Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults презентация
Содержание
- 2. Publication Information This slide set is adapted from the 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/ NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention,
- 3. 2017 High Blood Pressure Guideline Writing Committee *American Society for Preventive Cardiology Representative. †ACC/AHA Representative. ‡Lay
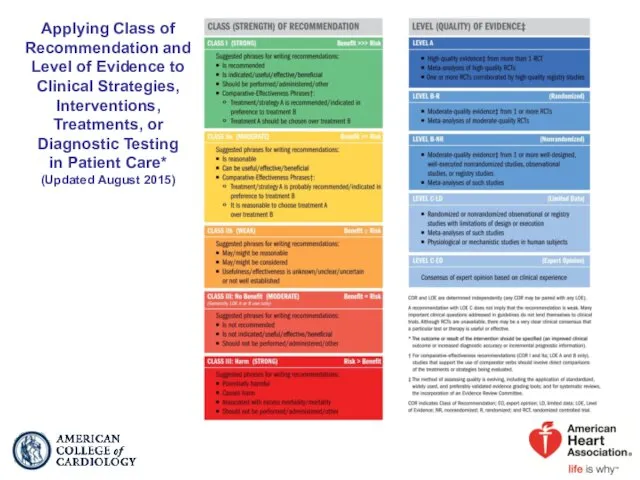
- 4. Applying Class of Recommendation and Level of Evidence to Clinical Strategies, Interventions, Treatments, or Diagnostic Testing
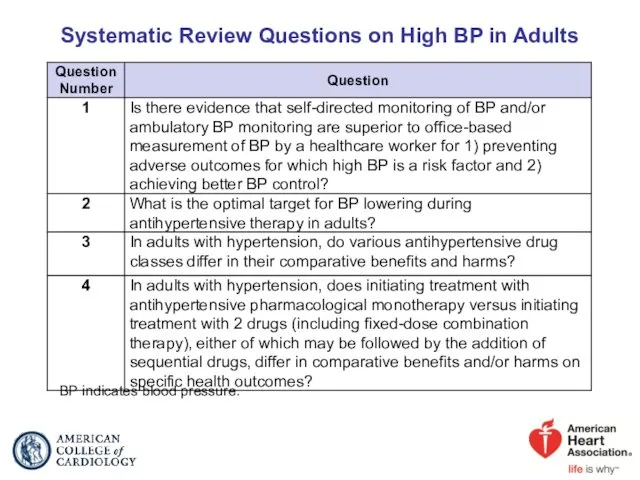
- 5. Systematic Review Questions on High BP in Adults BP indicates blood pressure.
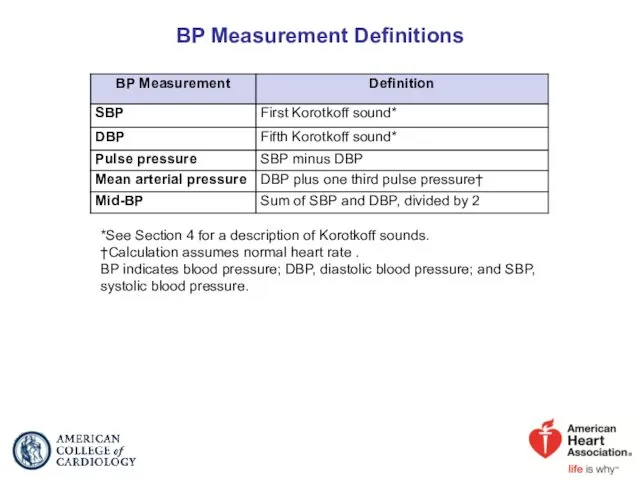
- 6. BP Measurement Definitions *See Section 4 for a description of Korotkoff sounds. †Calculation assumes normal heart
- 7. BP and CVD Risk 2017 Hypertension Clinical Practice Guidelines
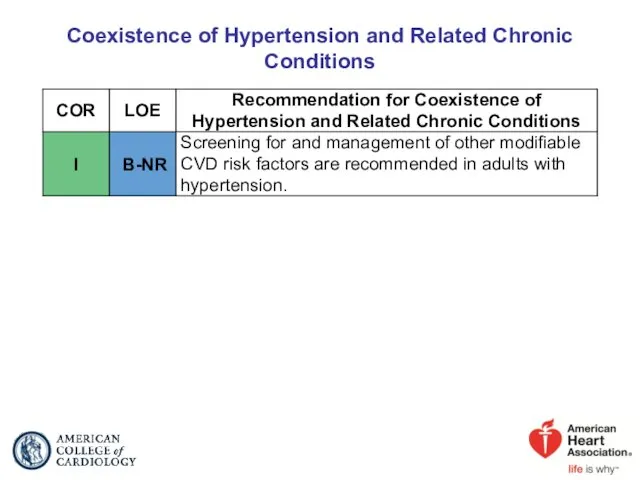
- 8. Coexistence of Hypertension and Related Chronic Conditions
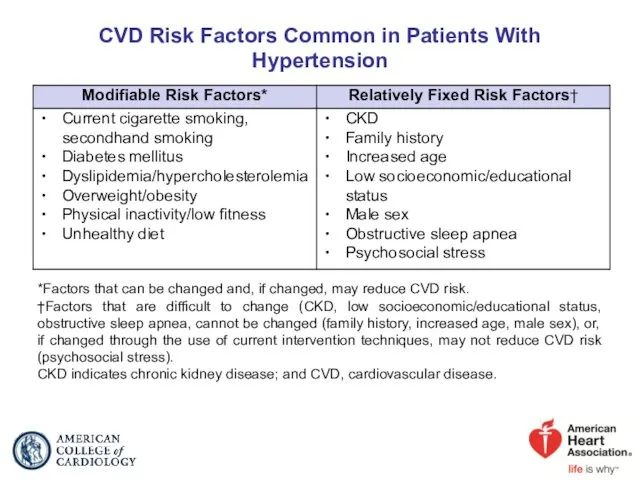
- 9. CVD Risk Factors Common in Patients With Hypertension *Factors that can be changed and, if changed,
- 10. Classification of BP 2017 Hypertension Guideline
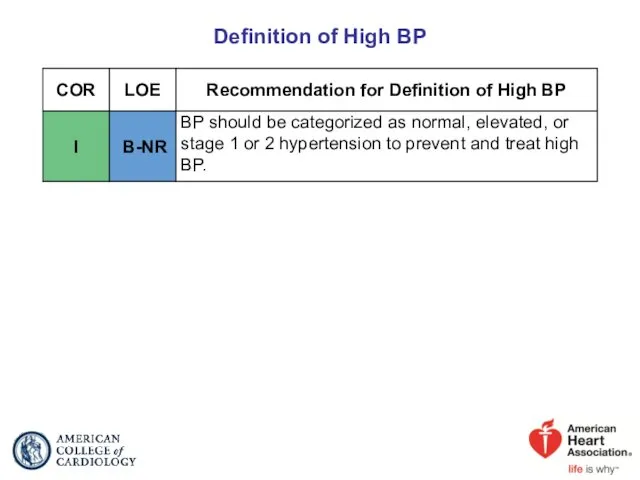
- 11. Definition of High BP
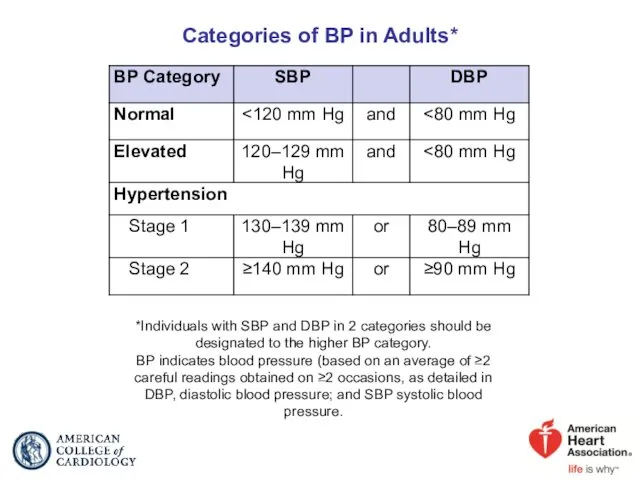
- 12. Categories of BP in Adults* *Individuals with SBP and DBP in 2 categories should be designated
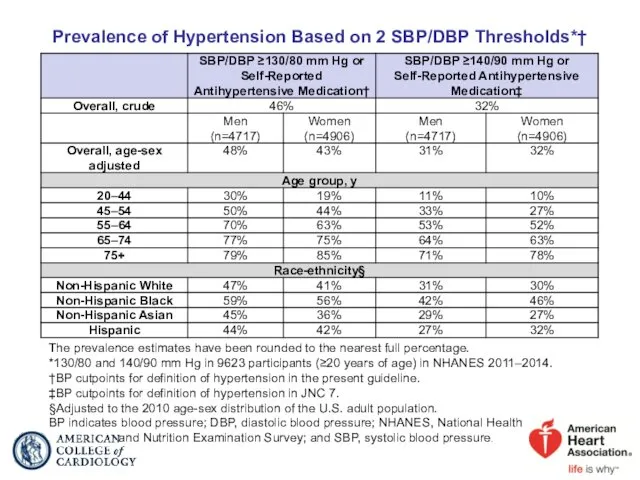
- 13. Prevalence of Hypertension Based on 2 SBP/DBP Thresholds*† The prevalence estimates have been rounded to the
- 14. Measurement of BP 2017 Hypertension Guideline
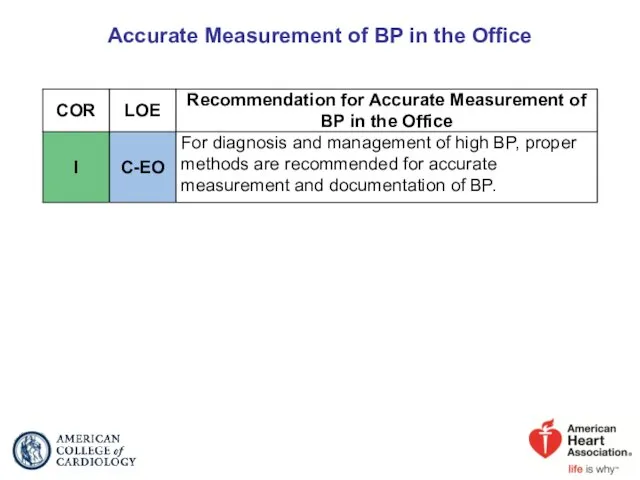
- 15. Accurate Measurement of BP in the Office
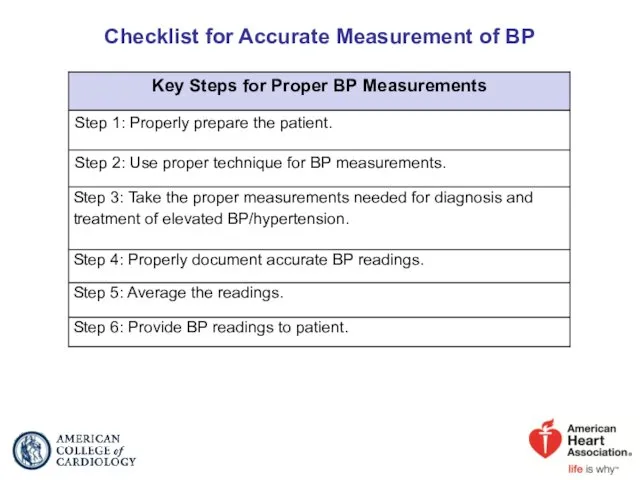
- 16. Checklist for Accurate Measurement of BP
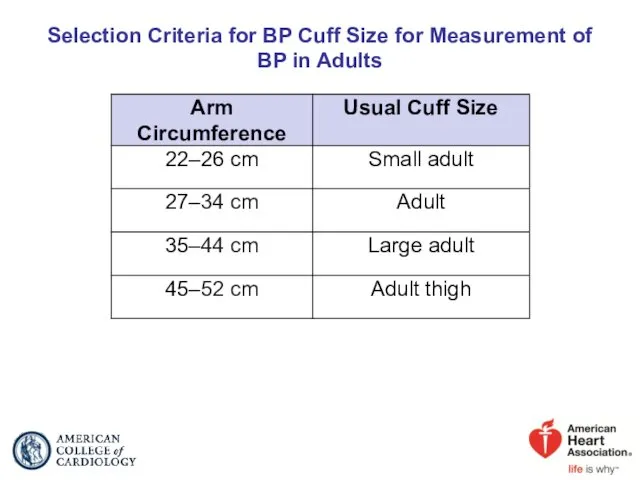
- 17. Selection Criteria for BP Cuff Size for Measurement of BP in Adults
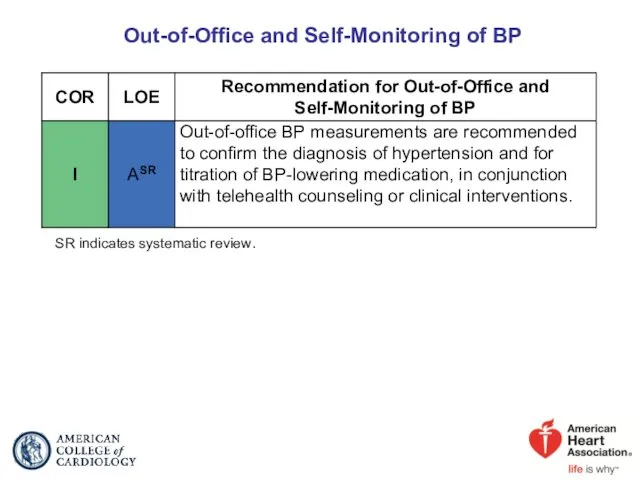
- 18. Out-of-Office and Self-Monitoring of BP SR indicates systematic review.
