- Главная
- Менеджмент
- Workplace Organization. Lean OS Development & Global BOP Team

Содержание
- 2. 1. Workplace Organization Purpose To provide an ergonomic and safe work environment for operators, standardized processes
- 3. 3. Handling & Protection How to Accommodate Components at the Point of Use In order to
- 4. 3. Handling & Protection Summary Matrix 3.2 Wires: 700mm Length: 700mm 1300mm
- 5. 3. Handling & Protection How to Accommodate Wires at the Cutting Supermarket Following the Cutting Guidelines,
- 6. 3. Handling & Protection How to Accommodate Wires at the Point of Use Wire Presentation should
- 7. 3. Handling & Protection How to Accommodate Wires at the Point of Use Short Wires Use
- 8. Physical Separators between Wires 3. Handling & Protection Wires at Point of Use Examples 1. Terminals
- 9. 3. Handling & Protection Wires at Point of Use Examples 6. Terminals Protection from the front
- 10. 3. Handling & Protection Wires at Point of Use Examples 8. Terminals Protection from the back
- 11. 3. Handling & Protection Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
- 12. 3. Handling & Protection Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
- 13. 3. Handling & Protection Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
- 14. Wire Rack Design Criteria: Minimum reaching point for all materials/ Splice / kit/ lead coil is
- 15. Rack Design Concept Example of Europe - Rack Type 3 FRONT VIEW BACK VIEW CUBICAL VIEW
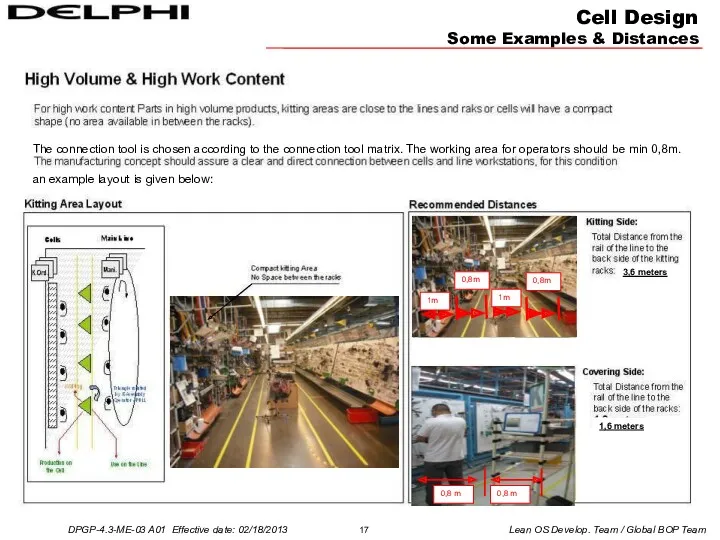
- 16. Cell Design Some Examples & Distances The connection tool is chosen according to the connection tool
- 17. Cell Design Some Examples & Distances The connection tool is chosen according to the connection tool
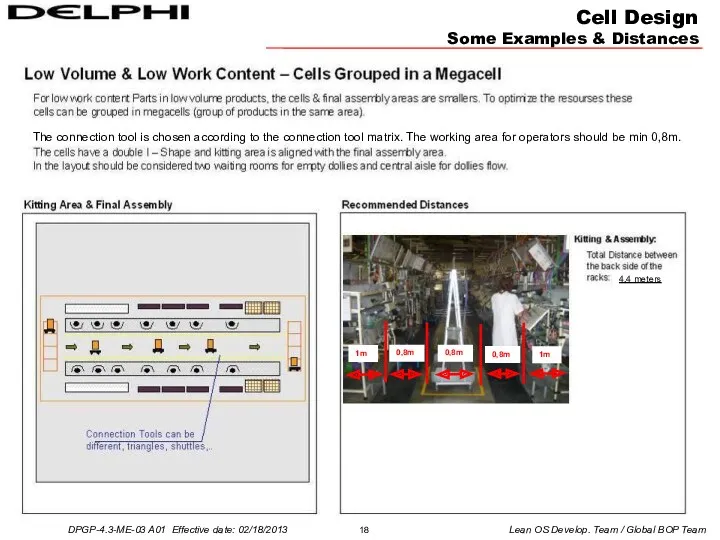
- 18. Cell Design Some Examples & Distances The connection tool is chosen according to the connection tool
- 19. Assembly area layout has to support clear material flow and the Visual Management. Address system has
- 20. 5. Standardized Work Impact of the Workplace Organization on the Manpower Results Good WPO can lead
- 22. Скачать презентацию
1. Workplace Organization Purpose
To provide an ergonomic and safe work environment
1. Workplace Organization Purpose
To provide an ergonomic and safe work environment
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Components at the Point of
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Components at the Point of
In order to develop a good parts presentation for the operators follow the Delivery Routes Guideline. Key points are the following:
D. Routes have to be performed based on fixed time & 1 hour frequency, due to that at the point of use is necessary to have 2 kanban cards (one behind the other) representing 2 hours by kanban
Define Right Container to be used at point of use (definition is done by PC&L based on the dimensions of the components and the line targets submitted by ME and afterwards the assigned container sizes are confirmed together by ME and PC&L):
Define 3 container type that can contain 2 hours consumption per part ( 1 liter / 2,5 liters / 5 liters)
a Cup for very small parts – (seals, secondary lock,…), cup is just to measure the quantity to be loaded to the small container
If supplier pack represents less than 8 hours consumption should be delivery in the original pack to the point of use (ME / PCL should analyze if it is feasible)
If necessary to repack it should be selected the smallest container that contains 2 hours consumption.
