Содержание
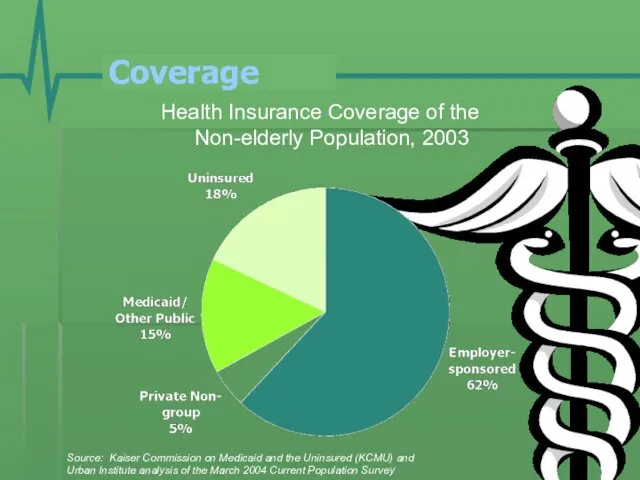
- 2. Coverage Health Insurance Coverage of the Non-elderly Population, 2003 Source: Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the
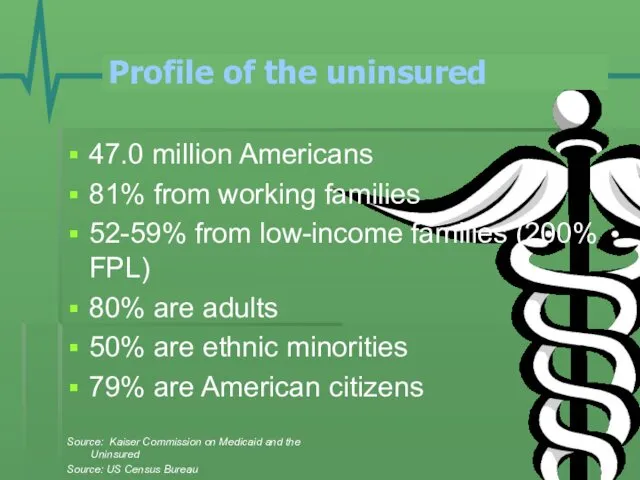
- 3. Profile of the uninsured 47.0 million Americans 81% from working families 52-59% from low-income families (200%
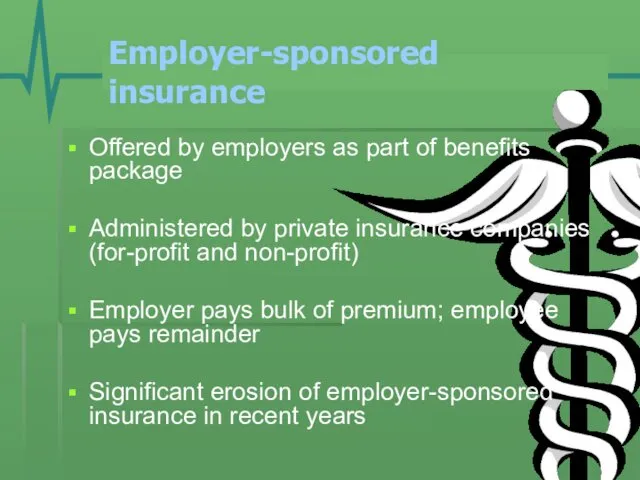
- 4. Employer-sponsored insurance Offered by employers as part of benefits package Administered by private insurance companies (for-profit
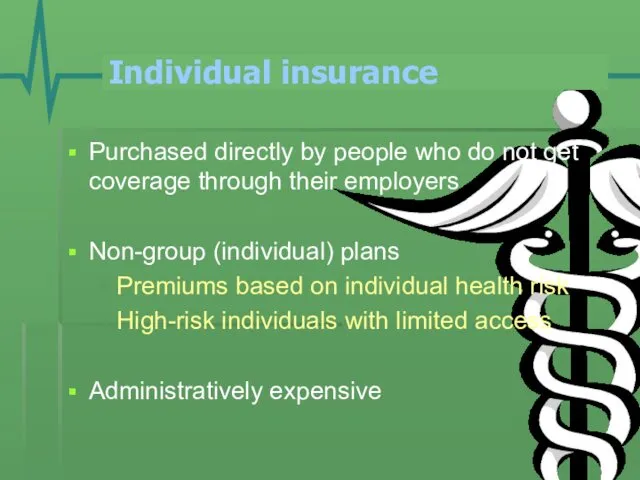
- 5. Individual insurance Purchased directly by people who do not get coverage through their employers Non-group (individual)
- 6. Medicare Covers elderly (ages 65 and older) and non-elderly with disabilities Administered by the federal government
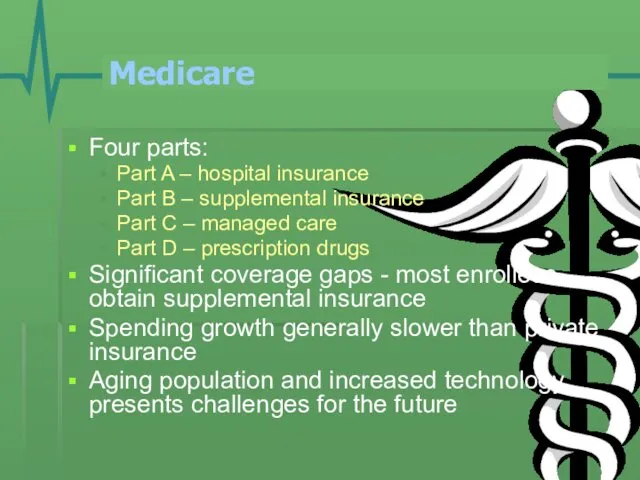
- 7. Medicare Four parts: Part A – hospital insurance Part B – supplemental insurance Part C –
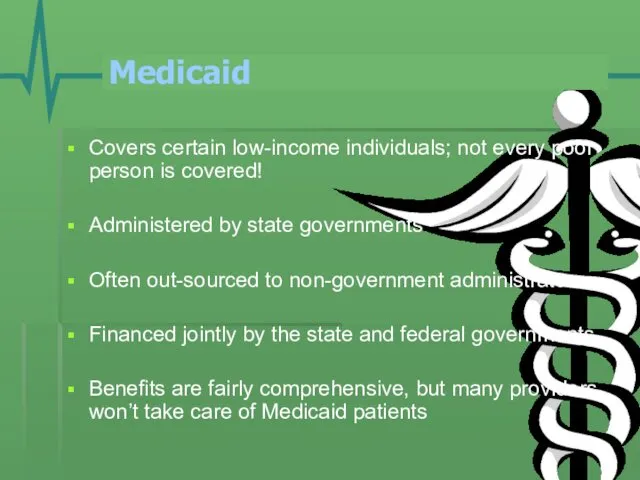
