Содержание
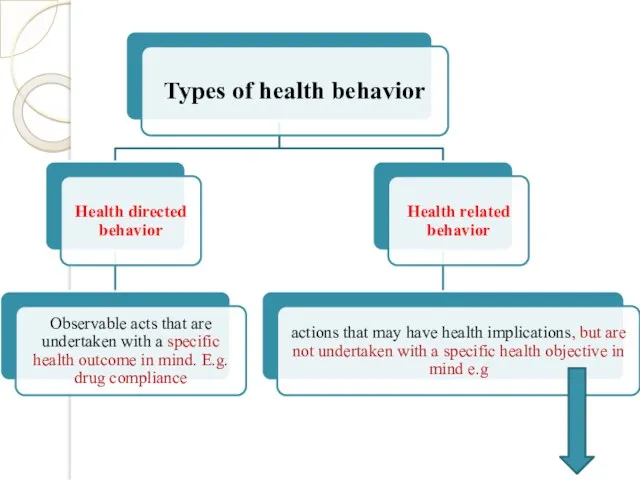
- 3. Definition of behavior: It is the response of the organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether
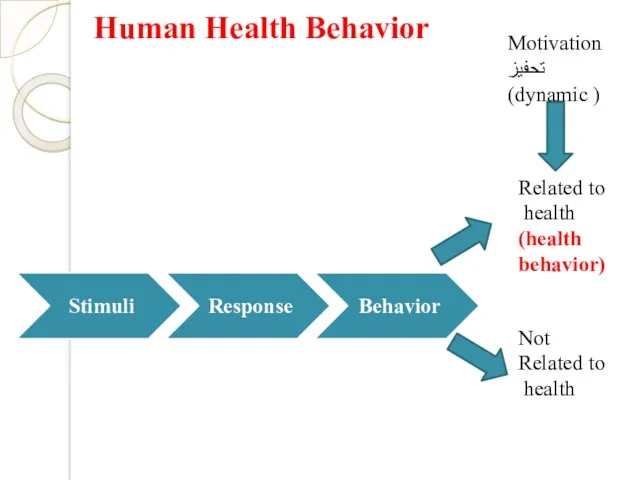
- 4. Human Health Behavior Related to health (health behavior) Not Related to health Motivation تحفيز (dynamic )
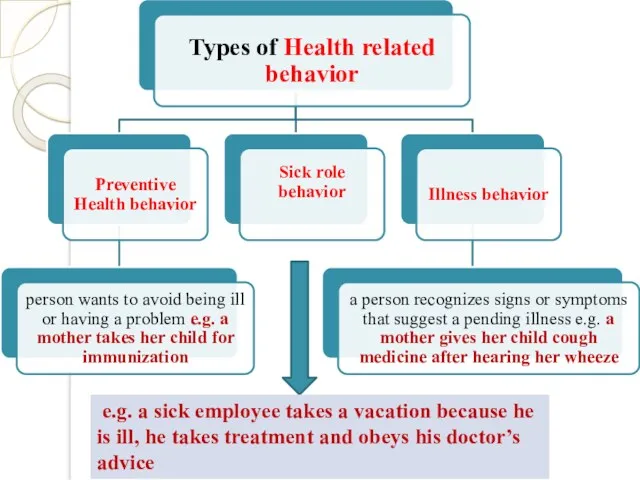
- 6. e.g. a sick employee takes a vacation because he is ill, he takes treatment and obeys
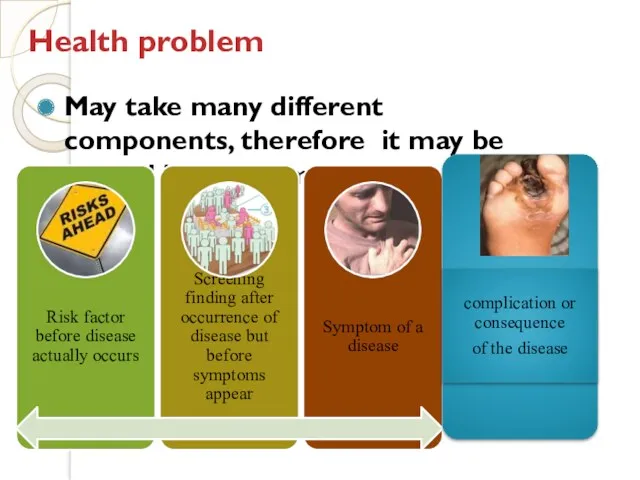
- 7. Health problem May take many different components, therefore it may be viewed in the form of.
