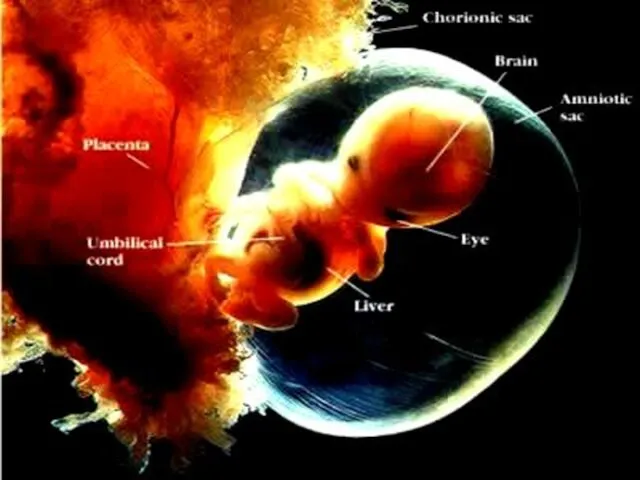
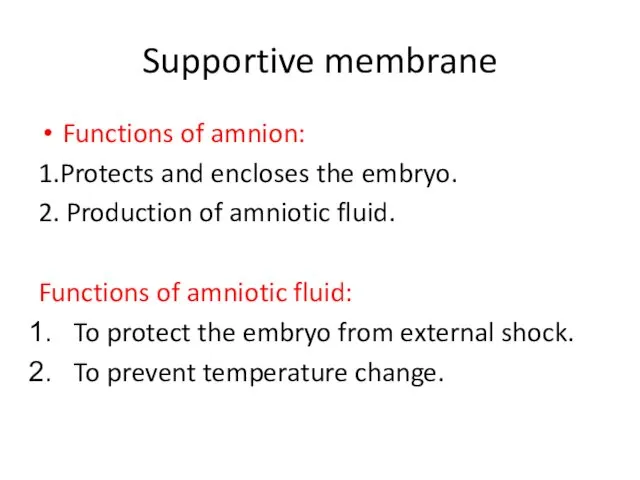
- 43. Supportive membrane Functions of amnion: 1.Protects and encloses the embryo. 2. Production of amniotic fluid. Functions
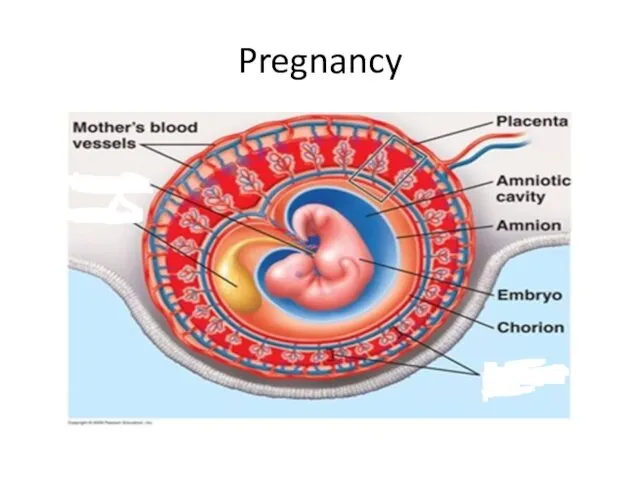
- 44. Pregnancy
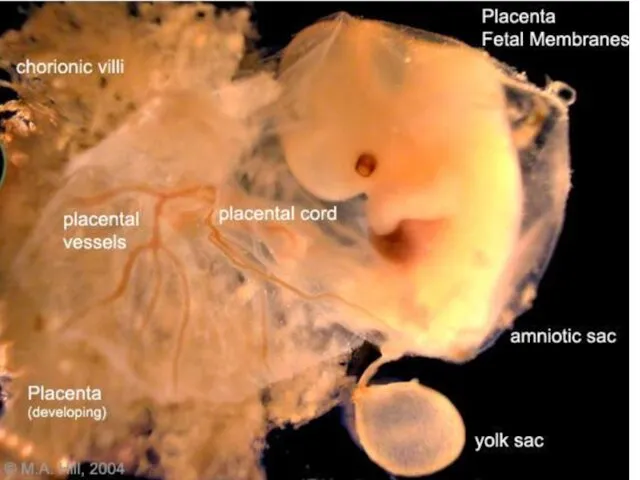
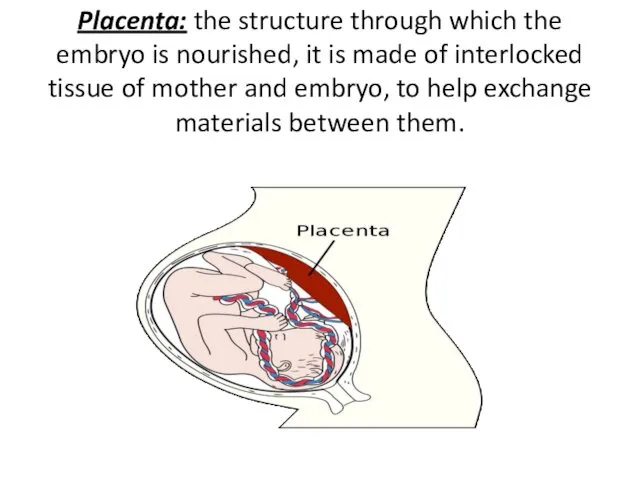
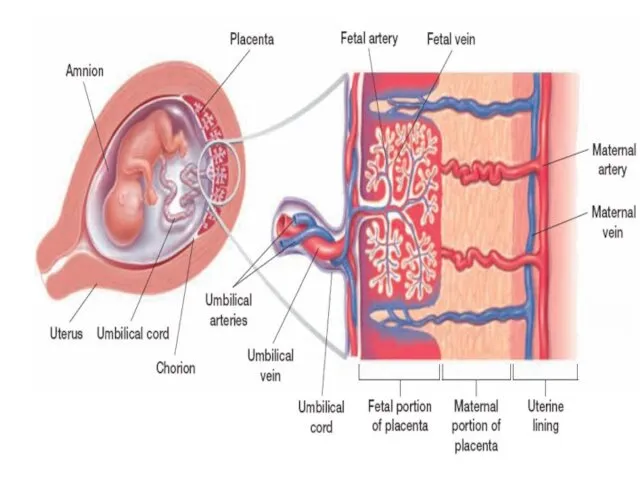
- 45. Placenta: the structure through which the embryo is nourished, it is made of interlocked tissue of
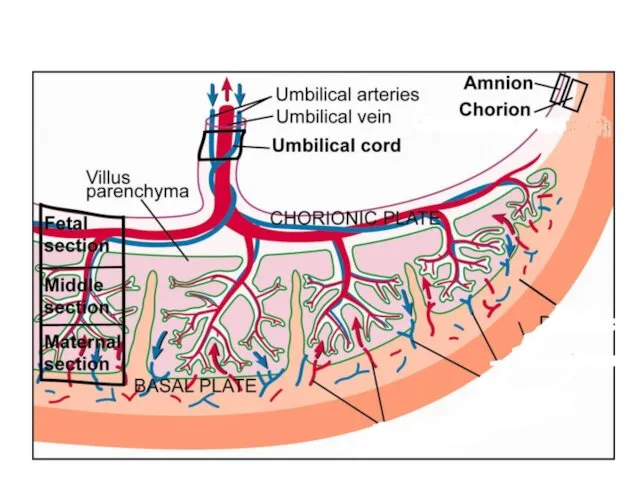
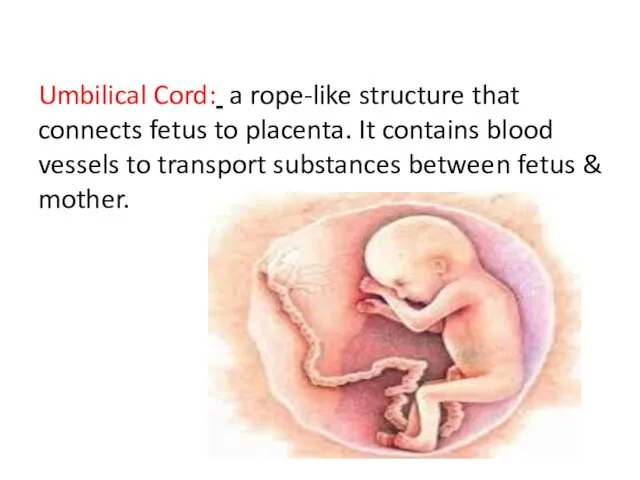
