Содержание
- 2. “DISTANCE” A mnemonic recently introduced Simplify reporting rectal cancer staging MRI
- 3. Overview MR imaging sequences The report for MR rectal cancer staging and “DISTANCE” Primary rectal cancer
- 4. We have come such a long way… CT tomogram from the 1980’s Courtesy Dr. Stephen Esler
- 5. The radiologist plays a central role in the multidisciplinary approach to rectal cancer MRI can accurately
- 6. Technique and sequences No need for bowel preparation, filling of rectum with contrast/air Antispasmodic agents can
- 7. Additional sequences to consider: DWI T2 fat sat T1
- 8. Austin protocol: Three Plane Localiser Coronal T2 3D SPACE Whole Pelvis Axial T1 Whole Pelvis Axial
- 9. Overview MR imaging sequences The report for MR rectal cancer staging and “DISTANCE” Primary rectal cancer
- 10. 4 critical questions need to be answered Location of the tumor (high, middle, low) (you can
- 11. Other things that need to go in the report: Tumor length, tumor description/morphology (polypoid, ulcerative etc.)
- 12. Pedersen et al. reported in 2011 that the report quality overall could be significantly improved There
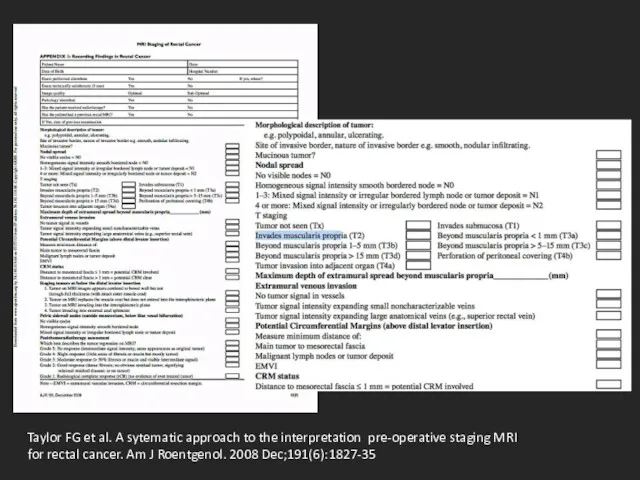
- 13. Taylor FG et al. A sytematic approach to the interpretation pre-operative staging MRI for rectal cancer.
- 14. DIS – distance from inferior part of tumor to transitional skin T – T-staging A -