- 8. Medicaid Covers certain low-income individuals; not every poor person is covered! Administered by state governments Often
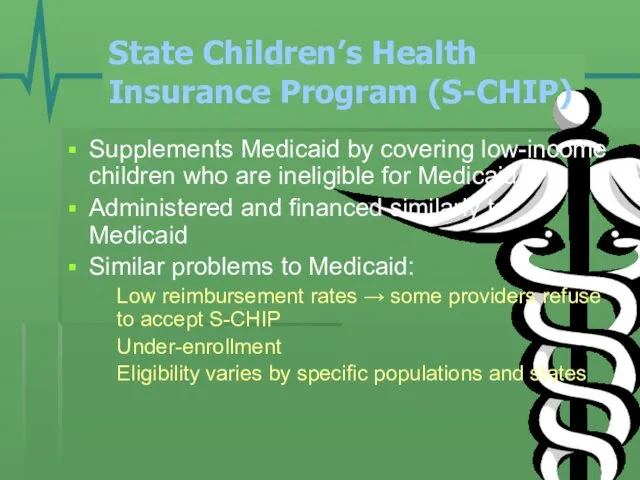
- 9. State Children’s Health Insurance Program (S-CHIP) Supplements Medicaid by covering low-income children who are ineligible for
- 10. Other public insurance programs Veterans Health Administration Health benefits plan available to all veterans Services delivered
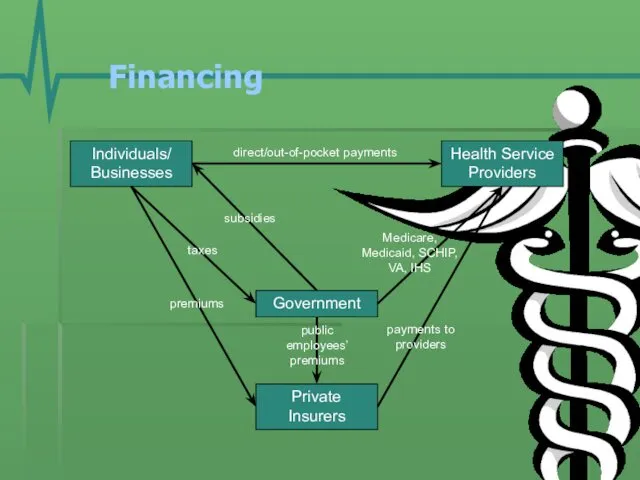
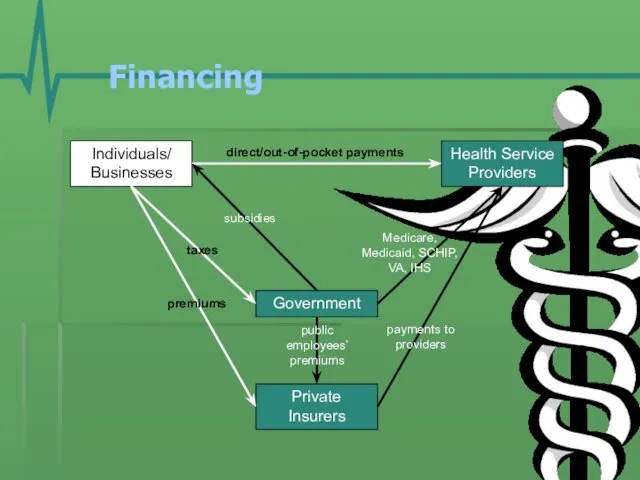
- 11. Financing Individuals/ Businesses Government Health Service Providers Private Insurers premiums taxes direct/out-of-pocket payments Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP,
- 12. Financing Individuals/ Businesses Government Health Service Providers Private Insurers premiums taxes direct/out-of-pocket payments Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP,
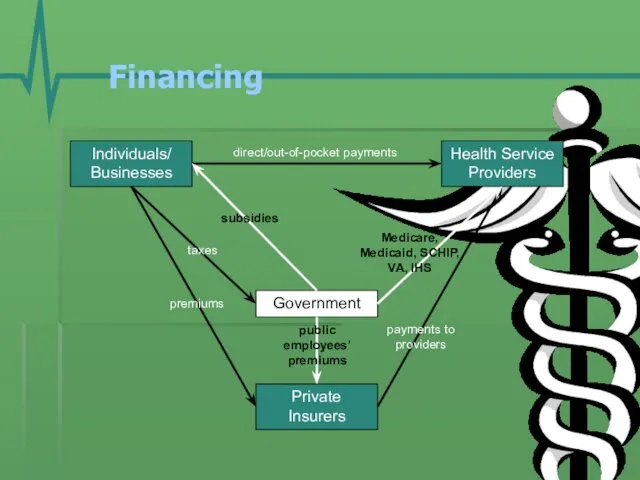
- 13. Financing Individuals/ Businesses Government Health Service Providers Private Insurers premiums taxes direct/out-of-pocket payments Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP,
