Содержание
- 2. Research Methods Why is it important to understand research methods for interdisciplinary researchers? Types of research
- 3. Research methods as boundary object in interdisciplinary research Study of cross-disciplinary research collaboration (Mercier, Penuel, Remold,
- 4. … [a child] was brought back for me to test, and I was putting [an ERP]
- 5. It’s difficult because you do form close relationships with the families…. So it was then much
- 6. Two Types of Research Quantitative Experimental Surveys (usually) Qualitative Biography, phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography & case
- 7. What do you want your data & results to look like? Do you want to show
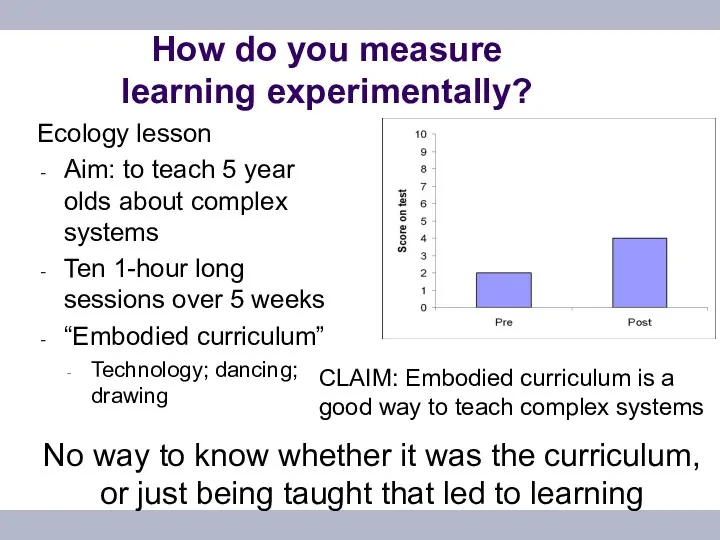
- 8. How do you measure learning experimentally? Ecology lesson Aim: to teach 5 year olds about complex
- 9. How do you measure learning experimentally? (and know that it’s because of what you did…) Pre/post
- 10. How do you measure learning experimentally? (and know that it’s because of what you did…) Control
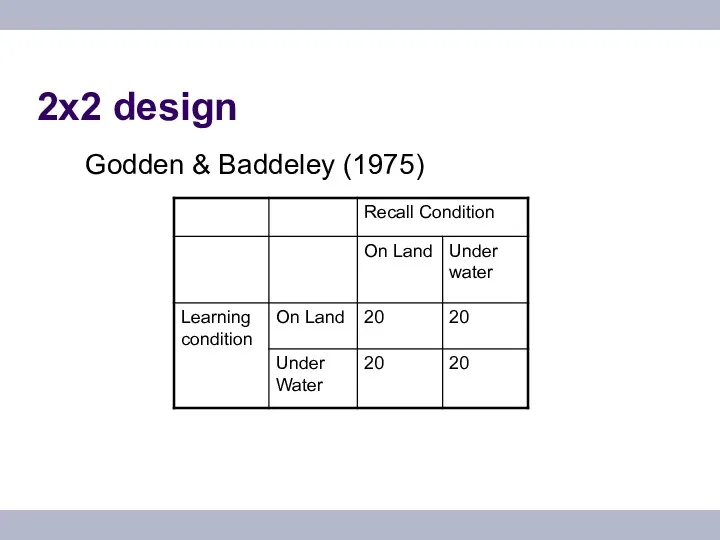
- 11. 2x2 design Godden & Baddeley (1975)
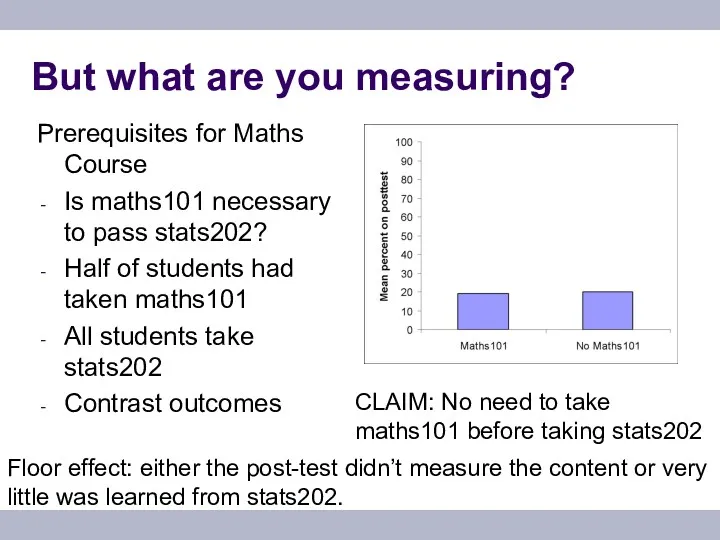
- 12. But what are you measuring? Prerequisites for Maths Course Is maths101 necessary to pass stats202? Half
- 13. But what are you measuring… Is it valid? Internal validity (is the effect caused by the
- 14. What sort of learning will you measure?