- 8. Illness behavior People are differently in front of symptoms: Fail to go to the doctor. Go
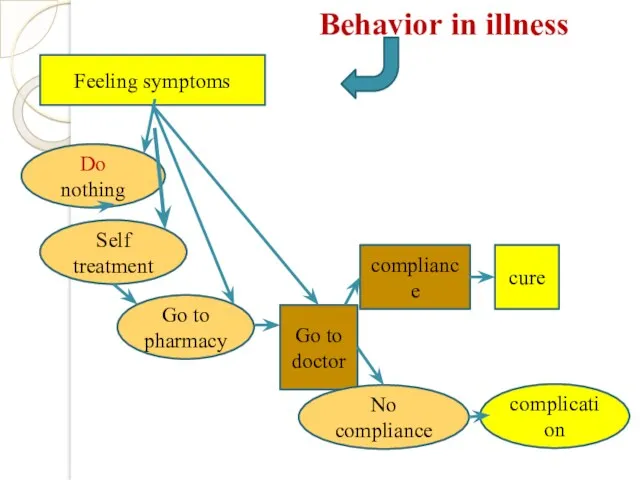
- 9. Behavior in illness Feeling symptoms Do nothing Go to pharmacy Self treatment Go to doctor compliance
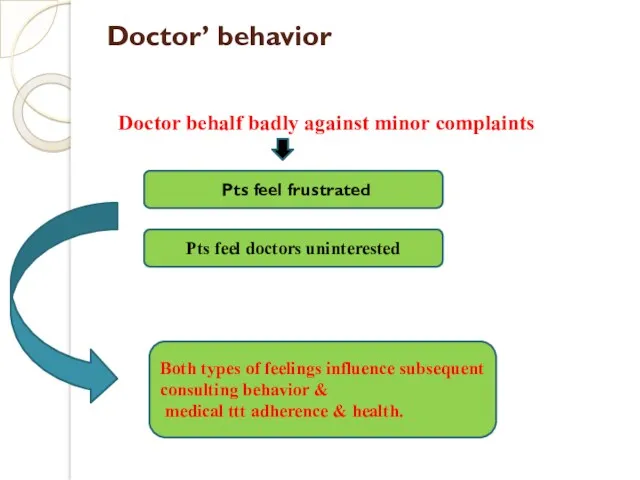
- 10. Doctor’ behavior Pts feel frustrated Doctor behalf badly against minor complaints Pts feel doctors uninterested Both
- 11. Factors that affect illness behavior Age, sex, level of education, culture, religion, past experience Seriousness of
- 12. Patient’s compliance Adherence to the advice of health care professionals [includes]: Preventive health behavior. Keeping medical
- 13. Patient’s incompliance Almost 50% of prescribed medications have health impacts. Doctors may be effective with only
- 14. Factors associated with adherence First: Pts has to understand what they are really asked to do.
