Содержание
- 2. Despite the achievements of modern medicine and the emergence of new effective antibacterial drugs, pneumonia is
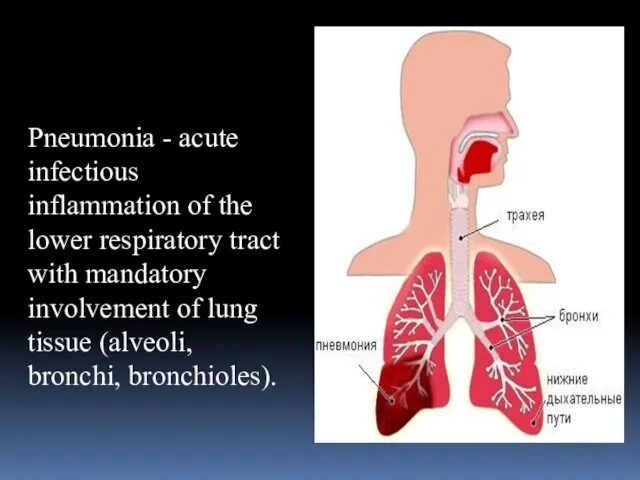
- 3. Pneumonia - acute infectious inflammation of the lower respiratory tract with mandatory involvement of lung tissue
- 4. 1) Community-acquired pneumonia is the most common type of disease. 2) Nosocomial or hospital pneumonia. This
- 6. CAUSES OF PNEUMONIA Pneumonia is, above all, a bacterial disease The main pathogens of pneumonia: pneumococcus
- 7. Пусковым фактором развития пневмонии могут быть различные вирусные инфекции. Они вызывают воспаление верхних дыхательных путей и
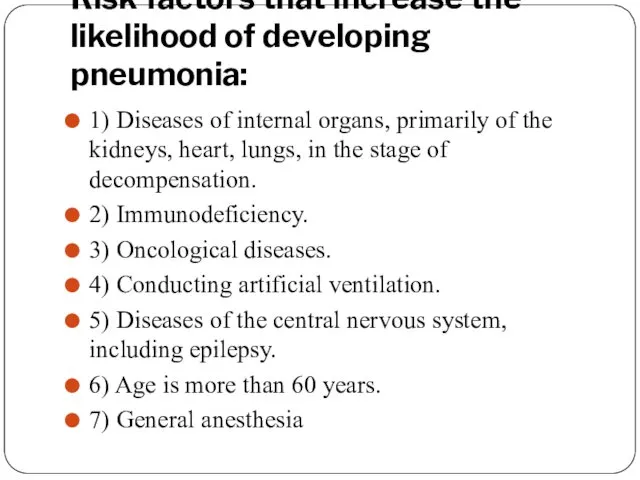
- 8. Risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing pneumonia: 1) Diseases of internal organs, primarily of
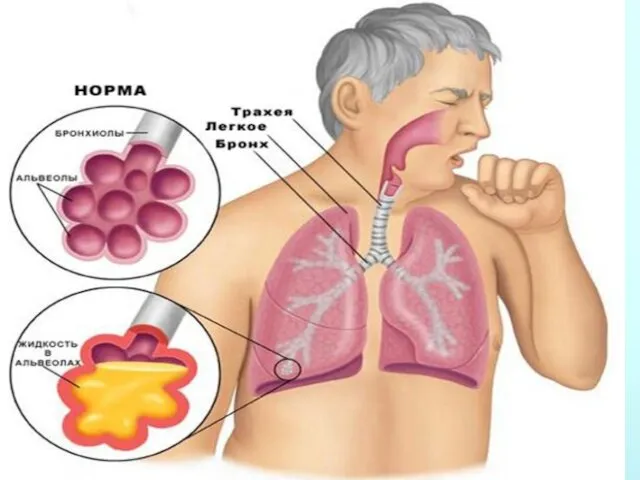
- 9. The main symptoms of pneumonia are fever with a rise in temperature to 38-39.5 degrees C,
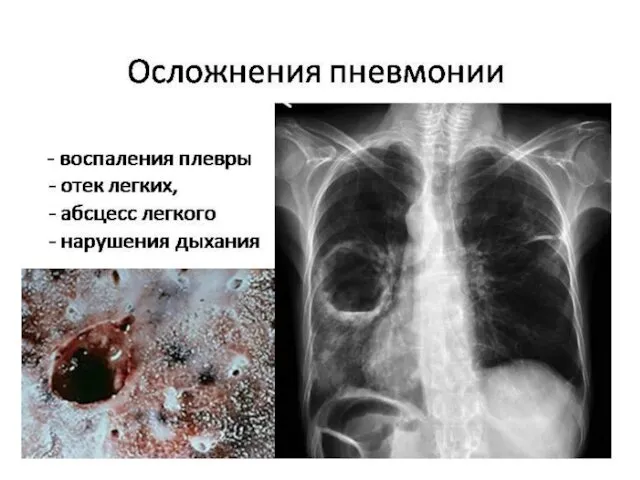
- 10. Возможные осложнения пневмонии и прогноз Пневмония может привести к развитию целого ряда осложнений со стороны легких:
- 11. What tests should I take if I suspect a pneumonia If you suspect a pneumonia and
- 12. Indispensable for the formulation of an accurate diagnosis of pneumonia is the chest X-ray. It is
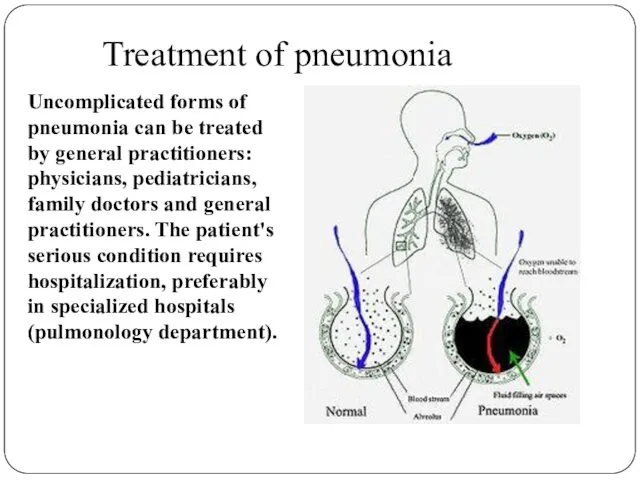
- 14. Treatment of pneumonia Uncomplicated forms of pneumonia can be treated by general practitioners: physicians, pediatricians, family
- 15. Indications for hospitalization for pneumonia: 1) Objective examination data: impairment of consciousness, respiratory rate more than
- 16. Доказано эффективной мерой профилактики заболеваний легких, в том числе пневмонии, является отказ от курения. Часто пневмония
- 17. FEATURES OF NUTRITION AND LIFESTYLE FOR THE TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF PNEUMONIA The regime is bed,
- 18. Пайдаланылған әдебиеттер: www.google.com Учебник английского языка: A.M. Maslova Z.I. Winestein L.S. Plebeyskay
- 20. Скачать презентацию










 Пневмококковая иммунопрофилактика
Пневмококковая иммунопрофилактика Щитовидная железа Комарова С.А.2022
