Содержание
- 2. Program Disclosure This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and
- 3. Learning Objectives Describe current data on approved and experimental DAA’s used in combination with Pegylated Interferon
- 4. Glenn: Patient Characteristics 55 year old male Shift worker History/risk factors BMI=34 Hypertension and dyslipidemia Moderate
- 5. Glenn: Baseline Labs Hemoglobin Neutrophils Platelets AST/ALT Albumin Bilirubin 15.6 g/dL 1400 cells/mm3 210,000 cells/mm3 55/75
- 6. Glenn: Disease Characteristics Treatment naïve Genotype IL28B METAVIR BL viral load 1a CC F3 1,300,000 IU/mL
- 7. Clinical Decision 1 How would you manage this patient? Continue to monitor patient but do not
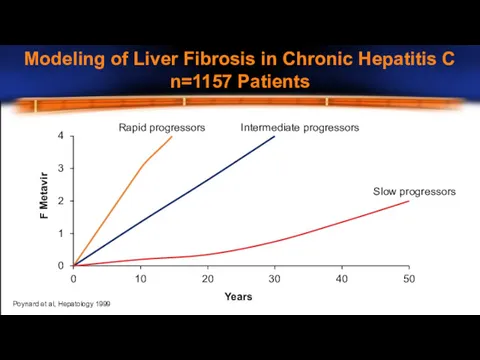
- 8. Modeling of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C n=1157 Patients 0 1 2 3 4 0
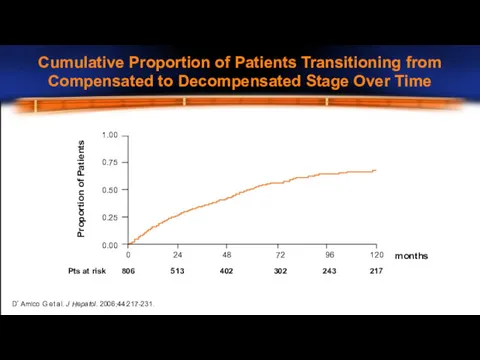
- 9. D’Amico G et al. J Hepatol. 2006;44:217-231. Proportion of Patients 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0.00 Pts
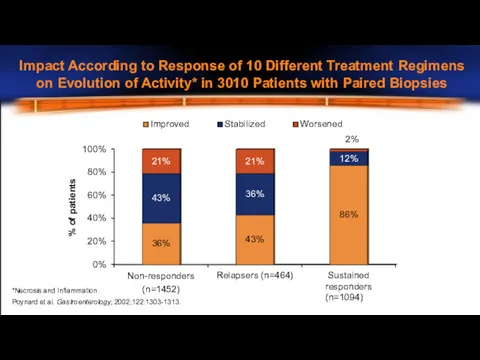
- 10. 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Non-responders (n=1452) Relapsers (n=464) Sustained responders (n=1094) 36% 43% 86%
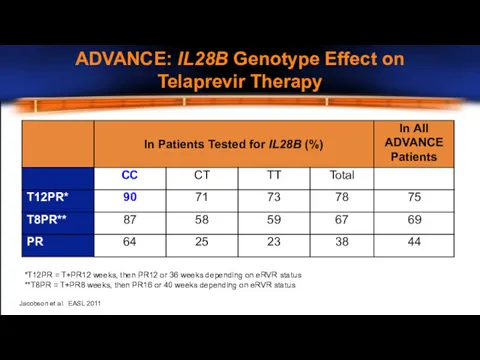
- 11. *T12PR = T+PR12 weeks, then PR12 or 36 weeks depending on eRVR status **T8PR = T+PR8
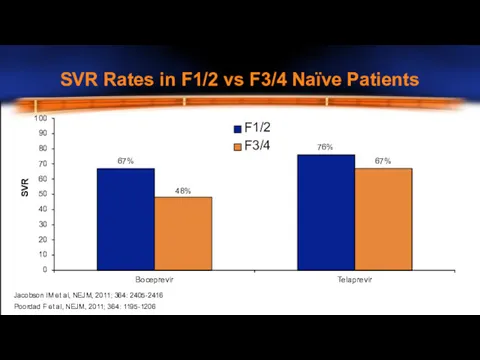
- 12. SVR Rates in F1/2 vs F3/4 Naïve Patients 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30
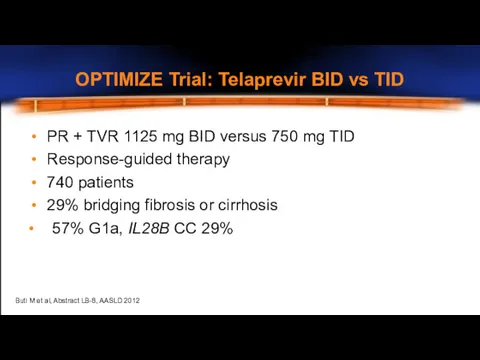
- 13. OPTIMIZE Trial: Telaprevir BID vs TID PR + TVR 1125 mg BID versus 750 mg TID
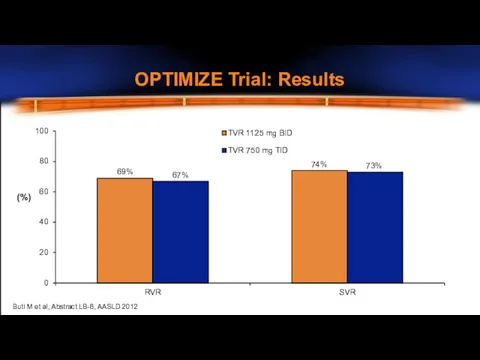
- 14. OPTIMIZE Trial: Results 0 20 40 60 80 100 RVR SVR TVR 1125 mg BID TVR