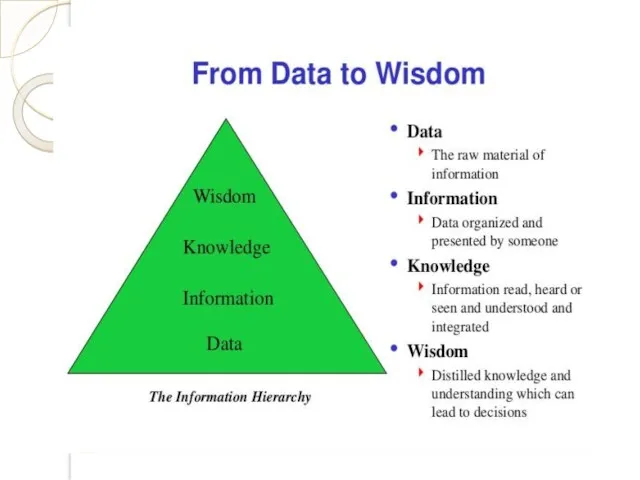
- 15. Knowledge & behavior
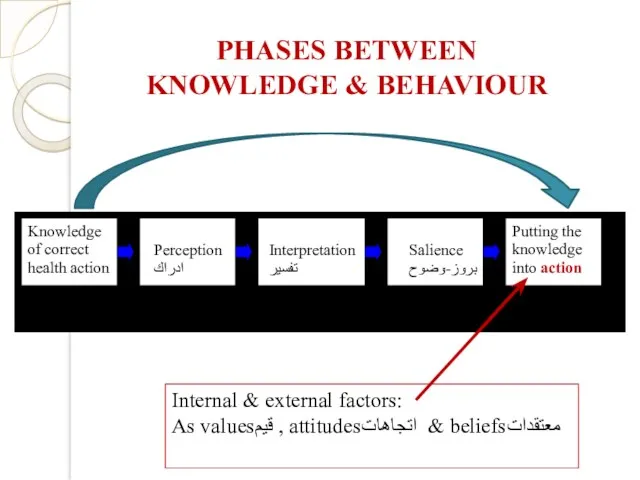
- 17. PHASES BETWEEN KNOWLEDGE & BEHAVIOUR Internal & external factors: As valuesقيم , attitudesاتجاهات & beliefsمعتقدات
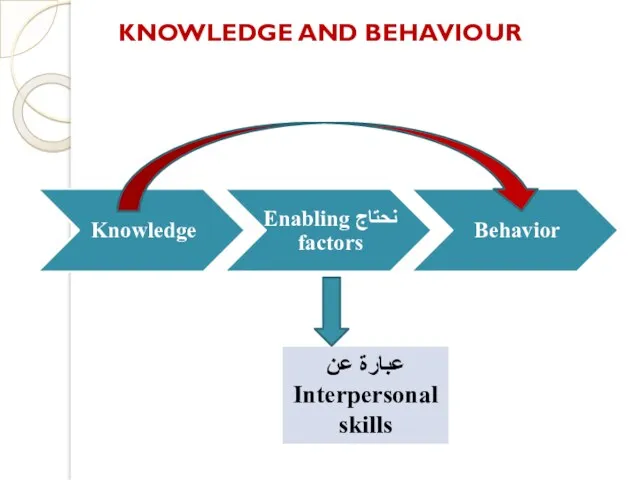
- 18. KNOWLEDGE AND BEHAVIOUR عبارة عن Interpersonal skills
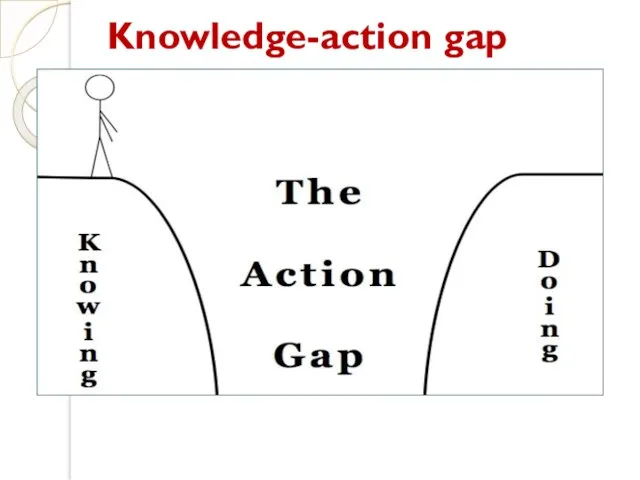
- 19. Knowledge-action gap
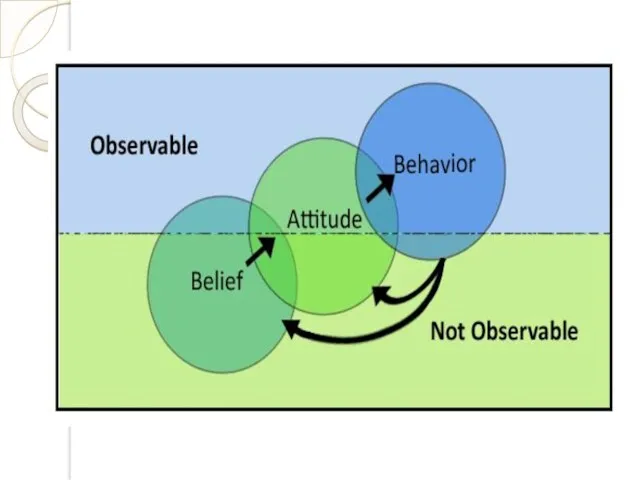
- 20. Believesمعتقدات , Attitudesالاتجاهات , valuesقيم & behaviorالسلوك
- 22. Believes, VALUES AND BEHAVIOR A belief معتقدrepresents the information a person has about an object or
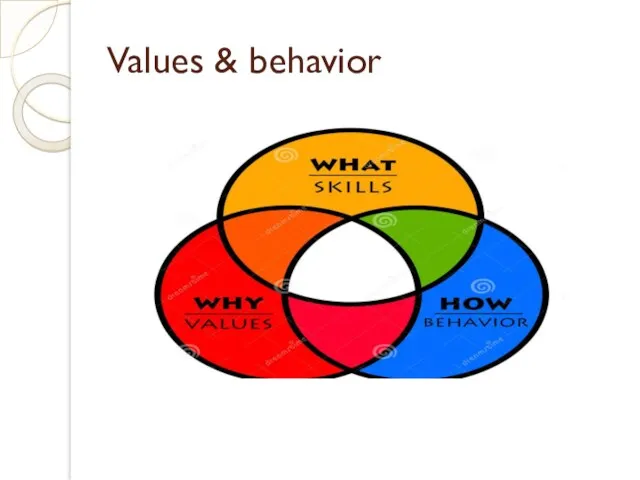
- 23. Values & behavior
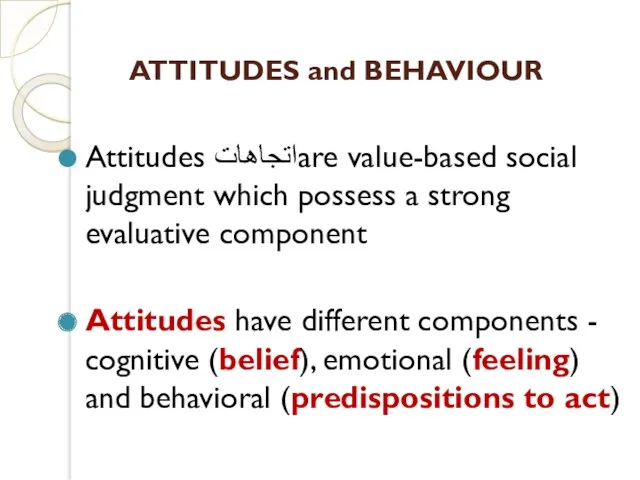
- 24. ATTITUDES and BEHAVIOUR Attitudes اتجاهاتare value-based social judgment which possess a strong evaluative component Attitudes have
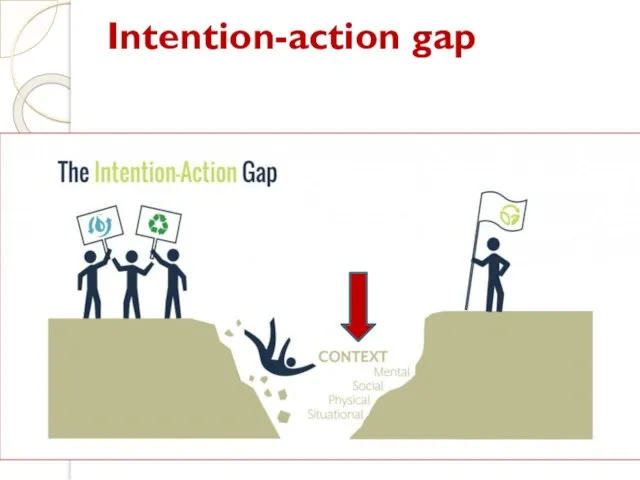
- 25. Intention-action gap
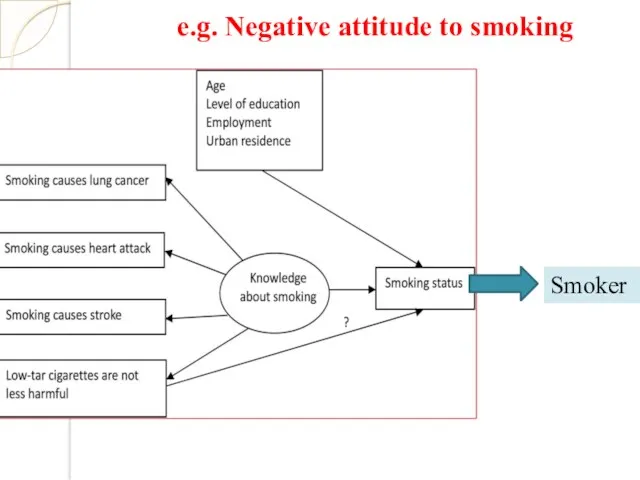
- 26. Smoker e.g. Negative attitude to smoking
- 28. Models of behavior change
- 29. How do we translate the models/theories into practice? Aim of all models: For diseased: to decrease