Quality should define what are the parts that cannot be repacked and this information should exist in PFMEA.
All parts have to be identified all the time and visible from the operator’s point of view.
Material should be available at the exact point of use, rack should provide conditions to avoid mixed parts and to assure the FIFO. Cells should be prepared in order to be loaded by the exterior not to disturb operators. Special shuttles to reorder the parts have to be installed (see in cell design chapter)
3. Handling & Protection
Summary Matrix
3.2 Wires:
700mm
Length: 700mm<α<1300mm
1300mm
3. Handling & Protection
Summary Matrix
3.2 Wires:
700mm
Length: 700mm<α<1300mm
1300mm
3. Handling & Protection
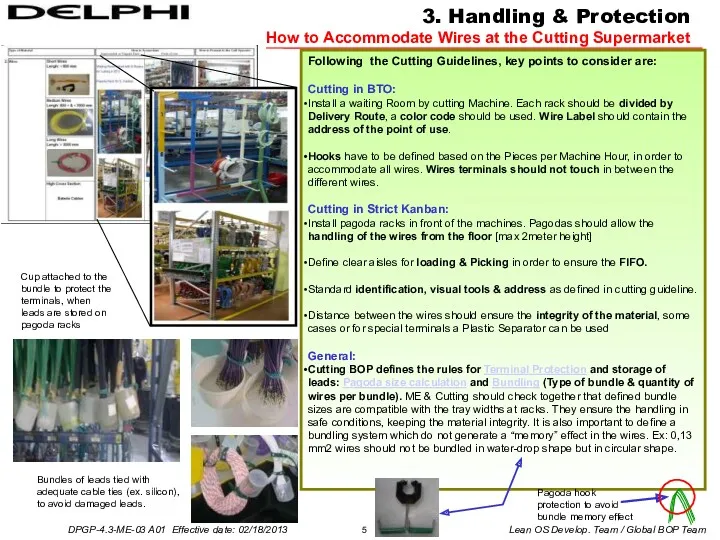
How to Accommodate Wires at the Cutting Supermarket
Following
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Wires at the Cutting Supermarket
Following
Cutting in BTO:
Install a waiting Room by cutting Machine. Each rack should be divided by Delivery Route, a color code should be used. Wire Label should contain the address of the point of use.
Hooks have to be defined based on the Pieces per Machine Hour, in order to accommodate all wires. Wires terminals should not touch in between the different wires.
Cutting in Strict Kanban:
Install pagoda racks in front of the machines. Pagodas should allow the handling of the wires from the floor [max 2meter height]
Define clear aisles for loading & Picking in order to ensure the FIFO.
Standard identification, visual tools & address as defined in cutting guideline.
Distance between the wires should ensure the integrity of the material, some cases or for special terminals a Plastic Separator can be used
General:
Cutting BOP defines the rules for Terminal Protection and storage of leads: Pagoda size calculation and Bundling (Type of bundle & quantity of wires per bundle). ME & Cutting should check together that defined bundle sizes are compatible with the tray widths at racks. They ensure the handling in safe conditions, keeping the material integrity. It is also important to define a bundling system which do not generate a “memory” effect in the wires. Ex: 0,13 mm2 wires should not be bundled in water-drop shape but in circular shape.
