Содержание
- 2. OCLC: Why another linked data project? OCLC: What is it? OCLC: Who is building it? OCLC:
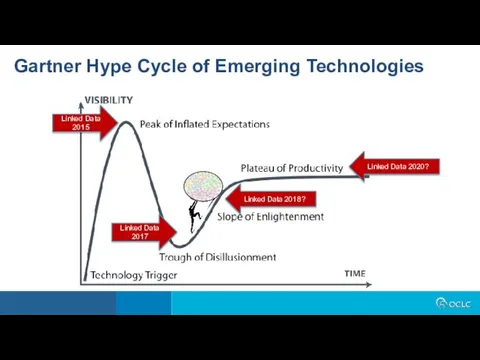
- 3. Gartner Hype Cycle of Emerging Technologies Linked Data 2017 Linked Data 2015 Linked Data 2018? Linked
- 4. Why?--Efficient, impactful workflows Today Searching Copy cataloging Original cataloging Authorities In the future Amplified searching Adding
- 5. A project vision statement Work with our members through a foundational shift in the collaborative work
- 6. Phase I Partners (Dec ’17 - Apr ‘18) Cornell University University of California, Davis Who Phase
- 7. WHAT & HOW
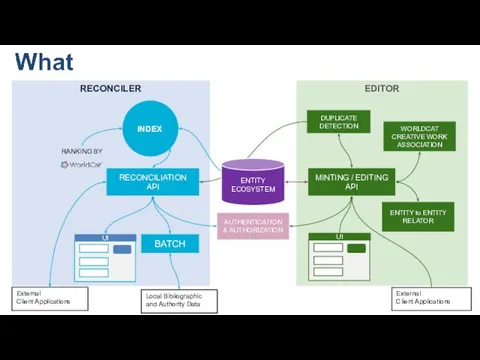
- 8. What Develop an Entity Ecosystem that facilitates: Creation and editing of new entities Connecting entities to
- 9. RECONCILER INDEX RECONCILIATION API BATCH Local Bibliographic and Authority Data RANKING BY EDITOR DUPLICATE DETECTION WORLDCAT
- 10. How: A few key technologies
- 11. Wikipedia – a multilingual web-based free-content encyclopedia MediaWiki - a free and open-source wiki software Wikidata.org
- 12. Search/Autosuggest/APIs Multilingual UI Wikitext editor Change history Discussion pages Users and rights Watchlists Maintenance reports Etc.
- 13. Search/Autosuggest/APIs/Linked Data/SPARQL Multilingual UI Structured data editor Change history Discussion pages Users and rights Watchlists Maintenance
- 14. Open source An all-purpose data model that takes knowledge diversity, sources, and multilingual usage seriously Collaborative
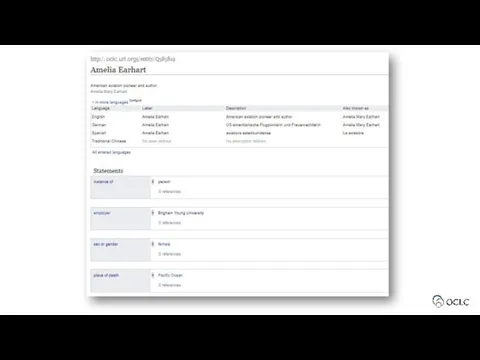
- 15. Entity – the content of a page in the system that represents an item or a
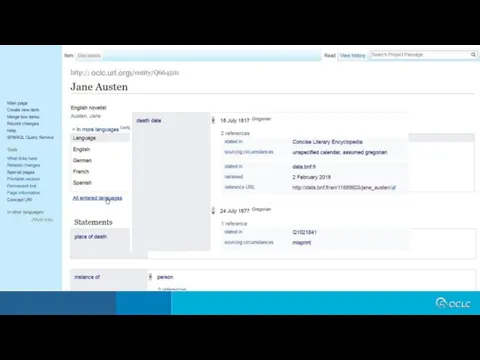
