Содержание
- 2. The Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system 1.Replinish blood oxygen levels which is needed for
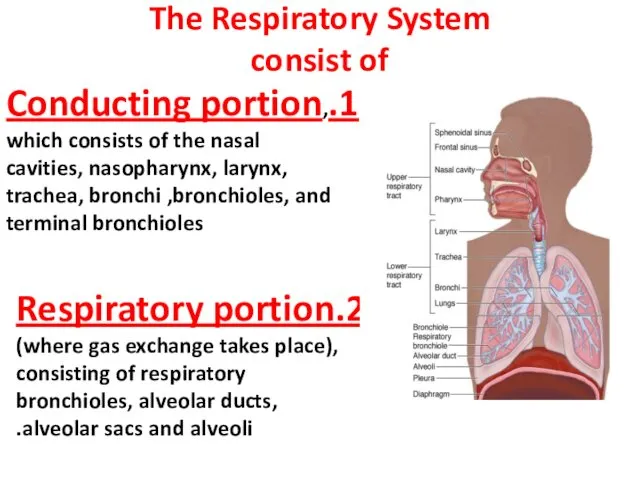
- 3. The Respiratory System consist of 1.Conducting portion, which consists of the nasal cavities, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea,
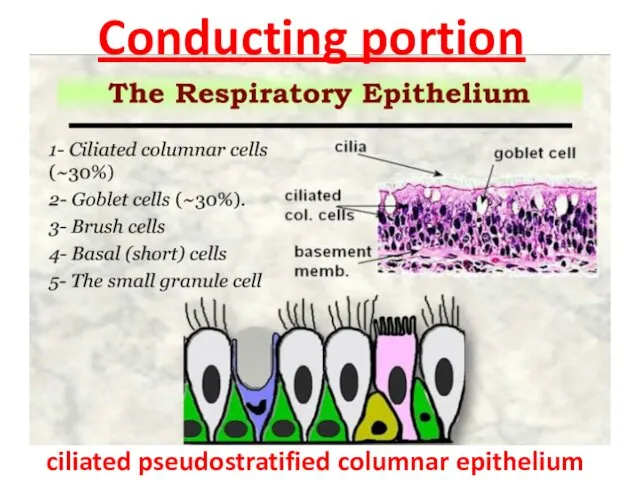
- 4. Conducting portion ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
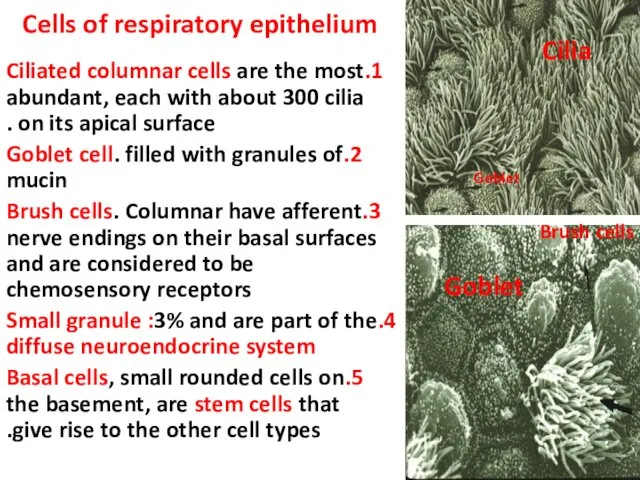
- 5. Cells of respiratory epithelium 1.Ciliated columnar cells are the most abundant, each with about 300 cilia
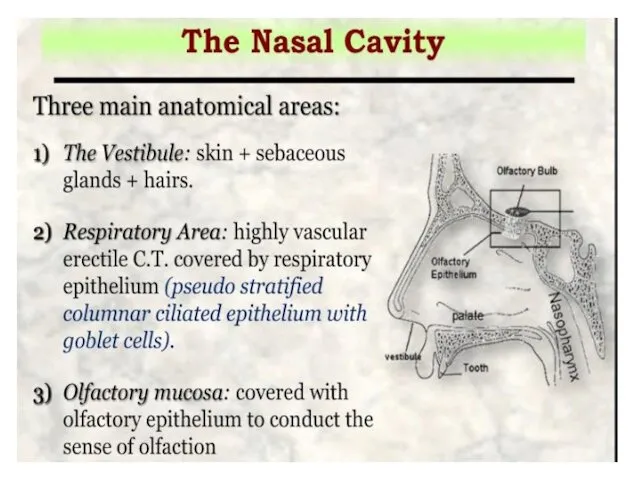
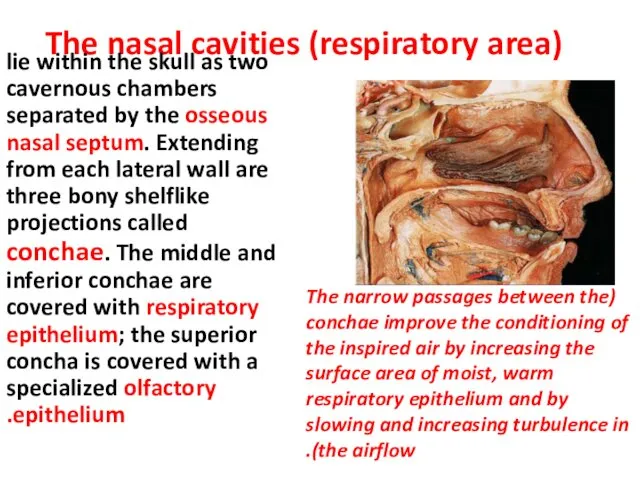
- 7. The nasal cavities (respiratory area) lie within the skull as two cavernous chambers separated by the
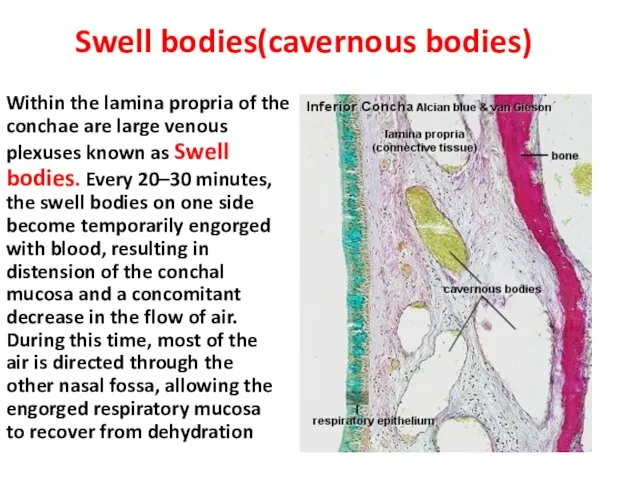