- 15. Should Glenn Be Treated Now? F3 disease – risk of progression with waiting IL28B CC Potential
- 16. Multiple issues with current therapy Compliance – pill burden Co-morbidities Adverse effects New treatments on the
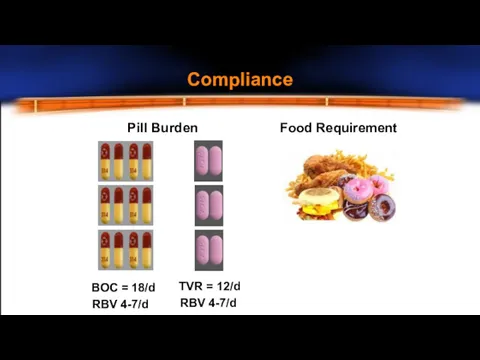
- 17. Pill Burden Food Requirement BOC = 18/d RBV 4-7/d TVR = 12/d RBV 4-7/d Compliance
- 18. Cardiac Risk Factors Hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoker Pre Treatment DDI – Statin with TVR/BOC ? likely just
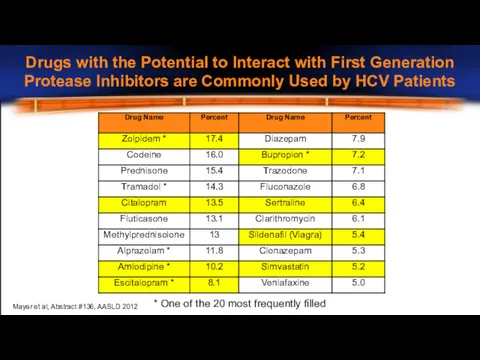
- 19. Drugs with the Potential to Interact with First Generation Protease Inhibitors are Commonly Used by HCV
- 20. No clinically significant interactions Boceprevir Prednisone (abstract #1896) Omeprazole (abstract #1808) Ethinyl estrodiol/norethidrone (abstract #1901) Simeprevir
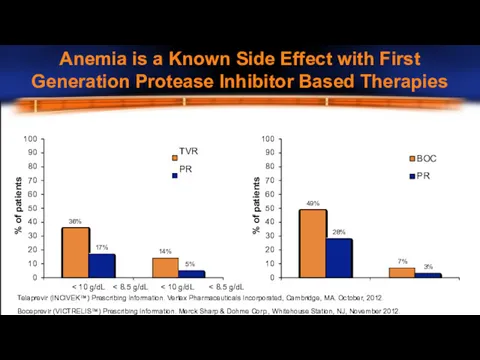
- 21. 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 BOC PR 100 90 80
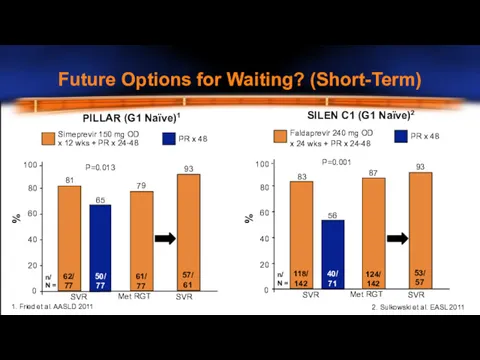
- 22. Future Options for Waiting? (Short-Term) x 12 wks + PR x 24-48 81 0 20 40
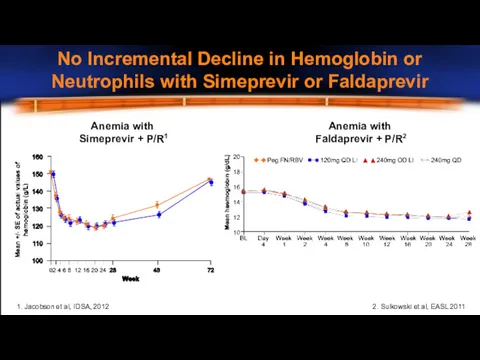
- 23. Anemia with Simeprevir + P/R1 Anemia with Faldaprevir + P/R2 2. Sulkowski et al, EASL 2011
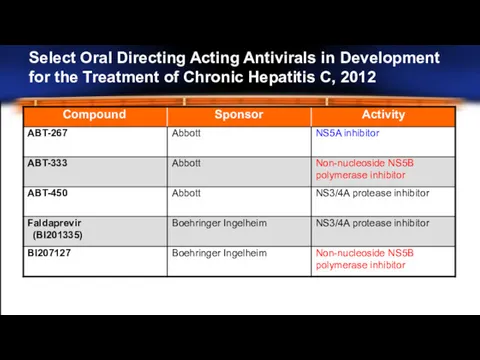
- 24. Select Oral Directing Acting Antivirals in Development for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C, 2012
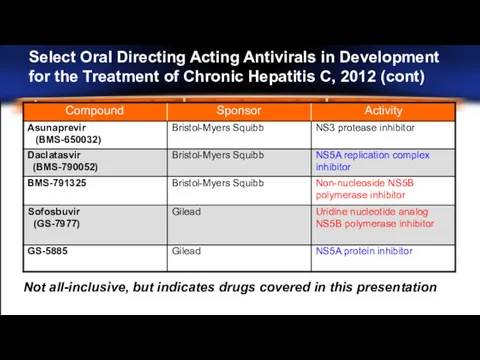
- 25. Select Oral Directing Acting Antivirals in Development for the Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C, 2012 (cont)
- 26. Should Glenn Delay Treatment? IL28B CC ? ~80% chance of shortened therapy - 80-90% chance of