- 16. Statement -- a piece of data about an item, recorded on the item's page. A statement
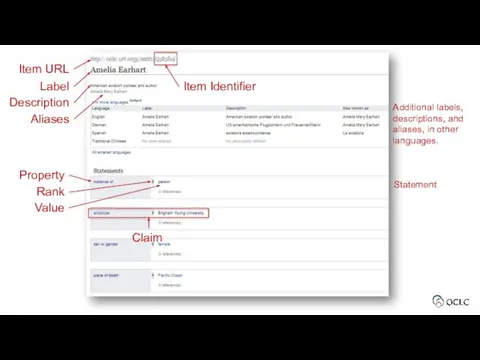
- 18. Item URL Item Identifier Label Description Aliases Additional labels, descriptions, and aliases, in other languages. Property
- 19. FUNCTIONAL USE CASES
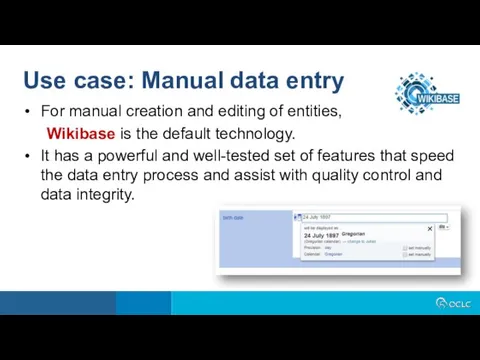
- 20. For manual creation and editing of entities, Wikibase is the default technology. It has a powerful
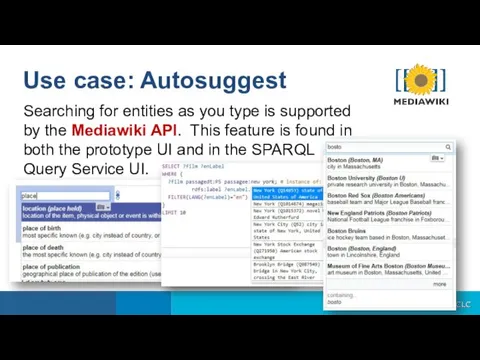
- 23. Searching for entities as you type is supported by the Mediawiki API. This feature is found
- 24. SPARQL (pronounced "sparkle") is an RDF query language … a semantic query language for databases. The
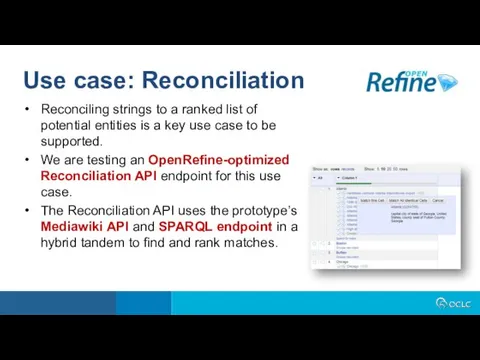
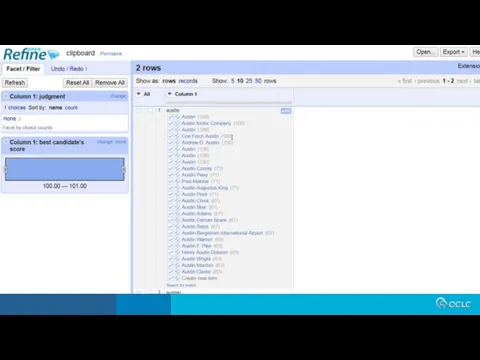
- 25. Reconciling strings to a ranked list of potential entities is a key use case to be
- 27. For batch loading new items and properties, and subsequent batch updates and deletions, OCLC staff use
- 29. The Why: Cornell's Motivations and Potential Uses
- 30. Local authority management system National Strategy for Shareable Local Name Authorities National Forum Local entities Motivation
- 31. Motivation : Complementary Effort #2 Minting person and organization identities &
- 32. Look-up services within cataloging environments Motivation : Complementary Effort #3
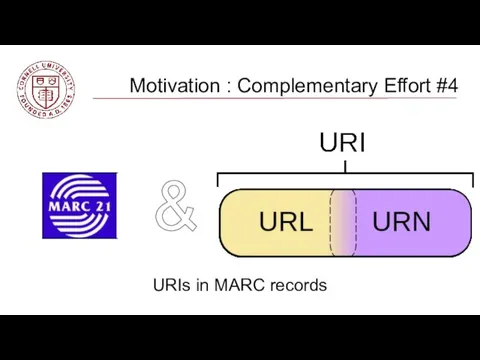
- 33. URIs in MARC records Motivation : Complementary Effort #4 &
- 34. New ILS affords new opportunities Motivation : Complementary Effort #5
- 35. Hopes & Dreams Low-threshold entity creation Streamlining workflows across processes Reconciliation services in MARC-2-RDF conversion Data
- 36. Finally... What's in it for us (condensed)?