- 15. Overview MR imaging sequences The report for MR rectal cancer staging and “DISTANCE” Primary rectal cancer
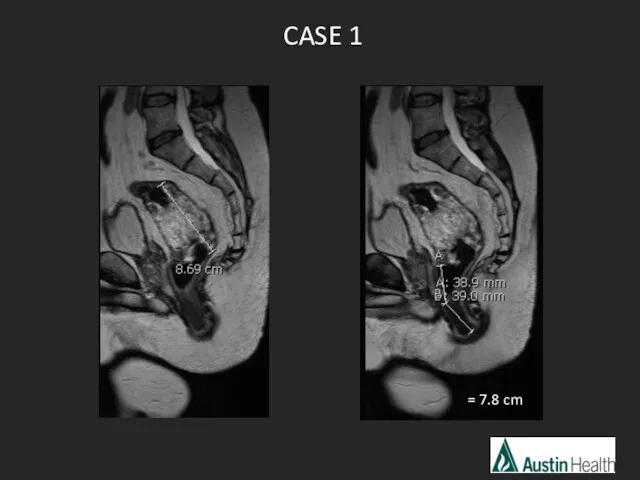
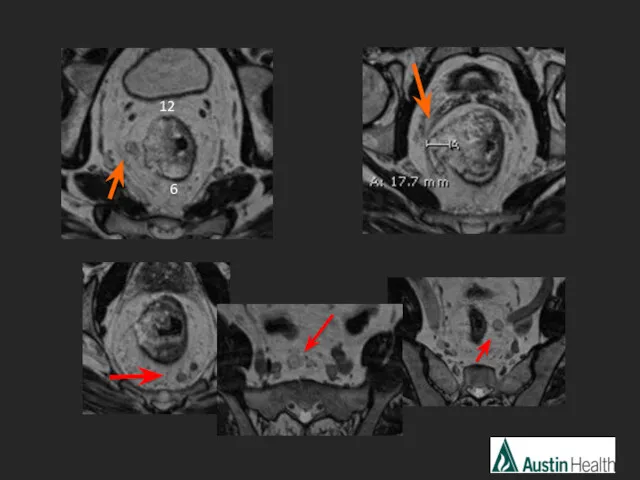
- 16. CASE 1 = 7.8 cm
- 17. 12 6
- 18. Report conclusion: T3 N2 mid rectal tumour with a length of approximately 8.6 cm which reaches
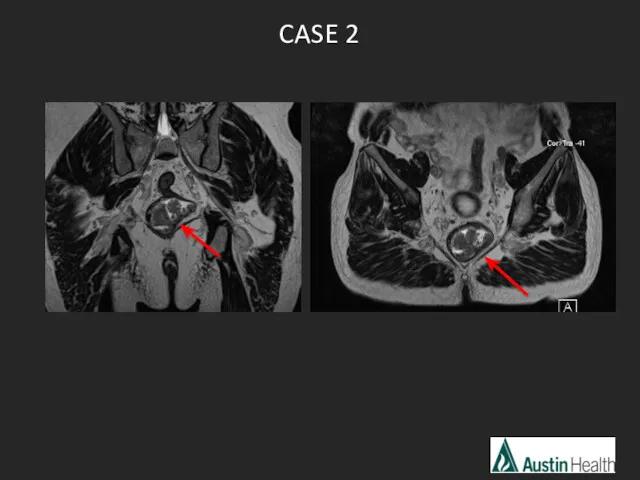
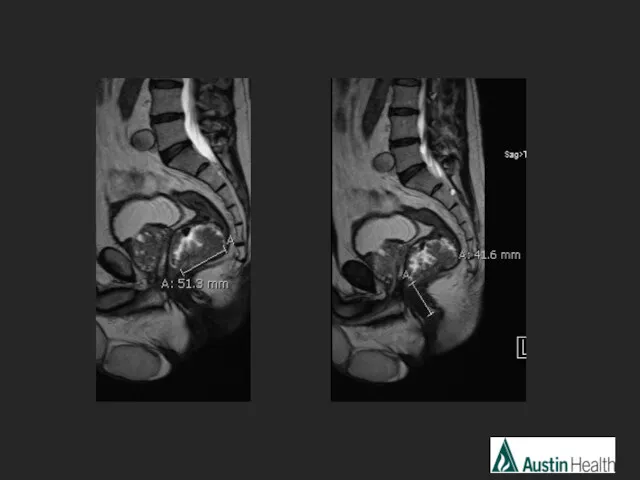
- 19. CASE 2
- 21. Report conclusion: T2 N0 low rectal tumour with a length of 5.1 cm and reaches approximately
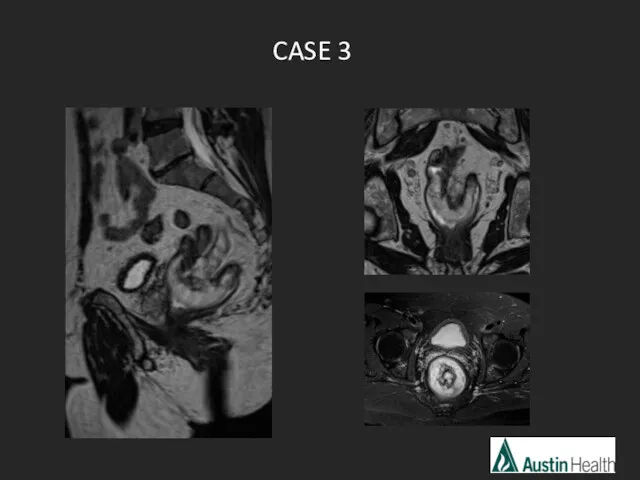
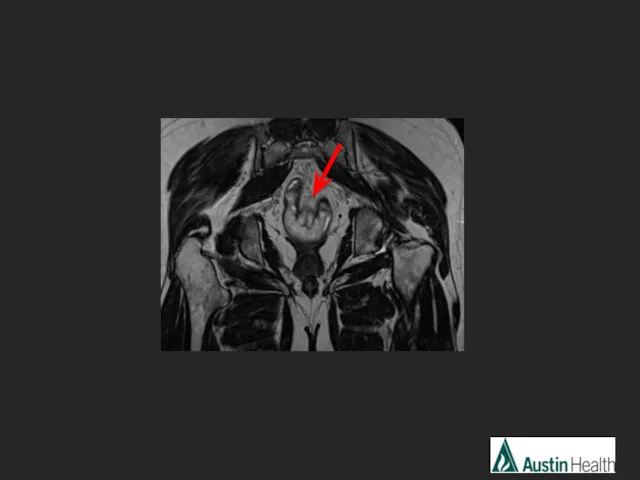
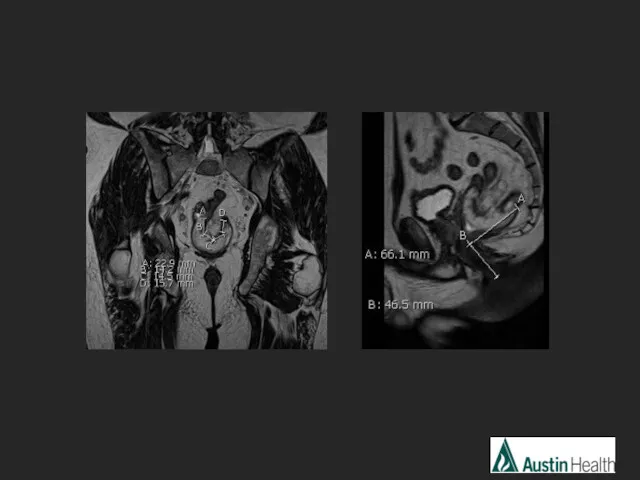