- 8. Swell bodies(cavernous bodies) Within the lamina propria of the conchae are large venous plexuses known as
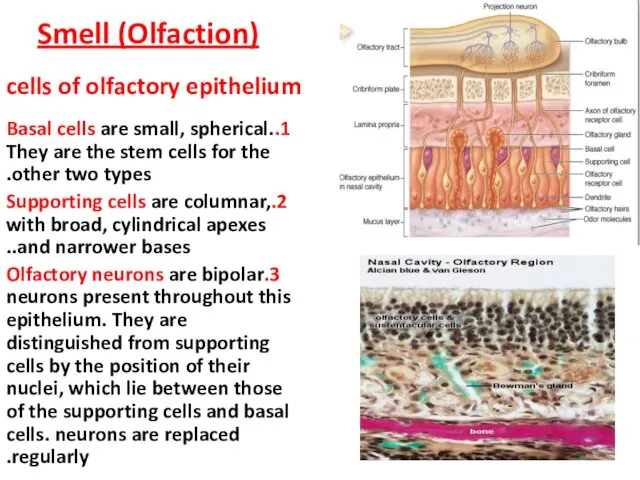
- 9. cells of olfactory epithelium 1.Basal cells are small, spherical. They are the stem cells for the
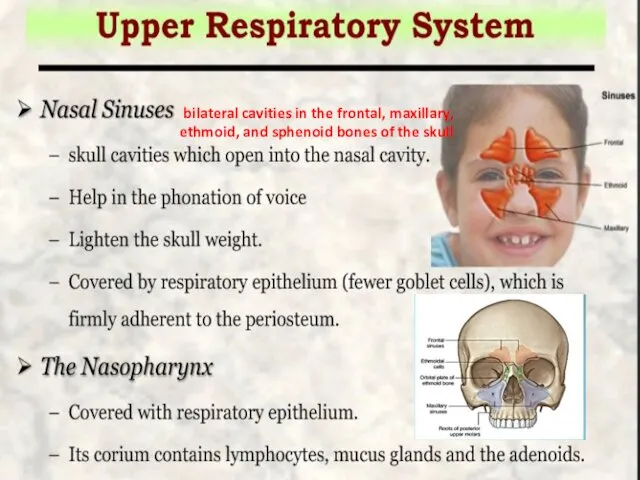
- 10. bilateral cavities in the frontal, maxillary, ethmoid, and sphenoid bones of the skull
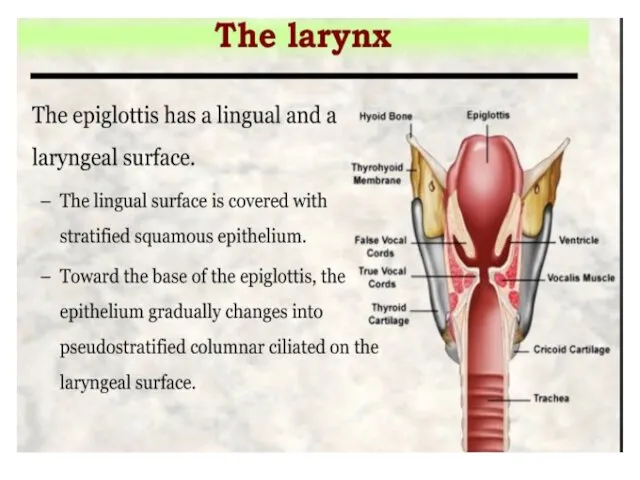
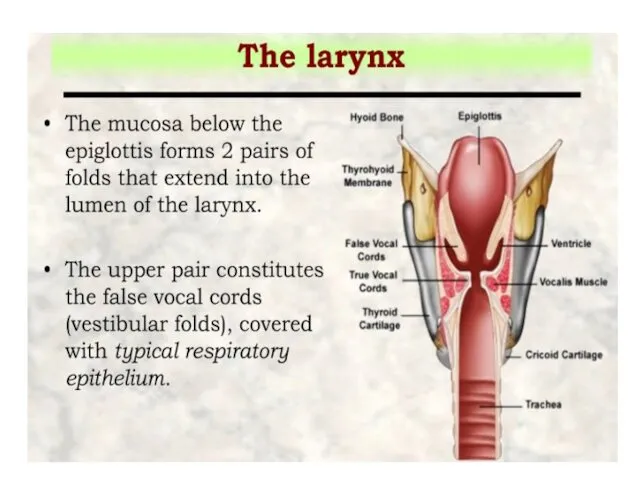
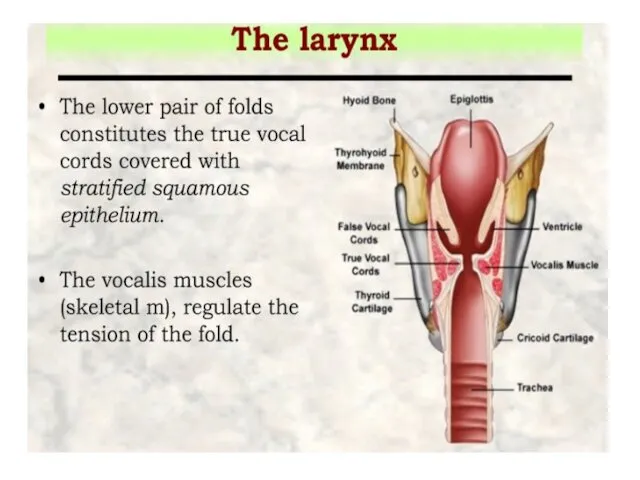
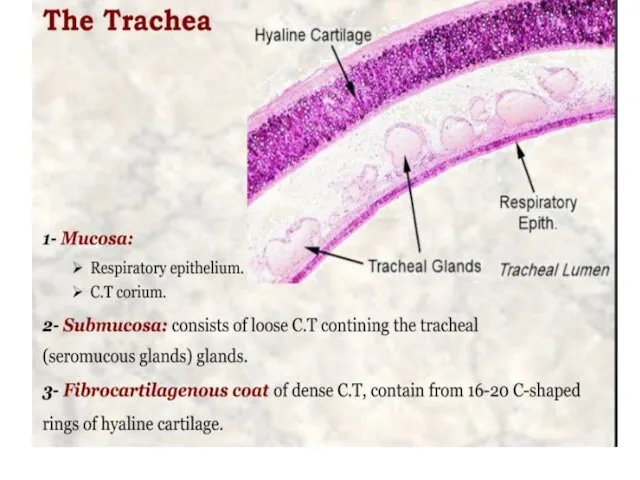
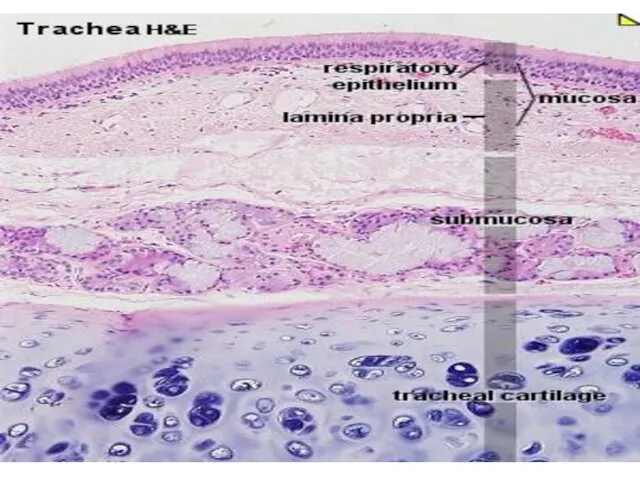
- 11. the thyroid, cricoid, and the inferior arytenoid epiglottis, cuneiform, corniculate, and the superior arytenoid cartilages
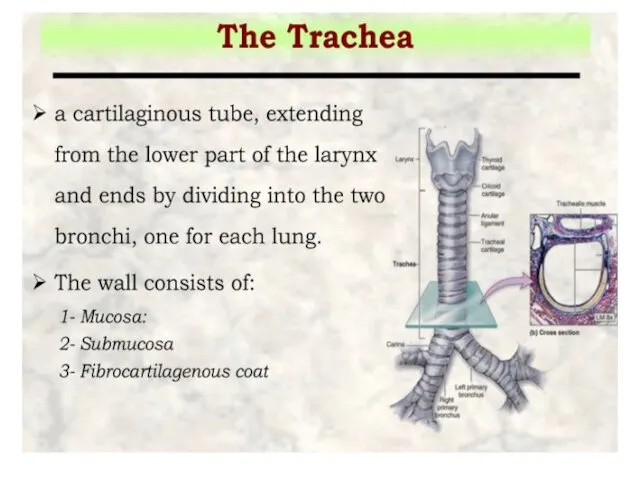
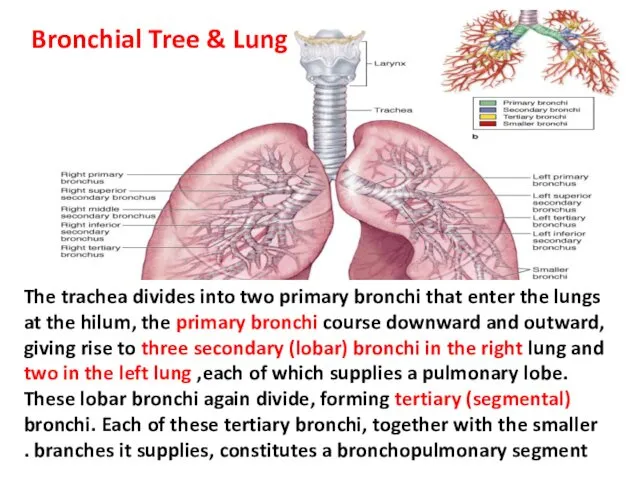
- 18. The trachea divides into two primary bronchi that enter the lungs at the hilum, the primary
