Содержание
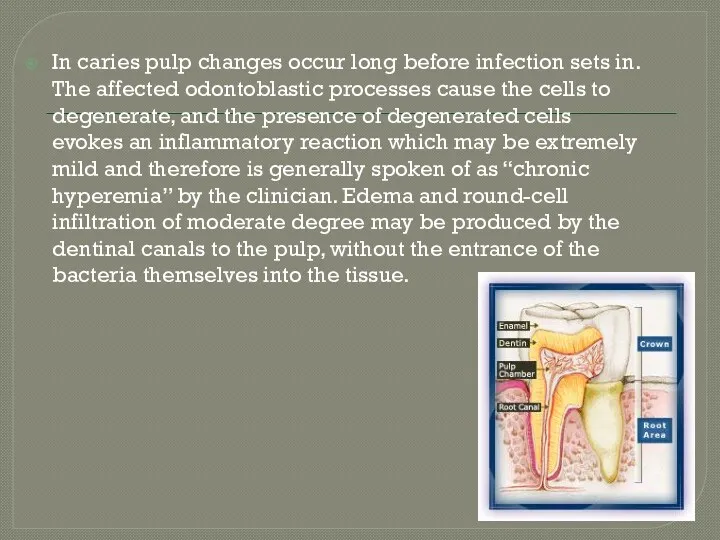
- 2. In caries pulp changes occur long before infection sets in. The affected odontoblastic processes cause the
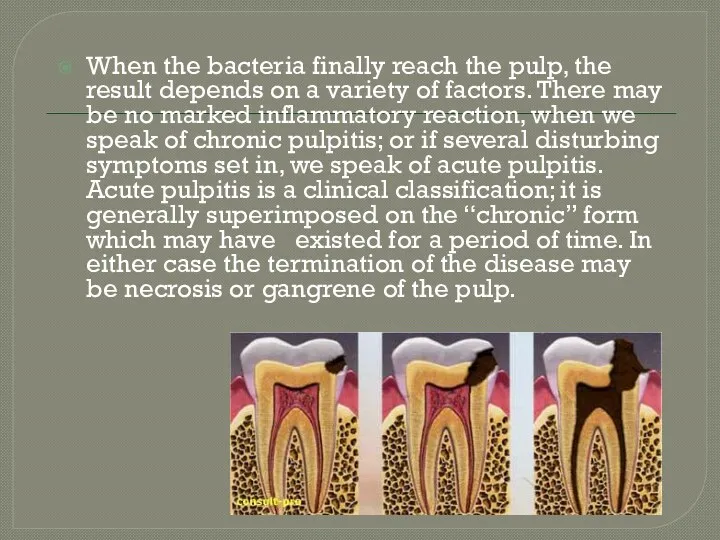
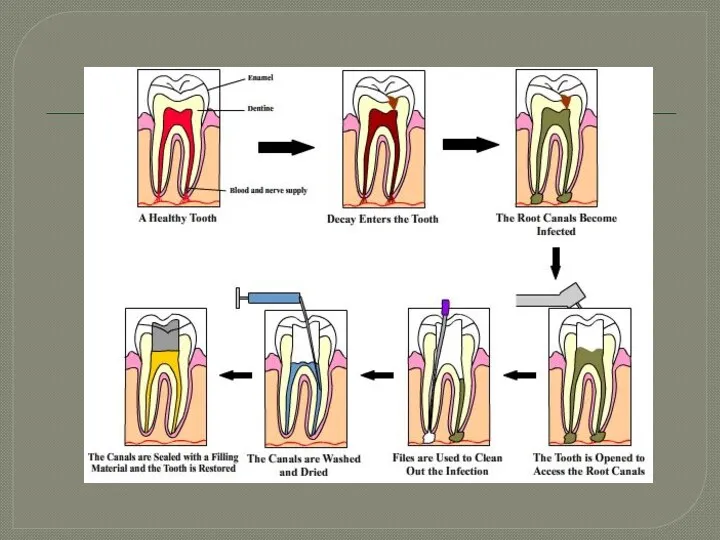
- 3. When the bacteria finally reach the pulp, the result depends on a variety of factors. There
- 4. Chronic Pulpitis Chronic pulpitis is a response to a mild injurious agent, such as bacterial toxins
- 6. Chronic pulpitis in most cases requires pulp extirpation, or, if the infection has gone beyond the
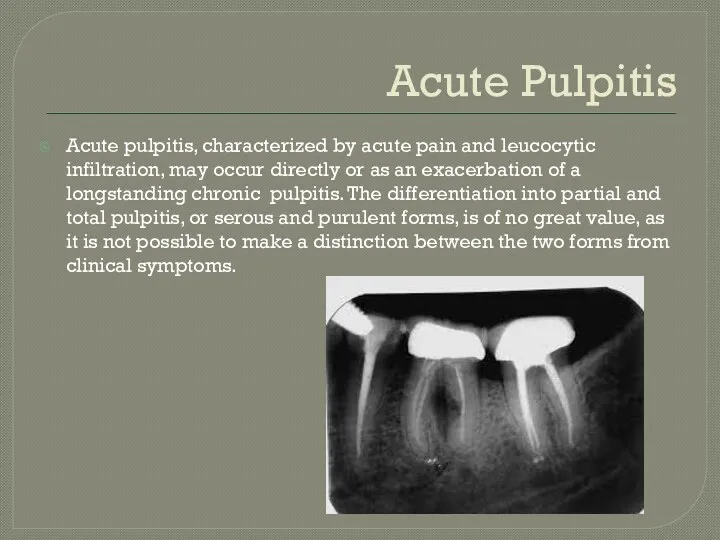
- 7. Acute Pulpitis Acute pulpitis, characterized by acute pain and leucocytic infiltration, may occur directly or as
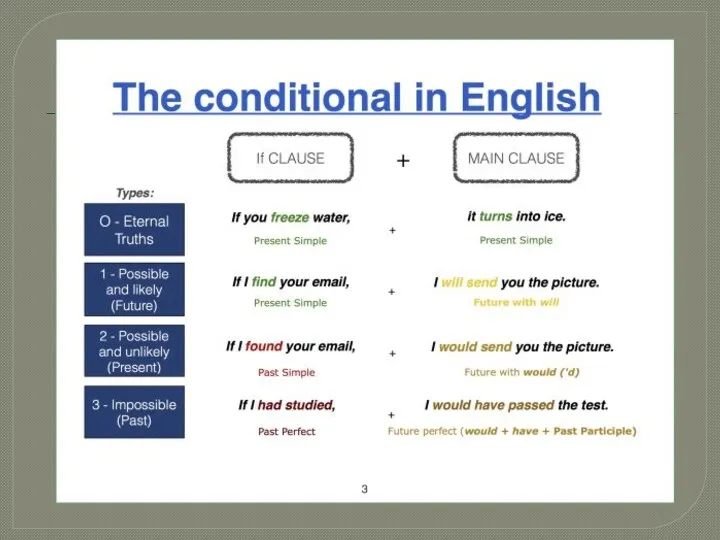
- 8. Conditional sentences Условными предложениями называются сложноподчиненные предложения, в которых в придаточном предложении называется условие, а в
- 10. Тип I-(а) - реальные события (Придаточное – Present Indefinite; Главное – Future Indefinite.). If I have
- 11. . If I should have a lot of money, I will buy a car. Если вдруг
- 12. Тип II - почти нереальные события (Придаточное – Subjunctive I (Past Subjunctive); Главное – Subjunctive II-1
- 13. Тип III - абсолютно нереальные события (Придаточное – Subjunctive I (Past Perfect Subjunctive); Главное – Subjunctive
- 15. Скачать презентацию







 Синдром болей в левой половине грудной клетки. ИБС в практике терапевта поликлиники
Синдром болей в левой половине грудной клетки. ИБС в практике терапевта поликлиники Жүкті әйелдердегі эндокриндік жүйе.Қант диабеті
Жүкті әйелдердегі эндокриндік жүйе.Қант диабеті Правильная осанка – залог здоровья
Правильная осанка – залог здоровья Мүгедектерге көрсетілетін әлеуметтік көмек түрлері
Мүгедектерге көрсетілетін әлеуметтік көмек түрлері Туберкулездің алдын алу. Туберкулездің алдын алу туралы тұрғындар арасындағы санитарлы - ағарту жұмысы
Туберкулездің алдын алу. Туберкулездің алдын алу туралы тұрғындар арасындағы санитарлы - ағарту жұмысы Грыжи пищеводного отверстия диафрагмы