- 30. 1. MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS (Maslow - 1968)
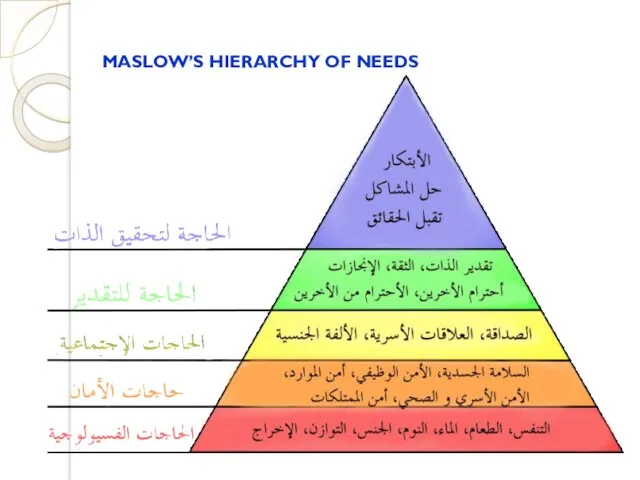
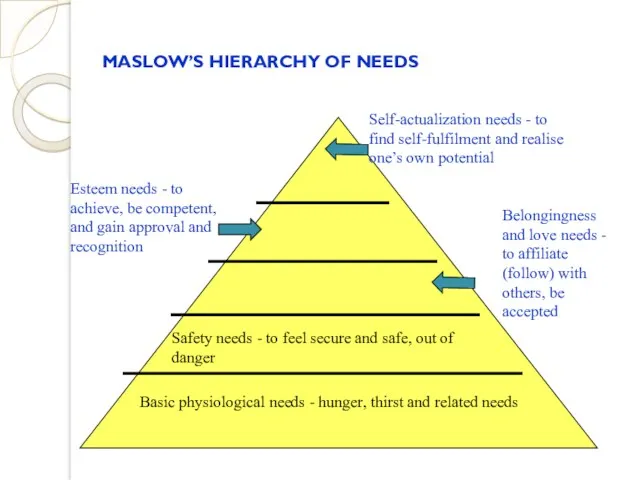
- 31. MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS
- 32. MASLOW’S HIERARCHY OF NEEDS Basic physiological needs - hunger, thirst and related needs Safety needs -
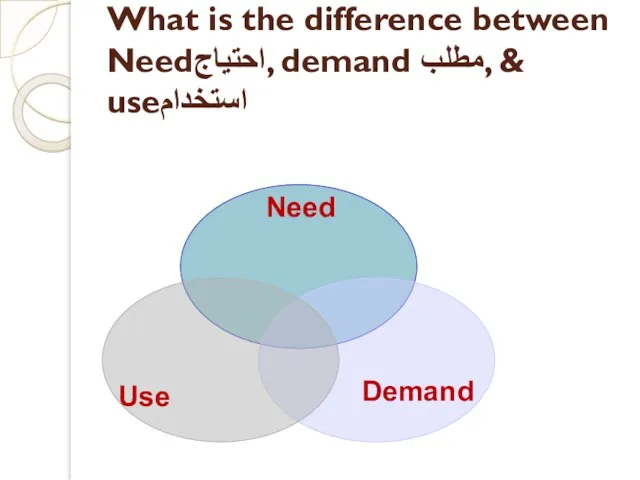
- 33. Needs Demands Use ما الفرق بينهم؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟؟
- 34. What is the difference between Needاحتياج, demand مطلب, & useاستخدام
- 35. Need: Require (something) because it is essential or very important rather than just desirable. What are
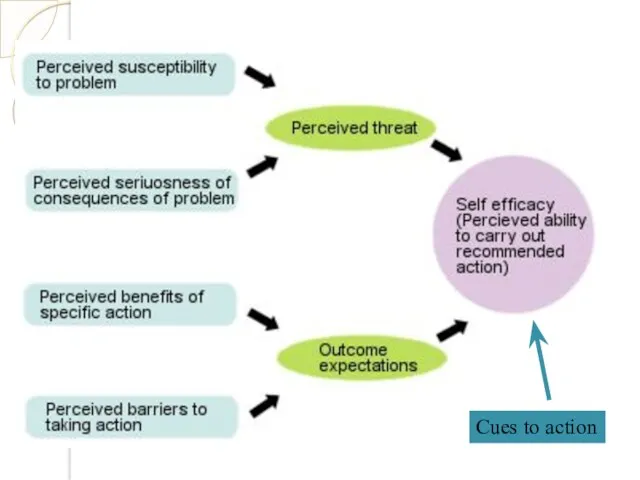
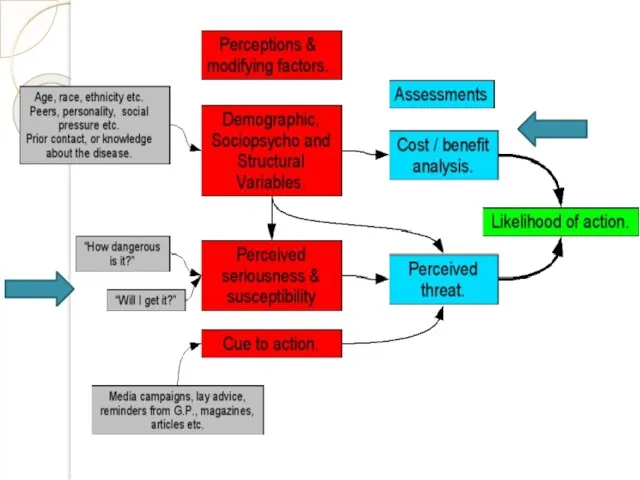
- 36. 2. THE HEALTH BELIEF MODEL (Rosenstock and Becker - 1974)
- 37. Cues to action
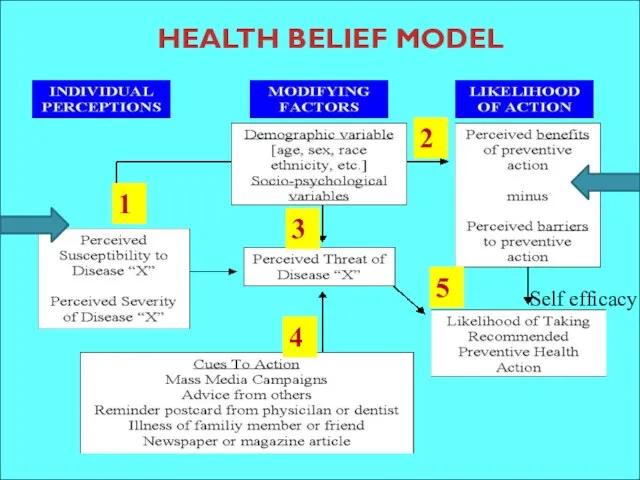
- 38. HEALTH BELIEF MODEL 1 2 3 4 5 Self efficacy
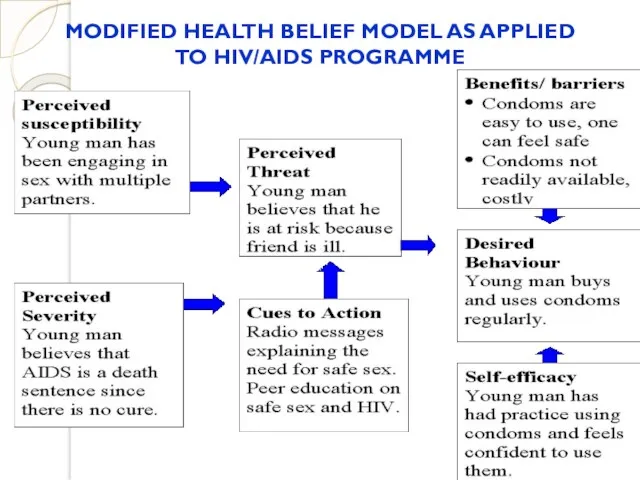
- 40. MODIFIED HEALTH BELIEF MODEL AS APPLIED TO HIV/AIDS PROGRAMME
- 41. HEALTH BELIEF MODEL Two major factors influence the likelihood that a person will adopt a recommended
