Содержание
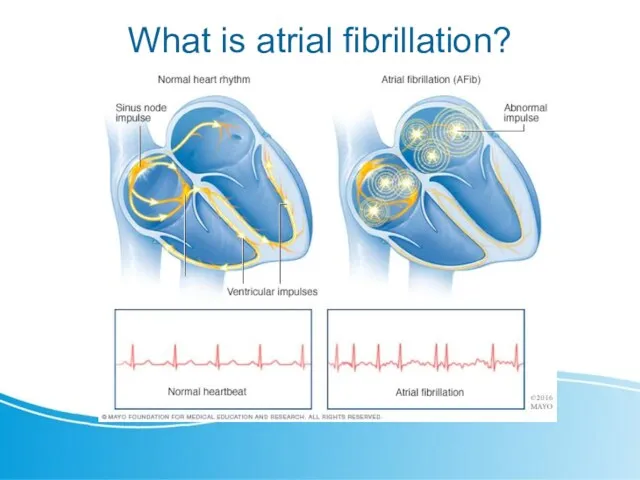
- 2. What is atrial fibrillation?
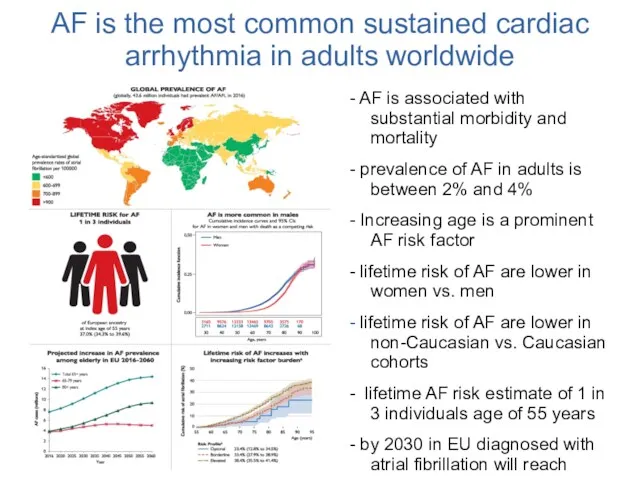
- 3. AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia in adults worldwide - AF is associated with
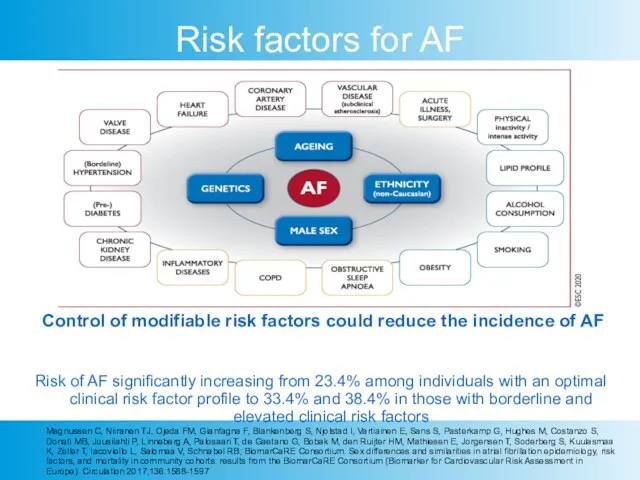
- 4. Risk factors for AF Control of modifiable risk factors could reduce the incidence of AF Risk
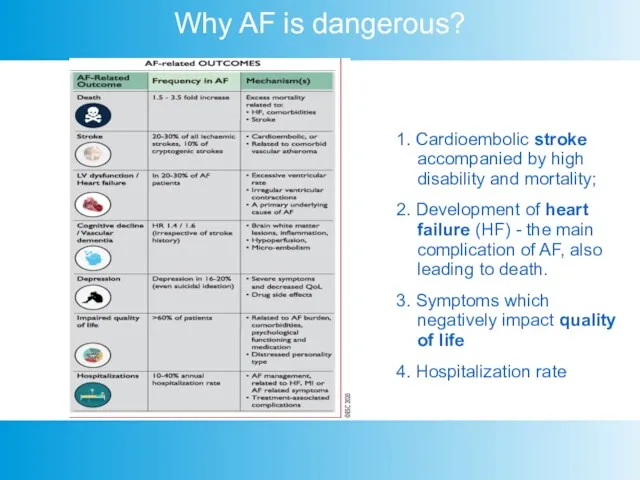
- 5. Why AF is dangerous? 1. Cardioembolic stroke accompanied by high disability and mortality; 2. Development of
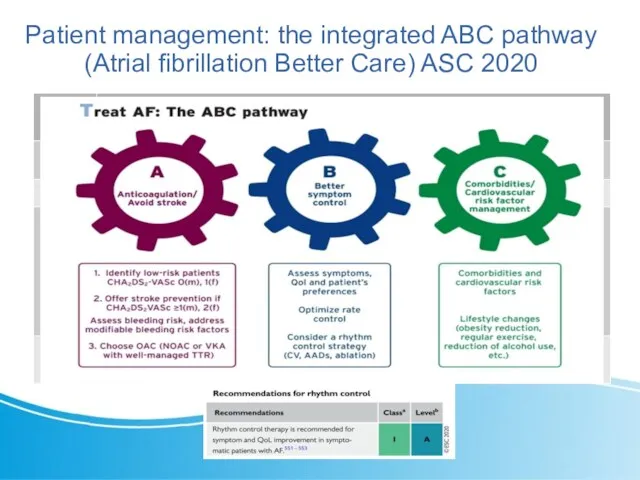
- 6. Patient management: the integrated ABC pathway (Atrial fibrillation Better Care) ASC 2020
- 7. Classification of AF ESC 2020 rhythm control strategy
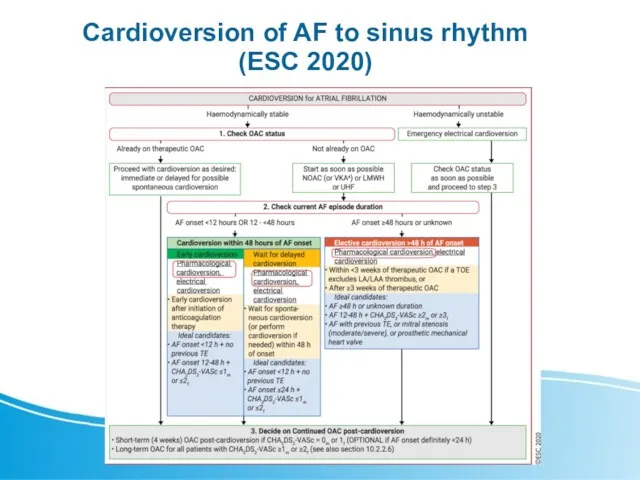
- 8. Cardioversion of AF to sinus rhythm (ESC 2020)
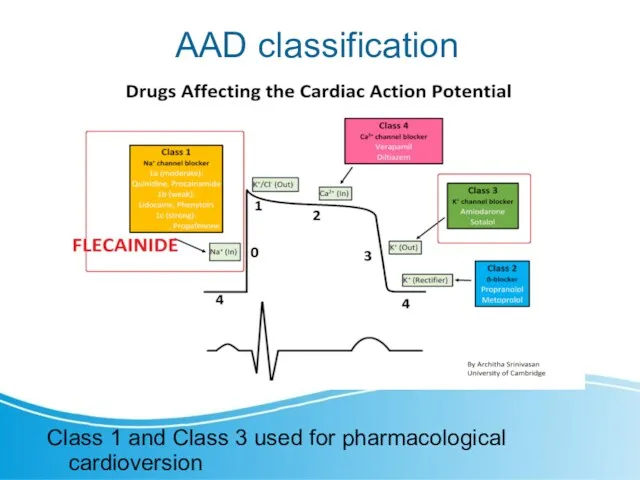
- 9. AAD classification Class 1 and Class 3 used for pharmacological cardioversion
