Содержание
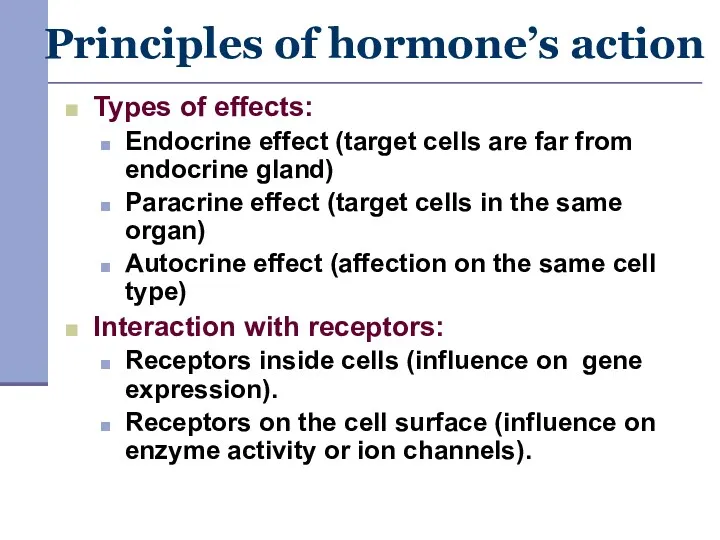
- 2. Principles of hormone’s action Types of effects: Endocrine effect (target cells are far from endocrine gland)
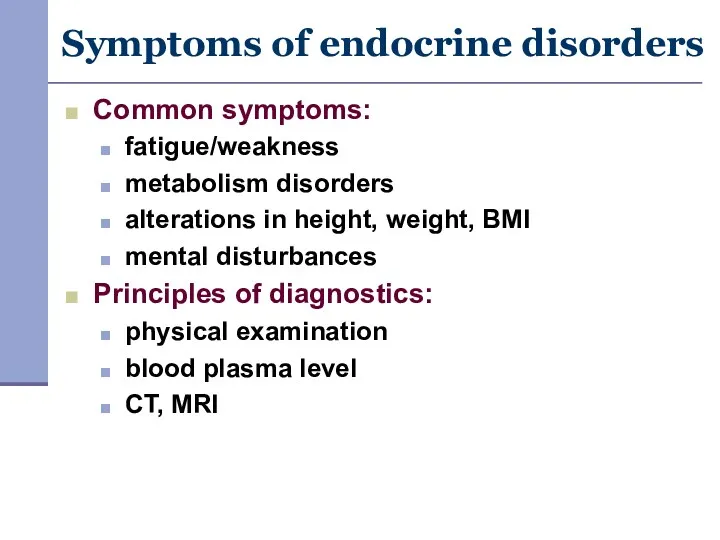
- 3. Symptoms of endocrine disorders Common symptoms: fatigue/weakness metabolism disorders alterations in height, weight, BMI mental disturbances
- 4. Endocrine Gland Hypofunction
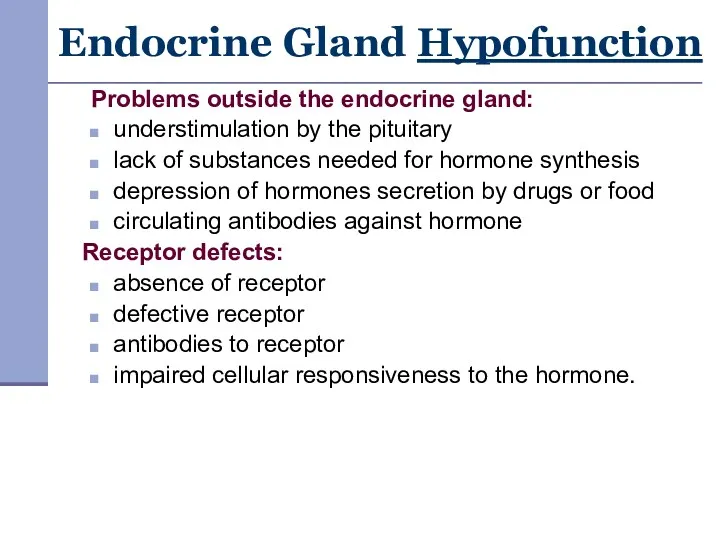
- 5. Endocrine Gland Hypofunction Problems outside the endocrine gland: understimulation by the pituitary lack of substances needed
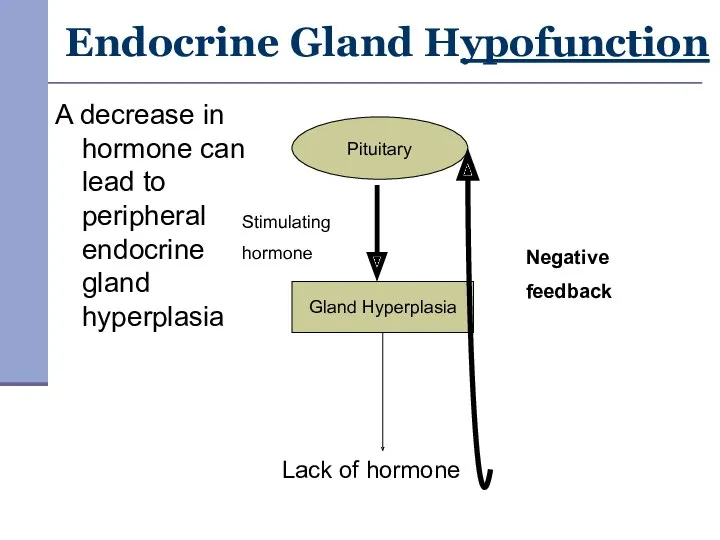
- 6. Endocrine Gland Hypofunction A decrease in hormone can lead to peripheral endocrine gland hyperplasia Pituitary Gland
- 7. Endocrine Gland Hyperfunction Causes of increased hormone level: overstimulation by the pituitary hyperplasia or neoplasia of
- 8. General principles of therapy Hypofunction: replacement of the hormone ? hormone resistance. Hyperfunction: radiation therapy surgery
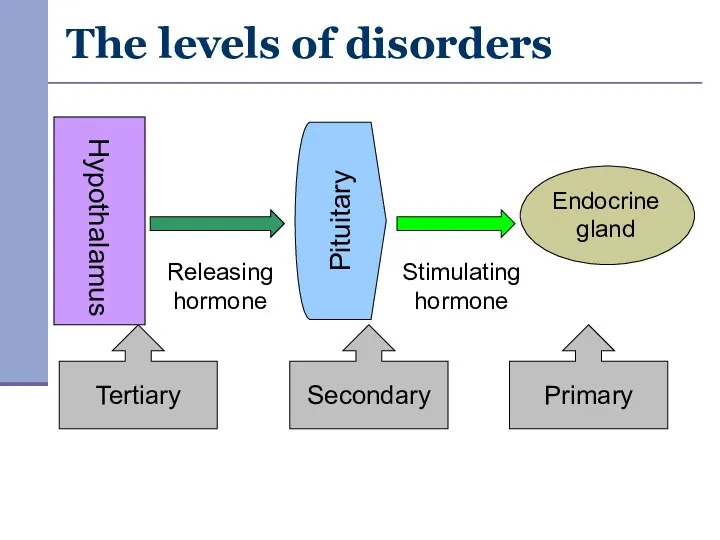
- 9. The levels of disorders
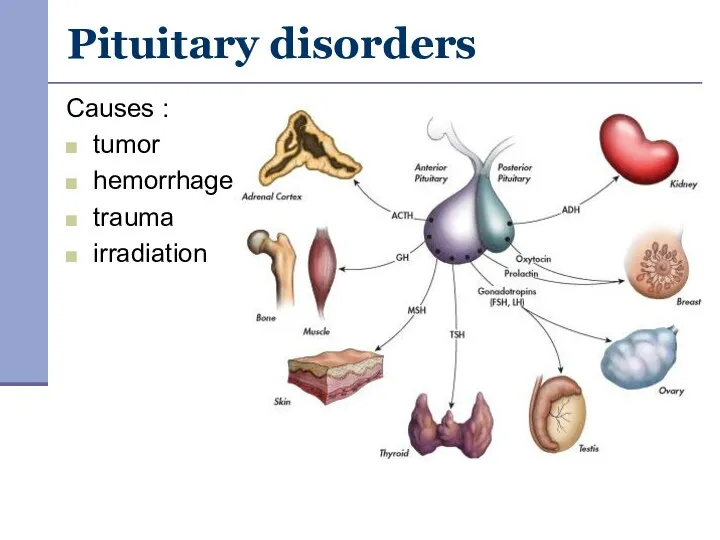
- 10. Pituitary disorders Causes : tumor hemorrhage trauma irradiation
