Содержание
- 2. Organization of this lecture Research and Methodology: Research defined and described Some classifications of research Define
- 3. Research Defined and Described “Research is the systematic approach to obtaining and confirming new and reliable
- 4. Notice that: “… truth was not used in the definition of research” (p 16) “This concept
- 5. Research is not Accidental discovery : Accidental discovery may occur in structured research process Usually takes
- 6. Research is not … cont. Data Collection an intermediate step to gain reliable knowledge collecting reliable
- 7. Research is not … cont. Searching out published research results in libraries (or the internet) This
- 8. Research is… Searching for explanation of events, phenomena, relationships and causes What, how and why things
- 9. All well designed and conducted research has potential application. Failure to see applications can be due
- 10. Public good Public research is a public good May be more rigorous and objective because it
- 11. Classification of Research Before classification, we must first define types of research Different criteria are used
- 12. Basic vs Applied Research Basic – to determine or establish fundamental facts and relationships within a
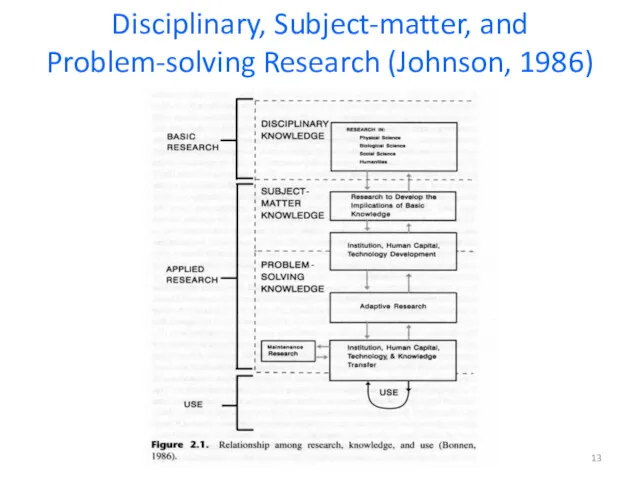
- 13. Disciplinary, Subject-matter, and Problem-solving Research (Johnson, 1986)
- 14. designed to improve a discipline dwells on theories, fundamental relationships and analytical procedures and techniques In
- 15. Provides the foundations for applied research Circular as applied research reveals the shortcomings of disciplinary research
- 16. Subject-matter research “research on a subject of interest to a set of decision makers “ (p
- 17. Subject-matter research … cont. Provides policy makers with general knowledge to make decisions about various problems.
- 18. Problem-solving research Designed to solve a specific problem for a specific decision maker Often results in
- 19. Analytic vs Descriptive Research Descriptive Research – the attempt to determine, describe, or identify something The
- 20. Methodology Defined & Described Methodology and Method are often (incorrectly) used interchangeable Methodology – the study
- 21. Contrast research methodology in economics (the approach to research) to economic methodology (the general approach to
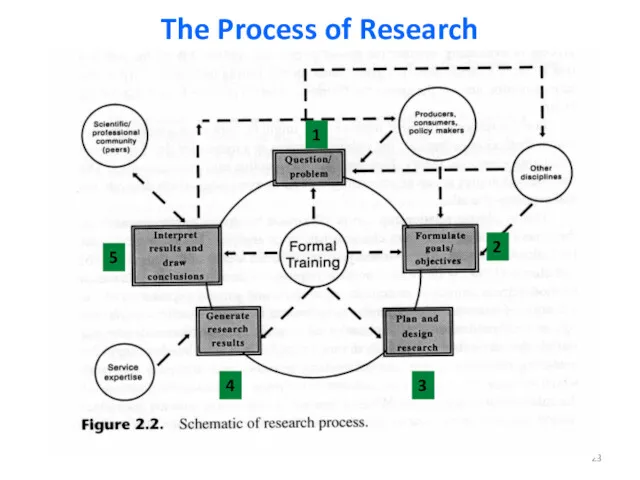
- 22. The Process of Research The process is initiated with a question or problem (step 1) Next,
- 23. The Process of Research
- 24. Creativity in the Research Process Research is a creative process “…research includes far more than mere
- 25. Fostering Creativity (Ladd 1987) Gather and use previously developed knowledge Exchange ideas Apply deductive logic Look
- 27. Скачать презентацию






















 Обобщение опыта работы
Обобщение опыта работы Презентация Технология продуктивного чтения
Презентация Технология продуктивного чтения Организация учебно-воспитательного процесса в 2020-2021 учебном году, в школе
Организация учебно-воспитательного процесса в 2020-2021 учебном году, в школе Набирая высоту. Московский Государственный Технический Университет Гражданской Авиации