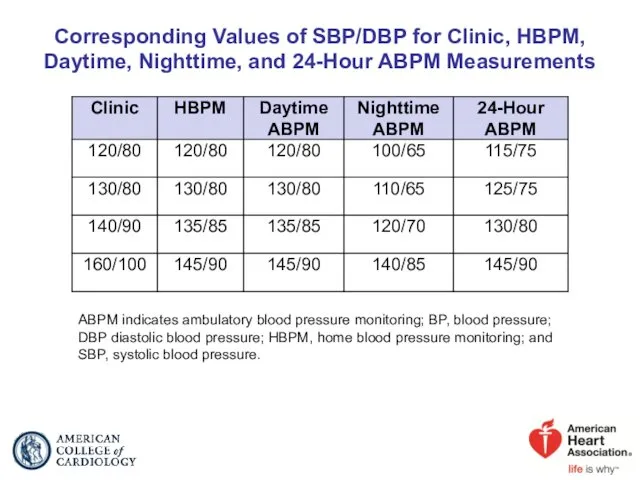
- 19. Corresponding Values of SBP/DBP for Clinic, HBPM, Daytime, Nighttime, and 24-Hour ABPM Measurements ABPM indicates ambulatory
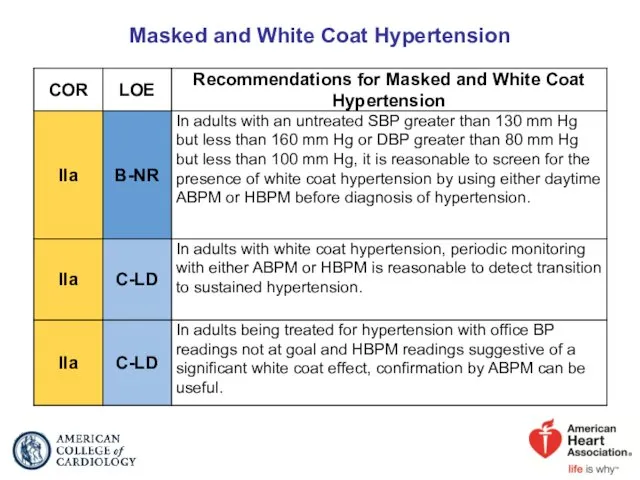
- 20. Masked and White Coat Hypertension
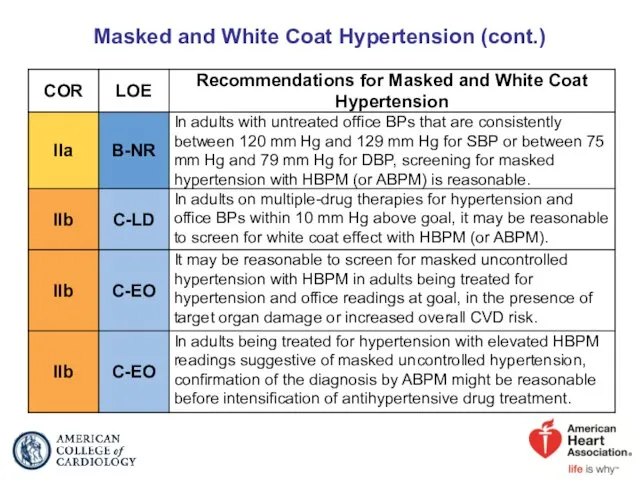
- 21. Masked and White Coat Hypertension (cont.)
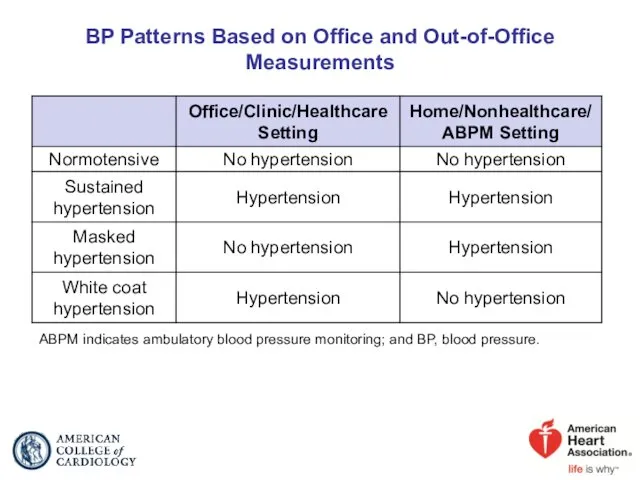
- 22. BP Patterns Based on Office and Out-of-Office Measurements ABPM indicates ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; and BP,
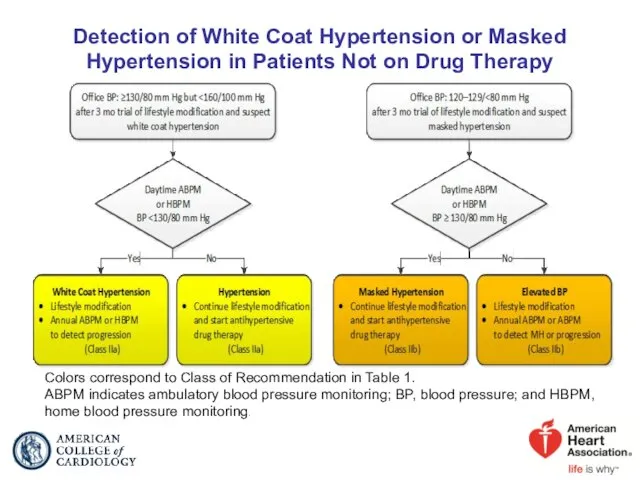
- 23. Detection of White Coat Hypertension or Masked Hypertension in Patients Not on Drug Therapy Colors correspond
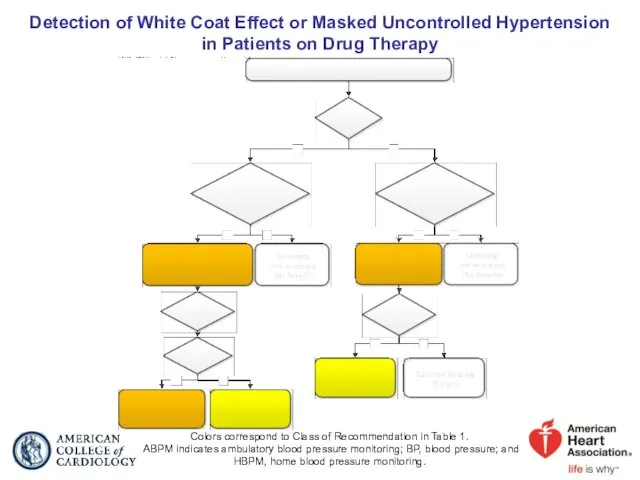
- 24. Detection of White Coat Effect or Masked Uncontrolled Hypertension in Patients on Drug Therapy Colors correspond
- 25. Causes of Hypertension 2017 Hypertension Guideline
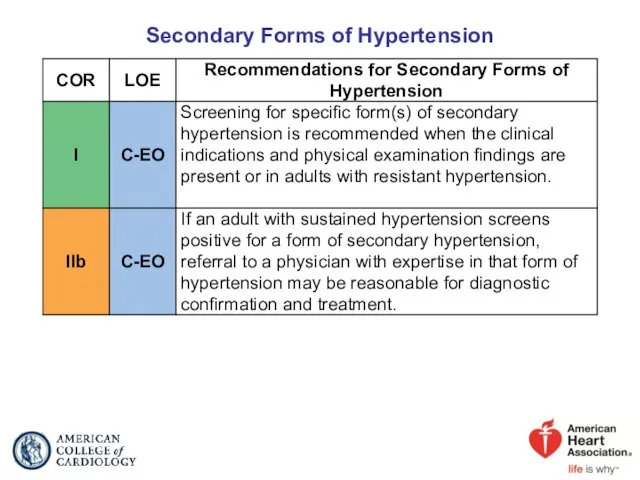
- 26. Secondary Forms of Hypertension
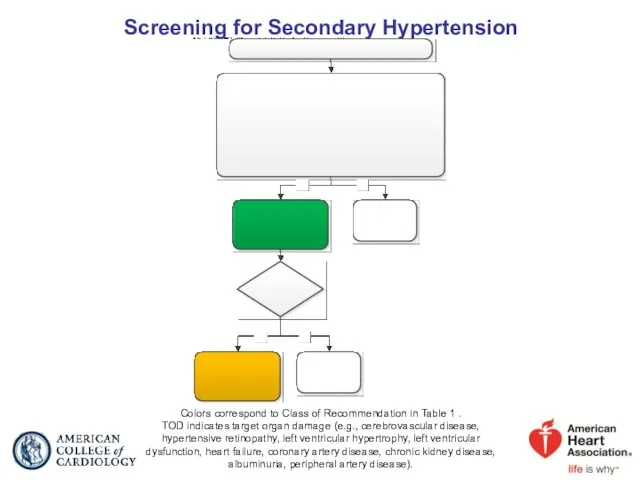
- 27. Screening for Secondary Hypertension Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1 . TOD indicates
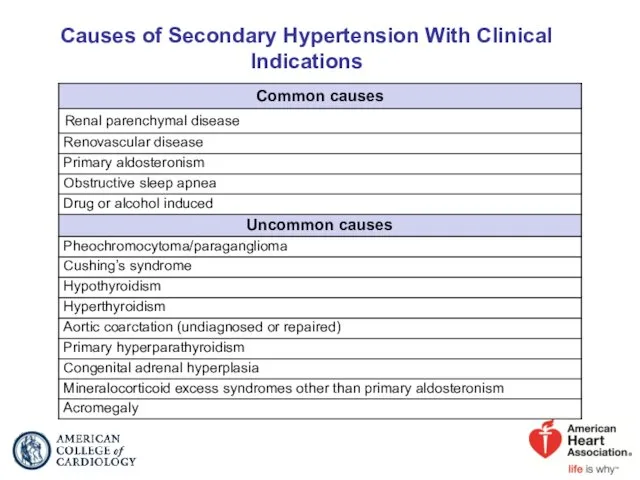
