Содержание
- 2. the most frequent words in medical English 1
- 3. IS DEFINED AS Определяется как Pleural effusion is defined as excess fluid accumulation in pleural space
- 4. REFERS TO Относится к Uncomplicated UTI refers to acute cystitis or pyelonephritis in non-pregnant outpatient woman
- 5. IS CHARACTERIZED BY Характеризуется (чем-либо) COPD is characterized by airflow obstruction.
- 6. OCCUR Встречаются, возникают In the US more than 700,000 cases of sepsis occur every year.
- 7. Affect поражать, оказывать воздействие This disease affects 5-10% of the population. It is estimated than 15%
- 8. ARE DIVIDED INTO Делятся на Gallbladder are divided into two major types: cholesterol stoned and pigment
- 9. ARE CLASSIFIED INTO классифицируется на Gastrinomas are classified into sporadic tumors and those associated with multiple
- 10. ARE CLASSIFIED AS Классифицируются как Strategies for predicting and preventing SCD (sudden cardiac death) are classified
- 11. FALL INTO (categories) Попадают в (категории) This drugs are fallen into four main categories.
- 12. clinical syndromes you might meet in your practice 2
- 13. A SYNDROME is: a set of medical signs and symptoms collection of diseases which are not
- 14. Acute Brain Syndrome What is Acute Brain Syndrome ? Delirium Confusion Disorientation Developing suddenly in a
- 15. Acute Brain Syndrome Causes: Brain injury due to trauma Breathing conditions Cardiovascular disorders Degenerative disorders Infections
- 17. Acute Brain Syndrome Diagnosis and Tests: Electroencephalography (EEG) Computed tomography (CT) Scan of Brain Magnetic resonance
- 18. Portal hypertension Portal hypertension is hypertension in the hepatic portal system – made up of the
- 19. Portal hypertension Prehepatic causes: Portal vein thrombosis Splenic vein thrombosis Arteriovenous fistula Splenomegaly (increased portal blood
- 20. Portal hypertension Hepatic causes: Cirrhosis of any cause. Primary sclerosing cholangitis Chronic pancreatitis Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
- 21. Portal hypertension Posthepatic causes: Inferior vena cava obstruction Right-sided heart failure, e.g. from constrictive pericarditis Budd–Chiari
- 22. Portal hypertension Signs and symptoms: Ascites Increased spleen size (splenomegaly) and spleen function (hypersplenism), which may
- 24. Portal hypertension Diagnosis: Ultrasonography (US): a dilated portal vein (diameter of greater than 13mm) is a
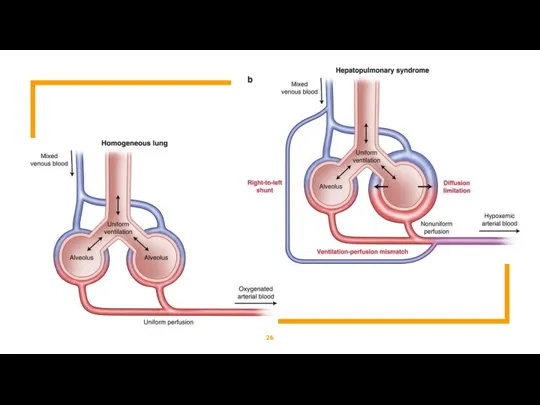
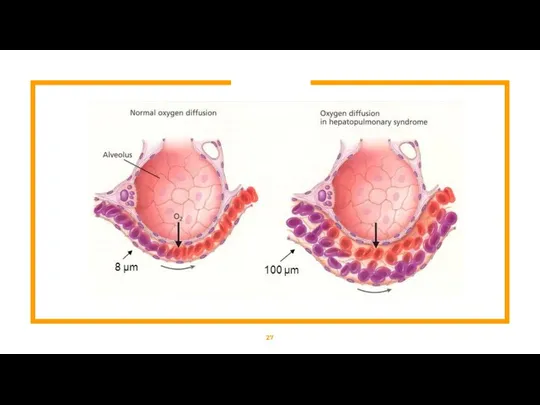
- 25. Hepatopulmonary Syndrome What is a Hepatopulmonary Syndrome ? HPS is a disease process with a triad
- 28. Hepatopulmonary Syndrome Cause(s) : Chronic and acute liver failure can cause formation of microscopic intrapulmonary arteriovenous
- 29. Metabolic Syndrome What is a Metabolic Syndrome ? Metabolic syndrome is the malfunctioning of energy utilization
- 30. Metabolic Syndrome Cause(s) : Stress Overweight and obesity Inactive or sedentary lifestyle Aging Diabetes mellitus type
- 31. Metabolic Syndrome Symptoms : Central obesity (abdominal obesity, visceral obesity or apple-shaped obesity) High blood pressure
- 33. Metabolic Syndrome Diagnosis and Tests : Central obesity - waist circumference greater than 102 cm or
- 34. Malabsorption Syndrome What is a Malabsorption Syndrome ? A number of disorders in which the ability
- 35. Malabsorption Syndrome Causes: Inflammation, disease or injury to the lining of stomach and intestine Body’s failure
- 37. Malabsorption Syndrome Symptoms: Deficiency of certain nutrients cause specific symptoms: Fats deficiency - Foul smelling, light
- 38. Meigs Syndrome What is a Meigs Syndrome ? Meigs syndrome presents as a triad of ascites,
- 39. Meigs Syndrome Causes: Unknown Symptoms : Fatigue Dyspnea (difficulty in breathing) usually on exertion Weigth gain
- 41. Premenstrual Syndrome What is a Premenstrual Syndrome ? The collection of physical and emotional symptoms a
- 42. Premenstrual Syndrome Emotional: Stress, anxiety, mood swings Crying spells Food cravings Insomnia Social withdrawal Poor concentration
- 43. Reactive Arthritis What is a Reactive Arthritis ? Reactive Arthritis is a chronic type of arthritis
- 44. Reactive Arthritis Symptoms : Arthritis symptoms: Pain, swelling, redness and stiffness of joints, usually involving Conjunctivitis:
- 46. Drug withdrawal Drug withdrawal is the group of symptoms that occur upon the abrupt discontinuation or