Щитовидная железа Комарова С.А.2022 Инфекционный эндокардит
Инфекционный эндокардит Патология почек
Патология почек Оториноларингология. Заболевания глотки
Оториноларингология. Заболевания глотки Заболевания молочной железы
Заболевания молочной железы Артериальная гипертензия у беременных
Артериальная гипертензия у беременных Дети с ограниченными возможностями здоровья, причины их возникновения
Дети с ограниченными возможностями здоровья, причины их возникновения Профилактика ОРВИ и гриппа
Профилактика ОРВИ и гриппа Өкпенің инфильтратты туберкулезі
Өкпенің инфильтратты туберкулезі Основные стандарты клинических исследований. Принципы надлежащей клинической практика (GCP). Словарь основных терминов
Основные стандарты клинических исследований. Принципы надлежащей клинической практика (GCP). Словарь основных терминов PRISCA - биохимический скрининг хромосомной патологии плода
PRISCA - биохимический скрининг хромосомной патологии плода Основы лечения боли
Основы лечения боли Гонорея. Возбудитель гонореи
Гонорея. Возбудитель гонореи Общая фармакология
Общая фармакология Воспалительные заболевания вспомогательных органов глаза и орбиты
Воспалительные заболевания вспомогательных органов глаза и орбиты Клещевой энцефалит
Клещевой энцефалит Недостаточность кровообращения
Недостаточность кровообращения Сифилис
Сифилис Жаңа туған нәрестелердегі сарғаю
Жаңа туған нәрестелердегі сарғаю Травматизм. Первичная и вторичная профилактика. Первая помощь при травмах
Травматизм. Первичная и вторичная профилактика. Первая помощь при травмах Захворювання органів травлення у дітей старшого віку. Лекція №7
Захворювання органів травлення у дітей старшого віку. Лекція №7 Нейропсихология развития в раннем детстве и дошкольном возрасте (лекция 3)
Нейропсихология развития в раннем детстве и дошкольном возрасте (лекция 3) Острый панкреатит
Острый панкреатит Рак предстательной железы
Рак предстательной железы Оценка функционального состояния
Оценка функционального состояния Диагностика и лечение аритмий (А) и блокад (Б) сердца
Диагностика и лечение аритмий (А) и блокад (Б) сердца Эндокриндік жүйе аурулары
Эндокриндік жүйе аурулары