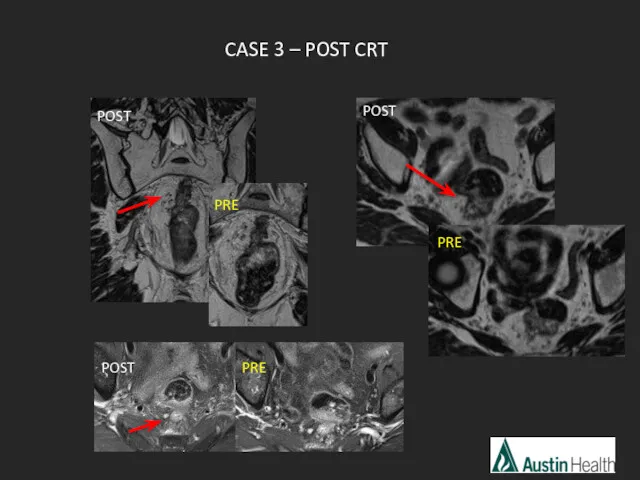
- 22. CASE 3
- 25. Report conclusion: T3 N1 mid rectal tumour with a length of 6.7 cm with a distance
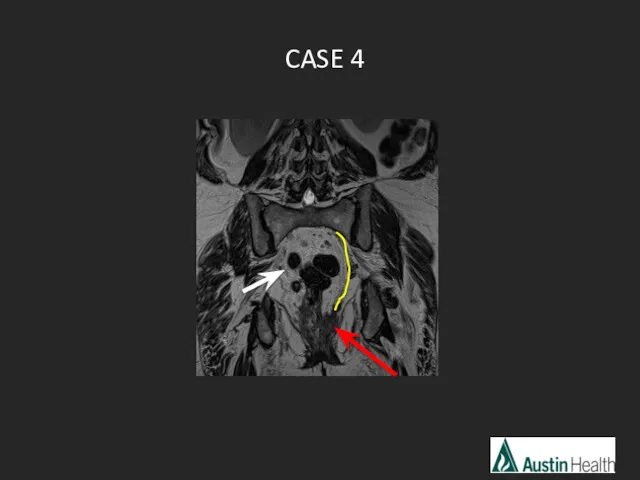
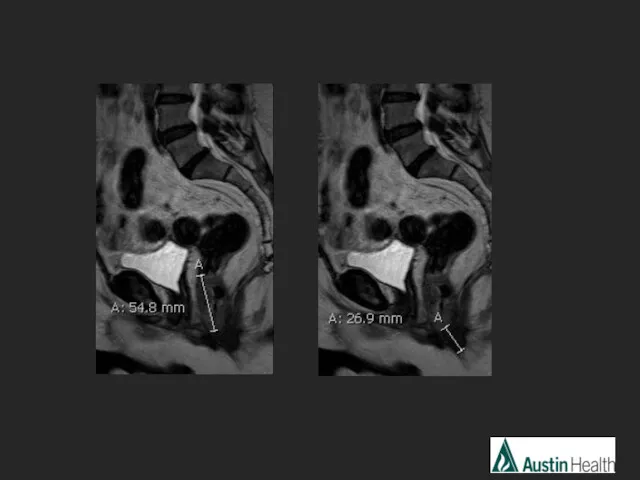
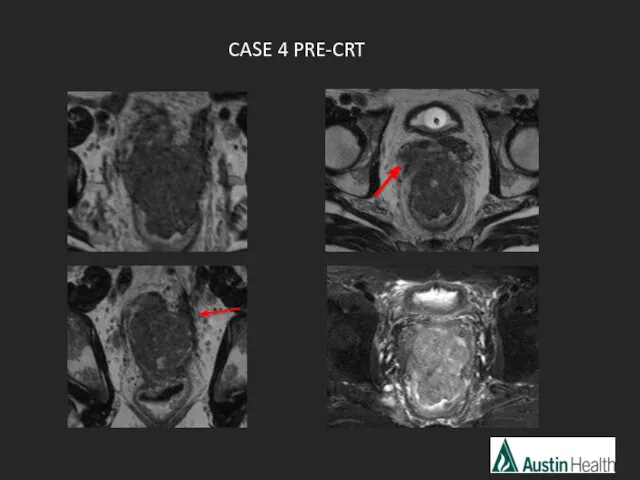
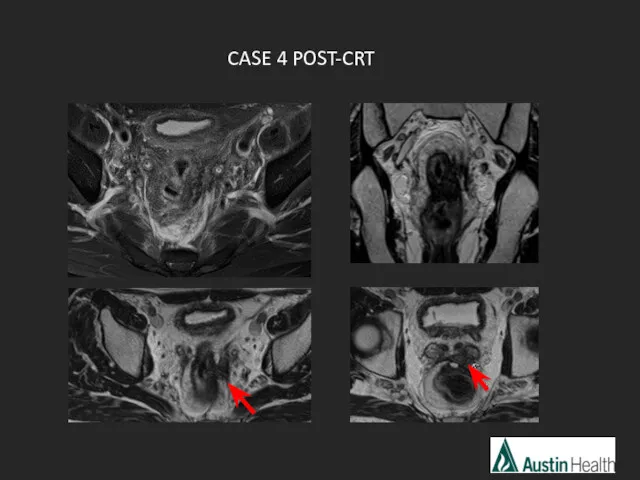
- 26. CASE 4
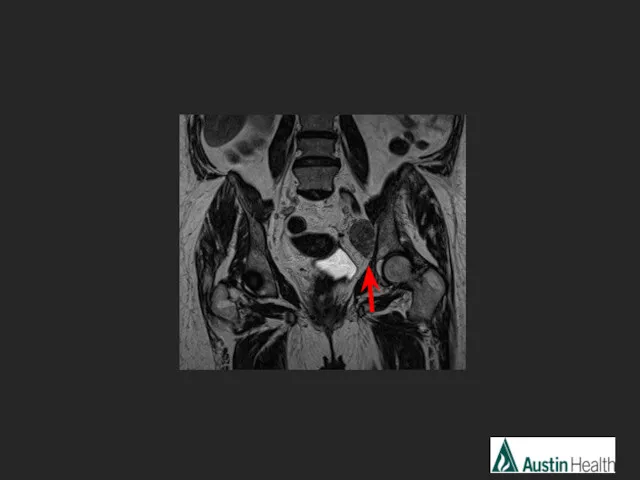
- 29. Report conclusion: Low rectal tumour with a length of 5.5 cm with extension to and involvement
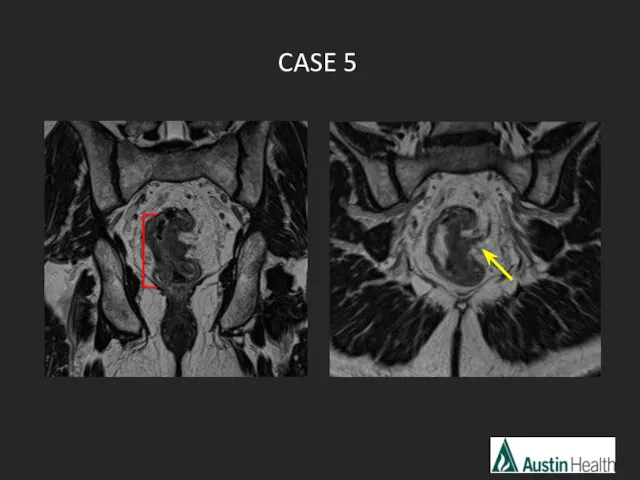
- 30. CASE 5
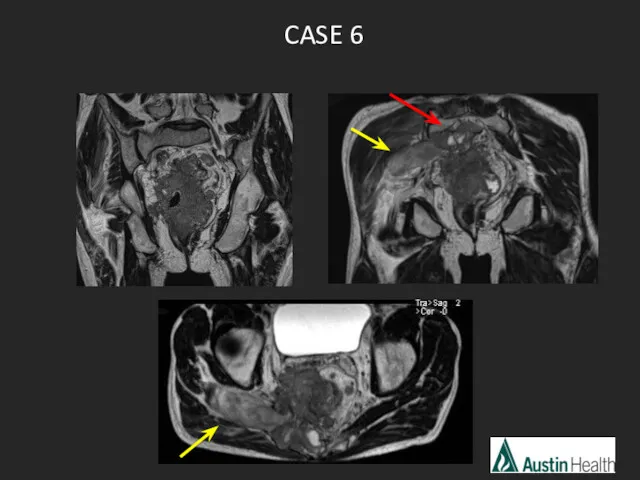
- 31. CASE 6
- 33. Overview MR imaging sequences The report of MR rectal cancer staging and “DISTANCE” Primary rectal cancer
