Содержание
- 2. Student Learning Objectives Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 5 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and
- 3. What is the role of information policy and data administration in the management of organizational data
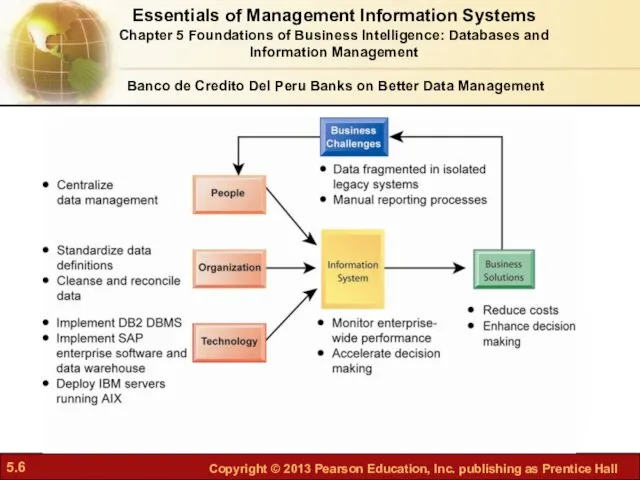
- 4. Banco de Credito Del Peru Banks on Better Data Management Problem: Multiple outdated systems, duplicate, inconsistent
- 5. SAP integrated software suite included modules for enterprise resource planning and a data warehouse to support
- 6. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 5 Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Banco
- 7. The Database Approach to Data Management Database: Collection of related files containing records on people, places,
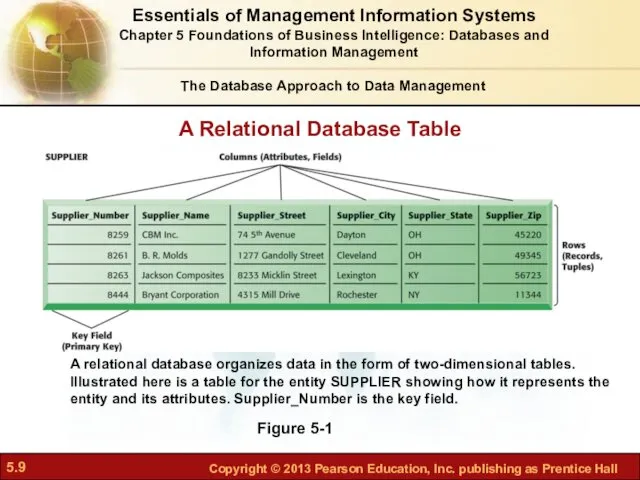
- 8. The Database Approach to Data Management Relational database: Organize data into two-dimensional tables (relations) with columns