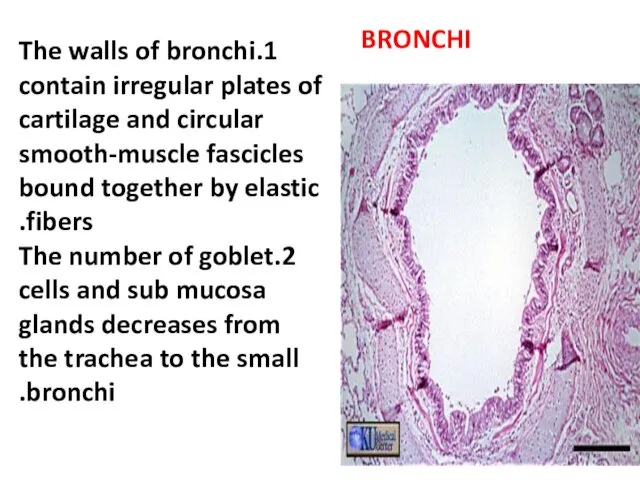
- 19. BRONCHI 1.The walls of bronchi contain irregular plates of cartilage and circular smooth-muscle fascicles bound together
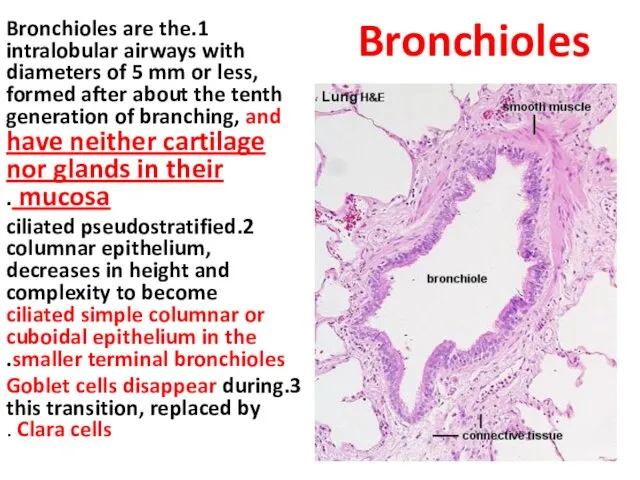
- 20. Bronchioles 1.Bronchioles are the intralobular airways with diameters of 5 mm or less, formed after about
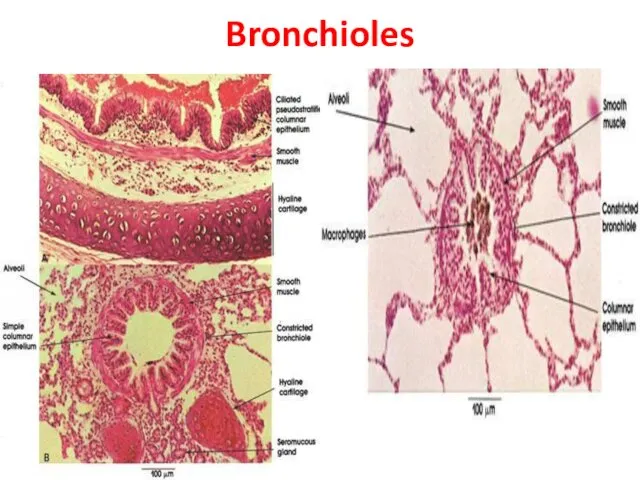
- 21. Bronchioles
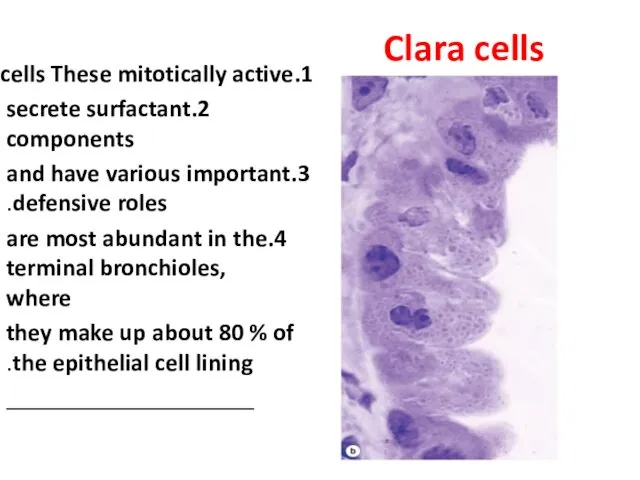
- 22. Clara cells 1.These mitotically active cells 2.secrete surfactant components 3.and have various important defensive roles. 4.are
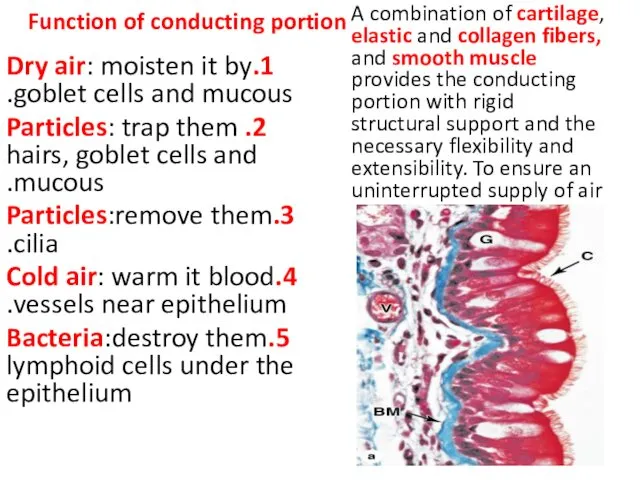
- 23. Function of conducting portion 1.Dry air: moisten it by goblet cells and mucous. 2. Particles: trap
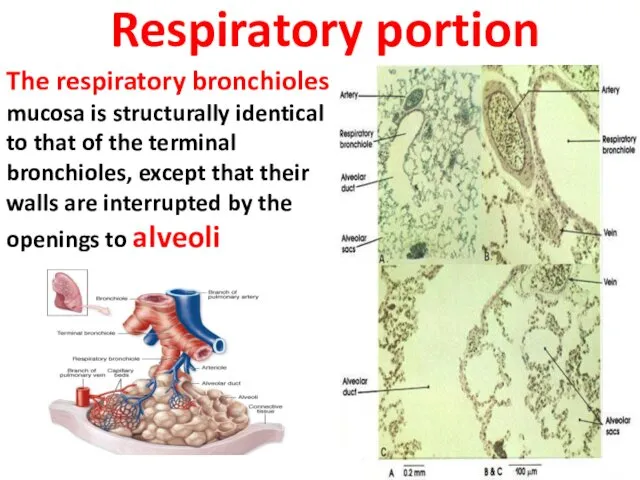
- 24. Respiratory portion The respiratory bronchioles mucosa is structurally identical to that of the terminal bronchioles, except
