Содержание
- 2. Neuroleptics (Antipsychotic Drugs)
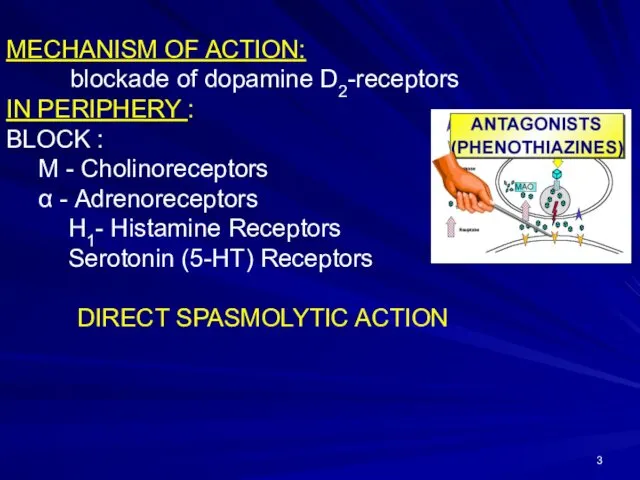
- 3. MECHANISM OF ACTION: blockade of dopamine D2-receptors IN PERIPHERY : BLOCK : M - Cholinoreceptors α
- 4. Pharmacological Effects: Antipsychotic Actions: ⇓ Hallucination and Agitation Antiemetic Effects Extrapyramidal Effects: D2-Rs blockade in the
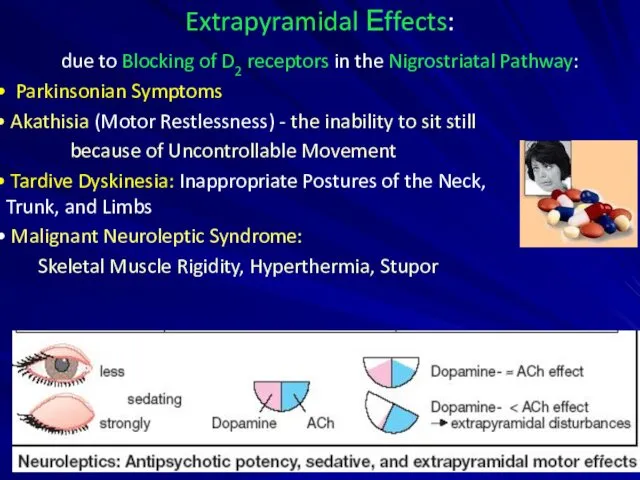
- 7. Extrapyramidal Еffects: due to Blocking of D2 receptors in the Nigrostriatal Pathway: Parkinsonian Symptoms Akathisia (Motor
- 8. Clinical Uses of Neuroleptics 1. SCHIZOPHRENIA: Positive Symptoms of Schizophrenia : DELUSIONS, HALLUCINATIONS and THOUGHT DISORDERS
- 9. Aminazine (Chlorpromazine) - blocks CNS D2 receptors α-Recetor and GANGLIONIC BLOCKADE ? HISTAMINE- and SEROTONIN -mediated
- 10. DROPERIDOL amp. 0.25%-10 ml – a BUTYROPHENONE derivative, more potent and to have fewer autonomic effects
- 11. Lithium Salts Lithium Carbonate – Caps. 0.15 and 0.3 g; Tab. 0.3 g Lithium Citrate –
- 12. CLINICAL USES Bipolar Affective Disorders Major Depression Schizoaffective Disorder Alcohol Dependence ADVERSE EFFECTS Psychomotor retardation Lethargy
- 13. TRANQUILIZERS (ANXIOLYTIC DRUGS) I. Benzodiazepines (BZDs): Diazepam (Sibazon ) – amp. 0.5%-2 ml; Tab. 0.005 g
- 14. BENZODIAZEPINES according to their Duration of Action: 1. Long-acting (24-48 hours): Diazepam Phenasepam Chlordiazepoxide 2. Intermediate-acting
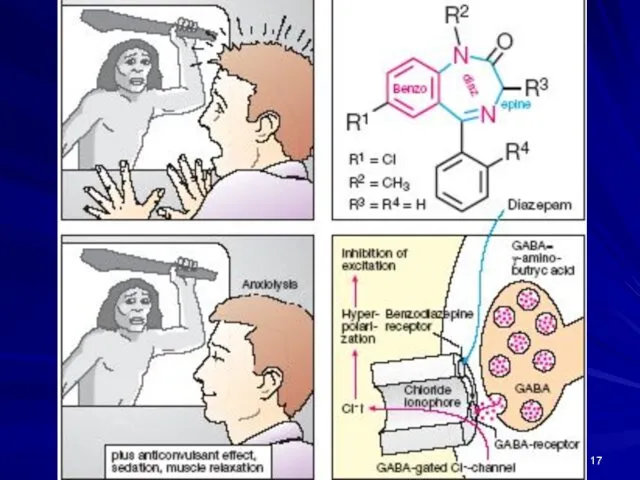
- 16. MECHANISM OF ACTION of BZDs: Bind to the α-subunit of the GABAA Rs surrounding the Cl
- 18. CLINICAL USES of BZDs 1.ANXIETY and PANIC DISORDERS 2. MUSCULAR DISORDERS: DIAZEPAM – ⮟ Skeletal Muscle
- 19. Psychological and Physical Dependence - if high doses are given over a prolonged period ADVERSE EFFECTS
- 20. BZD Antagonist: FLUMAZENIL – a GABA receptor competitive antagonist that can rapidly reverse the effects of
- 21. DIAZEPAM (Sibazon) amp. 0.5%-2 ml; Tab. 0.005 g is a Tranquilizer, a LONG ACTING BENZODIAZEPINE MECHANISM
- 22. Gidazepam Tab. 0.02 g; 0.05 g – DAY TRANQUILIZER – has ACTIVATING EFFECT a SHORT ACTING
- 23. Busbirone - Tab. 10 mg - an non-BZD anxiolytic MECHANISM OF ACTION: ⮟ Blocks 5-HT1A Serotonin
- 24. Sedative Drugs: 1. BROMINE SALTS: Sodium Bromide - NaBr Potassium Bromide - KBr 2. VALERIAN’S PREPARATIONS:
- 25. BROMISM – chronic intoxication with BROM salts. Bromides eliminate slowly (T1/2=12 days), MANIFESTATION: total retardation, apathy,
- 26. Valerian’s and Motherwort’s Preparations - are widely used sedative drugs. VALERIAN’S preparations - Infusion, Tincture, Extract
- 28. Скачать презентацию






















 Косыночные повязки. Первая помощь. Остановка кровотечения
Косыночные повязки. Первая помощь. Остановка кровотечения Программа добровольного медицинского страхования Доктор РЕСО. Новосибирск