- 28. Causes of Secondary Hypertension With Clinical Indications
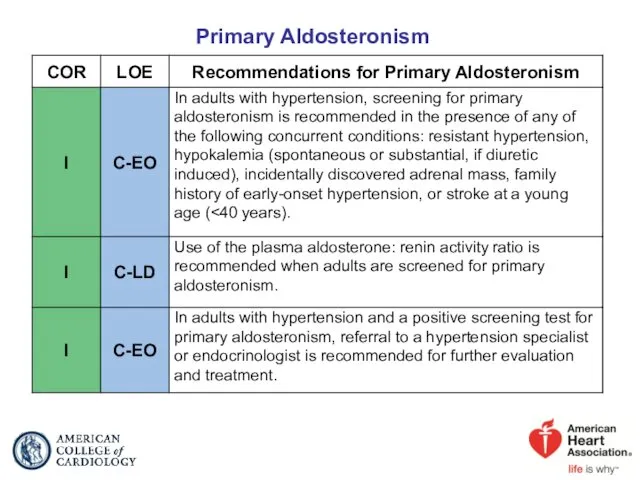
- 29. Primary Aldosteronism
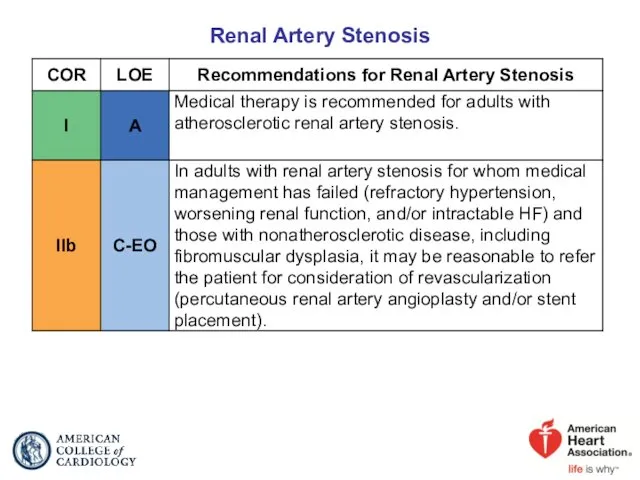
- 30. Renal Artery Stenosis
- 31. Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- 32. Nonpharmacological Interventions 2017 Hypertension Guideline
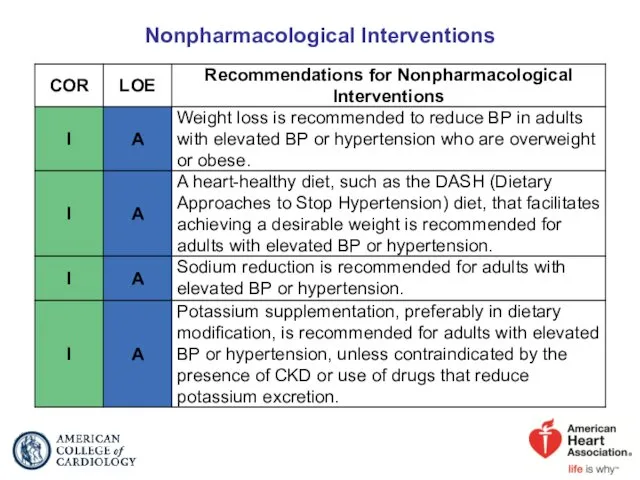
- 33. Nonpharmacological Interventions
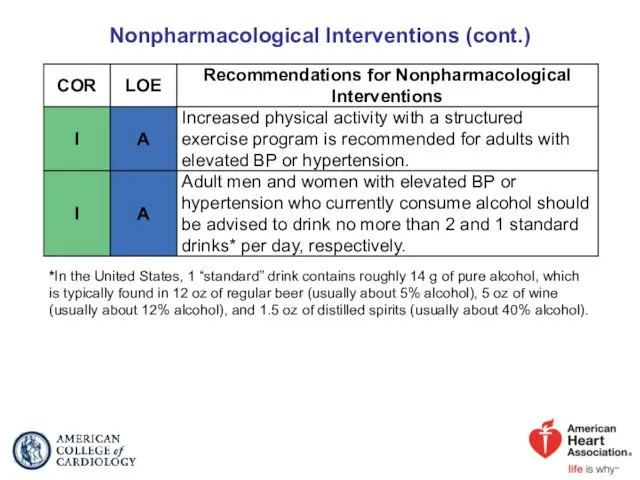
- 34. Nonpharmacological Interventions (cont.) *In the United States, 1 “standard” drink contains roughly 14 g of pure
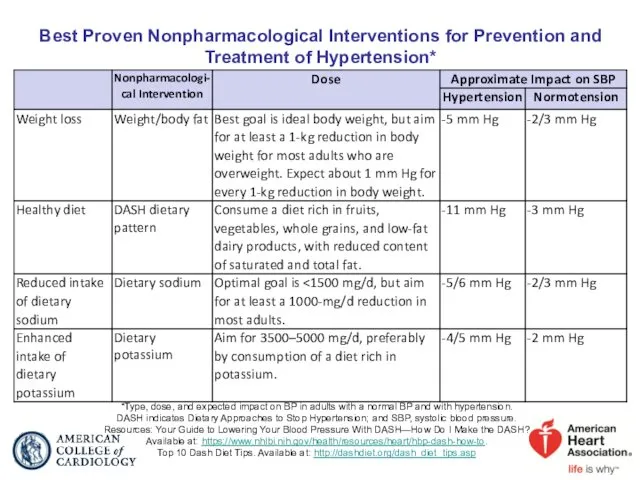
- 35. Best Proven Nonpharmacological Interventions for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension* *Type, dose, and expected impact on
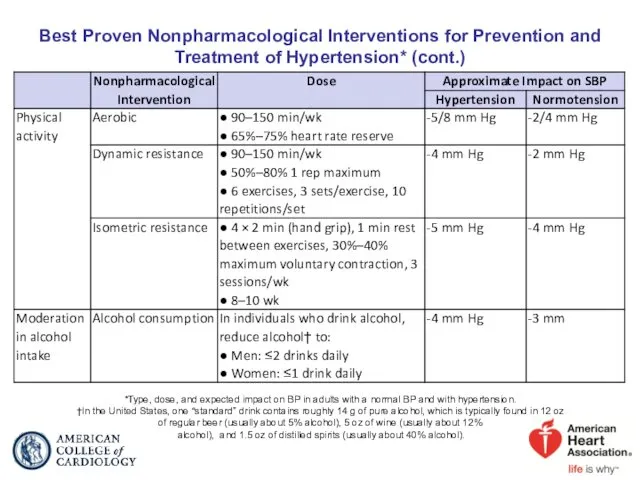
- 36. Best Proven Nonpharmacological Interventions for Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension* (cont.) *Type, dose, and expected impact
- 37. Patient Evaluation 2017 Hypertension Guideline
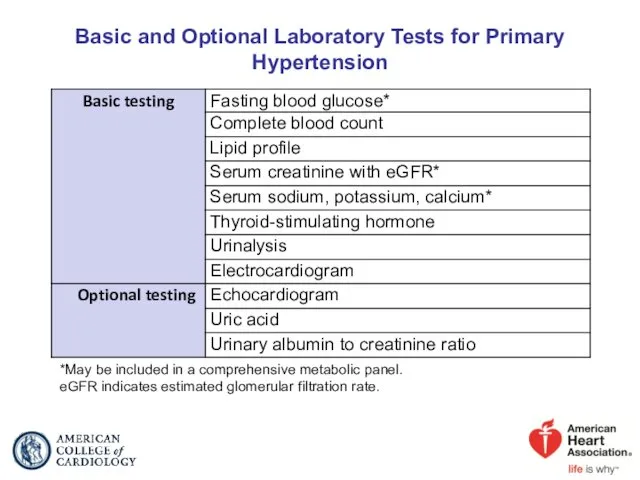
- 38. Basic and Optional Laboratory Tests for Primary Hypertension *May be included in a comprehensive metabolic panel.