- 10. Recommendations for pharmacological cardioversion ESC 2020 Symptomatic, haemodynamically stable No severe structural HD Structural HD or
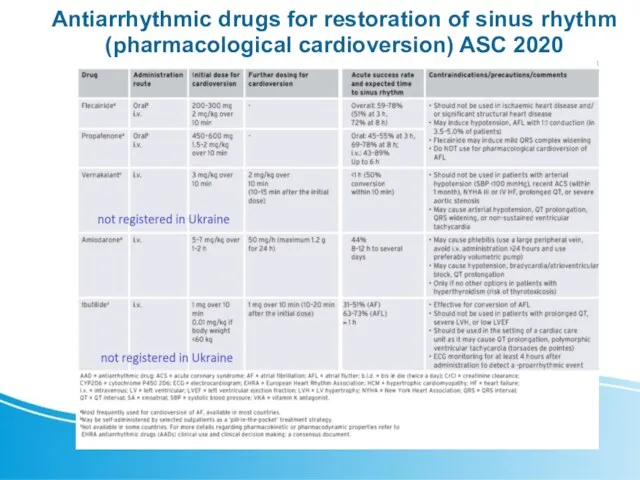
- 11. Antiarrhythmic drugs for restoration of sinus rhythm (pharmacological cardioversion) ASC 2020
- 12. Flecainide (Lexarit) Flecainide acetate is an oral class Ic antiarrhythmic drug (AAD) which blocks cardiac Na+
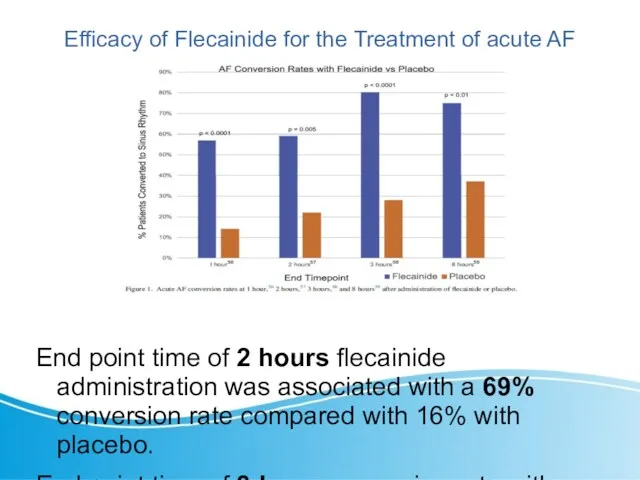
- 13. Efficacy of Flecainide for the Treatment of acute AF End point time of 2 hours flecainide
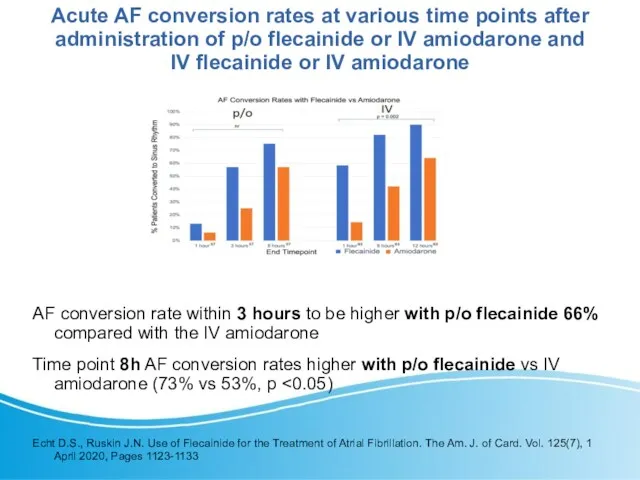
- 14. Acute AF conversion rates at various time points after administration of p/o flecainide or IV amiodarone
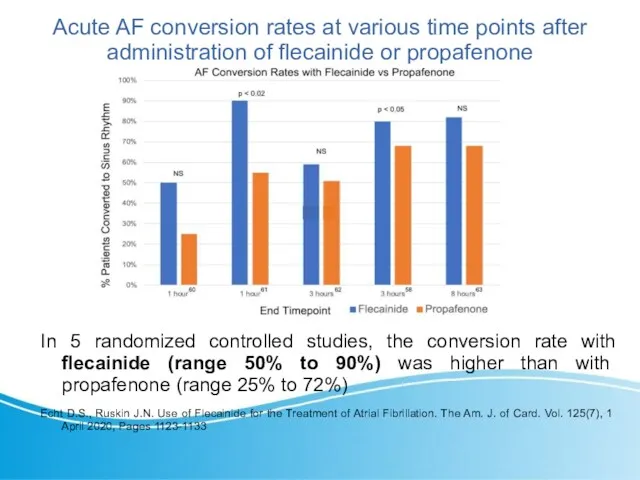
- 15. Acute AF conversion rates at various time points after administration of flecainide or propafenone In 5
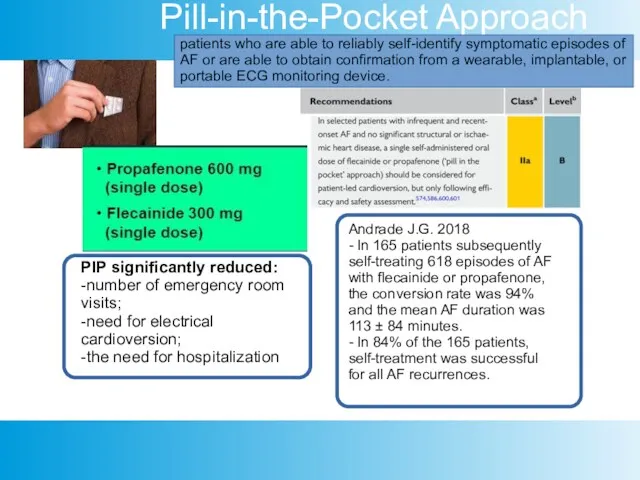