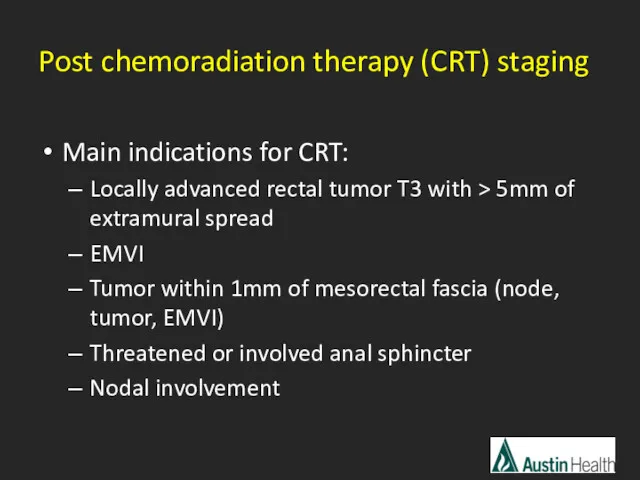
- 34. Main indications for CRT: Locally advanced rectal tumor T3 with > 5mm of extramural spread EMVI
- 35. Locally advanced rectal cancer has a poor prognosis Benefits of downstaging and downsizing with neoadjuvant CRT:
- 36. MRI is developing a central role in identifying good and poor responders Can provide a basis
- 37. Tumour volume reduction of at least 70% predicts disease free survival and good histologic regression. Nougaret
- 38. Post CRT MRI interpretation Predicting the stage prior to CRT ~ 85%, after CRT ~ 50%
- 39. Post CRT T-staging and Tumour Response Grading Difficult to differentiate between tumour and post-therapeutic changes on