- 39. Treatment of High BP 2017 Hypertension Guideline
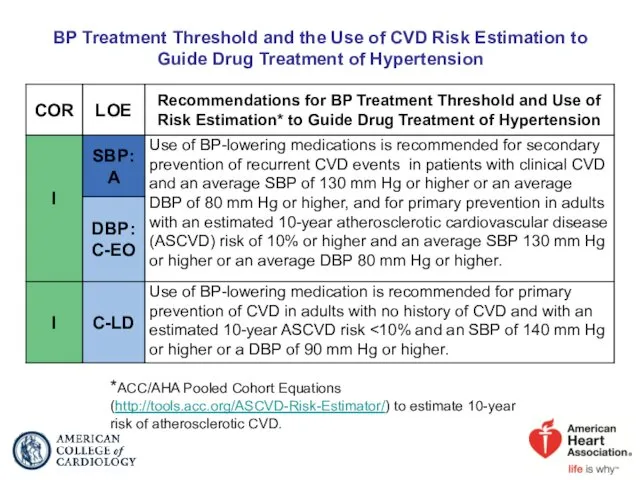
- 40. BP Treatment Threshold and the Use of CVD Risk Estimation to Guide Drug Treatment of Hypertension
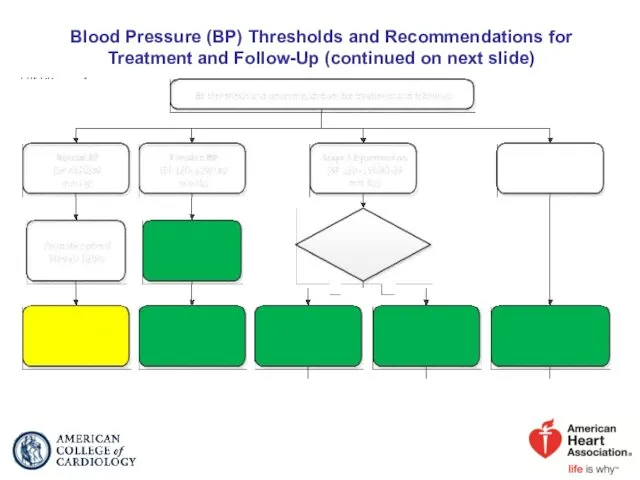
- 41. Blood Pressure (BP) Thresholds and Recommendations for Treatment and Follow-Up (continued on next slide)
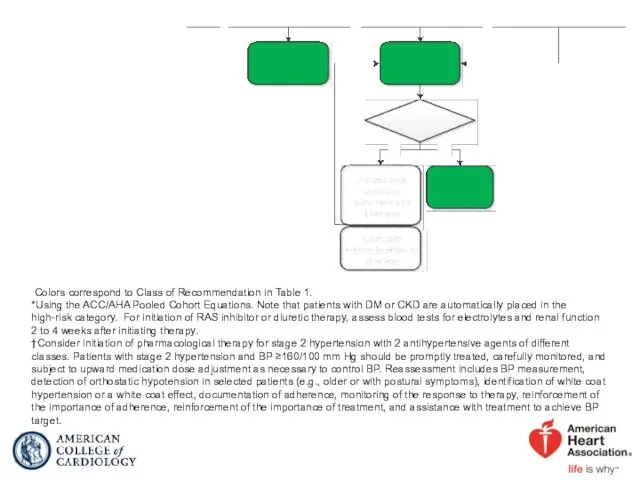
- 42. Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1. *Using the ACC/AHA Pooled Cohort Equations. Note
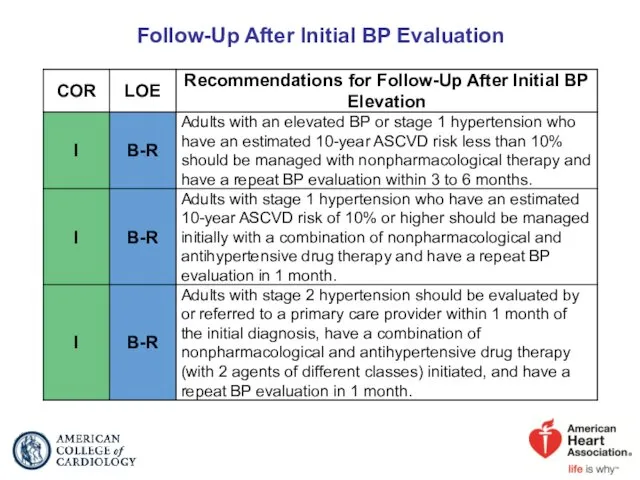
- 43. Follow-Up After Initial BP Evaluation
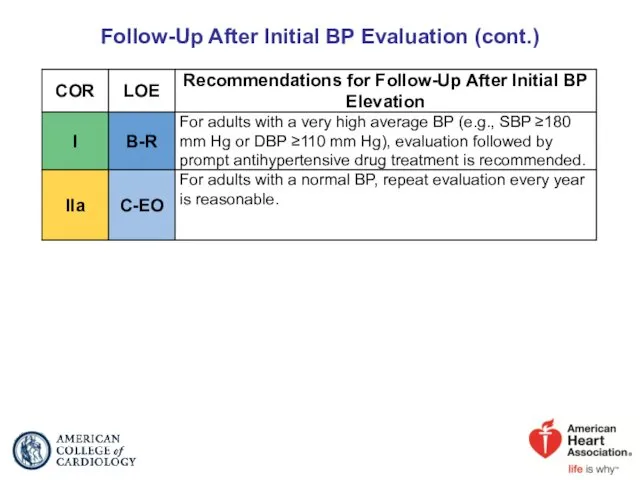
- 44. Follow-Up After Initial BP Evaluation (cont.)
- 45. General Principles of Drug Therapy
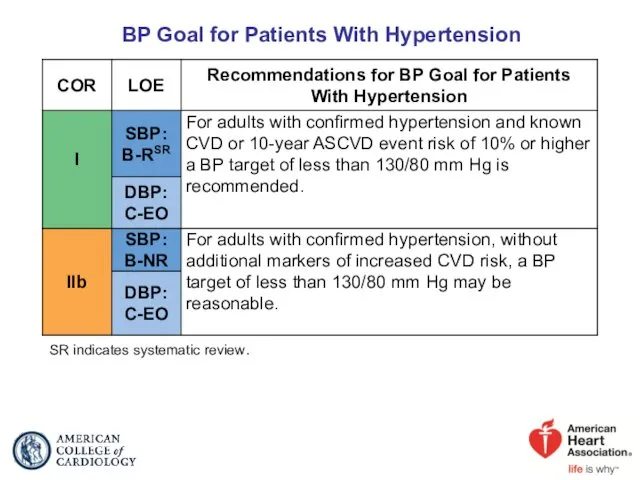
- 46. BP Goal for Patients With Hypertension SR indicates systematic review.
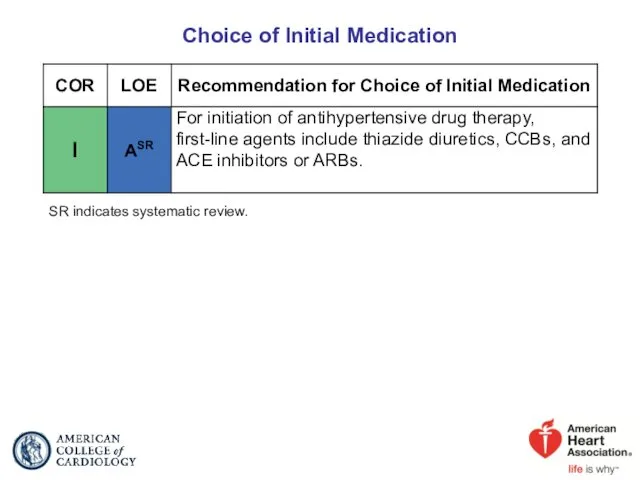
- 47. Choice of Initial Medication SR indicates systematic review.
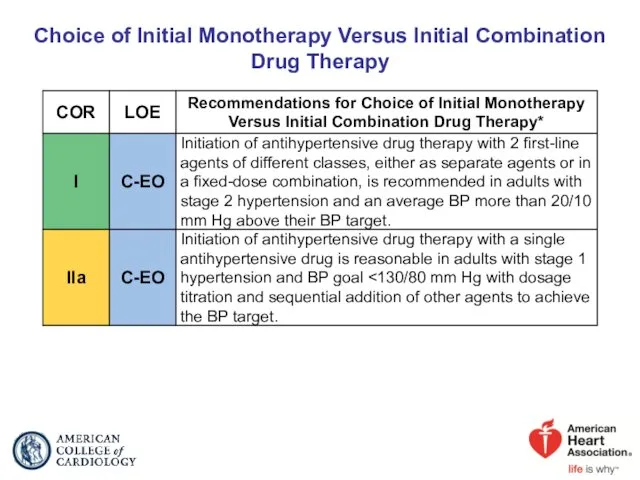
- 48. Choice of Initial Monotherapy Versus Initial Combination Drug Therapy
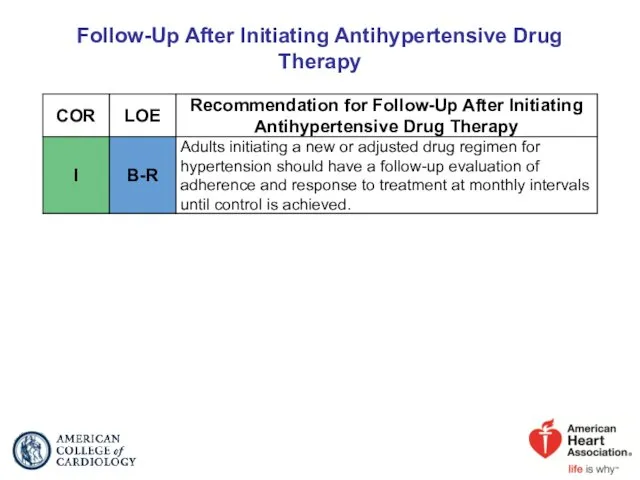
- 49. Follow-Up After Initiating Antihypertensive Drug Therapy
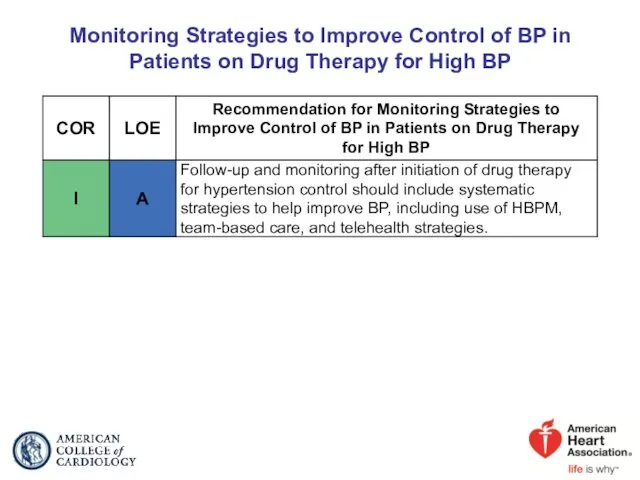
- 50. Monitoring Strategies to Improve Control of BP in Patients on Drug Therapy for High BP
- 51. Hypertension in Patients With Comorbidities 2017 Hypertension Guideline
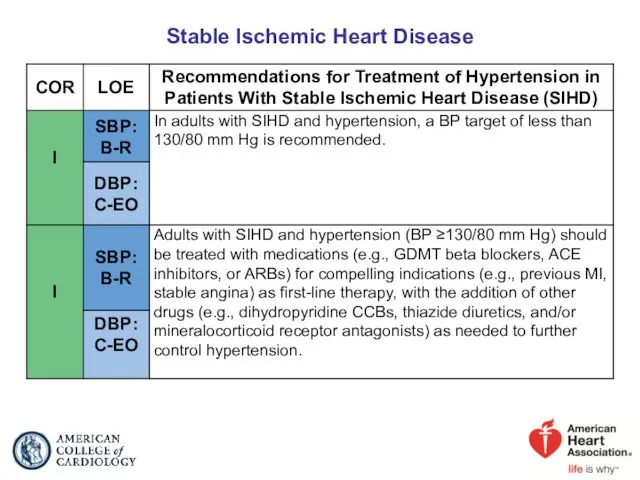
- 52. Stable Ischemic Heart Disease
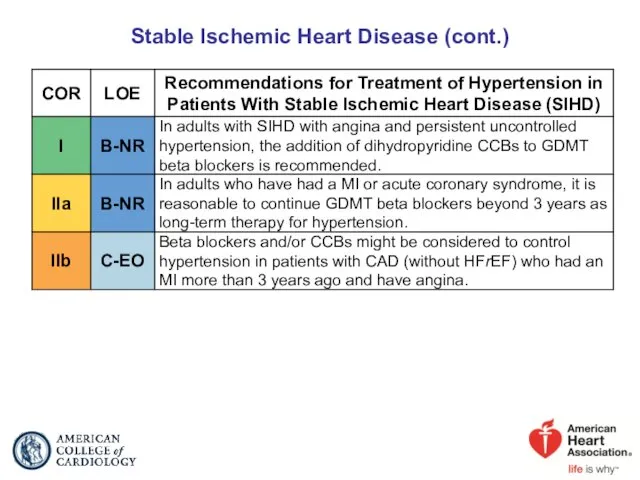
- 53. Stable Ischemic Heart Disease (cont.)
