The problem of iodine deficiency: an epidemiological, clinical, social values. Solutions презентация
Содержание
- 2. Goiter - History 1811 - Curtua - opening element Iodine 1850 - Chatin - iodine therapy
- 3. Iodine deficiency disorders Some of the most common non-communicable diseases in humans In general, the Earth:
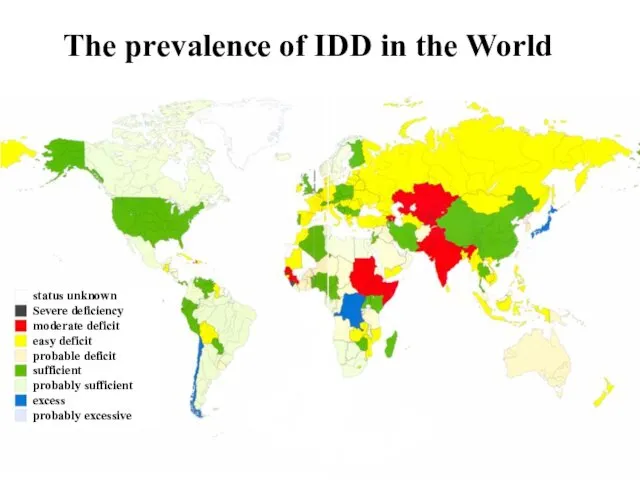
- 4. The prevalence of IDD in the World status unknown Severe deficiency moderate deficit easy deficit probable
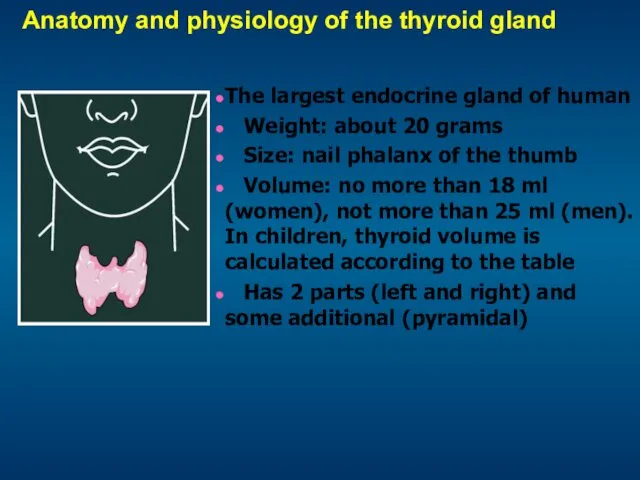
- 5. Anatomy and physiology of the thyroid gland The largest endocrine gland of human Weight: about 20
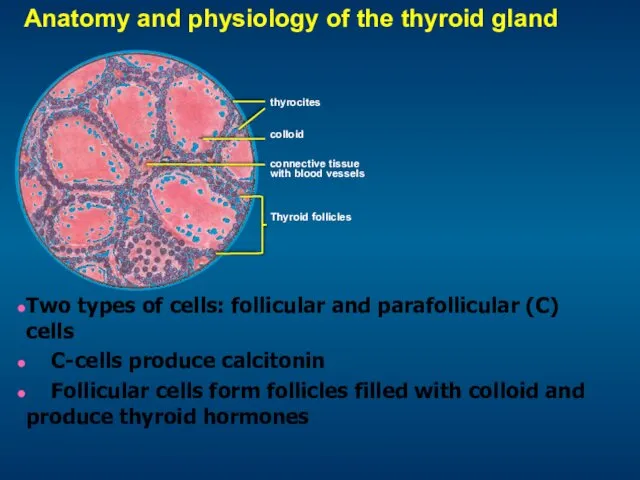
- 6. Anatomy and physiology of the thyroid gland Two types of cells: follicular and parafollicular (C) cells
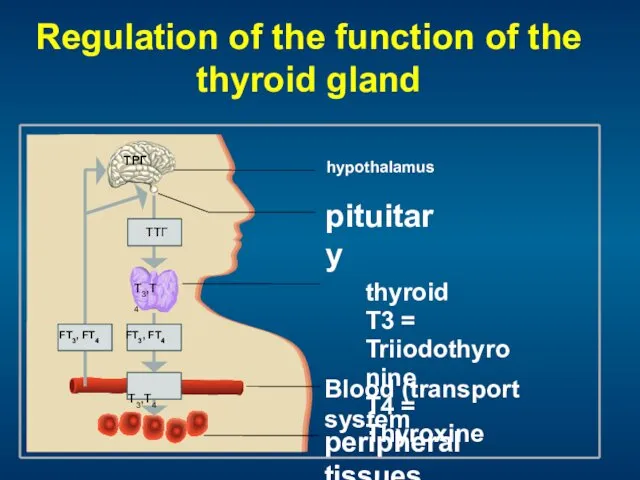
- 7. Regulation of the function of the thyroid gland
- 8. Hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid system TSH - the main stimulant of secretion of T3 and T4 TSH secretion is