- 9. A Relational Database Table Figure 5-1 A relational database organizes data in the form of two-dimensional
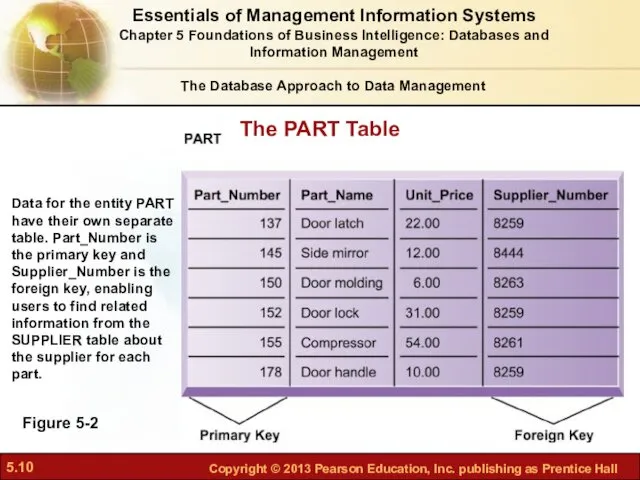
- 10. The PART Table Figure 5-2 Data for the entity PART have their own separate table. Part_Number
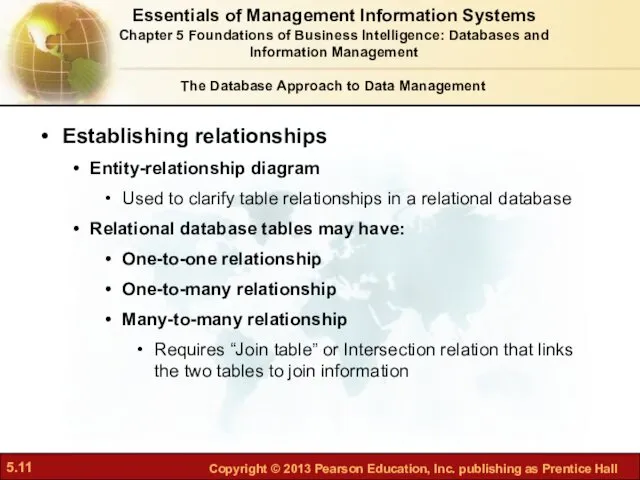
- 11. The Database Approach to Data Management Establishing relationships Entity-relationship diagram Used to clarify table relationships in
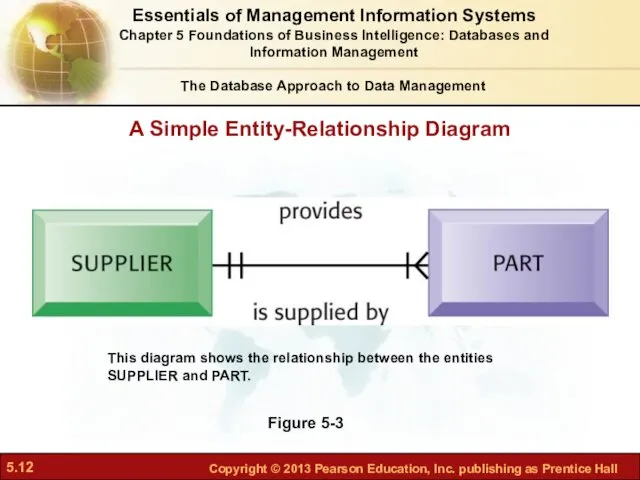
- 12. A Simple Entity-Relationship Diagram Figure 5-3 This diagram shows the relationship between the entities SUPPLIER and
- 13. The Database Approach to Data Management Normalization Process of streamlining complex groups of data to: Minimize
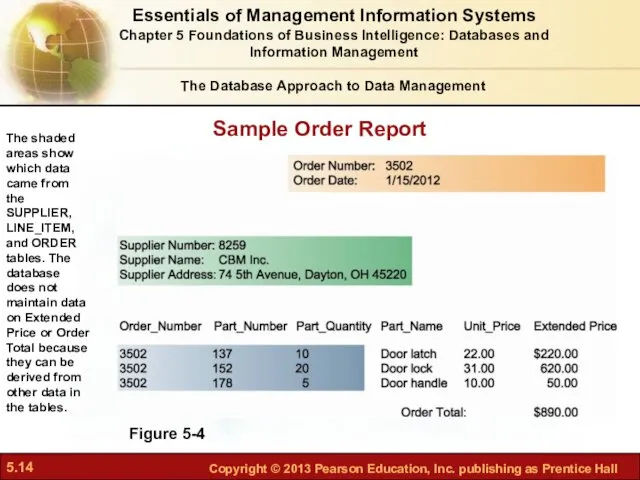
- 14. Sample Order Report Figure 5-4 The shaded areas show which data came from the SUPPLIER, LINE_ITEM,
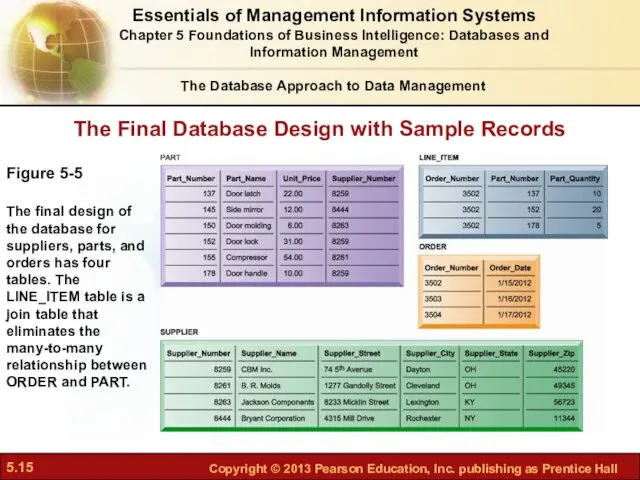