- 27. Glenn: On Treatment Response Glenn was started on TVR/PEG/RBV TW4 and TW12 – HCV RNA undetectable
- 28. Clinical Decision 2 Which regimen should Glenn receive? 12 weeks TVR/PEG/RBV 12 weeks TVR/PEG/RBV + 12
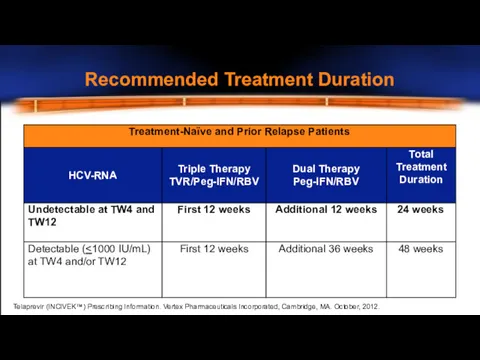
- 29. Recommended Treatment Duration Telaprevir (INCIVEK™) Prescribing Information. Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Cambridge, MA. October, 2012.
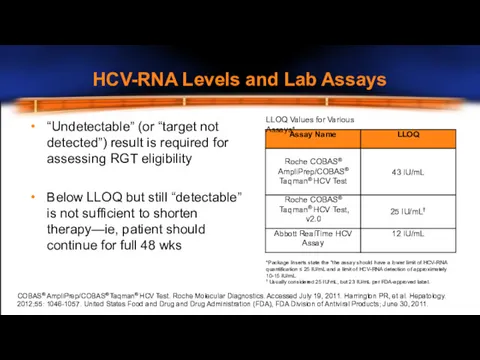
- 30. HCV-RNA Levels and Lab Assays LLOQ Values for Various Assays* “Undetectable” (or “target not detected”) result
- 32. Скачать презентацию













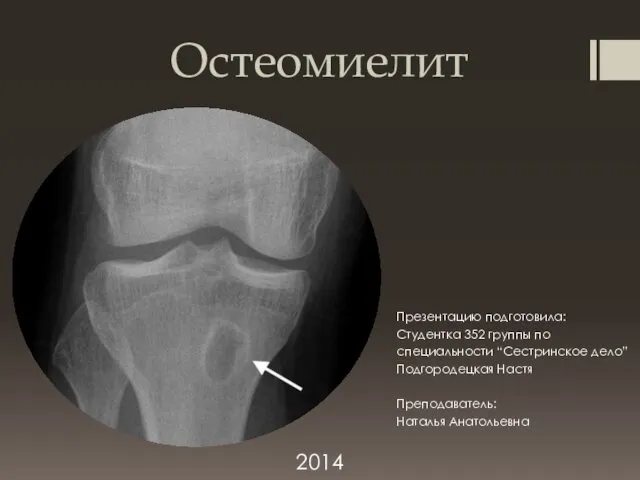 Остеомиелит. Острый гематогенный остеомиелит
Остеомиелит. Острый гематогенный остеомиелит Воздушно - капельные инфекции: Скарлатина
Воздушно - капельные инфекции: Скарлатина Виды Сухожильных швов
Виды Сухожильных швов Укусы насекомых
Укусы насекомых Инфекции, передаваемые половым путем. Уголовная ответственность за заражение этими болезнями
Инфекции, передаваемые половым путем. Уголовная ответственность за заражение этими болезнями Травмы. Травматический шок
Травмы. Травматический шок Защитные функции антител
Защитные функции антител Использование КТ для диагностики травм у мелких домашних животных
Использование КТ для диагностики травм у мелких домашних животных Факторы риска и профилактика болезней пародонта, зубочелюстных аномалий у детей. (Лекция 15)
Факторы риска и профилактика болезней пародонта, зубочелюстных аномалий у детей. (Лекция 15) Синдром Ретта
Синдром Ретта Жүрек ишемия ауруы. Стенокардия
Жүрек ишемия ауруы. Стенокардия Асқазанның және ас қорыту бездерінің топографиялық анатомиясы және балалардағы ерекшеліктері