Грыжи пищеводного отверстия диафрагмы Патологическая стираемость генерализованного типа
Патологическая стираемость генерализованного типа Синдром уплотнения легочной ткани
Синдром уплотнения легочной ткани Malignant Melanoma
Malignant Melanoma Нарушение зрения. Дефицитарное развитие
Нарушение зрения. Дефицитарное развитие Острые аллергические состояния у детей
Острые аллергические состояния у детей Вирусные инфекции. Задачи
Вирусные инфекции. Задачи Нарушение ритма сердца. Экстренная медицинская помощь. Показания для госпитализации
Нарушение ритма сердца. Экстренная медицинская помощь. Показания для госпитализации Взаимодействие лекарственных средств. Фармакологическая несовместимость
Взаимодействие лекарственных средств. Фармакологическая несовместимость Абдоминальный болевой синдром
Абдоминальный болевой синдром Новообразования дизонтогенетической природы у детей
Новообразования дизонтогенетической природы у детей Хронический бескаменный холецистит
Хронический бескаменный холецистит Методика расчета парентерального питания у новорожденных
Методика расчета парентерального питания у новорожденных Сестринский уход при травмах органов зрения
Сестринский уход при травмах органов зрения Рассеянный склероз
Рассеянный склероз Инфузионная терапия в детской инфекционной патологии
Инфузионная терапия в детской инфекционной патологии Home Remedy - Ayurveda
Home Remedy - Ayurveda Роль медицинской сестры в реабилитации ишемического инсульта
Роль медицинской сестры в реабилитации ишемического инсульта Тұқым қуалаушылық жүйке-бұлшықет аурулары
Тұқым қуалаушылық жүйке-бұлшықет аурулары Рак кожи
Рак кожи Строение сердца
Строение сердца Туберкулез внутригрудных лимфатических узлов
Туберкулез внутригрудных лимфатических узлов Оздоровительные технологии, психологические и медико-биологические проблемы физической культуры и спорта
Оздоровительные технологии, психологические и медико-биологические проблемы физической культуры и спорта