- 15. The Final Database Design with Sample Records Figure 5-5 The final design of the database for
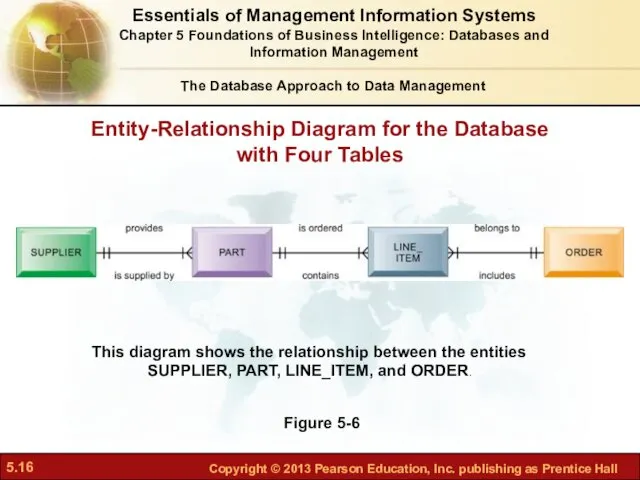
- 16. Entity-Relationship Diagram for the Database with Four Tables Figure 5-6 This diagram shows the relationship between
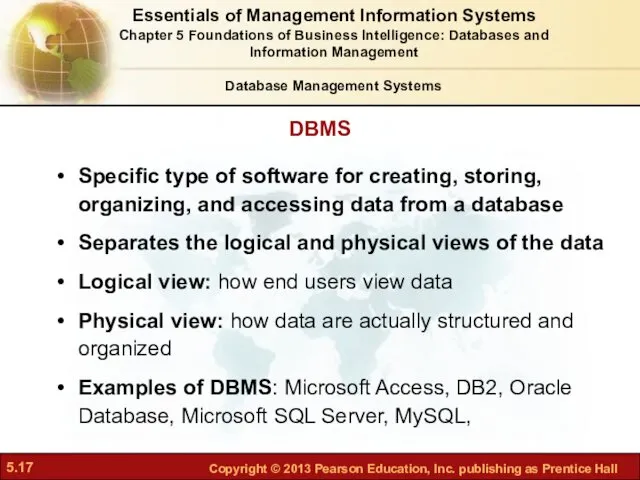
- 17. Specific type of software for creating, storing, organizing, and accessing data from a database Separates the
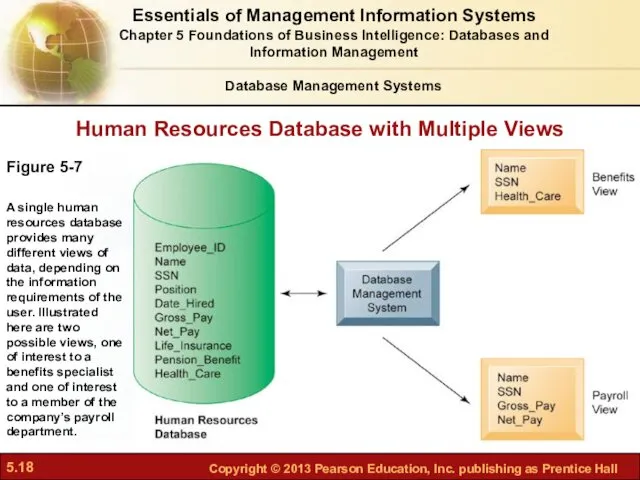
- 18. Human Resources Database with Multiple Views Figure 5-7 A single human resources database provides many different
- 19. Operations of a Relational DBMS Select: Creates a subset of all records meeting stated criteria Join:
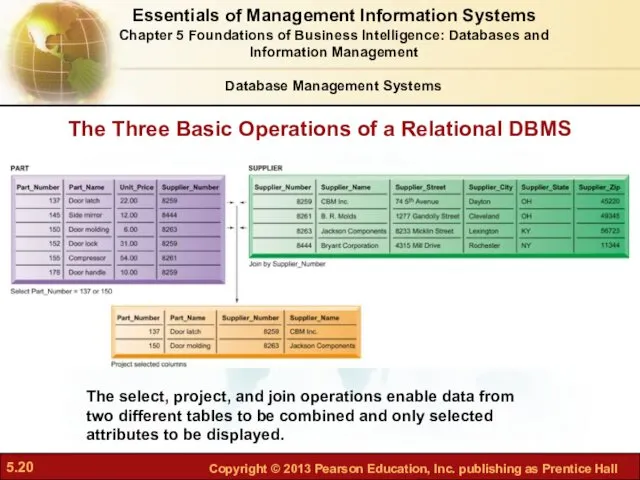
- 20. The Three Basic Operations of a Relational DBMS Figure 5-8 The select, project, and join operations
- 21. Capabilities of Database Management Systems Data definition capabilities: Specify structure of content of database Data dictionary:
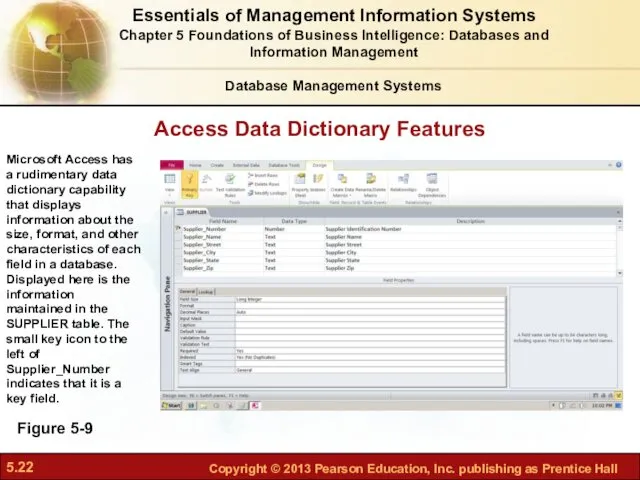
- 22. Access Data Dictionary Features Figure 5-9 Microsoft Access has a rudimentary data dictionary capability that displays
- 23. Example of an SQL Query Figure 5-10 Illustrated here are the SQL statements for a query
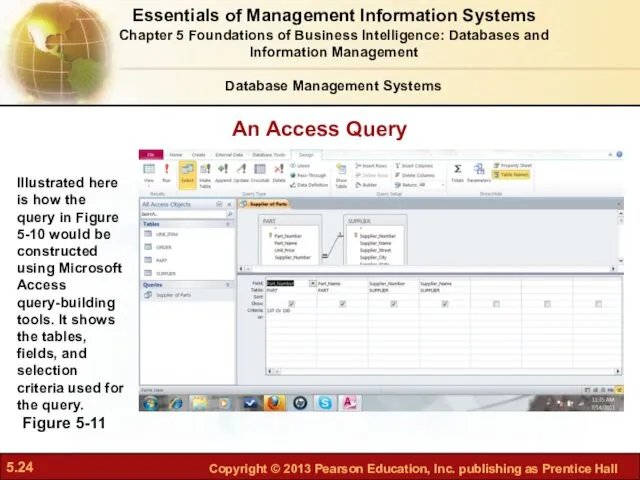
- 24. An Access Query Figure 5-11 Illustrated here is how the query in Figure 5-10 would be
- 25. Object-Oriented DBMS (OODBMS) Stores data and procedures that act on those data as objects to be
- 26. Using Databases to Improve Business Performance and Decision Making Databases provide information to help the company
- 27. Data Warehouses Using Databases to Improve Business Performance and Decision Making Data warehouse: Database that stores
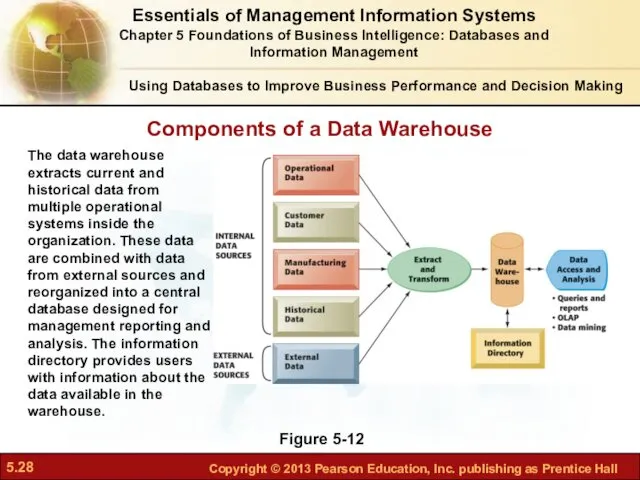
- 28. Components of a Data Warehouse Figure 5-12 The data warehouse extracts current and historical data from