- 46. Umbilical Cord: a rope-like structure that connects fetus to placenta. It contains blood vessels to transport
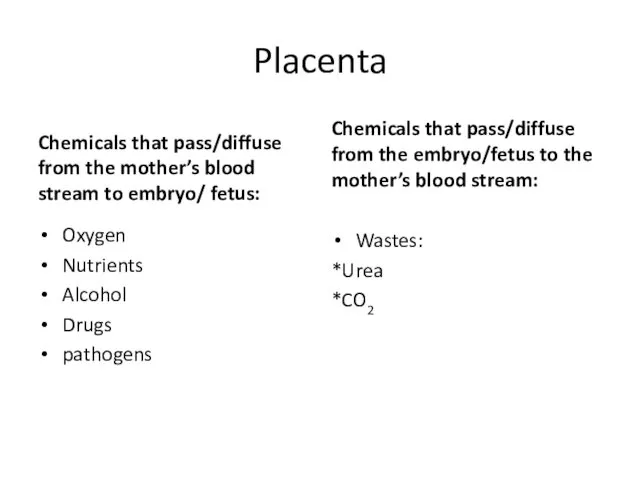
- 47. Placenta Chemicals that pass/diffuse from the mother’s blood stream to embryo/ fetus: Oxygen Nutrients Alcohol Drugs
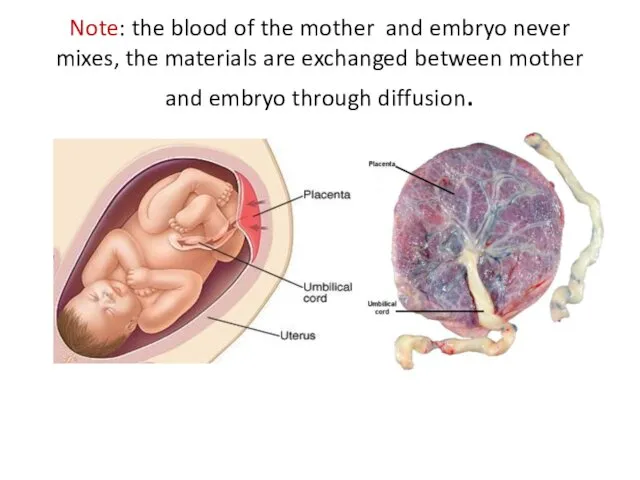
- 49. Note: the blood of the mother and embryo never mixes, the materials are exchanged between mother
- 51. Features of placenta to allow substances to diffuse easily 1. Placenta is folded (villi-like structure) to
