Содержание
- 2. Geert Hofstede High vs Low context cultures Power distance Collectivism vs Individualism Masculinity vs Femininity Uncertainty
- 3. Geert Hofstede Geert Hofstede, (born 2 October 1928 in Haarlem, Netherlands) is an influential Dutch researcher
- 4. This division, which stems from E. T. Hall’s1 research, applies to the reliance on the immediate
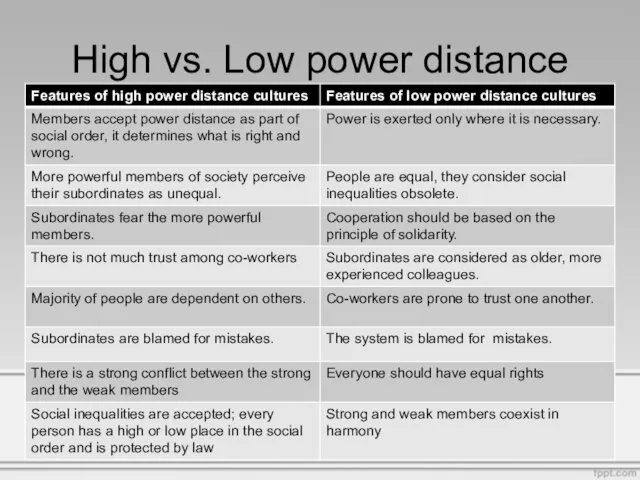
- 5. High vs. Low power distance
- 6. This dimension applies to the perception of power and authority by the less influential members of
- 7. It is the degree to which individuals are integrated into groups. In individualistic societies, the stress
- 8. Individualism vs Collectivism
- 9. Masculine cultures value success, money and material possessions, whereas feminine cultures place more value on relationships
- 10. Masculinity vs Femininity
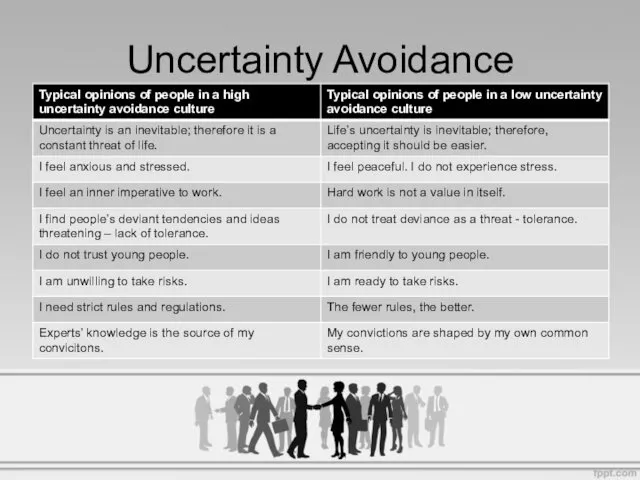
- 11. High uncertainty avoidance stems from striving for truth and the belief that it is in fact
- 12. Uncertainty Avoidance
- 13. This distinction was added as the last one to Hofstede's typology. It describes societies’ time perspective.
- 15. Скачать презентацию










 Социально – значимый проект: Комплекс Экопарк Учкуевка
Социально – значимый проект: Комплекс Экопарк Учкуевка Мир начинается с мамы
Мир начинается с мамы Метод Наблюдения
Метод Наблюдения Социальные ценнсти и нормы
Социальные ценнсти и нормы Профессии наших родителей
Профессии наших родителей Презентация к уроку Классификация налогов - 8 класс
Презентация к уроку Классификация налогов - 8 класс Топ 10 үздік рэпер
Топ 10 үздік рэпер Место молодежи в современном обществе
Место молодежи в современном обществе Generations
Generations Нации и национальные отношения
Нации и национальные отношения Этика семейных отношений. Этапы развития отношений мужчины и женщины
Этика семейных отношений. Этапы развития отношений мужчины и женщины Социально-психологическая сущность брака и семьи
Социально-психологическая сущность брака и семьи День пожилого человека
День пожилого человека Понятие социального контракта
Понятие социального контракта Своя игра по обществознанию Мы живем в обществе 7 класс
Своя игра по обществознанию Мы живем в обществе 7 класс Единая информационная система Добровольцы России
Единая информационная система Добровольцы России Человек и человечность. Гуманизм
Человек и человечность. Гуманизм Социальные институты и социальные организации
Социальные институты и социальные организации Общественная организация лиц, пострадавших от радиационных катастроф Союз-Чернобыль г. Рыбинска
Общественная организация лиц, пострадавших от радиационных катастроф Союз-Чернобыль г. Рыбинска Социальная стратификация и мобильность
Социальная стратификация и мобильность Женщины Архангельска в социальном пространстве города. Конференция
Женщины Архангельска в социальном пространстве города. Конференция Роль семьи в становлении личности
Роль семьи в становлении личности Опыт организации добровольческой (волонтерской) деятельности в стационарном учреждении социального обслуживания
Опыт организации добровольческой (волонтерской) деятельности в стационарном учреждении социального обслуживания Презентация к повторительно-обощающему уроку на тему: Социальные нормы
Презентация к повторительно-обощающему уроку на тему: Социальные нормы презентация Конституция РФ
презентация Конституция РФ Роль семьи в социализации личности. Семейные ценности
Роль семьи в социализации личности. Семейные ценности Структура молодежной общероссийской общественной организации Российские студенческие отряды
Структура молодежной общероссийской общественной организации Российские студенческие отряды Доброта спасет мир
Доброта спасет мир