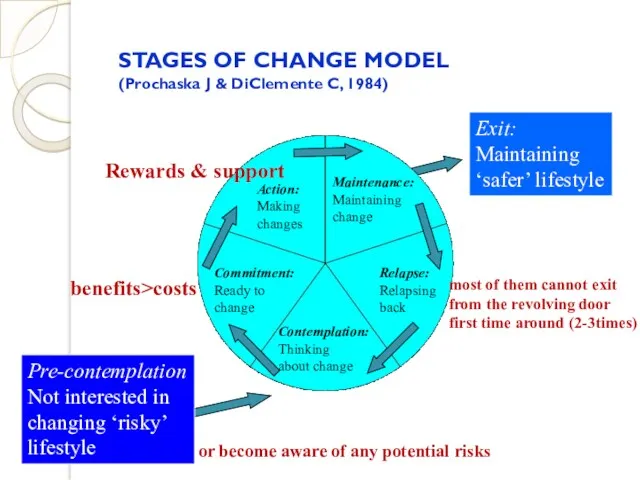
- 42. 3. STAGES OF CHANGE MODEL (Prochaska and DiClemente -1984) Revolving door
- 43. STAGES OF CHANGE MODEL (Prochaska J & DiClemente C, 1984) Pre-contemplation Not interested in changing ‘risky’
- 44. STAGES OF CHANGE MODEL It takes a holistic approach, integrating a range of factors such as
- 45. Cons may spend more money and time on food may need to cook more often at
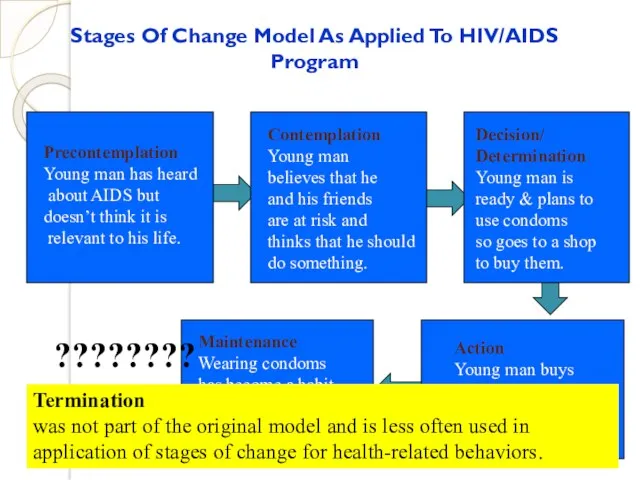
- 46. Stages Of Change Model As Applied To HIV/AIDS Program Precontemplation Young man has heard about AIDS
- 47. Conclusion From all these theories & models we can conclude that the most important variables underlying
- 48. Variables underlying behavioral performance 1. The person must have formed a strong positive intention (or made
- 49. 4. The person believes that the advantages (benefits, anticipated positive outcomes) of performing the behavior outweigh
- 50. 6. The person perceives that performance of the behavior is more consistent than inconsistent with his
- 51. 8. The person perceives that he or she has the capability to perform the behavior under