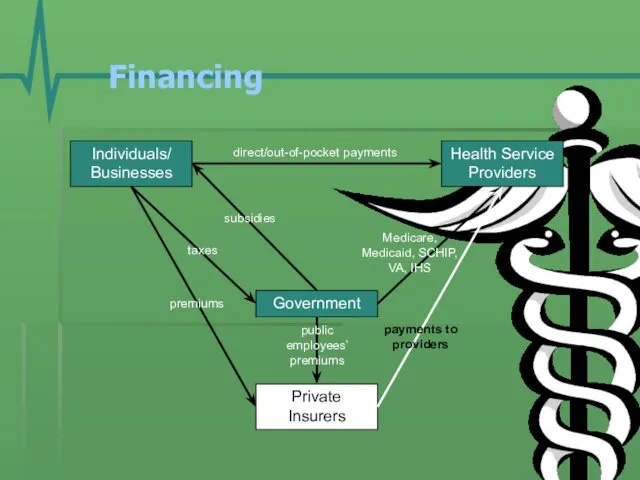
- 14. Financing Individuals/ Businesses Government Health Service Providers Private Insurers premiums taxes direct/out-of-pocket payments Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP,
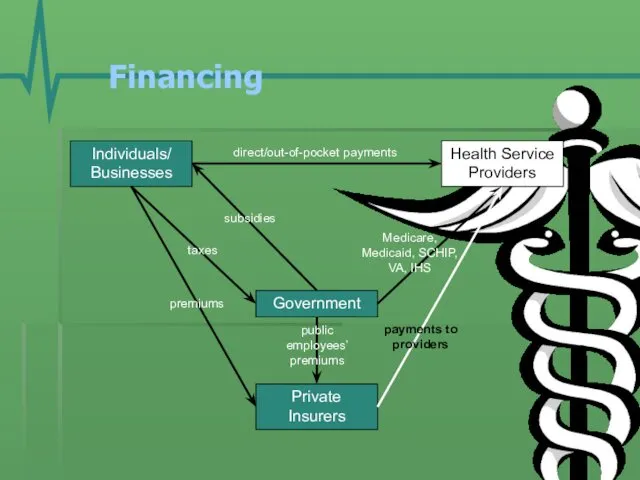
- 15. Financing Individuals/ Businesses Government Health Service Providers Private Insurers premiums taxes direct/out-of-pocket payments Medicare, Medicaid, SCHIP,
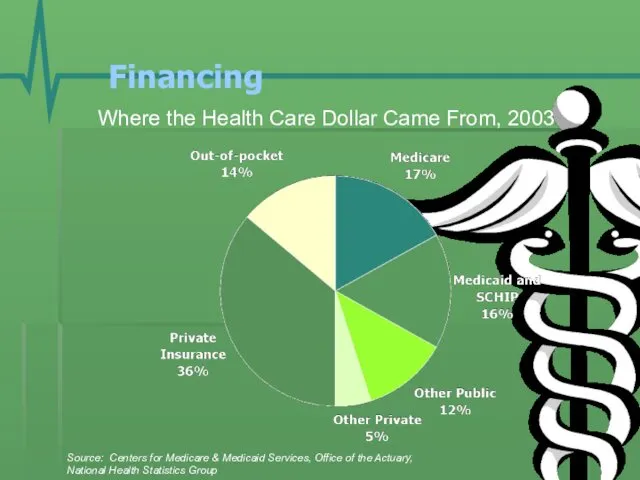
- 16. Financing Where the Health Care Dollar Came From, 2003 Source: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services,
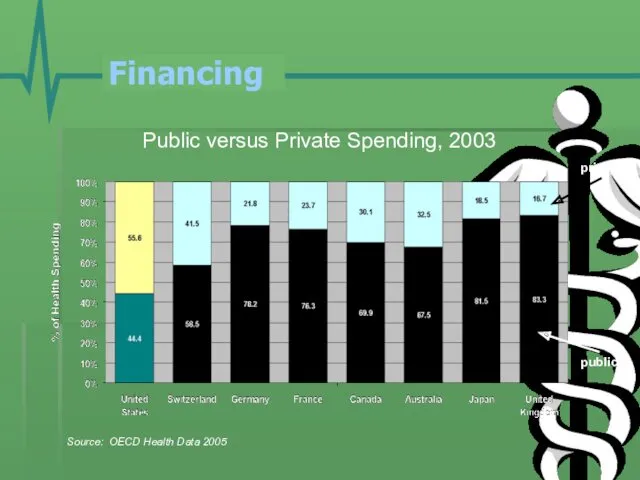
- 17. Financing Public versus Private Spending, 2003 Source: OECD Health Data 2005 public private
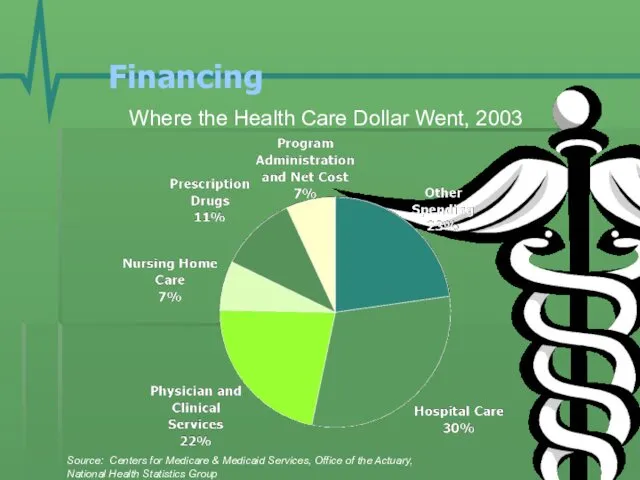
- 18. Financing Where the Health Care Dollar Went, 2003 Source: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Office
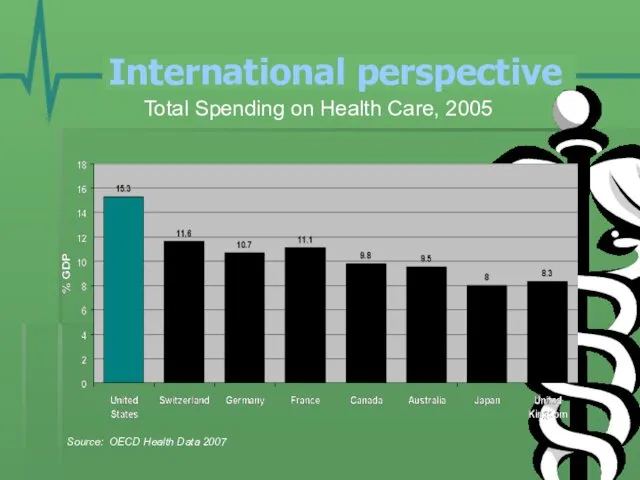