- 52. Role of placenta in maintaining pregnancy: Producing progesterone & estrogen to: *prevent ovulation *maintain a thick
- 53. Role of placenta in development of embryo: Oxygen and nutrients in the mother's blood diffuse through
- 54. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Drinking alcohol , smoking or using drugs during pregnancy can cause : Fetal
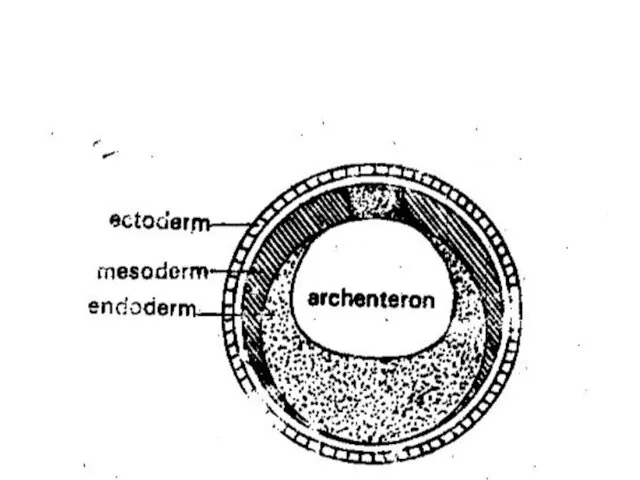
- 55. Continue Events of 1st Trimester: Formation of embryo: * After placenta forms, the inner cells of
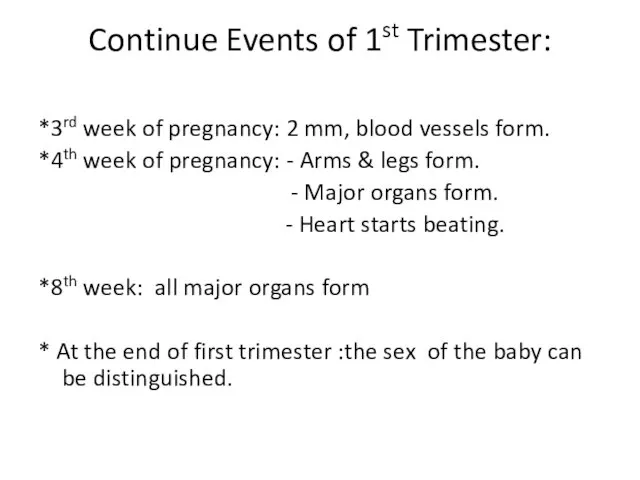