- 9. Participation of thyroid hormones in the development and regulation: Nervous system and psyche thyroid Gastro-intestinal tract
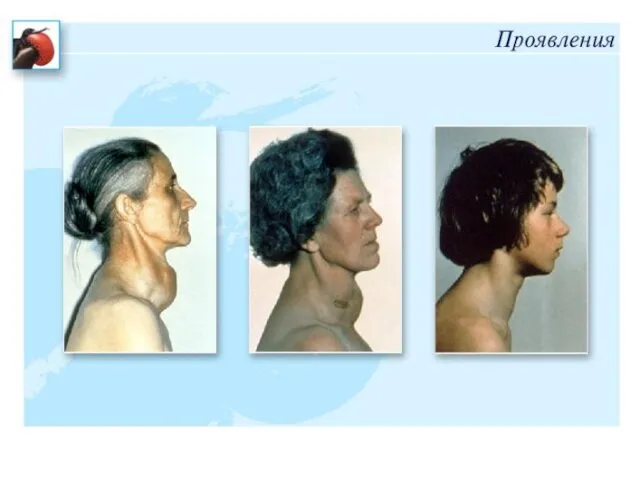
- 10. Goiter - diffuse thyroid enlargement, defined either by palpation or by imaging Goiter is indicated increased
- 11. SCA - increase in thyroid Goiter - diffuse enlargement of thyroid in the population by more
- 12. Single international classification of thyroid disease is still there is no The most widely used is
- 13. Classification of thyroid disease Thyroid function 1. Normal - euthyroidism 2. Increased - thyrotoxicosis (hyperthyroidism) 3.
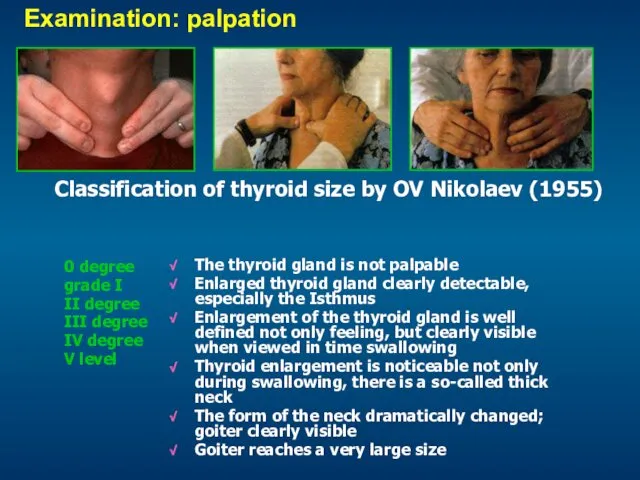
- 14. Examination: palpation Modern classification of goitre (WHO, 2001) 0 st. - 1 st. - 2 st.
- 15. Classification of thyroid size by OV Nikolaev (1955) 0 degree grade I II degree III degree
- 17. External factors (cause of endemic goiter) various strumogeny, namely Etiology of diffuse toxic goiter (1811-2002 gg.)