Pagoda hook protection to avoid bundle memory effect
Cup attached to the bundle to protect the terminals, when leads are stored on pagoda racks
Bundles of leads tied with adequate cable ties (ex. silicon), to avoid damaged leads.
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Wires at the Point of
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Wires at the Point of
Wire Presentation should provide the conditions to produce in high quality & with High Manpower Utilization:
General
Wire quantity at the point of use is defined based on the bundle size and on delivery route frequency. Rack should accommodate this volume. Second bundle should be at the point of use. For hourly routes kanban should represent 2 hours.
Based on the terminal analysis, the following wires must be hung so that the problematic terminal is in front (to the operator side).
- Sensitive terminals (easily bent or broken while pulling or transporting - e.g. male terminals).
- Sealed terminals
- Sharp terminals (sharp terminal damage the insulation of wires)
- Double crimped terminals
- Wide terminals that may cause the bundle to fall down when being pulled by the operator e.g. 0,13mm2 gage wires, busbar terminals
0,13mm2 wires which are longer than 4000mm should be hanged with cups at both ends in order to give the bundle some weight. The plugging operator is going to take out the cup but the bundle should still be bind with plastic straps if not in use.
Wires, kits and harnesses must be hung as high as necessary to keep a distance to the floor of at least 15 cm.
Different wires part number should not touch in between them, so it is necessary either to implement physical separators – [ see rack chapter]
The rack and the physical separators must not have sharp edges or rough surfaces that may hurt the operator or damage the wires.
Wires should be presented for the operators in sequence, according to the method (see MFS #10). Separate similar wires (colors, lengths, cross-sections…) for error proofing (see MFS #2)
Wire identification & wire Kit option should be visible from the operator point of view.
Wire Cutting Label should be positioned close to the end at the operator side and should be the last wire of the bundle to be consumed.
Point of use
Back side
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Wires at the Point of
3. Handling & Protection
How to Accommodate Wires at the Point of
Short Wires
Use Horizontal Tubes or U metal profile support. All the wire should be inside of the tool, in terms of length and height.
Medium & Long Wires
Use the Rack [see rack chapter]
Special Wires
Do not hang fiber optic leads or water / vacuum pipes. They must be coiled and presented in a box or hung as a coil in a hook. The fiberoptics can be brought in their original boxes as long as the space in racks allow.
Check the bending radius of the tubes to hang the wires, as the higher the cross section the bigger the radius
Bus bar leads must be stored in a box if they are short enough.
Special workplace for battery cable and fuse-box leads (wires with big terminals on both sides). High Cross Section &/ Big Terminals & AL Cables (ex: batery cables, etc) are placed into the trays. Tray length is defined according to the wire length.
Terminal Protection
All Racks or wire tools should provide the conditions to protect terminals. All tools where leads are placed, must be free of sharp edges or any shape which could damage the terminals / cable.
Short Wires
Medium & Long Wires
Physical Separators between Wires
Enough Room to accommodate all wires
Next slide more examples
Physical Separators between Wires
3. Handling & Protection
Wires at Point of Use
Physical Separators between Wires
3. Handling & Protection
Wires at Point of Use
1. Terminals Protection from both side of the rack
2. Short Wires
3. High cross section Wires
4. Rack where the space between wires ensures terminals & wires are not mixed
5. Separators in front not to mix wires
3. Handling & Protection
Wires at Point of Use Examples
6. Terminals Protection
3. Handling & Protection
Wires at Point of Use Examples
6. Terminals Protection
7. Terminals Protection from the back side of the rack with transparent flexible tool
All systems with an easy concept to load & pick up leads
Different leads codes will not touch the other ones placed close on the racks.