- 16. Pill-in-the-Pocket Approach Andrade J.G. 2018 - In 165 patients subsequently self-treating 618 episodes of AF with
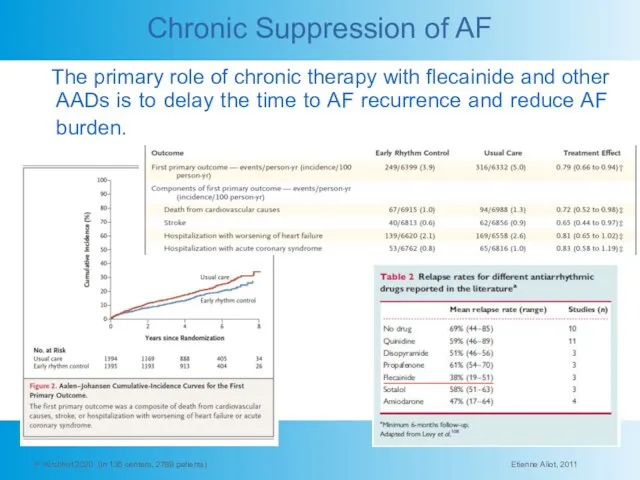
- 17. Chronic Suppression of AF The primary role of chronic therapy with flecainide and other AADs is
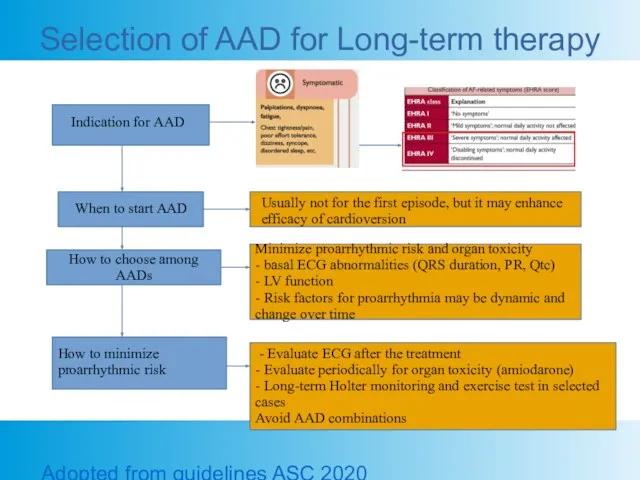
- 18. Selection of AAD for Long-term therapy Adopted from guidelines ASC 2020 Indication for AAD When to
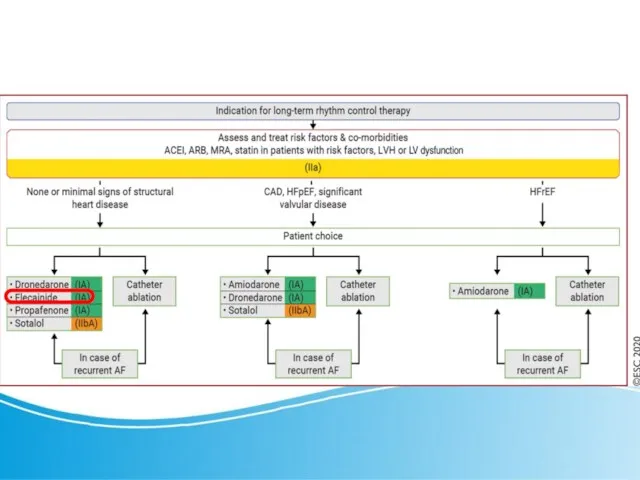
- 19. Long-term rhythm control therapy ESC 2020
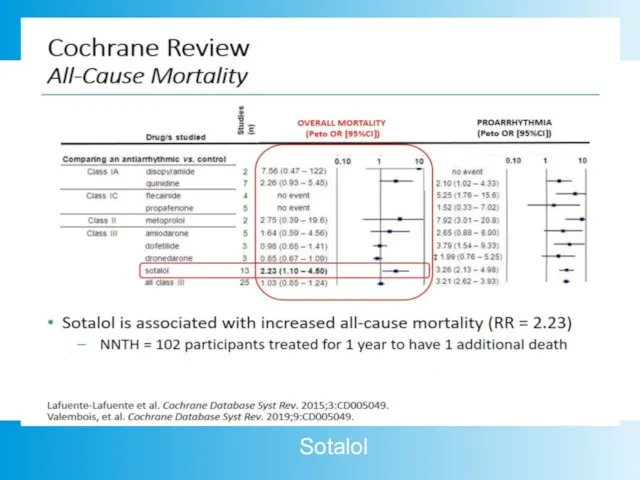
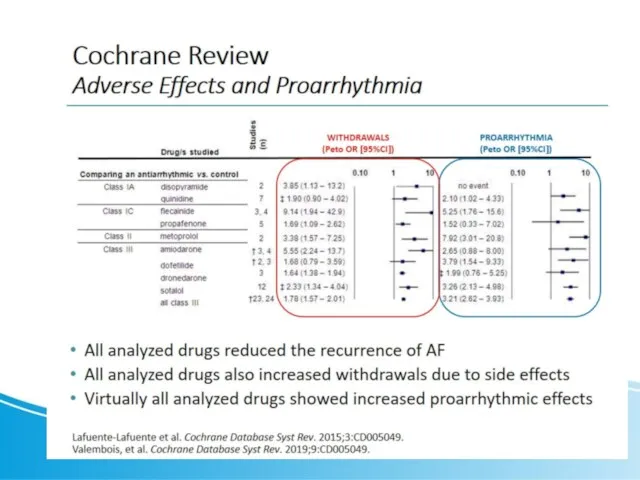
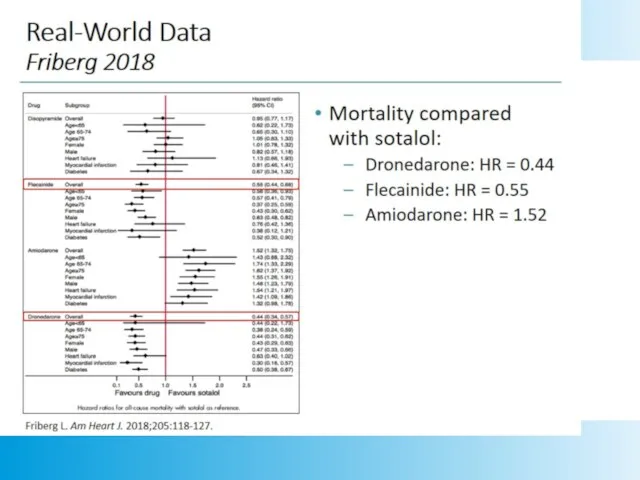
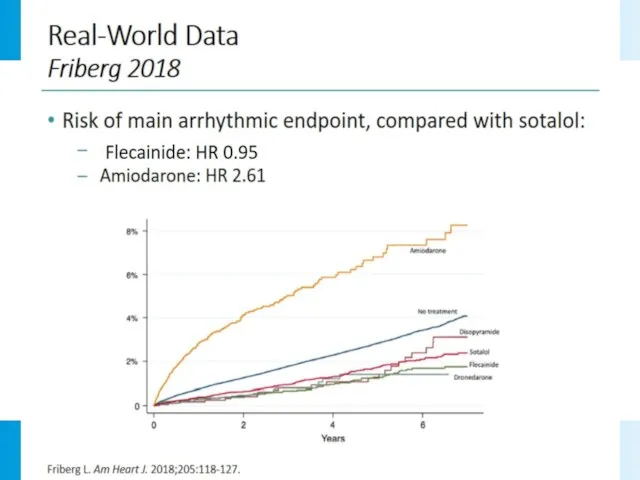
- 21. Sotalol
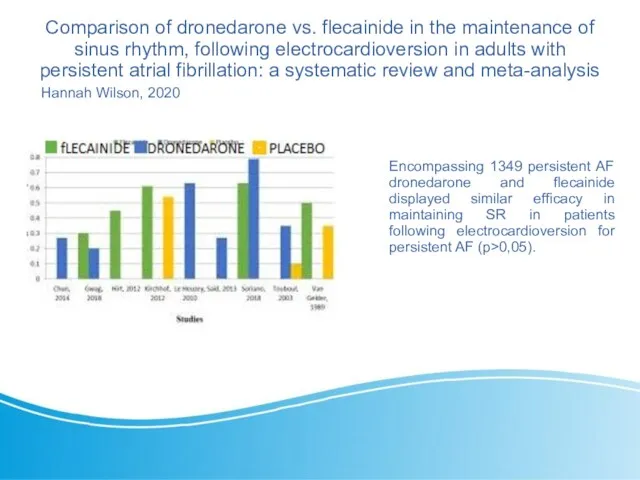
- 26. Comparison of dronedarone vs. flecainide in the maintenance of sinus rhythm, following electrocardioversion in adults with
- 27. Flecainide for chronic suppression of AF 1. For the chronic prevention of AF recurrence, it is