- 15. Important statistical ideas Independent variables The thing you manipulate/control for Main effects & Interaction effects between
- 16. Important statistical ideas Level of measurement Nominal Ordinal Interval (& ranking) Population & sample Normal distribution
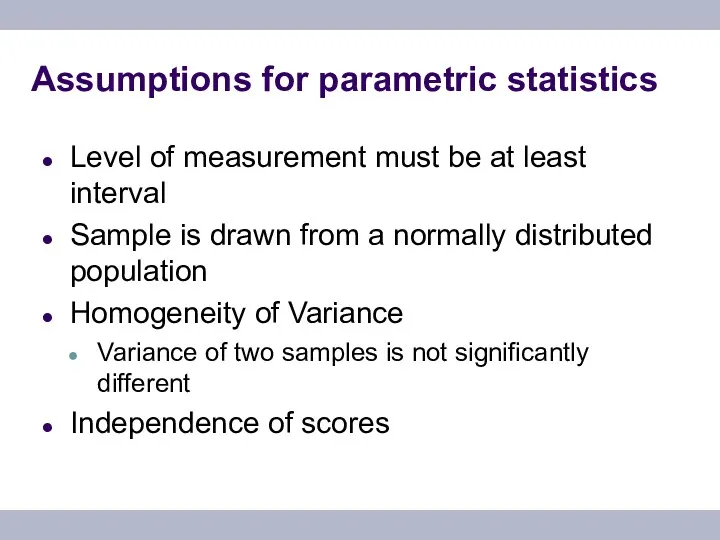
- 17. Assumptions for parametric statistics Level of measurement must be at least interval Sample is drawn from
- 18. Questions?
- 19. Key things to look for: Are the differences between conditions significant: T-tests, ANOVA, Chi Square Is
- 20. Survey design In the past 24 hours, did you watch more than an hour of television
- 22. Скачать презентацию


![… [a child] was brought back for me to test,](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/288030/slide-3.jpg)











 Pskov Technical Lyceum
Pskov Technical Lyceum Как создать свой социальный проект
Как создать свой социальный проект Ознайомча практика курсантами першого курсу юридичного факультету
Ознайомча практика курсантами першого курсу юридичного факультету Месячник школьных библиотек
Месячник школьных библиотек ВУЗы России
ВУЗы России Тукай безнең күңелләрдә
Тукай безнең күңелләрдә Технология создания модульных программ
Технология создания модульных программ Презентация Следы на снегу к занятию по экологии родного края.
Презентация Следы на снегу к занятию по экологии родного края. Организация профориентационной работы с младшими школьниками в условиях реализации ФГОС НОО
Организация профориентационной работы с младшими школьниками в условиях реализации ФГОС НОО Аттестация педагогических кадров в Пермском крае
Аттестация педагогических кадров в Пермском крае Шаблон презентации
Шаблон презентации Методика оформления научных работ
Методика оформления научных работ Презентация Первое знакомство с В.П. Астафьевым
Презентация Первое знакомство с В.П. Астафьевым Исследовательская работа по теме: Образование в России и США
Исследовательская работа по теме: Образование в России и США Использование ИКТ на уроках математики.
Использование ИКТ на уроках математики. Психолого-медико-педагогический консилиум образовательного учреждения
Психолого-медико-педагогический консилиум образовательного учреждения Отношение к ребёнку в разные эпохи
Отношение к ребёнку в разные эпохи Строительный институт. 08.03.01 Строительство (академический бакалавриат)
Строительный институт. 08.03.01 Строительство (академический бакалавриат) Global Citizen. Международная программа молодежных обменов AIESEC
Global Citizen. Международная программа молодежных обменов AIESEC Гражданско-патриотическое воспитание учащихся в системе СПО (НПО)
Гражданско-патриотическое воспитание учащихся в системе СПО (НПО) Общие требования к оформлению учебно-практических работ (рефератов, докладов)
Общие требования к оформлению учебно-практических работ (рефератов, докладов) портфолио
портфолио Профсоюзный комитет
Профсоюзный комитет Конкурс Знатоки истории
Конкурс Знатоки истории Презентация Животные водоемов Астраханской области
Презентация Животные водоемов Астраханской области Правила оформления научных работ
Правила оформления научных работ Авторские школы России
Авторские школы России Энциклопедия школьной жизни
Энциклопедия школьной жизни