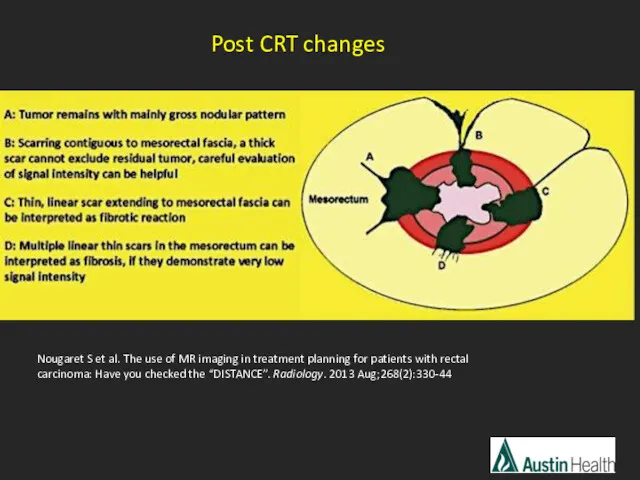
- 40. Morphologic descriptions used in T-staging and Tumour Response Grading Fibrosis within tumour and rectal wall: low
- 41. Nougaret S et al. The use of MR imaging in treatment planning for patients with rectal
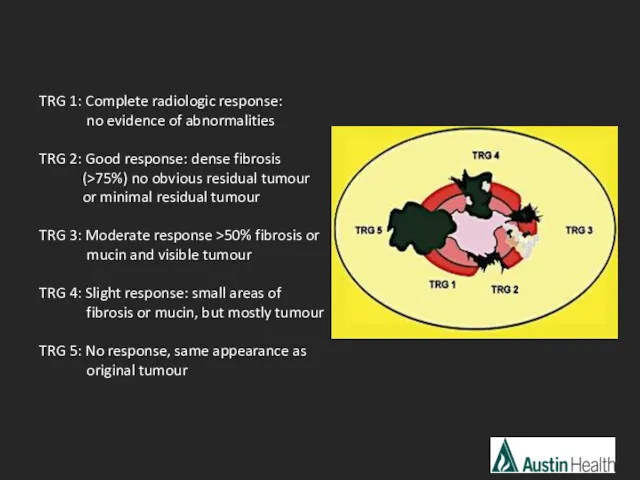
- 42. TRG 1: Complete radiologic response: no evidence of abnormalities TRG 2: Good response: dense fibrosis (>75%)
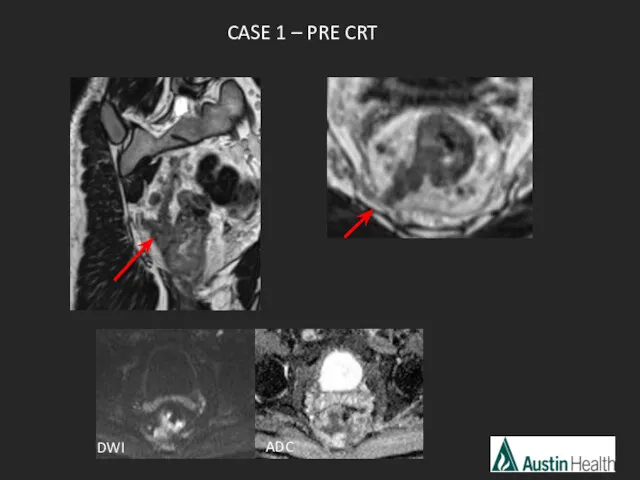
- 43. CASE 1 – PRE CRT ADC DWI
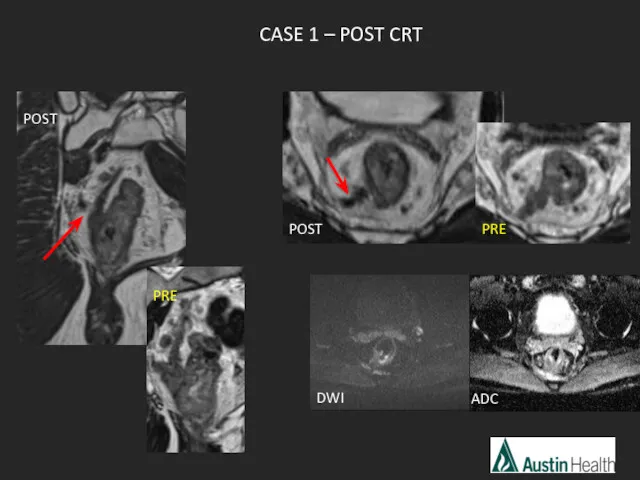
- 44. ADC CASE 1 – POST CRT POST PRE POST PRE DWI
- 45. mrTRG2 Good response with tumour replaced by dense fibrosis with no obvious tumour left.