- 28. Conclusion 1. Flecainide acetate is highly effective for the acute termination of recent onset AF and
- 30. Скачать презентацию






 Корь: осложнения
Корь: осложнения Профилактика постинъекционных осложнений
Профилактика постинъекционных осложнений Бронхиальная астма у детей
Бронхиальная астма у детей Рекомендации по профилактике гриппа А/Н1N1 и острых респираторных инфекций среди сотрудников системы МЧС России
Рекомендации по профилактике гриппа А/Н1N1 и острых респираторных инфекций среди сотрудников системы МЧС России Физические упражнения для детей грудного возраста
Физические упражнения для детей грудного возраста Нодулярный дерматит крупного рогатого скота
Нодулярный дерматит крупного рогатого скота Дезинфекция
Дезинфекция Гастрит, асқазан ойық жарасы
Гастрит, асқазан ойық жарасы Эхинококкоз человека
Эхинококкоз человека Антибиотики и химиотерапия. Химиотерапевтические препараты
Антибиотики и химиотерапия. Химиотерапевтические препараты Болезнь Нимана-Пика
Болезнь Нимана-Пика Организмнің сыртқы ортаға бейімделудегі талдағыштар рөлі
Организмнің сыртқы ортаға бейімделудегі талдағыштар рөлі Основы офтальмохирургии
Основы офтальмохирургии Геморрагическая лихорадка с почечным синдромом
Геморрагическая лихорадка с почечным синдромом Противовирусные и противогрибковые средства
Противовирусные и противогрибковые средства Переливание крови
Переливание крови Коронавирусная инфекция, клиника, диагностика, профилактика
Коронавирусная инфекция, клиника, диагностика, профилактика Группы крови, резус-фактор. Правила переливания крови, кровезамещающие растворы
Группы крови, резус-фактор. Правила переливания крови, кровезамещающие растворы Подписание медицинской документации (электронные медицинские документы)
Подписание медицинской документации (электронные медицинские документы) Деконтаминация в ЛПО. Подбор дезинфицирующих средств. Практикум 7
Деконтаминация в ЛПО. Подбор дезинфицирующих средств. Практикум 7 Вирустар– өсімдік, жануар және бактерия клеткаларының ішінде болатын паразиттер
Вирустар– өсімдік, жануар және бактерия клеткаларының ішінде болатын паразиттер Магнітні бурі і їхній вплив на здоров'я людина
Магнітні бурі і їхній вплив на здоров'я людина Клиническая электрокардиография. Нормальная электрокардиограмма
Клиническая электрокардиография. Нормальная электрокардиограмма Эмбриональный гистогенез и органогенез дыхательной системы. Аномалии развития. Лекция № 4
Эмбриональный гистогенез и органогенез дыхательной системы. Аномалии развития. Лекция № 4 Меланома. Методы диагностики меланомы
Меланома. Методы диагностики меланомы Полиомиелит
Полиомиелит Строение сердца. Функции сердца
Строение сердца. Функции сердца Т-В+тяжелые клеточные иммунодефициты
Т-В+тяжелые клеточные иммунодефициты