3. Handling & Protection
Wires at Point of Use Examples
8. Terminals Protection
3. Handling & Protection
Wires at Point of Use Examples
8. Terminals Protection
9. Terminals Protection from the front side of the rack
10. Optical Fibers in containers
11. Battery Cable in special trays with 2 positions per wire to support delivery routes
12. For high cross section cables with not very big terminals, waterfall type special trays
3. Handling & Protection
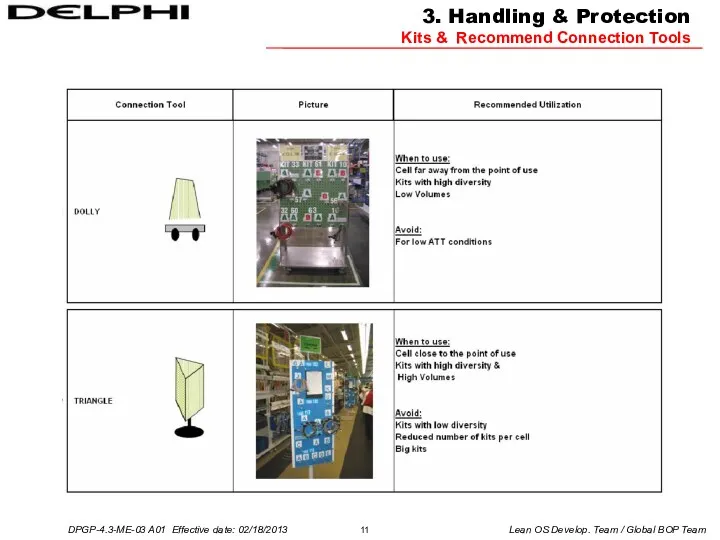
Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
3. Handling & Protection
Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
3. Handling & Protection
Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
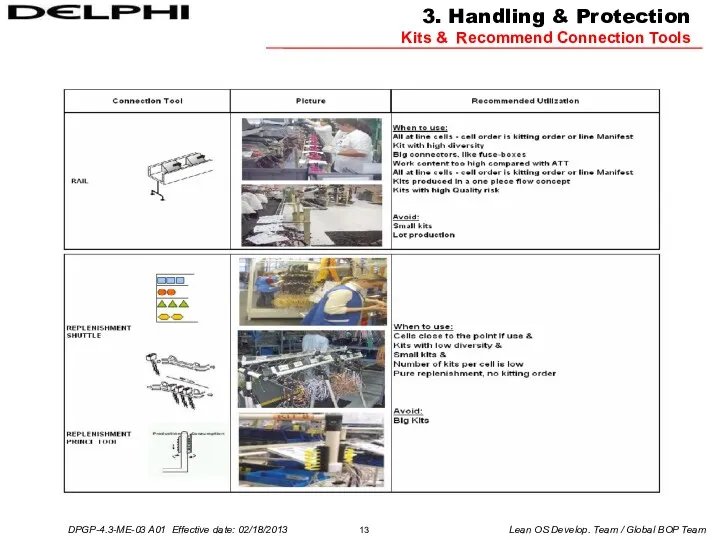
3. Handling & Protection
Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
3. Handling & Protection
Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
3. Handling & Protection
Kits & Recommend Connection Tools
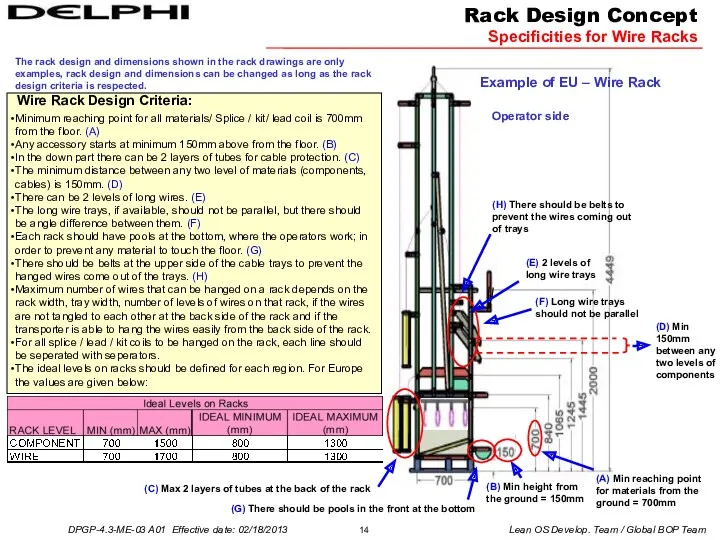
Wire Rack Design Criteria:
Minimum reaching point for all materials/ Splice /
Wire Rack Design Criteria:
Minimum reaching point for all materials/ Splice /
Any accessory starts at minimum 150mm above from the floor. (B)
In the down part there can be 2 layers of tubes for cable protection. (C)
The minimum distance between any two level of materials (components, cables) is 150mm. (D)
There can be 2 levels of long wires. (E)
The long wire trays, if available, should not be parallel, but there should be angle difference between them. (F)
Each rack should have pools at the bottom, where the operators work; in order to prevent any material to touch the floor. (G)
There should be belts at the upper side of the cable trays to prevent the hanged wires come out of the trays. (H)
Maximum number of wires that can be hanged on a rack depends on the rack width, tray width, number of levels of wires on that rack, if the wires are not tangled to each other at the back side of the rack and if the transporter is able to hang the wires easily from the back side of the rack.