Асқазанның және ас қорыту бездерінің топографиялық анатомиясы және балалардағы ерекшеліктері Морфологические особенности крови крупного рогатого скота
Морфологические особенности крови крупного рогатого скота Беременность при туберкулезе
Беременность при туберкулезе Остановка наружного кровотечения
Остановка наружного кровотечения Управління якістю у фармацевтичній галузі. Державна система забезпечення якості лікарських засобів в Україні
Управління якістю у фармацевтичній галузі. Державна система забезпечення якості лікарських засобів в Україні Остеобластокластома челюстей. Фиброзная дисплазия челюстей
Остеобластокластома челюстей. Фиброзная дисплазия челюстей Патология пищеварительной системы
Патология пищеварительной системы Диагностика и лечение черепно–мозговой травмы
Диагностика и лечение черепно–мозговой травмы Ротавирусная инфекция
Ротавирусная инфекция Операции в области живота. Абдоминальная хирургия
Операции в области живота. Абдоминальная хирургия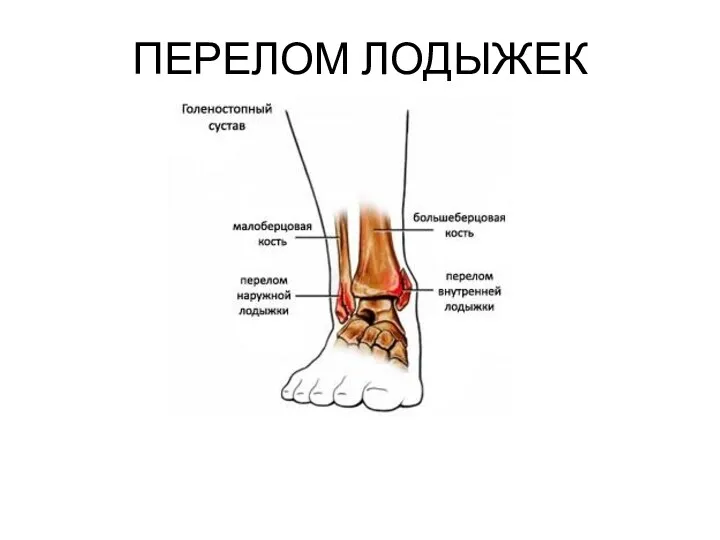 Перелом лодыжек
Перелом лодыжек Schizophrenia is a mental illness
Schizophrenia is a mental illness Недостаточность кровообращения: принципы фармакотерапии. Кардиотонические средства
Недостаточность кровообращения: принципы фармакотерапии. Кардиотонические средства Система методов лечебных воздействий
Система методов лечебных воздействий Динамикалык қатар. Медициналық ұйымдардағы динамикалық көрсеткішін сраптау есептеу
Динамикалык қатар. Медициналық ұйымдардағы динамикалық көрсеткішін сраптау есептеу Несеп шығару жүйесінің балалардағы ерекшеліктері
Несеп шығару жүйесінің балалардағы ерекшеліктері Общая гигиена. Климат. (Лекция 12-13)
Общая гигиена. Климат. (Лекция 12-13)