- 25. Alveolar Ducts and sacs 1.Respiratory bronchioles branch into tubes called alveolar ducts that are completely lined
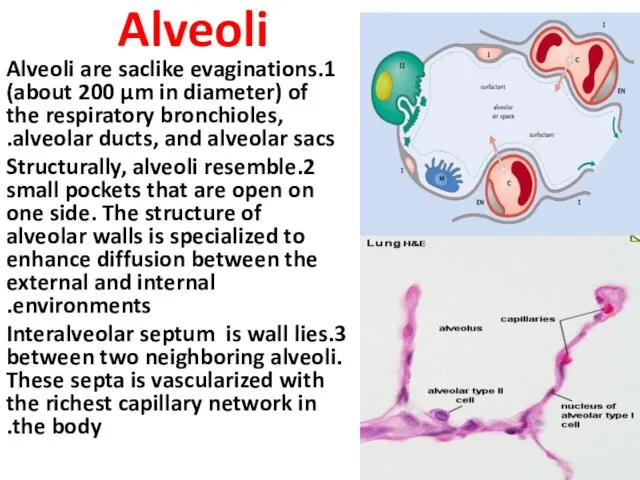
- 26. Alveoli 1.Alveoli are saclike evaginations (about 200 µm in diameter) of the respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts,
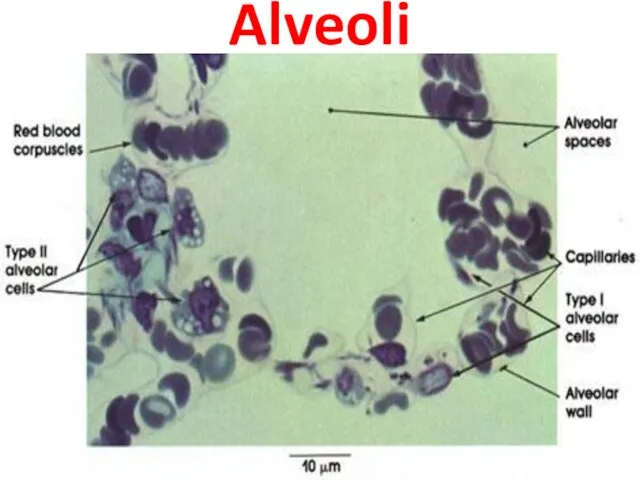
- 27. The cells of alveoli 1.Type I alveolar cells are extremely attenuated cells that line the alveolar
- 28. Alveoli
- 30. Скачать презентацию




 Физиология сердечно-сосудистой системы. (Лекция 14)
Физиология сердечно-сосудистой системы. (Лекция 14) Медицинские средства защиты
Медицинские средства защиты Қарыншалар гипертрофиясының ЭКГ белгілері
Қарыншалар гипертрофиясының ЭКГ белгілері Шистосомозы. Этиологиясы. Эпидемиологиясы. Патогенезі. Классификациясы. Клиникасы. Диагностикасы. Екшеу диагностикасы. Емі