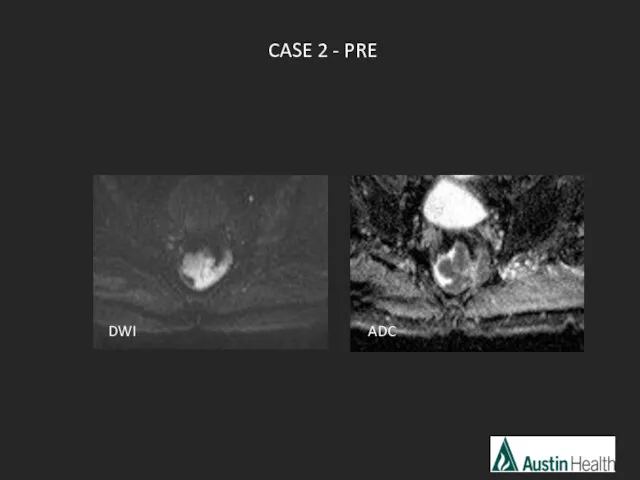
- 46. CASE 2 - PRE DWI ADC
- 47. Rectal cancers may exhibit restricted or increased diffusion dependant on tumour cellularity, intra-tumoral oedema, and presence
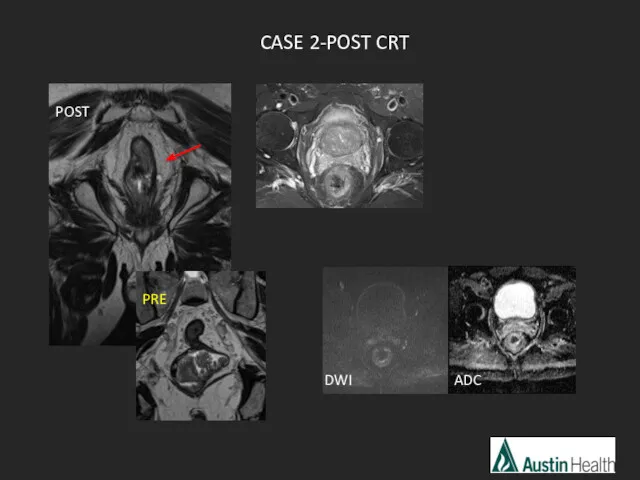
- 48. DWI ADC CASE 2-POST CRT POST PRE
- 49. mrTRG 1 Complete radiological response
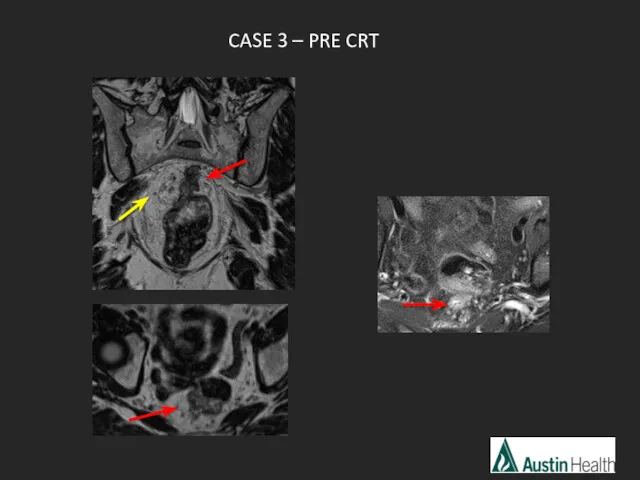
- 50. CASE 3 – PRE CRT
- 51. CASE 3 – POST CRT POST PRE POST PRE POST PRE
- 52. mrTRG 4 Slight response with some fibrosis but mostly tumour.
- 53. CASE 4 PRE-CRT
- 54. CASE 4 POST-CRT
- 55. mrTRG 2-3 Moderate - good response with > 50% fibrosis and minimal remaining visible tumour. T4
- 56. Summary Imaging techniques DISTANCE easy mnemonic to help us remember what to report on Some example
- 57. Now… challenge yourself to report rectal staging!