- 57. Continue Events of 1st Trimester: *3rd week of pregnancy: 2 mm, blood vessels form. *4th week
- 58. Second & Third Trimester: Rapid growth of fetus occurs. Organs become functional. At the end of
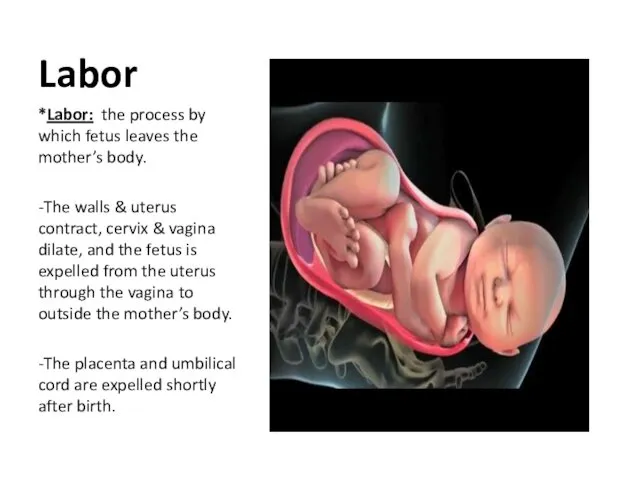
- 59. Labor *Labor: the process by which fetus leaves the mother’s body. -The walls & uterus contract,
- 60. After birth Physical growth and neurological development continue for years after birth.
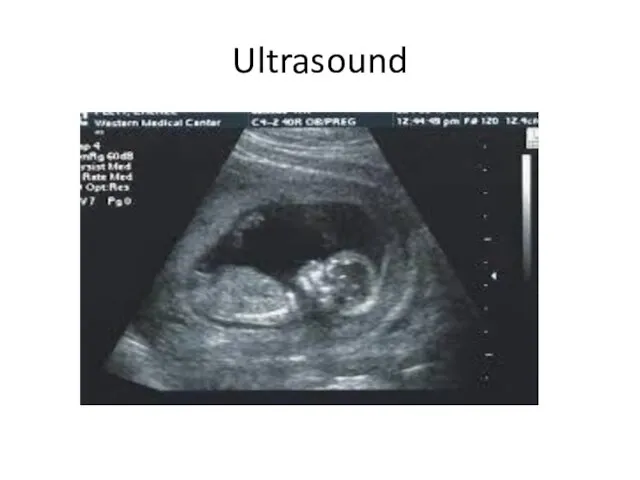
- 61. Ultrasound
- 62. Uses of ultrasound Indicates the fetus age. Indicate the health of the fetus. Diagnose fetal abnormalities.