Шистосомозы. Этиологиясы. Эпидемиологиясы. Патогенезі. Классификациясы. Клиникасы. Диагностикасы. Екшеу диагностикасы. Емі Введение в медицинскую информатику. Определения, терминология
Введение в медицинскую информатику. Определения, терминология Заманауи эндодонттық аспаптар
Заманауи эндодонттық аспаптар СПИД и его профилактика
СПИД и его профилактика Юношеская дисфункция ВНЧС
Юношеская дисфункция ВНЧС Анемия. Анемияны емдеу және одан сақтану шаралары
Анемия. Анемияны емдеу және одан сақтану шаралары Болезнь крона
Болезнь крона Особенности применения базисных противовоспалительных препаратов при беременности, лактации и у пожилых
Особенности применения базисных противовоспалительных препаратов при беременности, лактации и у пожилых Комплексное лечение зубочелюстных аномалий и деформаций
Комплексное лечение зубочелюстных аномалий и деформаций Иммунопатология. Патологическая анатомия
Иммунопатология. Патологическая анатомия Асқазан-12-елі ішіктің ойық жара аурулары
Асқазан-12-елі ішіктің ойық жара аурулары Противотуберкулезные и противосифилитические препараты
Противотуберкулезные и противосифилитические препараты Рак яичников
Рак яичников Мастоидит, түрлері, клиникасы, диагностикасы, емі
Мастоидит, түрлері, клиникасы, диагностикасы, емі Беттің туа біткен патологиясын алдын алу. Беттің, жақсүйектерінің және ауыз қуысының ағзаларының ақаулары болған кездегі
Беттің туа біткен патологиясын алдын алу. Беттің, жақсүйектерінің және ауыз қуысының ағзаларының ақаулары болған кездегі Заболевания поджелудочной железы
Заболевания поджелудочной железы Пересадка (трансплантация) костного мозга
Пересадка (трансплантация) костного мозга Наркотики и их влияние на развитие полноценной личности
Наркотики и их влияние на развитие полноценной личности Профилактика вирусных инфекций
Профилактика вирусных инфекций Хроническое воспаление. Гранулематозное и специфическое воспаление
Хроническое воспаление. Гранулематозное и специфическое воспаление Восстановление двигательного акта (навыка)
Восстановление двигательного акта (навыка) Моральные проблемы суррогатного материнства
Моральные проблемы суррогатного материнства Влияние приобретенного дальтонизма на социальную адаптацию (социализацию) молодежи в России
Влияние приобретенного дальтонизма на социальную адаптацию (социализацию) молодежи в России Известный наркотик СНЮС
Известный наркотик СНЮС Фармациядағы менеджменттің функционалдық мазмұны. Басқару шешімдері
Фармациядағы менеджменттің функционалдық мазмұны. Басқару шешімдері