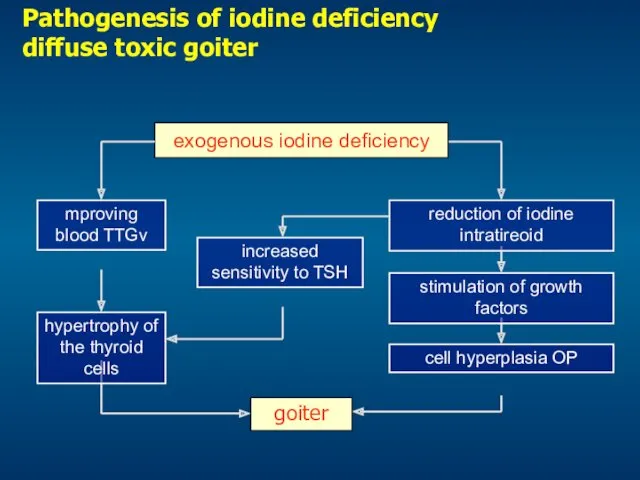
- 18. Pathogenesis of iodine deficiency diffuse toxic goiter exogenous iodine deficiency mproving blood TTGv hypertrophy of the
- 19. Diagnosis of IDD . Evaluation of epidemiology (prevalence) of IDD in the country as a whole
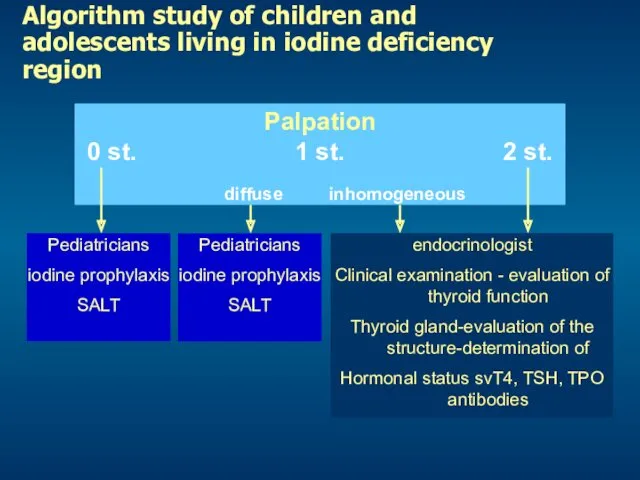
- 20. Algorithm study of children and adolescents living in iodine deficiency region 0 st. 1 st. 2
- 21. TSH T3 T4 antibodies Laboratory studies regulator of the thyroid gland, the main parameter in assessing
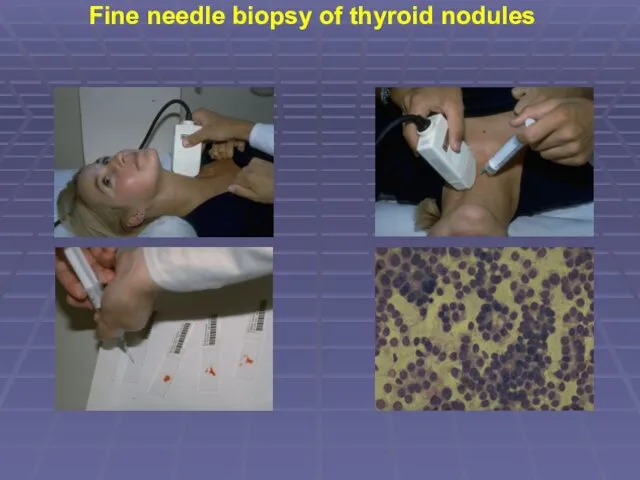
- 22. Fine needle biopsy of thyroid nodules
- 23. Clinical indicator: incidence of goiter in the population (quantitative, indirect indicator of iodine deficiency) Estimation of
- 24. Biochemical parameters: urinary iodine concentration (quantitative, direct indicator of iodine provision) Method is used for population
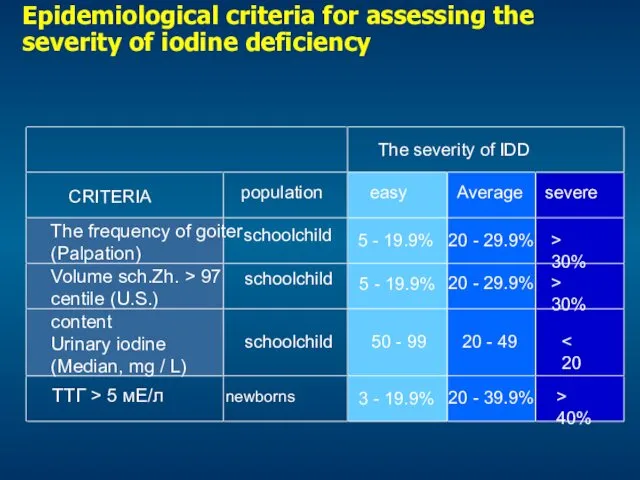
- 25. Epidemiological criteria for assessing the severity of iodine deficiency ▪ ▪ ▪
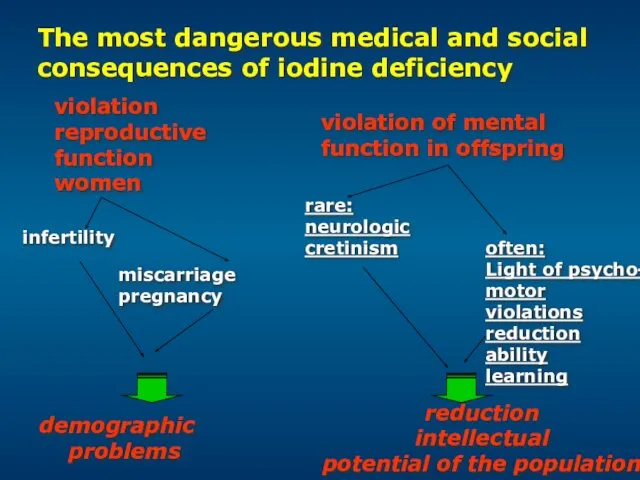
- 26. The most dangerous medical and social consequences of iodine deficiency demographic problems violation reproductive function women
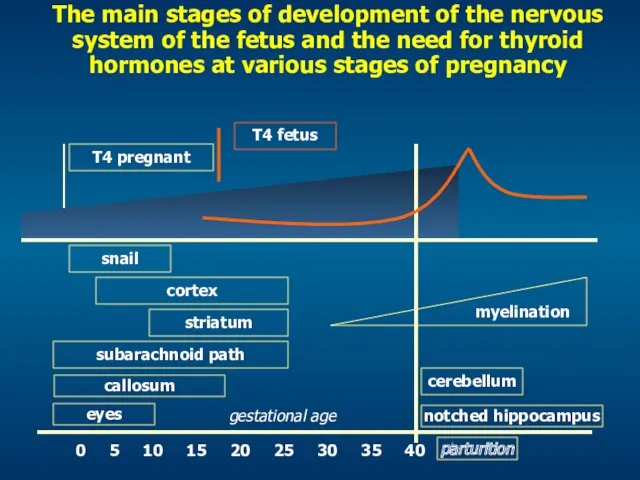
- 27. The main stages of development of the nervous system of the fetus and the need for
- 28. At risk of developing IDD children adolescents pregnant women lactating women