- 63. Sexually transmitted diseases STD’s Pathogens are present in body fluid such as SEMEN and can be
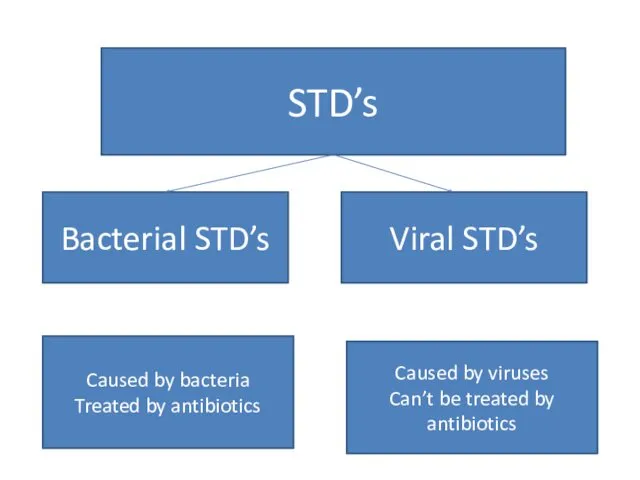
- 64. STD’s Bacterial STD’s Viral STD’s Caused by bacteria Treated by antibiotics Caused by viruses Can’t be
- 66. Скачать презентацию
























 Реакция на тяжелый стресс и нарушения адаптации
Реакция на тяжелый стресс и нарушения адаптации Методы пломбирования корневых каналов
Методы пломбирования корневых каналов Тыныс алу ағзаларының жедел ауруларында және обструктивті аурулар кезіндегі ауруханаға дейінгі шұғыл
Тыныс алу ағзаларының жедел ауруларында және обструктивті аурулар кезіндегі ауруханаға дейінгі шұғыл Введение в медицинскую микологию. Кандидозы
Введение в медицинскую микологию. Кандидозы Актуальные направления и инновации в медицине
Актуальные направления и инновации в медицине Нефролгия и урология
Нефролгия и урология Основные принципы диагностики гемолитической болезни плода
Основные принципы диагностики гемолитической болезни плода Болезни склеры
Болезни склеры Неспецифические воспалительные заболевания мочеполовой системы
Неспецифические воспалительные заболевания мочеполовой системы Организация медицинской помощи населению
Организация медицинской помощи населению Стоматологиялық науқасты негізгі және қосымша тексеру әдістері
Стоматологиялық науқасты негізгі және қосымша тексеру әдістері Структурные подразделения медицинского учреждения
Структурные подразделения медицинского учреждения Хирургиялық стоматологиядағы дәлелді медицина
Хирургиялық стоматологиядағы дәлелді медицина Диагностика и лечение хронических заболеваний вен нижних конечностей
Диагностика и лечение хронических заболеваний вен нижних конечностей Влияние наркотических препаратов на ЦНС
Влияние наркотических препаратов на ЦНС Сұйық дәрілік үлгілердің технологиясы
Сұйық дәрілік үлгілердің технологиясы Психостимуляторы. Классификация психостимуляторов
Психостимуляторы. Классификация психостимуляторов Папилломавирусная инфекция
Папилломавирусная инфекция Гидроцефалия
Гидроцефалия Этиология нарушений речи
Этиология нарушений речи Хронические заболевания печени
Хронические заболевания печени Изучение мнения пациентов об имидже врача
Изучение мнения пациентов об имидже врача Лекарственные средства, применяемые при злокачественных новообразованиях
Лекарственные средства, применяемые при злокачественных новообразованиях Методологические предпосылки и основные понятия теории динамической локализации ВПФ в приложении к детской нейропсихологии
Методологические предпосылки и основные понятия теории динамической локализации ВПФ в приложении к детской нейропсихологии Лекарственные препараты антидепрессанты
Лекарственные препараты антидепрессанты Раны. Классификация. Виды. Лечение
Раны. Классификация. Виды. Лечение Противоаллергические средства (ПАС)
Противоаллергические средства (ПАС) Перша допомога при ушкодженнях ОРС
Перша допомога при ушкодженнях ОРС