- 11. Pituitary disorders Growth hormone deficiency children - short stature (pituitary dwarfism), normal intelligence, obesity adults -
- 12. Pituitary disorders Excess of GH in childhood Pituitary gigantism ? growth velocity proportional enlargement of skeleton
- 13. Pituitary disorders Excess of GH in adults Acromegaly reason –somatotrope adenoma hyperplasia and hypertrophy of soft
- 14. Pituitary disorders GH excess – Metabolic disturbances ? GH and IGF-1. ?synthesis of lipids in adipocytes,
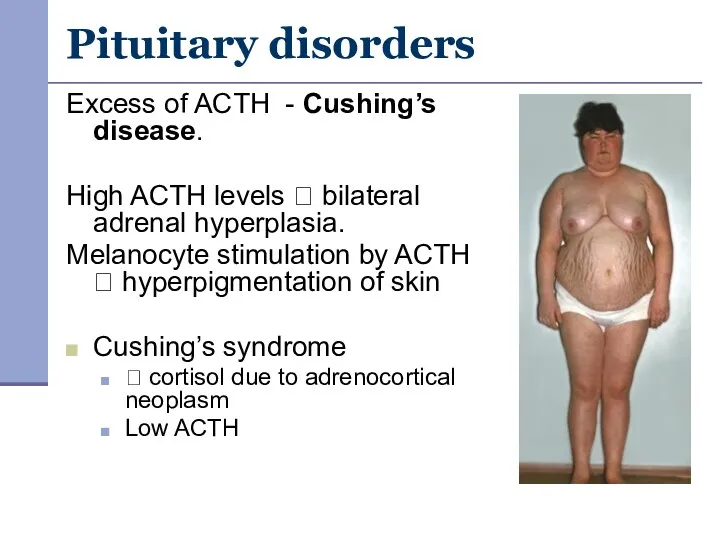
- 15. Pituitary disorders Excess of ACTH - Cushing’s disease. High ACTH levels ? bilateral adrenal hyperplasia. Melanocyte
- 16. Cushing disease/syndrome Clinical manifestation: "moon" face and "buffalo hump“. muscle wasting and weakness - due to
- 17. Cushing disease/syndrome Hypertension – due to water and salt retention, ? vessels tone. Osteoporosis – ?
- 18. Pituitary disorders Lack of ADH - Diabetes insipidus - polyuria, polydipsia, dehydration. Central Diabetes insipidus –
- 19. Thyroid disorders Thyroid Hormone Action: adequate fetal growth development of neural and skeletal systems. regulation of
- 20. Thyroid disorders Goiter - ? size of the thyroid gland. (not related of TH level) Complications