- 59. Скачать презентацию





























 ВИЧ и сексуальный либерализм ХХ века. Статистика и особенности эпидемий ВИЧ/СПИДа
ВИЧ и сексуальный либерализм ХХ века. Статистика и особенности эпидемий ВИЧ/СПИДа Endocrine pathology
Endocrine pathology Социальная ответственность аптечного бизнеса
Социальная ответственность аптечного бизнеса Психиатрияның зерттеу қағидалары мен диагностиканың заманауи
Психиатрияның зерттеу қағидалары мен диагностиканың заманауи Босанғаннан кейінгі ерте кезеңдегі қан кетудің себептері: травма,тромбин
Босанғаннан кейінгі ерте кезеңдегі қан кетудің себептері: травма,тромбин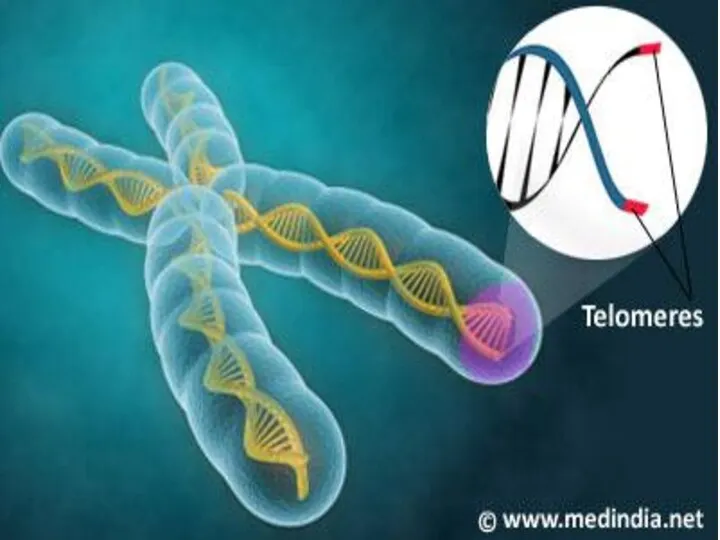 ДНК – ның теломерлік бөлімдерінің репликациялануы
ДНК – ның теломерлік бөлімдерінің репликациялануы Haemorrhagic shock in obstetrics
Haemorrhagic shock in obstetrics Вирусные дерматозы. Пузырные заболевания кожи
Вирусные дерматозы. Пузырные заболевания кожи Сестринский процесс. Документация к сестринскому процессу. 2018 г
Сестринский процесс. Документация к сестринскому процессу. 2018 г История изучения высшей нервной деятельности
История изучения высшей нервной деятельности Желтуха. Дифференциальная диагностика
Желтуха. Дифференциальная диагностика Гестациялық гипертензия кезінде антигипертензивті препараттарды қолдану
Гестациялық гипертензия кезінде антигипертензивті препараттарды қолдану Организация личной гигиены
Организация личной гигиены Здоровый человек и его окружение. Меню ребенка по месяцам
Здоровый человек и его окружение. Меню ребенка по месяцам Панкреатиттер,муковисцидоздар және целиакия кезінде тамақтандыру
Панкреатиттер,муковисцидоздар және целиакия кезінде тамақтандыру Ботулизм
Ботулизм Таблетки (продолжение)
Таблетки (продолжение) Спорт залдарының жабдықталуына қойылатын гигиеналық талаптар
Спорт залдарының жабдықталуына қойылатын гигиеналық талаптар Медицинская генетика. (Лекция 1)
Медицинская генетика. (Лекция 1) Химические и физико-химические методы стандартизации и контроля качества лекарственных. (Лекция 3)
Химические и физико-химические методы стандартизации и контроля качества лекарственных. (Лекция 3) Сучасні перинатальні технології та спостереження за новонародженим в перші 72 години життя
Сучасні перинатальні технології та спостереження за новонародженим в перші 72 години життя Тромбоцитопатия Бернара-Сулье
Тромбоцитопатия Бернара-Сулье Сучасні тенденції діагностики та лікуваня раку передміхурової залози
Сучасні тенденції діагностики та лікуваня раку передміхурової залози Удаление аденоидов (операция аденотомия): показания, методы, проведение, послеоперационный период
Удаление аденоидов (операция аденотомия): показания, методы, проведение, послеоперационный период Аномалии родовой деятельности. Лекция 2
Аномалии родовой деятельности. Лекция 2 Рак матки и рак маточной трубы
Рак матки и рак маточной трубы Влияние стресса на организм человека
Влияние стресса на организм человека Реабилитация. Медицинская реабилитация
Реабилитация. Медицинская реабилитация