- 29. Business intelligence: tools for consolidating, analyzing, and providing access to large amounts of data to improve
- 30. Supports multidimensional data analysis, enabling users to view the same data in different ways using multiple
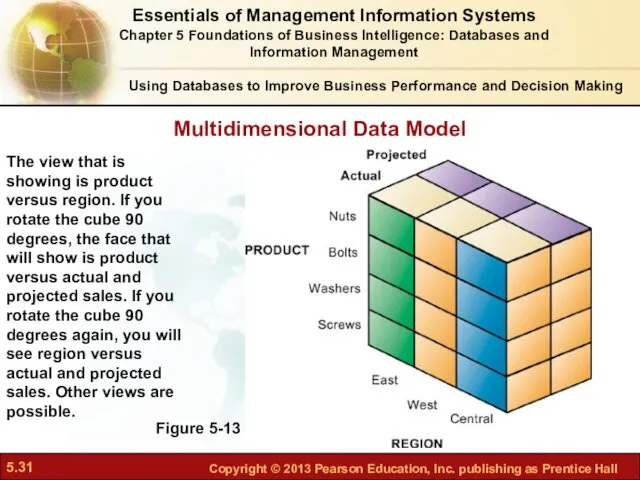
- 31. Using Databases to Improve Business Performance and Decision Making Figure 5-13 The view that is showing
- 32. Finds hidden patterns and relationships in large databases and infers rules from them to predict future
- 33. Interactive Session: People Asking the Customer by Asking the Database Using Databases to Improve Business Performance
- 34. One popular use of data mining: analyzing patterns in customer data for one-to-one marketing campaigns or
- 35. Text Mining Unstructured data (mostly text files) accounts for 80% of an organization’s useful information Text
- 36. Firms use the Web to make information from their internal databases available to customers and partners.