- 21. Thyroid disorders Congenital hypothyroidism - cretinism Causes congenital absence of the thyroid gland abnormal biosynthesis of
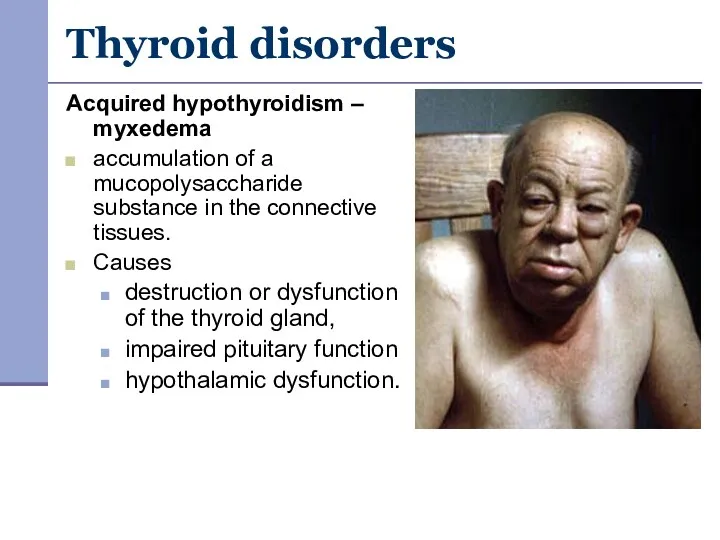
- 22. Thyroid disorders Acquired hypothyroidism – myxedema accumulation of a mucopolysaccharide substance in the connective tissues. Causes
- 23. Thyroid disorders hypometabolic state weakness and fatigue, tendency to gain weight, cold intolerance, decreased GIT motility,
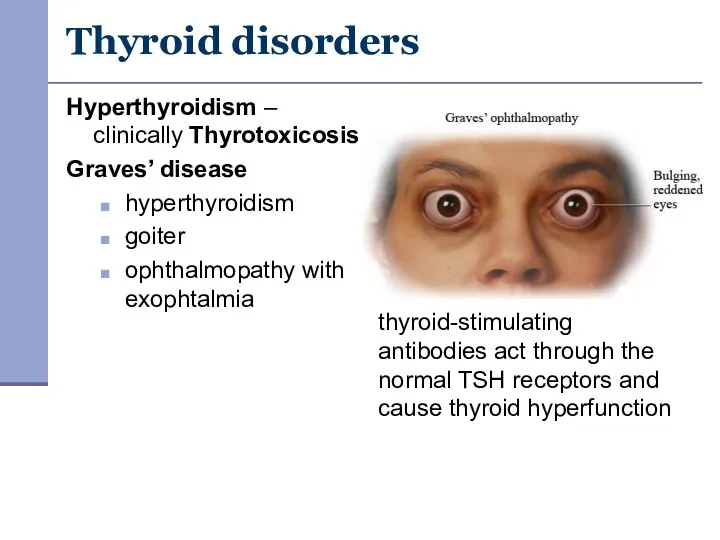
- 24. Thyroid disorders Hyperthyroidism – clinically Thyrotoxicosis Graves’ disease hyperthyroidism goiter ophthalmopathy with exophtalmia thyroid-stimulating antibodies act
- 25. Thyroid disorders Clinical manifestation: ? BMR and heat production, heat intolerance prevailing of sympathetic influences warm
- 26. Thyroid disorders Clinical manifestation: tachycardia, ? of stroke volume hypertension, widening of the pulse pressure heart
- 27. Parathyroid disorders Hypoparathyroidism reasons surgical removal of the gland autoimmune destruction Di George's syndrome Low calcium,