- 38. Скачать презентацию
























 Право на образование в РФ
Право на образование в РФ Обобщение опыта работы по теме: Здоровьесберегающие технологии в начальной школе.
Обобщение опыта работы по теме: Здоровьесберегающие технологии в начальной школе. Севооборот. Доступная среда образовательной организации
Севооборот. Доступная среда образовательной организации Бизнес-план по оказанию платных дополнительных образовательных услуг. Кружок изобразительной деятельности для детей 5-7 лет
Бизнес-план по оказанию платных дополнительных образовательных услуг. Кружок изобразительной деятельности для детей 5-7 лет Название доклада. Шаблон
Название доклада. Шаблон ИТ-факультет Московского Политеха: от идеи до тиражирования практик
ИТ-факультет Московского Политеха: от идеи до тиражирования практик Підготовка дітей до школи з урахуванням вимог сучасної школи
Підготовка дітей до школи з урахуванням вимог сучасної школи Центр поддержки добровольчества муниципального образования – Сапожковский муниципальный район Рязанской области
Центр поддержки добровольчества муниципального образования – Сапожковский муниципальный район Рязанской области Использование технологии Портфолио в работе органов ученического самоуправления на примере модели Класс-город
Использование технологии Портфолио в работе органов ученического самоуправления на примере модели Класс-город Описательно-систематическое направление в школьном естественнонаучном образовании
Описательно-систематическое направление в школьном естественнонаучном образовании Родительское собрание Проведение государственной итоговой аттестации выпускников 9 классов в 2022 году
Родительское собрание Проведение государственной итоговой аттестации выпускников 9 классов в 2022 году Основные итоги первого года реализации муниципальной Стратегии развития образования города Шарыпово
Основные итоги первого года реализации муниципальной Стратегии развития образования города Шарыпово Институциональная аккредитация Международного университета информационных технологий
Институциональная аккредитация Международного университета информационных технологий Предупреждение перегрузки учащихся при выполнении домашнего задания
Предупреждение перегрузки учащихся при выполнении домашнего задания Виїздне засідання методичного об'єднання вчителів української мови та літератури
Виїздне засідання методичного об'єднання вчителів української мови та літератури Что такое проект. Программа междисциплинарного индивидуального гуманитарного образования
Что такое проект. Программа междисциплинарного индивидуального гуманитарного образования Методические возможности завершённой предметной линии учебников Русский язык в реализации требований ФГОС НОО
Методические возможности завершённой предметной линии учебников Русский язык в реализации требований ФГОС НОО Об организации и проведении государственной итоговой аттестации по образовательным программам среднего общего образования
Об организации и проведении государственной итоговой аттестации по образовательным программам среднего общего образования Материалы к конкурсу Учитель года-2016 (урок по окружающему миру во 2 классе)
Материалы к конкурсу Учитель года-2016 (урок по окружающему миру во 2 классе) Государственная программа развития образования Республики Казахстан на 2011 – 2020 годы
Государственная программа развития образования Республики Казахстан на 2011 – 2020 годы Техногенная культура. Тема 4
Техногенная культура. Тема 4 Подготовка ИТ специалистов в университетах Твери
Подготовка ИТ специалистов в университетах Твери Государственная итоговая аттестация по образовательным программам основного общего образования в 2021 году
Государственная итоговая аттестация по образовательным программам основного общего образования в 2021 году Электронные формы учебников
Электронные формы учебников Музыкальное училище им. Г.И. Шадриной Ульяновского государственного университета
Музыкальное училище им. Г.И. Шадриной Ульяновского государственного университета Клуб семейного обучения Стимул
Клуб семейного обучения Стимул Профессия – химик-аналитик. Направления специализации
Профессия – химик-аналитик. Направления специализации Прогнозирование в сфере Образование и культура
Прогнозирование в сфере Образование и культура