- 52. Applications 1- Ahmed is 18 years old, student. He is drug addict, there are many students
- 53. 2- samia is 35 years old, she became obese after labor. She is not happy being
- 54. 3- Nada 20 years old was exercising plenty of sports in school and club. Now she
- 55. 4- How can you design a program for self examination of breast for Egyptian women for
- 57. Скачать презентацию




























 Внутричерепная гипертензия и отёк мозга
Внутричерепная гипертензия и отёк мозга Полная Программа Здоровья - Очищение
Полная Программа Здоровья - Очищение Генные болезни человека, связанные с нарушением систем репарации
Генные болезни человека, связанные с нарушением систем репарации Первая медицинская помощь при отравлениях
Первая медицинская помощь при отравлениях Физическая реабилитация при заболеваниях сердечно-сосудистой системы
Физическая реабилитация при заболеваниях сердечно-сосудистой системы Ветеринарна фармакологія. Антибіотики, фітонциди і противірусні препарати
Ветеринарна фармакологія. Антибіотики, фітонциди і противірусні препарати Травмы позвоночника и таза
Травмы позвоночника и таза Краснуха
Краснуха Оториноларингологиялық аурулардың қазіргі заманға сай диагностикасы мен емдеу әдістері
Оториноларингологиялық аурулардың қазіргі заманға сай диагностикасы мен емдеу әдістері Клетки иммунной системы. Цитокины
Клетки иммунной системы. Цитокины Болезни птиц. Классификация. Диагностические экспертизы
Болезни птиц. Классификация. Диагностические экспертизы Алкоголизм и наркомания в молодежной среде
Алкоголизм и наркомания в молодежной среде Дифференциальная диагностика синдрома крупа у детей
Дифференциальная диагностика синдрома крупа у детей Дисфункция синусового узла в электрокардиографии
Дисфункция синусового узла в электрокардиографии ВИЧ-инфекция у детей. Особенности течения
ВИЧ-инфекция у детей. Особенности течения Анатомия и физиология печени
Анатомия и физиология печени Этиология и патогенез болезней пародонта
Этиология и патогенез болезней пародонта Первичная и реанимационная помощь новорожденным детям
Первичная и реанимационная помощь новорожденным детям Особенности формирования пищеварительной системы и их клиническое значение