- 28. Parathyroid disorders Hyperparathyroidism Causes : Primary (adenoma) Secondary Chronic renal insufficiency Vitamin D deficiency; Intestinal malabsorption;
- 29. Hyperparathyroidism Clinical manifestations: osteodystrophy, osteomalacia disturbances of excititation in nervous system and muscles kidney stones metastatic
- 30. Pathology of adrenal gland Hypofunction of adrenal cortex (cortisol, aldosterone, androgen). Primary adrenal hypofunction - ADDISON'S
- 31. Hypofunction of adrenal cortex Aldosterone deficiency ? excretion of Na and ? excretion of K, low
- 32. Addison's disease clinical manifestation Weakness, fatigue Increased pigmentation GIT: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea Hypometabolism Heart activity
- 33. Acute adrenal failure – Adrenal crisis Causes: trauma, hemorrhage (overdose of heparine, acute or fulminant sepsis)
- 34. Hypofunction of adrenal cortex Secondary hypofunction - due to a lack of ACTH. Causes: destruction of
- 35. Hyperfunction of adrenal cortex Causes congenital adrenal hyperplasia, acquired hyperplasia, adenomas, or adenocarcinomas. ADRENAL VIRILISM (Adrenogenital
- 36. Hyperaldosteronism Primary HyperAldosteronism - Conn's Syndrome Cause: tumor of the adrenal cortex or benign adrenal hyperplasia.