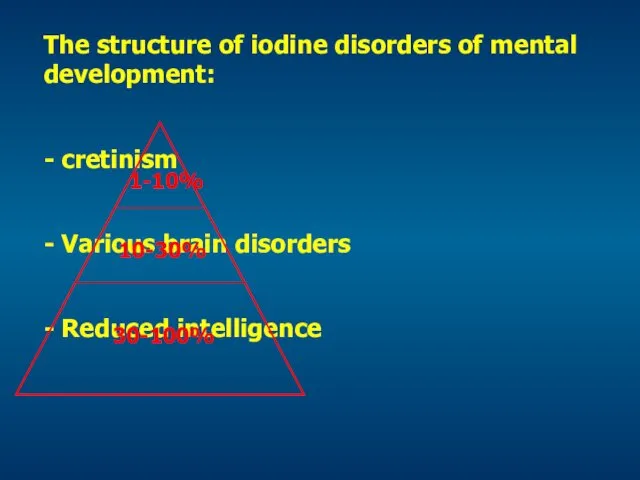
- 29. The structure of iodine disorders of mental development: - cretinism - Various brain disorders - Reduced
- 31. Скачать презентацию












 Фізіологічна класифікація та характеристика фізичних вправ
Фізіологічна класифікація та характеристика фізичних вправ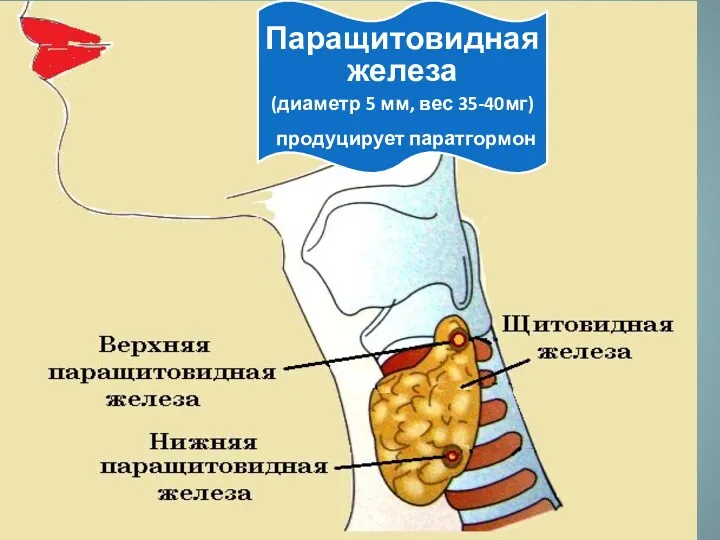 Паращитовидная железа
Паращитовидная железа Профилактика ОРВИ и гриппа
Профилактика ОРВИ и гриппа Хронический гепатит и цирроз печени
Хронический гепатит и цирроз печени Дыхательная недостаточность
Дыхательная недостаточность История развития логопедии как науки в России и зарубежом
История развития логопедии как науки в России и зарубежом Интерстициальные болезни легких (диффузные инфильтративные заболевания легких)
Интерстициальные болезни легких (диффузные инфильтративные заболевания легких) ЭКГ 1
ЭКГ 1 Организация лекарственного обеспечения лечебно-профилактических учреждений (БА, МБА)
Организация лекарственного обеспечения лечебно-профилактических учреждений (БА, МБА) ИБС. Стабильная стенокардия напряжения. Определение и классификация по ВОЗ. Патогенез
ИБС. Стабильная стенокардия напряжения. Определение и классификация по ВОЗ. Патогенез Side effects of chemotherapeutic drugs, cytostatics, hormonal medications
Side effects of chemotherapeutic drugs, cytostatics, hormonal medications Острый коронарный синдром