Особенности формирования пищеварительной системы и их клиническое значение Жаңа туған нәрестелердің механикалық сарғаюы кезінде өт айдайтын дәрілерді қолдану тиімділігі
Жаңа туған нәрестелердің механикалық сарғаюы кезінде өт айдайтын дәрілерді қолдану тиімділігі Syndrome of acute inflammation of mucous membranes of respiratory tracts. Tonsillitises
Syndrome of acute inflammation of mucous membranes of respiratory tracts. Tonsillitises Факоматозы. Туберозный склероз (болезнь Бурневилля - Прингла). Нейрофиброматоз
Факоматозы. Туберозный склероз (болезнь Бурневилля - Прингла). Нейрофиброматоз Асқорыту жүйесі құрылысы мен қызметтінің балалардағы ерекшеліктері
Асқорыту жүйесі құрылысы мен қызметтінің балалардағы ерекшеліктері Интенсивная терапия кардиогенного шока
Интенсивная терапия кардиогенного шока Научные основы рационального питания
Научные основы рационального питания Тимпанопластика и мирингопластика
Тимпанопластика и мирингопластика Особенности исследования ДС у детей. Гистология респираторного отдела лёгких у детей
Особенности исследования ДС у детей. Гистология респираторного отдела лёгких у детей Хирургиялық науқастарды тамақтандыру
Хирургиялық науқастарды тамақтандыру