- 38. Скачать презентацию






















 Алфлутоп - здоровье суставов в надежных руках
Алфлутоп - здоровье суставов в надежных руках Нейропсихологическая классификация. Критерии выделения форм афазии
Нейропсихологическая классификация. Критерии выделения форм афазии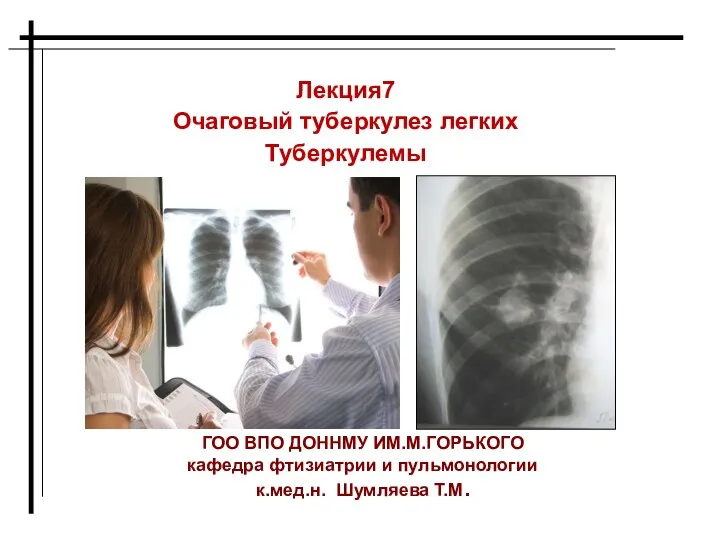 Очаговый туберкулез легких. Туберкулемы. Лекция 7
Очаговый туберкулез легких. Туберкулемы. Лекция 7 Листериоз - Listeria monocytoqenes қоздыратын
Листериоз - Listeria monocytoqenes қоздыратын Анатомо-физиологические особенности подросткового возраста
Анатомо-физиологические особенности подросткового возраста Ложные суставы
Ложные суставы Электрокинетические явления. Коагуляция. Способы очистки коллоидных растворов. Промышленная очистка воды. (Лекция 10)
Электрокинетические явления. Коагуляция. Способы очистки коллоидных растворов. Промышленная очистка воды. (Лекция 10) Инфекциялық иммунология негіздері. Иммунитет түрлері және формалары. Организмнің бейспецификалық қорғаныс
Инфекциялық иммунология негіздері. Иммунитет түрлері және формалары. Организмнің бейспецификалық қорғаныс Туберкулезге қарсы препараттар, фармакокинетикасы, фармакодинамикасы, жанама әсерлері және оларды жою
Туберкулезге қарсы препараттар, фармакокинетикасы, фармакодинамикасы, жанама әсерлері және оларды жою Фермент. Ферменттерді ауруларды диагностикалауға және емдеуге қолдану
Фермент. Ферменттерді ауруларды диагностикалауға және емдеуге қолдану Организм человека и его здоровье ЕГЭ по биологии 2016 год
Организм человека и его здоровье ЕГЭ по биологии 2016 год Диспансеризация. Снижение гинекологических заболевании
Диспансеризация. Снижение гинекологических заболевании Өкпе абцессі
Өкпе абцессі Система автоматизированного анализа степени радиационного поражения человека
Система автоматизированного анализа степени радиационного поражения человека Fruits comment les consommer
Fruits comment les consommer Хирургическое лечение неспецифического язвенного колита и болезни Крона. Неспецифический язвенный колит
Хирургическое лечение неспецифического язвенного колита и болезни Крона. Неспецифический язвенный колит Основы медицинской протозоологии. Тип простейшие. Представители классов споровики и инфузории
Основы медицинской протозоологии. Тип простейшие. Представители классов споровики и инфузории Қызылорда қаласы бойынша №3 қалалық емханада мектепке дейінгі балалардағы вакцина профилактиканы ұйымдастырудағы медбикенің рөлі
Қызылорда қаласы бойынша №3 қалалық емханада мектепке дейінгі балалардағы вакцина профилактиканы ұйымдастырудағы медбикенің рөлі Повреждение и гибель клеток и тканей: причины, механизмы, виды необратимого повреждения. Некроз. Апоптоз
Повреждение и гибель клеток и тканей: причины, механизмы, виды необратимого повреждения. Некроз. Апоптоз Дыхательная гимнастика
Дыхательная гимнастика Pneumonia. Currently, several types of pneumonia are distinguished
Pneumonia. Currently, several types of pneumonia are distinguished Қоғамдық денсаулық ғылым және оқыту пәні ретінде
Қоғамдық денсаулық ғылым және оқыту пәні ретінде Blood pressure. Measurement
Blood pressure. Measurement Әртүрлі жүйедегі бекітілістерді қолдана отырып алмалы конструкцияларды әзірлеу технологиясы
Әртүрлі жүйедегі бекітілістерді қолдана отырып алмалы конструкцияларды әзірлеу технологиясы Кизилунгач, ошкозон – ичак касалликлари
Кизилунгач, ошкозон – ичак касалликлари Основы эпидемиологии. (Лекция 5)
Основы эпидемиологии. (Лекция 5) Нарушения мышления: расстройства ассоциативного процесса. Патология суждений и умозаключений
Нарушения мышления: расстройства ассоциативного процесса. Патология суждений и умозаключений Економіка охорони здоров'я як наука і практика. Ціноутворення медичних послуг у стоматології
Економіка охорони здоров'я як наука і практика. Ціноутворення медичних послуг у стоматології