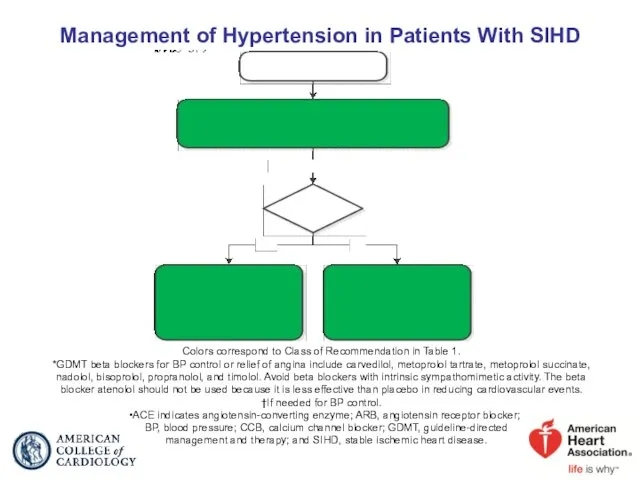
- 54. Management of Hypertension in Patients With SIHD ACE indicates angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BP,
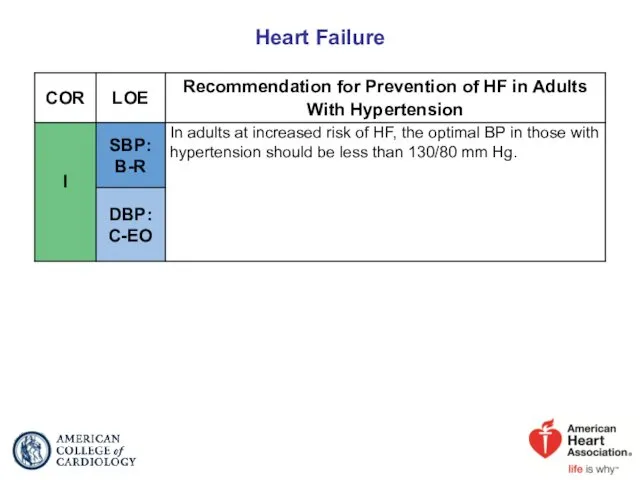
- 55. Heart Failure
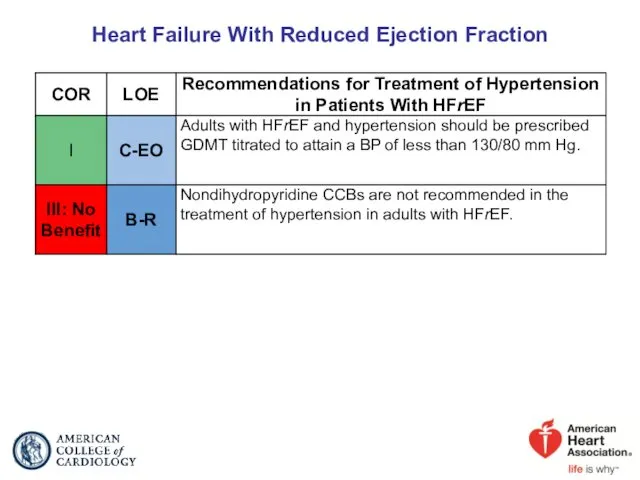
- 56. Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
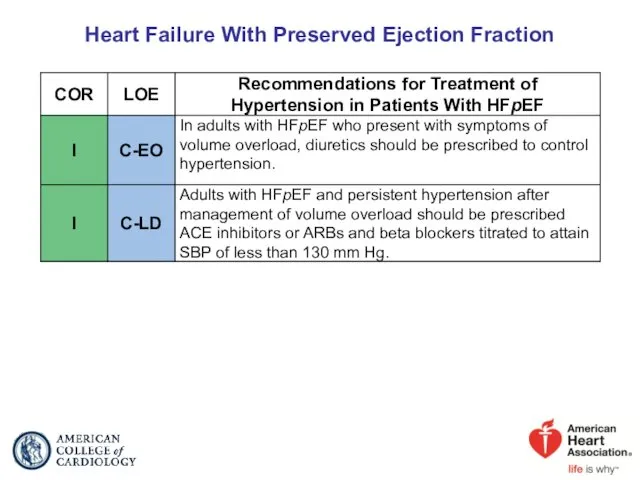
- 57. Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
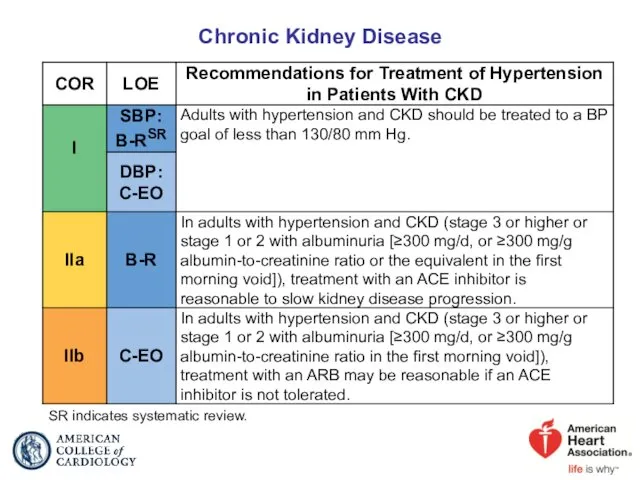
- 58. Chronic Kidney Disease SR indicates systematic review.
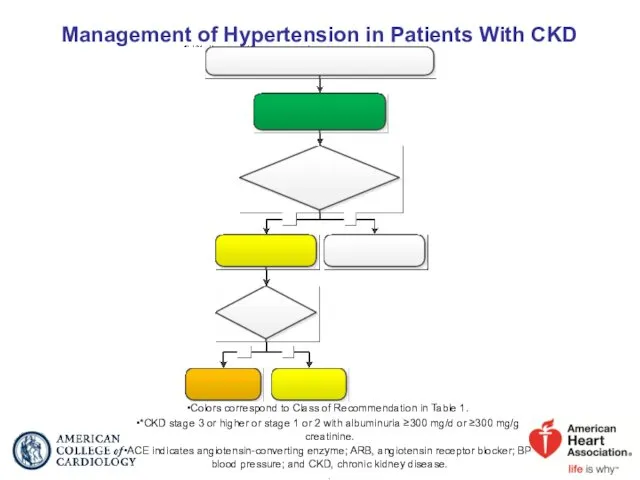
- 59. Management of Hypertension in Patients With CKD Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1.
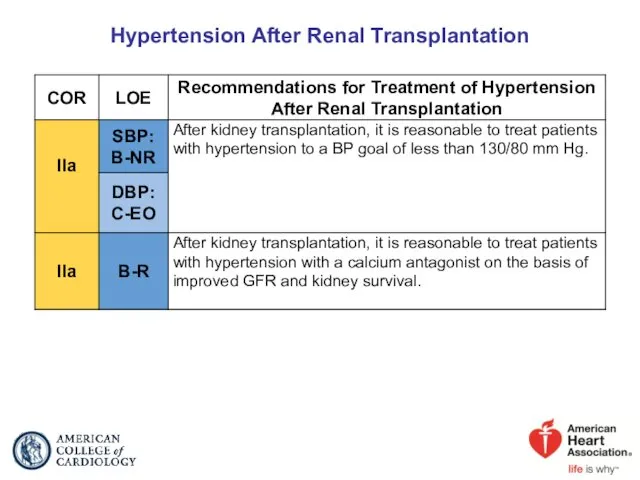
- 60. Hypertension After Renal Transplantation
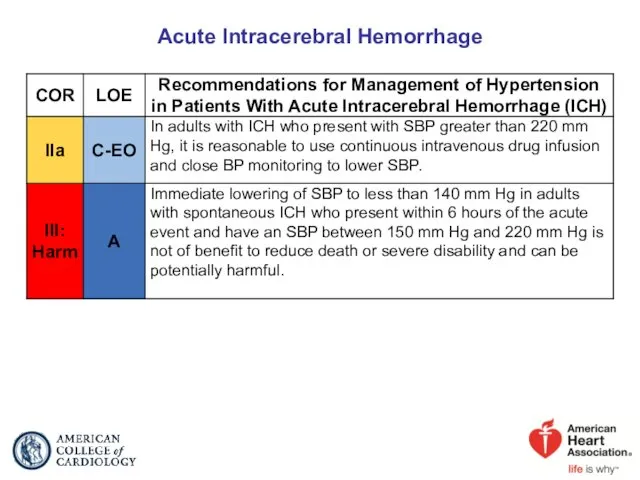
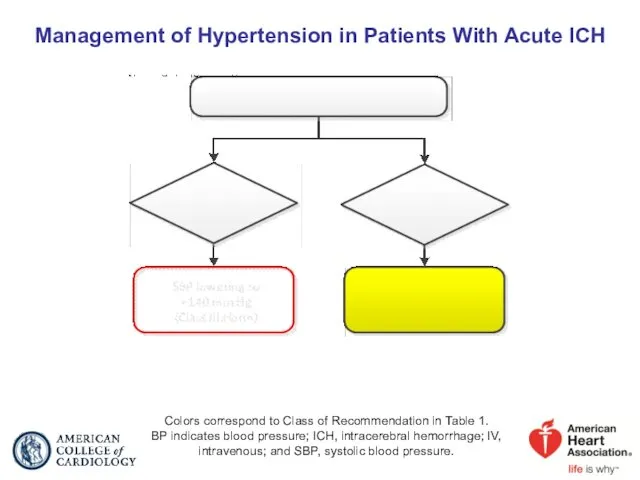
- 61. Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage
- 62. Management of Hypertension in Patients With Acute ICH Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table
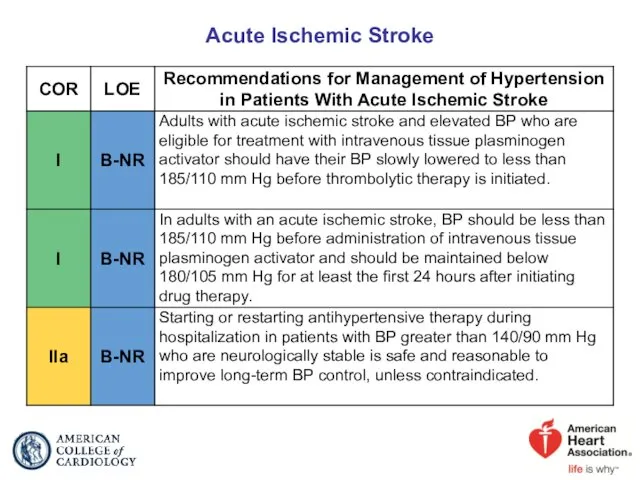
- 63. Acute Ischemic Stroke
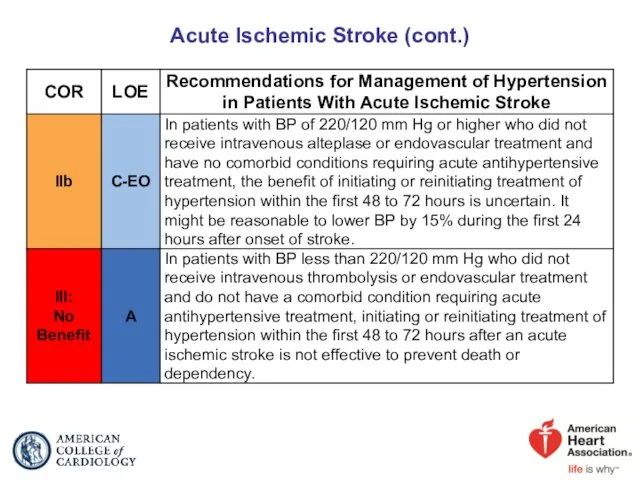
- 64. Acute Ischemic Stroke (cont.)