Набирая высоту. Московский Государственный Технический Университет Гражданской Авиации Красная книга
Красная книга Казанский (Приволжский) федеральный университет
Казанский (Приволжский) федеральный университет УМК Перспективная начальная школа
УМК Перспективная начальная школа Россия в международных промышленных выставках. Проблемы художественно-промышленного образования в России ХIХ – начала ХХ века
Россия в международных промышленных выставках. Проблемы художественно-промышленного образования в России ХIХ – начала ХХ века Техникалық және кәсіптік, орта білімнен кейінгі білім беру жүйесінің педагогі: еңбек функцияларын жетілдіру
Техникалық және кәсіптік, орта білімнен кейінгі білім беру жүйесінің педагогі: еңбек функцияларын жетілдіру Скрепка. Проект
Скрепка. Проект Тема урока: Разработка сценария и технического задания проекта
Тема урока: Разработка сценария и технического задания проекта Первое методическое свидание. Переход на новые ФГОС СПО
Первое методическое свидание. Переход на новые ФГОС СПО Образование как социокультурный феномен. Система образования Республики Беларусь
Образование как социокультурный феномен. Система образования Республики Беларусь Білім мазмұнын жаңарту аясында оқушылардың оқу жетістігін критериалды бағалау
Білім мазмұнын жаңарту аясында оқушылардың оқу жетістігін критериалды бағалау Образовательная система Школа 2100
Образовательная система Школа 2100 Институциональная аккредитация Международного университета информационных технологий
Институциональная аккредитация Международного университета информационных технологий Федеральный закон Об образовании в Российской Федерации
Федеральный закон Об образовании в Российской Федерации Ассоциация победителей олимпиад. Институт стран Азии и Африки МГУ
Ассоциация победителей олимпиад. Институт стран Азии и Африки МГУ Организация проектной деятельности обучающихся в условиях реализации ФГОС ООО
Организация проектной деятельности обучающихся в условиях реализации ФГОС ООО Круглый стол. Использование ИКТ как одно из средств оптимизации образовательного процесса в начальной школе
Круглый стол. Использование ИКТ как одно из средств оптимизации образовательного процесса в начальной школе Организация образовательной деятельности в рамках введения новых ФГОС НОО
Организация образовательной деятельности в рамках введения новых ФГОС НОО Конкурс на лучшее студенческое научное общество ФГБОУ ВО ПСПбГМУ им. И.П. Павлова
Конкурс на лучшее студенческое научное общество ФГБОУ ВО ПСПбГМУ им. И.П. Павлова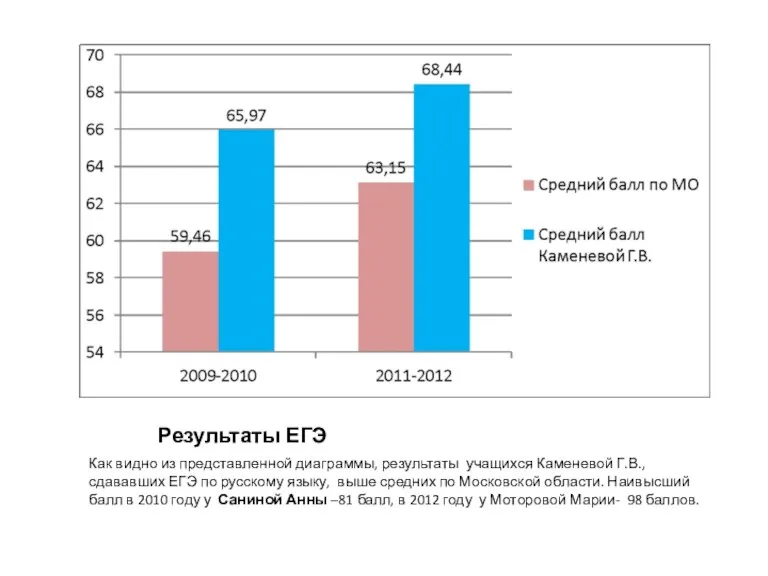 Результаты ЕГЭ
Результаты ЕГЭ Проблема междисциплинарных исследований в современной психолого-педагогической науке
Проблема междисциплинарных исследований в современной психолого-педагогической науке Правильное оформление бакалаврской работы. Работа с источниками
Правильное оформление бакалаврской работы. Работа с источниками История образования и педагогической мысли
История образования и педагогической мысли Портфолио. Фамилия имя
Портфолио. Фамилия имя Содержание образования как основа базовой культуры личности
Содержание образования как основа базовой культуры личности