For all splice / lead / kit coils to be hanged on the rack, each line should be seperated with seperators.
The ideal levels on racks should be defined for each region. For Europe the values are given below:
(B) Min height from the ground = 150mm
(A) Min reaching point for materials from the ground = 700mm
(C) Max 2 layers of tubes at the back of the rack
(E) 2 levels of long wire trays
(D) Min 150mm between any two levels of components
(G) There should be pools in the front at the bottom
(H) There should be belts to prevent the wires coming out of trays
Rack Design Concept
Specificities for Wire Racks
Example of EU – Wire Rack
(F) Long wire trays should not be parallel
Operator side
The rack design and dimensions shown in the rack drawings are only examples, rack design and dimensions can be changed as long as the rack design criteria is respected.
Rack Design Concept
Example of Europe - Rack Type 3
FRONT VIEW
Rack Design Concept
Example of Europe - Rack Type 3
FRONT VIEW
Operator side
Cell Design
Some Examples & Distances
The connection tool is chosen according to
Cell Design
Some Examples & Distances
The connection tool is chosen according to
an example layout is given below:
1m
1,6 m
2,6 meters
Cell Design
Some Examples & Distances
The connection tool is chosen according to
Cell Design
Some Examples & Distances
The connection tool is chosen according to
an example layout is given below:
Cell Design
Some Examples & Distances
The connection tool is chosen according to
Cell Design
Some Examples & Distances
The connection tool is chosen according to
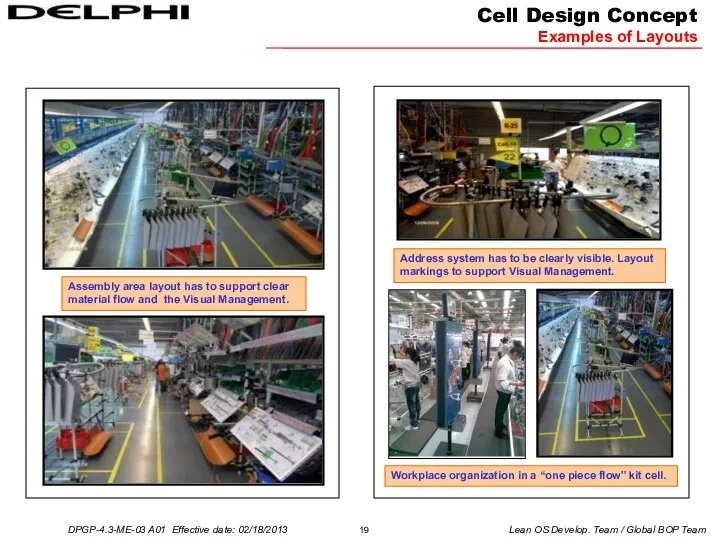
Assembly area layout has to support clear material flow and the
Assembly area layout has to support clear material flow and the
Address system has to be clearly visible. Layout markings to support Visual Management.
Cell Design Concept
Examples of Layouts
Workplace organization in a “one piece flow” kit cell.