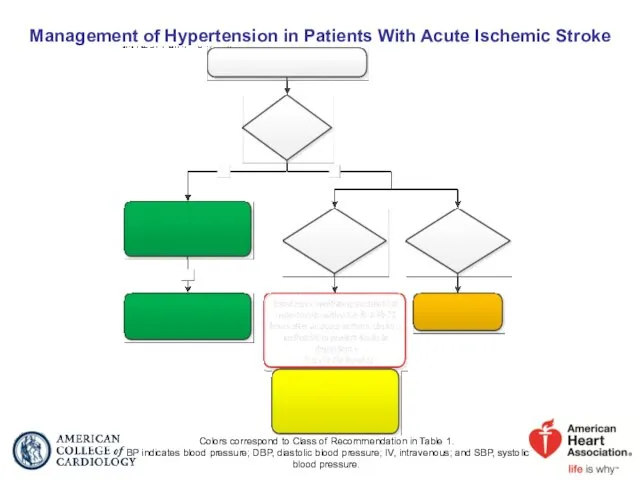
- 65. Management of Hypertension in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in
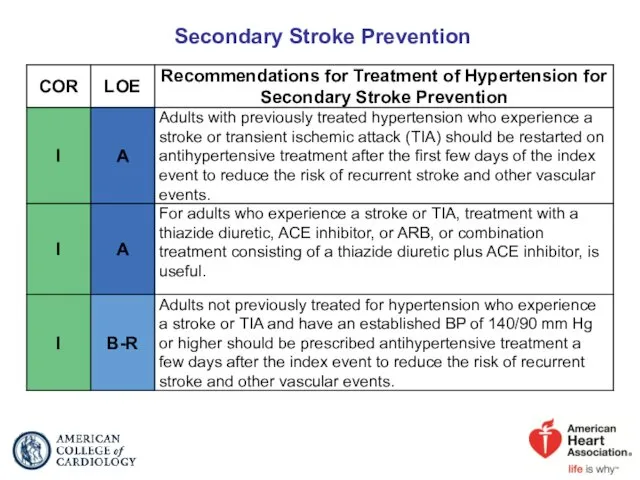
- 66. Secondary Stroke Prevention
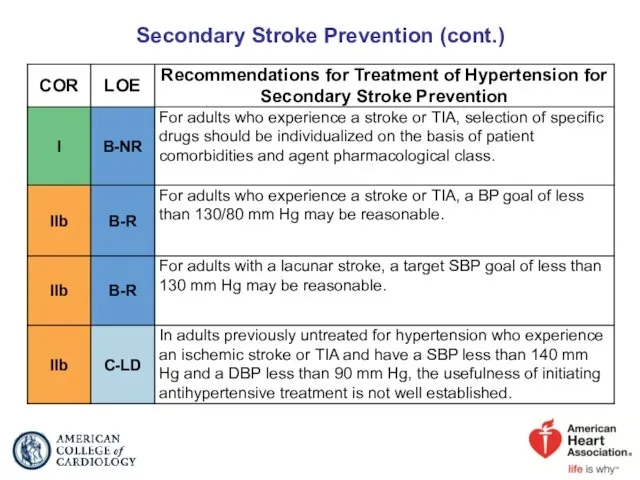
- 67. Secondary Stroke Prevention (cont.)
- 68. Management of Hypertension in Patients With a Previous History of Stroke (Secondary Stroke Prevention) Colors correspond
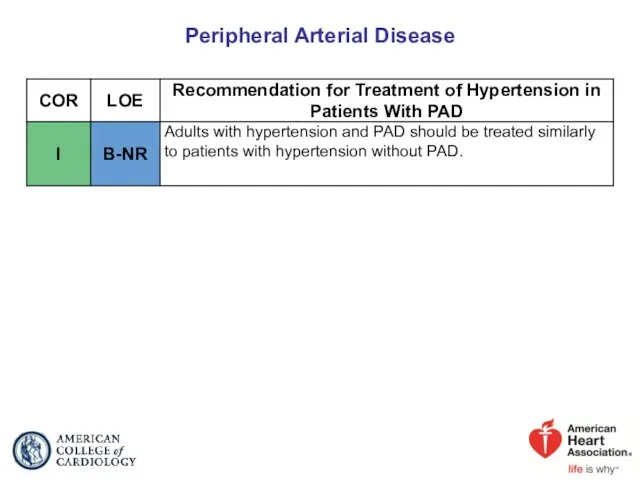
- 69. Peripheral Arterial Disease
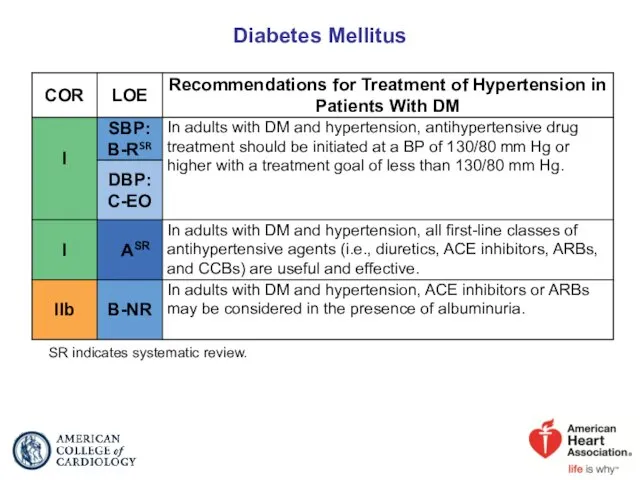
- 70. Diabetes Mellitus SR indicates systematic review.
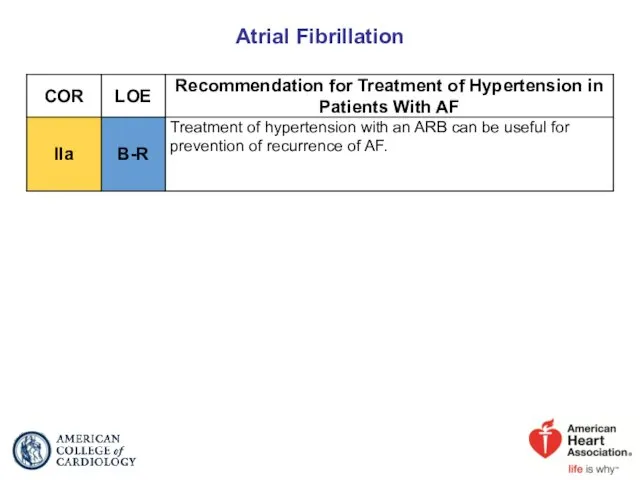
- 71. Atrial Fibrillation
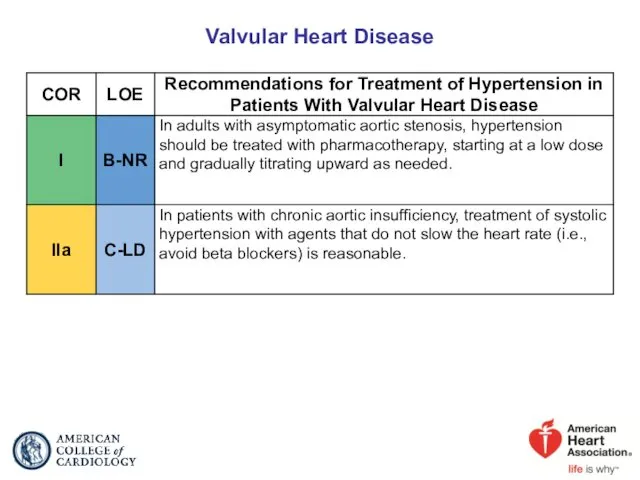
- 72. Valvular Heart Disease
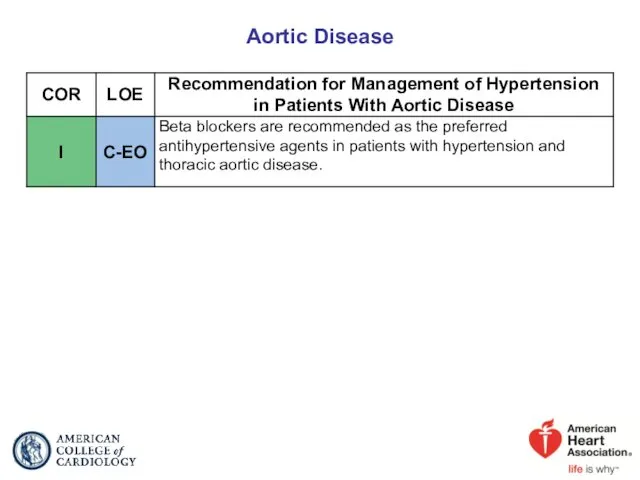
- 73. Aortic Disease
- 74. Special Patient Groups 2017 Hypertension Guideline
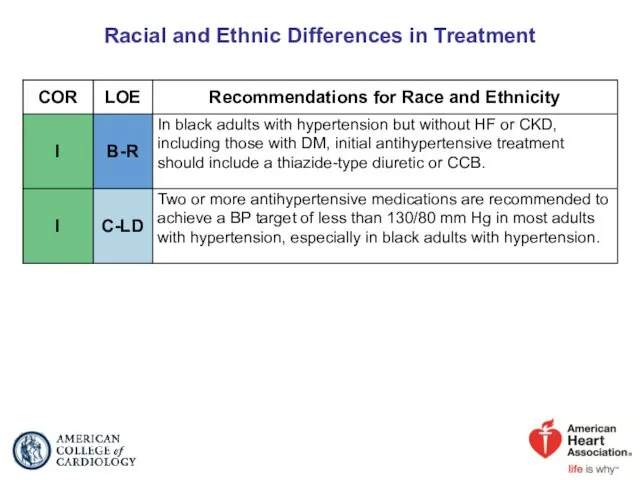