Программа добровольного медицинского страхования Доктор РЕСО. Новосибирск Комплексная оценка здоровья детей и подростков
Комплексная оценка здоровья детей и подростков Острая спаечная кишечная непроходимость у детей
Острая спаечная кишечная непроходимость у детей Инфекция костей и суставов
Инфекция костей и суставов Возраст и лекарство
Возраст и лекарство Областная клиническая больница скорой медицинской помощи (ГАУЗ КО ОКБСМП)
Областная клиническая больница скорой медицинской помощи (ГАУЗ КО ОКБСМП) Репродуктивті және жыныс жүйесінің дамуының бұзылу синдромы
Репродуктивті және жыныс жүйесінің дамуының бұзылу синдромы Этиопатогенез гиперкинезов. Основные клинические формы
Этиопатогенез гиперкинезов. Основные клинические формы Саркоидоз
Саркоидоз Косметология. Составление процедур по уходу за кожей рук и ног
Косметология. Составление процедур по уходу за кожей рук и ног Организация помощи больным муковисцидозом в РФ в показателях национального регистра
Организация помощи больным муковисцидозом в РФ в показателях национального регистра Опыт применения внутрикостного доступа поисково-спасательными службами МЧС России
Опыт применения внутрикостного доступа поисково-спасательными службами МЧС России Качество лекарственных средств при распределении, хранении и потреблении. (Лекция 4)
Качество лекарственных средств при распределении, хранении и потреблении. (Лекция 4) Кровотечения в последовом и раннем послеродовом периоде
Кровотечения в последовом и раннем послеродовом периоде Рак легкого. Опухоли средостения
Рак легкого. Опухоли средостения Психолептики. Нейролептики. Транквилизаторы. Нормотимики. Седативные средства
Психолептики. Нейролептики. Транквилизаторы. Нормотимики. Седативные средства Синдром поражения миокарда
Синдром поражения миокарда Основные принципы оценки иммунной системы. Возрастные особенности
Основные принципы оценки иммунной системы. Возрастные особенности Гонококова інфекція
Гонококова інфекція Теоретические основы экспертизы трудоспособности
Теоретические основы экспертизы трудоспособности Бронхолитические средства
Бронхолитические средства Бүйректе тас түзілудің себептері мен даму механизмдері
Бүйректе тас түзілудің себептері мен даму механизмдері Последствия нейротравмы
Последствия нейротравмы Острые гнойные заболевания мягких тканей
Острые гнойные заболевания мягких тканей Возрастная анатомия, физиология и гигиенаПредмет и содержание курса возрастной анатомии, физиологии и гигиены
Возрастная анатомия, физиология и гигиенаПредмет и содержание курса возрастной анатомии, физиологии и гигиены Биологиялық дозиметрия (электрондық парамагниттік резонанс және тағы басқалары) және олардың тәжірибеде қолданылуы
Биологиялық дозиметрия (электрондық парамагниттік резонанс және тағы басқалары) және олардың тәжірибеде қолданылуы Анемиялар
Анемиялар