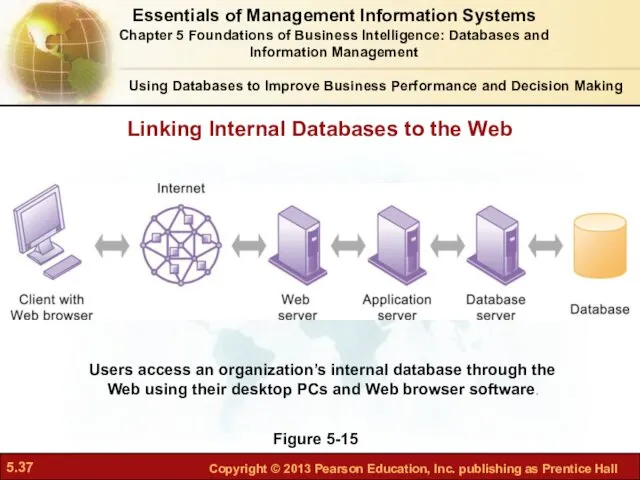
- 37. Using Databases to Improve Business Performance and Decision Making Figure 5-15 Users access an organization’s internal
- 38. Establishing an Information Policy Managing Data Resources Information policy States organization’s rules for organizing, managing, storing,
- 39. Ensuring Data Quality Poor data quality: major obstacle to successful customer relationship management Data quality problems
- 40. Read the Interactive Session and then discuss the following questions: What is the value of the
- 42. Скачать презентацию





















 Название компании. Слоган компании
Название компании. Слоган компании Основы целеполагания
Основы целеполагания Вклад отдельных исследователей в развитие управленческой мысли
Вклад отдельных исследователей в развитие управленческой мысли Технологии информационного моделирования на этапе строительства
Технологии информационного моделирования на этапе строительства Уровни управления
Уровни управления Управление человеческими ресурсами
Управление человеческими ресурсами Стратегияның рангтер сатысы
Стратегияның рангтер сатысы Питер Друкер
Питер Друкер Управление персоналом: место и роль в системе управления предприятием и организациями
Управление персоналом: место и роль в системе управления предприятием и организациями Jolly alon
Jolly alon Практика оценки бизнес-проектов
Практика оценки бизнес-проектов презентация Принципы СМК
презентация Принципы СМК Разработка бизнес-плана по увеличению производственных мощностей предприятия
Разработка бизнес-плана по увеличению производственных мощностей предприятия Баскет-метод
Баскет-метод Analiza opskrbnog lanca uz pomoć mapiranja toka vrijednosti
Analiza opskrbnog lanca uz pomoć mapiranja toka vrijednosti Теоретичні засади менеджменту готельно-ресторанного господарства
Теоретичні засади менеджменту готельно-ресторанного господарства Моделирование и оптимизация процессов и систем сервиса: понятия процесс и системы сервиса. Характеристика курса
Моделирование и оптимизация процессов и систем сервиса: понятия процесс и системы сервиса. Характеристика курса Управление капитального строительства администрации Лысьвенского городского округа
Управление капитального строительства администрации Лысьвенского городского округа Ранние теории мотивации: классические теории управления, теории человеческих отношений, теории человеческих ресурсов
Ранние теории мотивации: классические теории управления, теории человеческих отношений, теории человеческих ресурсов Стандартизация, сертификация
Стандартизация, сертификация Стимулирование труда работников предприятия и пути его совершенствования
Стимулирование труда работников предприятия и пути его совершенствования Менеджмент процесса производства зерна и повышение его экономической эффективности (ООО Маслово Орловского района)
Менеджмент процесса производства зерна и повышение его экономической эффективности (ООО Маслово Орловского района) Совершенствование процесса подбора и найма персонала
Совершенствование процесса подбора и найма персонала Деловая переписка
Деловая переписка Основні задачі проекту. Інструменти та можливості
Основні задачі проекту. Інструменти та можливості Risk management application problems
Risk management application problems Экспертные и комплексные методы принятия управленческих решений
Экспертные и комплексные методы принятия управленческих решений Разработка стратегической карты на основе сбалансированной системы показателей для эффективного управления компанией
Разработка стратегической карты на основе сбалансированной системы показателей для эффективного управления компанией