- 75. Racial and Ethnic Differences in Treatment
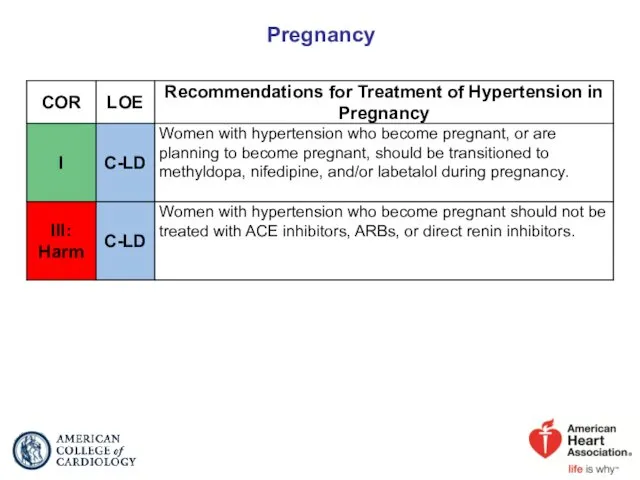
- 76. Pregnancy
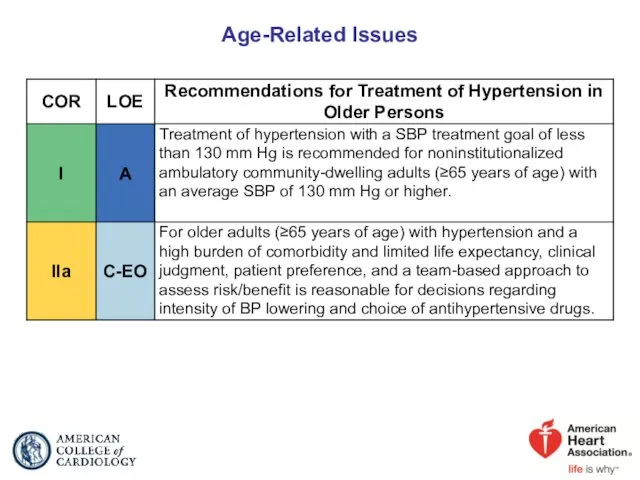
- 77. Age-Related Issues
- 78. Other Considerations 2017 Hypertension Guideline
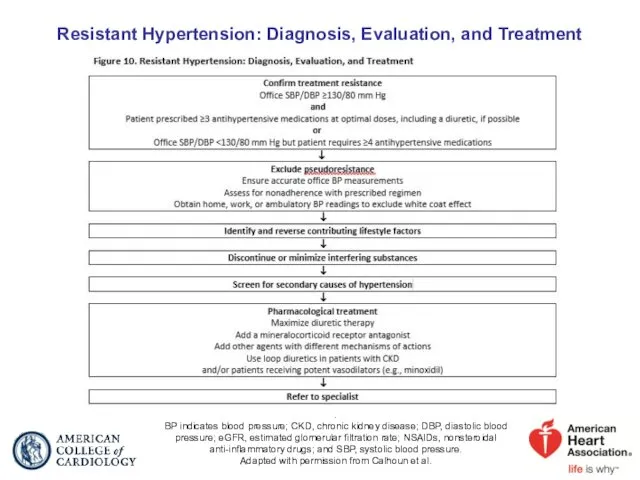
- 79. Resistant Hypertension: Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Treatment . BP indicates blood pressure; CKD, chronic kidney disease; DBP,
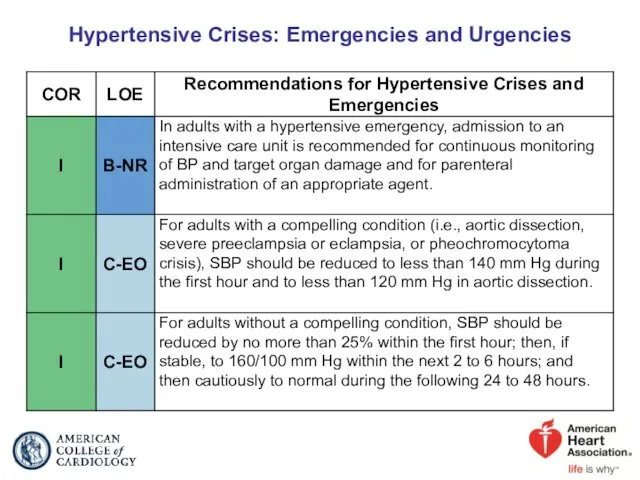
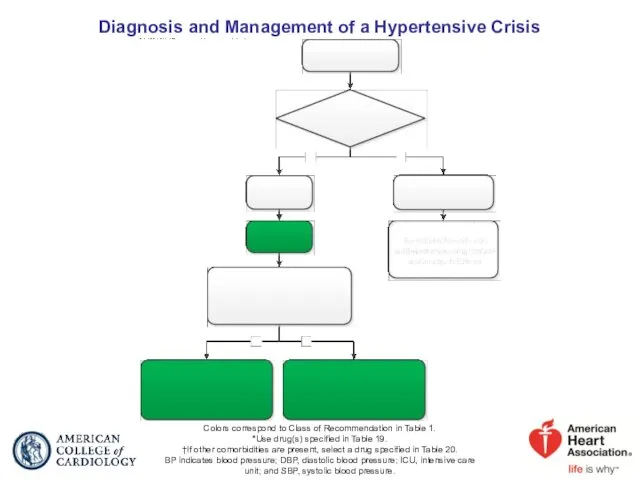
- 80. Hypertensive Crises: Emergencies and Urgencies
- 81. Colors correspond to Class of Recommendation in Table 1. *Use drug(s) specified in Table 19. †If
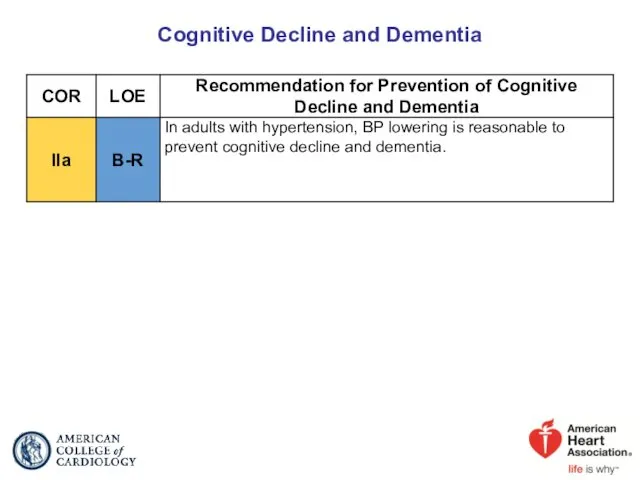
- 82. Cognitive Decline and Dementia
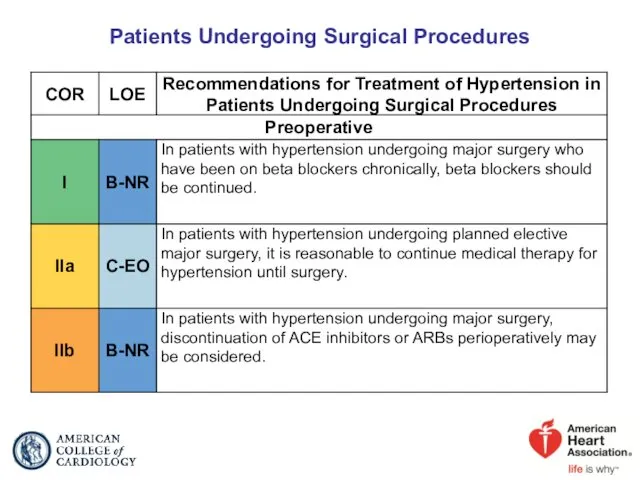
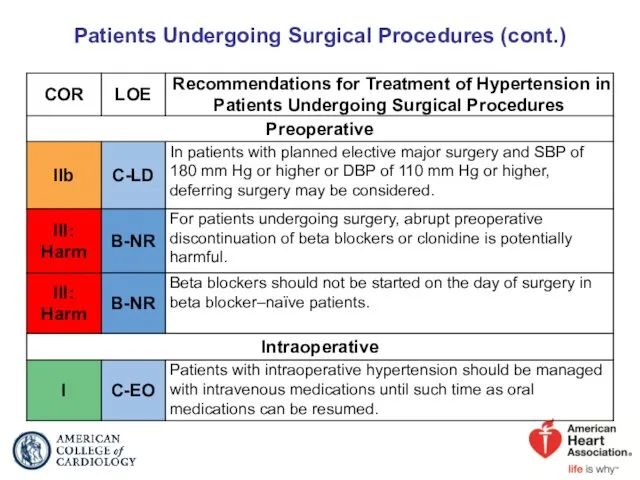
- 83. Patients Undergoing Surgical Procedures
- 84. Patients Undergoing Surgical Procedures (cont.)