- 19. Total Spending on Health Care, 2005 Source: OECD Health Data 2007 International perspective
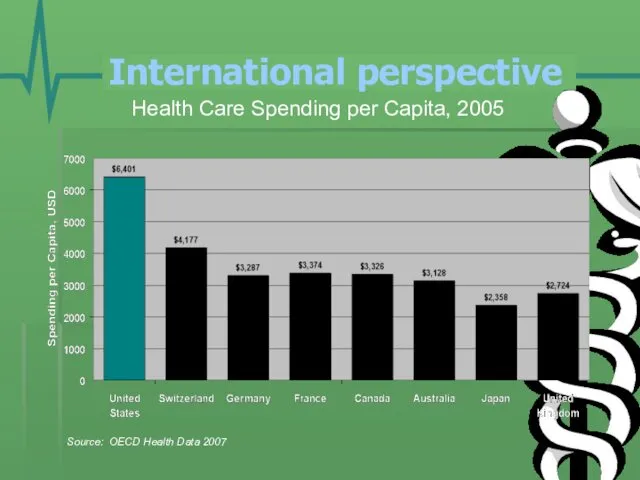
- 20. Health Care Spending per Capita, 2005 Source: OECD Health Data 2007 International perspective
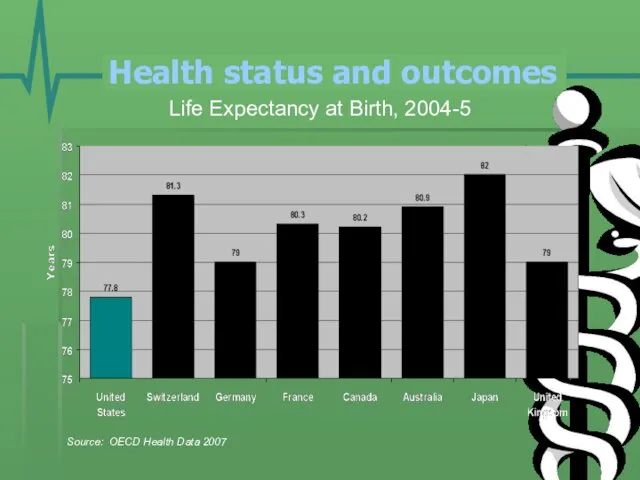
- 21. Health status and outcomes Life Expectancy at Birth, 2004-5 Source: OECD Health Data 2007
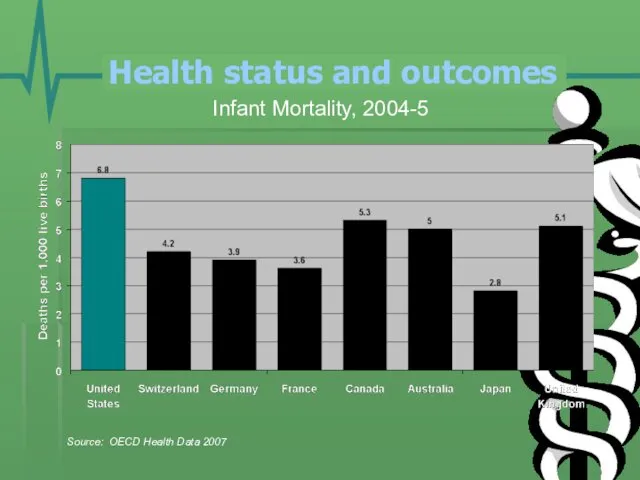
- 22. Health status and outcomes Infant Mortality, 2004-5 Source: OECD Health Data 2007
- 24. Скачать презентацию


 Вагітність та інфекційні захворювання
Вагітність та інфекційні захворювання Виды повязок
Виды повязок Репродуктивне здоров’я
Репродуктивне здоров’я Врожденные черепно - мозговые грыжи
Врожденные черепно - мозговые грыжи Секреты жизни
Секреты жизни Психологическая диагностика в геронтопсихиатрии
Психологическая диагностика в геронтопсихиатрии Медицинская терминология. Основные понятия
Медицинская терминология. Основные понятия Виллебранд ауруы. Вазопатиялар
Виллебранд ауруы. Вазопатиялар Язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки
Язвенная болезнь желудка и двенадцатиперстной кишки Антигипертензивные средства ( АГС ). Средства, применяемые при гипотонии
Антигипертензивные средства ( АГС ). Средства, применяемые при гипотонии Эстрогенді қабылдау мен әйелдердегі эндометрияның қатерлі ісігінің дамуы арасындағы байланысты анықтайтын ақпаратты табыңыз
Эстрогенді қабылдау мен әйелдердегі эндометрияның қатерлі ісігінің дамуы арасындағы байланысты анықтайтын ақпаратты табыңыз Занятие для детей по оказанию первой помощи при ИМ и МИ
Занятие для детей по оказанию первой помощи при ИМ и МИ Укусы насекомых и защита от них
Укусы насекомых и защита от них Оказание первой помощи при опасных для жизни состояниях
Оказание первой помощи при опасных для жизни состояниях Моделировочные материалы
Моделировочные материалы Соматикалық науқастардың психофизикалық қалпын клиникалық стандартын бағалау шкаласы
Соматикалық науқастардың психофизикалық қалпын клиникалық стандартын бағалау шкаласы Отбасын жоспарлау репродуктивтік денсаулық
Отбасын жоспарлау репродуктивтік денсаулық Адаптация. Срочная и долговременная адаптация
Адаптация. Срочная и долговременная адаптация Оздоровчі сили природи та гігієнічні чинники. Лекція 6
Оздоровчі сили природи та гігієнічні чинники. Лекція 6 Повреждения лучезапястного сустава
Повреждения лучезапястного сустава Средства, влияющие на органы пищеварения
Средства, влияющие на органы пищеварения Хто вони: Рослини чи Тварини?
Хто вони: Рослини чи Тварини? Вплив наушників на слух людини
Вплив наушників на слух людини 1 жасқа дейінгі балаларды табиғи тамақтандыру
1 жасқа дейінгі балаларды табиғи тамақтандыру Патология твердых тканей зуба, пульпы и периапикальных тканей зуба. Болезни пародонта
Патология твердых тканей зуба, пульпы и периапикальных тканей зуба. Болезни пародонта Гипертензия, ишемическая болезнь сердца
Гипертензия, ишемическая болезнь сердца Организация онкологической службы в России
Организация онкологической службы в России Сепсис новорождённого. Неонатальный сепсис
Сепсис новорождённого. Неонатальный сепсис