Острый коронарный синдром Жедел бүйрек жетіспеушілігі
Жедел бүйрек жетіспеушілігі Исключение острой хирургической патологии при остром животе у женщин
Исключение острой хирургической патологии при остром животе у женщин Аппарат Ulthera System
Аппарат Ulthera System Возраст и лекарство
Возраст и лекарство Методы оценки функционального состояния. Тема 3
Методы оценки функционального состояния. Тема 3 Психогимнастика в детском саду
Психогимнастика в детском саду Синдром Эдвардса
Синдром Эдвардса Бронхит. Классификация по течению болезни
Бронхит. Классификация по течению болезни Патофизиология центральной нервной системы
Патофизиология центральной нервной системы Этические проблемы в трансплантологии. Этические проблемы оказания психиатрической помощи. (Лекция 9)
Этические проблемы в трансплантологии. Этические проблемы оказания психиатрической помощи. (Лекция 9) Балалар ағзасының өсу мен дамуының негізгі заңдылықтары. Жас кезеңділік
Балалар ағзасының өсу мен дамуының негізгі заңдылықтары. Жас кезеңділік Формы и средства оказания помощи детям с ОВЗ
Формы и средства оказания помощи детям с ОВЗ Неотложные состояния в педиатрии
Неотложные состояния в педиатрии Гиподинамия. Причины гиподинамии
Гиподинамия. Причины гиподинамии Местное и общее обезболивание
Местное и общее обезболивание Хроническая обструктивная болезнь лёгких
Хроническая обструктивная болезнь лёгких