- 85. Strategies to Improve Hypertension Treatment and Control 2017 Hypertension Guideline
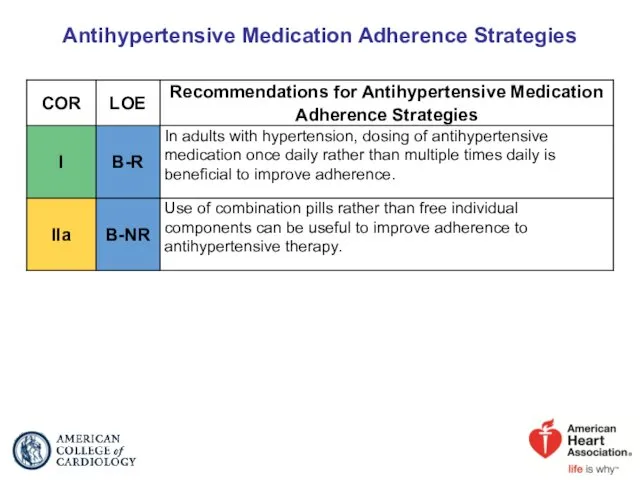
- 86. Antihypertensive Medication Adherence Strategies
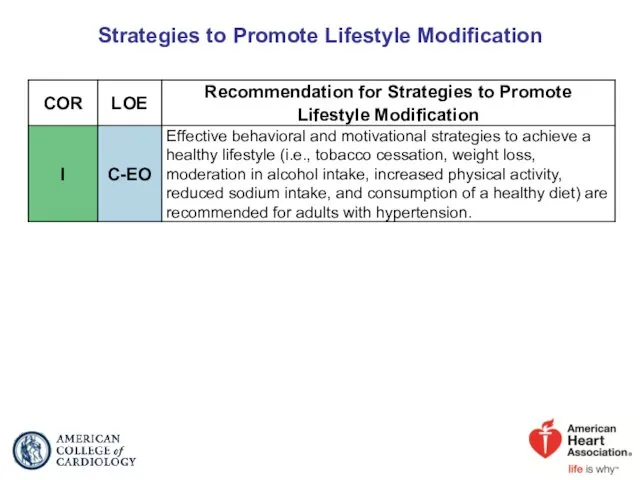
- 87. Strategies to Promote Lifestyle Modification
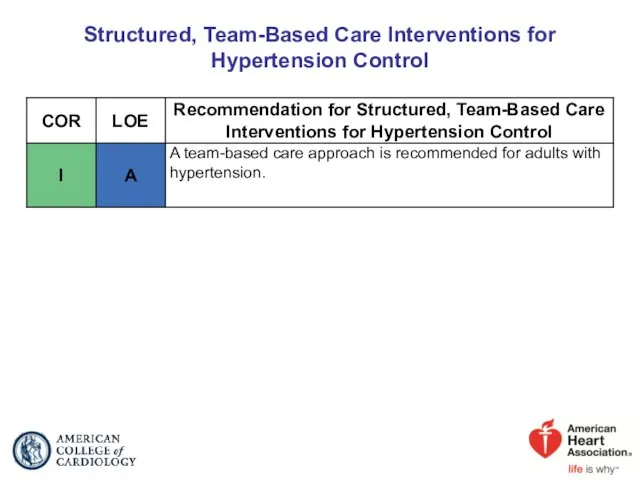
- 88. Structured, Team-Based Care Interventions for Hypertension Control
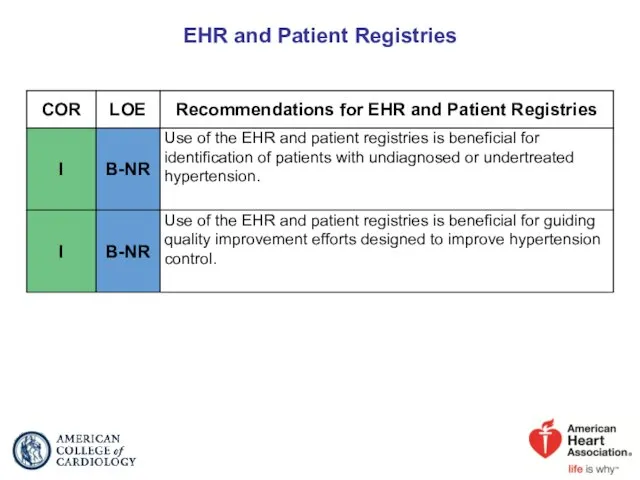
- 89. EHR and Patient Registries
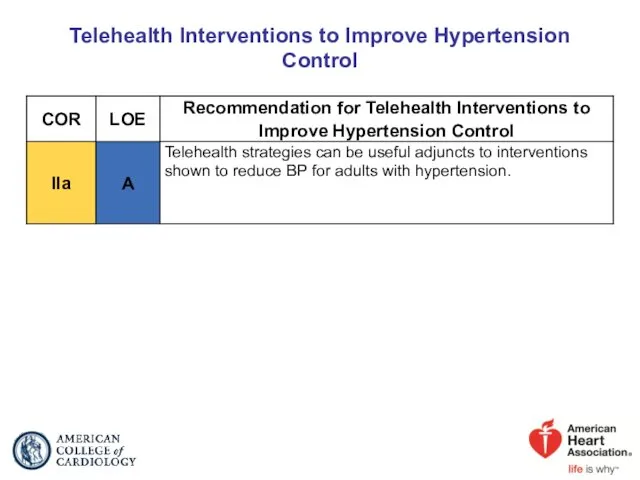
- 90. Telehealth Interventions to Improve Hypertension Control
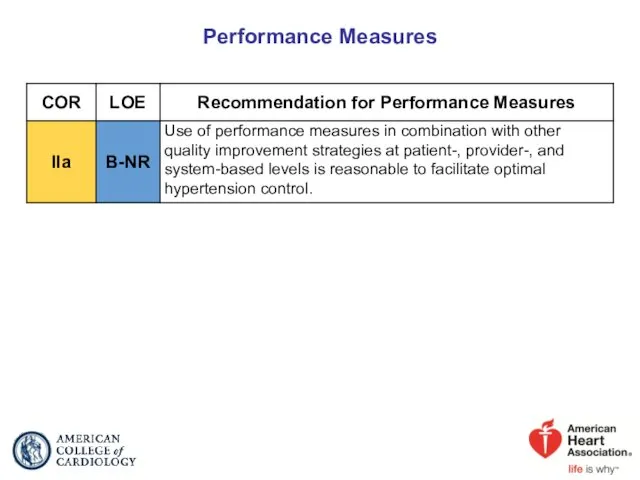
- 91. Performance Measures
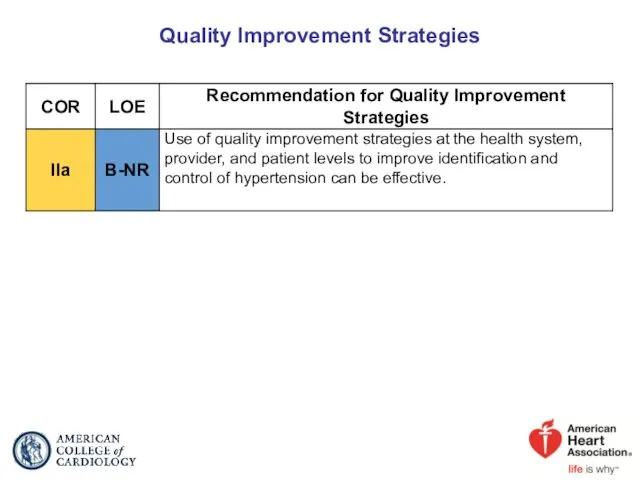
- 92. Quality Improvement Strategies
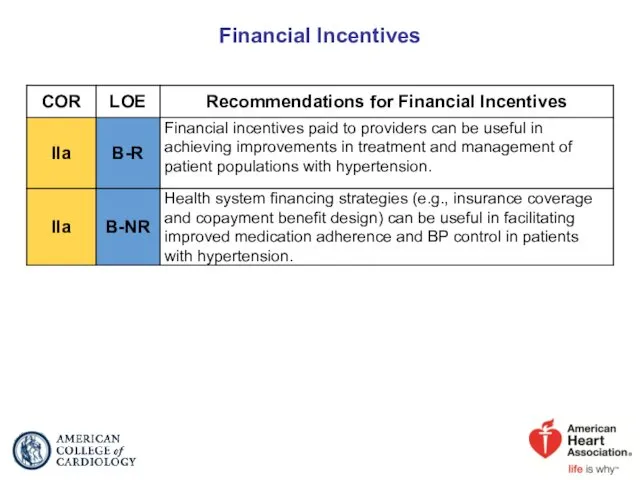
- 93. Financial Incentives
- 94. The Plan of Care for Hypertension 2017 Hypertension Guideline
- 95. The Plan of Care for Hypertension
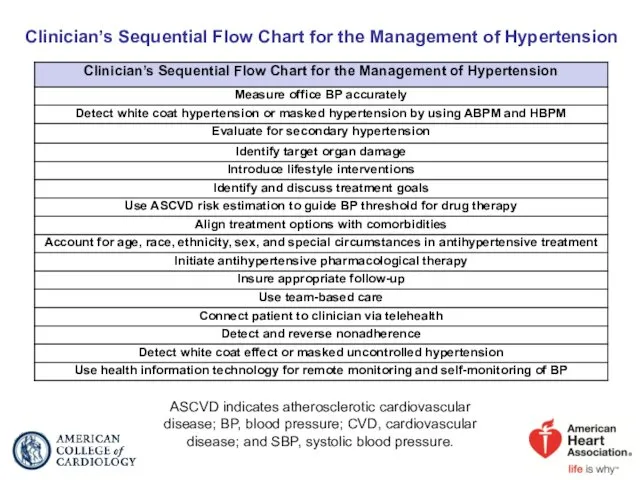
- 96. Clinician’s Sequential Flow Chart for the Management of Hypertension ASCVD indicates atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BP, blood
- 97. Summary of BP Thresholds and Goals for Pharmacological Therapy Plan of Care for Hypertension 2017 Hypertension
- 99. Скачать презентацию


















 Офтальмология. Патология вспомогательного аппарата глаза
Офтальмология. Патология вспомогательного аппарата глаза Техника транспортной иммобилизации верхней конечности
Техника транспортной иммобилизации верхней конечности Догоспитальный этап экстренной помощи детям при отеке легких, отеке мозга, отравлении
Догоспитальный этап экстренной помощи детям при отеке легких, отеке мозга, отравлении Гормональные нарушения и хроническая венозная недостаточность
Гормональные нарушения и хроническая венозная недостаточность Классификация звуков
Классификация звуков Профессиональная интоксикация пестицидами
Профессиональная интоксикация пестицидами Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем
Инфекции, передающиеся половым путем Деятельность медицинской сестры в организации ухода за пациентами с повреждениями нижних конечностей
Деятельность медицинской сестры в организации ухода за пациентами с повреждениями нижних конечностей Організація надання медичної допомоги населенню в умовах надзвичайних ситуацій
Організація надання медичної допомоги населенню в умовах надзвичайних ситуацій Утопление и погружение в воду
Утопление и погружение в воду Транспортная иммобилизация
Транспортная иммобилизация Вирусные инфекции. Задачи
Вирусные инфекции. Задачи Гигиена труда в металлургической промышленности. Основные профессиональные группы. Основные неблагоприятные факторы
Гигиена труда в металлургической промышленности. Основные профессиональные группы. Основные неблагоприятные факторы Тері физиологиясы
Тері физиологиясы Аллергия. Классификация аллергических процессов
Аллергия. Классификация аллергических процессов Патологические изменения кожи
Патологические изменения кожи Клиническая фармакология психотропных средств Часть 1. Антипсихотики (нейролептики)
Клиническая фармакология психотропных средств Часть 1. Антипсихотики (нейролептики) Почки. Синдромы
Почки. Синдромы Фармацевтическая опека при травматических и инфекционных повреждениях кожи
Фармацевтическая опека при травматических и инфекционных повреждениях кожи Прием у детского гинеколога. Методы исследования
Прием у детского гинеколога. Методы исследования Бинокулярное зрение. Косоглазие
Бинокулярное зрение. Косоглазие Нейросенсорная тугоухость
Нейросенсорная тугоухость Виды и стадии голодания. Изменения обмена веществ и функции организма при голодании
Виды и стадии голодания. Изменения обмена веществ и функции организма при голодании Правила чистки зубов
Правила чистки зубов Иерсинии - псевдотуберкулезный микроб. Микробиология
Иерсинии - псевдотуберкулезный микроб. Микробиология ҰлпАның қабынбалы аурулары
ҰлпАның қабынбалы аурулары Расстройства сознания
Расстройства сознания Питание человека и долголетие
Питание человека и долголетие