5. Standardized Work
Impact of the Workplace Organization on the Manpower Results
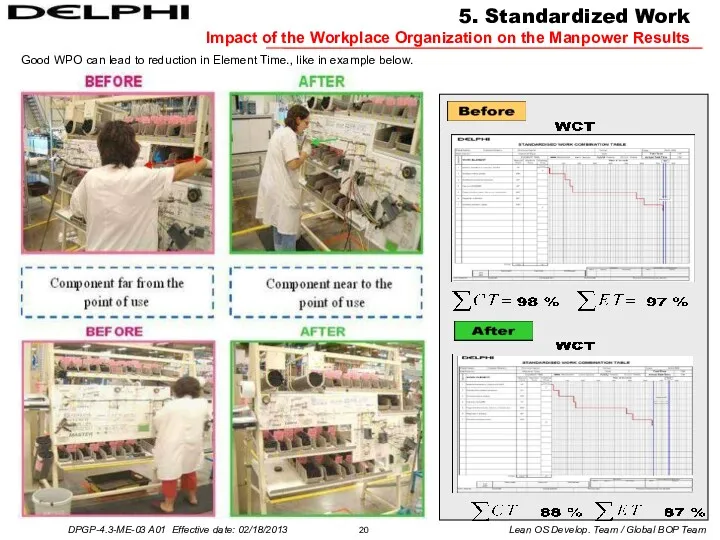
Good
5. Standardized Work
Impact of the Workplace Organization on the Manpower Results
Good











 Организация развлекательных услуг в гостинице
Организация развлекательных услуг в гостинице Комплекс транспортно-экспедиционного обслуживания
Комплекс транспортно-экспедиционного обслуживания Виды бизнес-процессов. Управление бизнес-процессами
Виды бизнес-процессов. Управление бизнес-процессами Институциональное управление проектами
Институциональное управление проектами Защита отчетов по производственной и преддипломной практикам. Специальность 38.00.00 Экономика и управление
Защита отчетов по производственной и преддипломной практикам. Специальность 38.00.00 Экономика и управление Операционная система предприятия
Операционная система предприятия Транспортная логистика. (Тема 6)
Транспортная логистика. (Тема 6) Власть и лидерство
Власть и лидерство Управление разработкой инновационными проектами. Понятия, основные этапы создания и реализация
Управление разработкой инновационными проектами. Понятия, основные этапы создания и реализация Продажі й обслуговування JYSK Тренінг для персоналу магазину
Продажі й обслуговування JYSK Тренінг для персоналу магазину Сертифицированный CQI и IRCA курс ведущего аудитора по стандарту ISO 45001 Системы менеджмента охраны здоровья и безопасности
Сертифицированный CQI и IRCA курс ведущего аудитора по стандарту ISO 45001 Системы менеджмента охраны здоровья и безопасности Диаграмма Исикавы. Рыбий скелет Исикавы
Диаграмма Исикавы. Рыбий скелет Исикавы Базовые понятия современной концепции управления проектом
Базовые понятия современной концепции управления проектом Емтихан үстіндегі сенімділік. Сенімділік күш береді
Емтихан үстіндегі сенімділік. Сенімділік күш береді Организация трудовых процессов и оплаты труда. Лекция 25
Организация трудовых процессов и оплаты труда. Лекция 25 Функции управления. Стратегическое планирование, предвидение, прогнозирование. Мотивация. Построение организаций (координация)
Функции управления. Стратегическое планирование, предвидение, прогнозирование. Мотивация. Построение организаций (координация)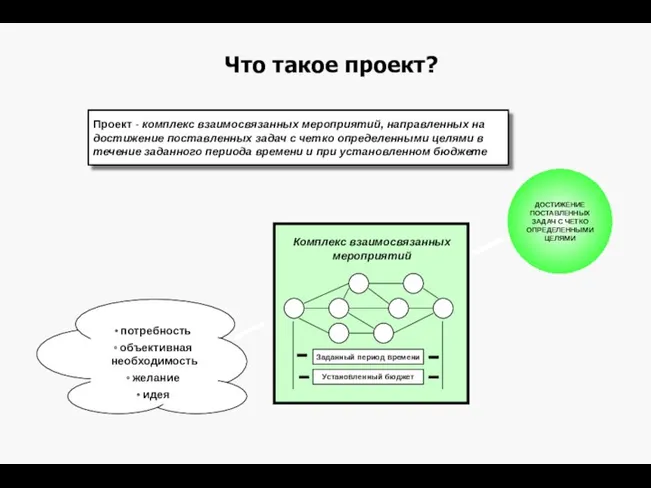 Управление проектами
Управление проектами Personalo valdymo metodologija
Personalo valdymo metodologija Аналіз ринку логістичних послуг в Україні
Аналіз ринку логістичних послуг в Україні Turistik deneyim
Turistik deneyim Работа менеджера. Содержание и базовые модели
Работа менеджера. Содержание и базовые модели Особенности организации обслуживания потребителей в сельском кафе Лидер
Особенности организации обслуживания потребителей в сельском кафе Лидер Организация государственного налогового менеджмента
Организация государственного налогового менеджмента Организация труда персонала
Организация труда персонала Новое общественное управление
Новое общественное управление Инновационный менеджмент
Инновационный менеджмент Swot-анализ. Особенности применения и методология проведени
Swot-анализ. Особенности применения и методология проведени Комплекс управленческих мероприятий по повышению эффективности деятельности организации ООО Неаполь
Комплекс управленческих мероприятий по повышению эффективности деятельности организации ООО Неаполь