- 47. Drug withdrawal Withdrawal symptoms from opiates include anxiety, sweating, vomiting, and diarrhea. Alcohol withdrawal symptoms include
- 49. Munchausen Syndrome What is a Munchausen Syndrome ? A Psychiatric disorder in which the person feigns
- 50. Munchausen Syndrome Cause(s) : Psychological disturbances due to abuse or neglect as a child History of
- 52. Munchausen Syndrome Symptoms : Inconsistent and dramatic medical history Unclear symptoms that become more severe or
- 53. Pica Syndrome What is a Pica Syndrome? Pica disorder refers to appetite for eating non-edible and
- 55. Restless Legs Syndrome What is a Restless Legs Syndrome? Restless legs syndrome is a neurological disorder
- 56. Restless Legs Syndrome Symptoms : About 40% of members have their first symptoms before the age
- 57. Restless Legs Syndrome Diagnosis and Tests : No specific diagnostic tests Clinical examination History of restlessness,
- 58. Serotonin Syndrome What is a Serotonin Syndrome ? A collection of symptoms in response to excess
- 59. Serotonin Syndrome Symptoms : Agitation or restlessness Dilated pupils Changes in blood pressure or temperature Nausea,
- 61. true goose-bump
- 62. Tumor Lysis Syndrome What is Tumor Lysis Syndrome ? A group of metabolic complications that can
- 63. Tumor Lysis Syndrome Symptoms : Hyperkalemia (High potassium levels in blood) Cardiac conduction abnormalities Severe muscle
- 64. Great job! You’ve deserved to take a break and have some fun Learn English Vocabulary for
- 65. Fake it until you make it.
- 67. Скачать презентацию
























































 Сыртқы сәулеленуден медициналық қорғау
Сыртқы сәулеленуден медициналық қорғау Характеристика лекарственного растительного сырья, влияющего на сердечнососудистую и мочевыделительную систему
Характеристика лекарственного растительного сырья, влияющего на сердечнососудистую и мочевыделительную систему Основы безопасности питания
Основы безопасности питания Компьютерная томография
Компьютерная томография Синдромы и методы функциональной диагностики при патологии ЖВП и печени
Синдромы и методы функциональной диагностики при патологии ЖВП и печени Кокжөтел мен дифтерия кезіндегі шаралар стандарттары мен алгоритмдері
Кокжөтел мен дифтерия кезіндегі шаралар стандарттары мен алгоритмдері Здоровый образ жизни (ЗОЖ)
Здоровый образ жизни (ЗОЖ) Тұқым қуалайтын аурулардың емдеудің негізгі принциптері
Тұқым қуалайтын аурулардың емдеудің негізгі принциптері Состав крови. Плазма крови. Функции эритроцитов. Защитные механизмы крови
Состав крови. Плазма крови. Функции эритроцитов. Защитные механизмы крови Жгутиконосцы - flagellata
Жгутиконосцы - flagellata Сердечно-сосудистая система ребенка
Сердечно-сосудистая система ребенка Острый рассеянный энцефаломиелит
Острый рассеянный энцефаломиелит Применение статистики для оценки здоровья. Лекция 1
Применение статистики для оценки здоровья. Лекция 1 Острый коронарный синдром (ОКС)
Острый коронарный синдром (ОКС) Послеродовые заболевания
Послеродовые заболевания Естің бұзылыстары. Нарушения памяти
Естің бұзылыстары. Нарушения памяти Properties of heart and vessels in children
Properties of heart and vessels in children ACOS: перекрестный синдром ХОБЛ и бронхиальной астмы
ACOS: перекрестный синдром ХОБЛ и бронхиальной астмы Зрительные функции и методы их исследования
Зрительные функции и методы их исследования Параллелометрия. Определение
Параллелометрия. Определение Кишечник. Строение кишечника
Кишечник. Строение кишечника Феохромоцитома
Феохромоцитома Клиникалық жағдай. Интоксикационная энцефалопатия головного мозга. Нейропатия лицевого нерва справа
Клиникалық жағдай. Интоксикационная энцефалопатия головного мозга. Нейропатия лицевого нерва справа Загальні організаційно-методичні основи фізичної терапії при порушенні діяльності дихальної системи
Загальні організаційно-методичні основи фізичної терапії при порушенні діяльності дихальної системи Носовые кровотечения
Носовые кровотечения Служение больницы и учреждения. Анонимные Наркоманы
Служение больницы и учреждения. Анонимные Наркоманы Методы исследования центральной нервной системы
Методы исследования центральной нервной системы Сестринская помощь при заболеваниях прямой кишки трещины заднего прохода, геморрой. Лекция 16
Сестринская помощь при заболеваниях прямой кишки трещины заднего прохода, геморрой. Лекция 16