Содержание
- 2. The technogenic catastrophe- is a major accident at an industrial site, entailing a massive loss of
- 3. And now we want to tell you about the 15 strongest technogenic catastrophes
- 4. Castle Bravo (March 1, 1954)
- 5. Соединенные Штаты в марте 1954 года произвели испытательный взрыв ядерного оружия в атолле Бикини, расположенного возле
- 6. Disaster in Seveso (July 10, 1976) The industrial disaster near Milan, Italy, occurred as a result
- 7. Catastrophe on the Three-Mile Island (March 28, 1979) The melting of part of the nuclear reactor
- 8. The release of oil from the tanker Exxon Valdez (March 24, 1989) As a result of
- 9. Explosion of the oil platform Horizon Oil (April 20, 2010) The explosion and flooding of the
- 10. The Disaster Love Channel (1978) In Niagara Falls, New York, about a hundred houses and a
- 11. Chemical pollution of Anniston, Alabama (1929-1971) В Аннистоне в районе, где сельскохозяйственный и биотехнологический гигант Монсанто
- 12. Oil fires in Kuwait (January / February 1991) During the military conflict in the Persian Gulf
- 13. Explosion at the Ziulin Chemical Plant (November 13, 2005) Several powerful explosions were blown up at
- 14. Pollution of Times Beach, Missouri (December, 1982) Spraying oil containing toxic dioxin led to the complete
- 15. Great smog (December, 1952) Within five days, smoke from coal burning and factory emissions covered London
- 16. Poisoning of Minamata Bay, Japan (1950s) For 37 years of plastics production, the petrochemical company Chisso
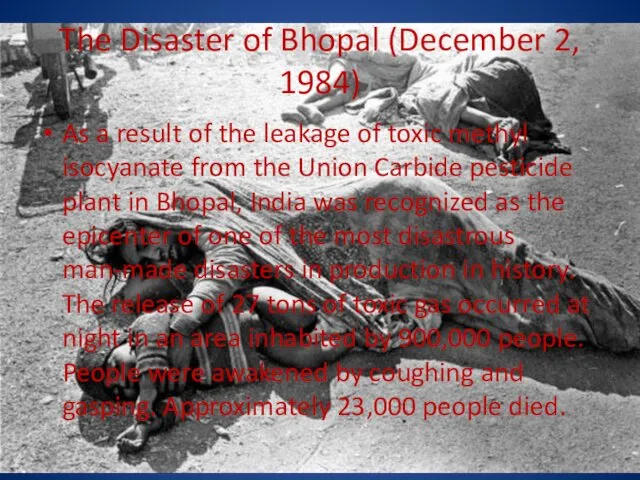
- 17. The Disaster of Bhopal (December 2, 1984) As a result of the leakage of toxic methyl
- 18. Chernobyl (April 26, 1986) The whole world knows about radiation contamination as a result of the
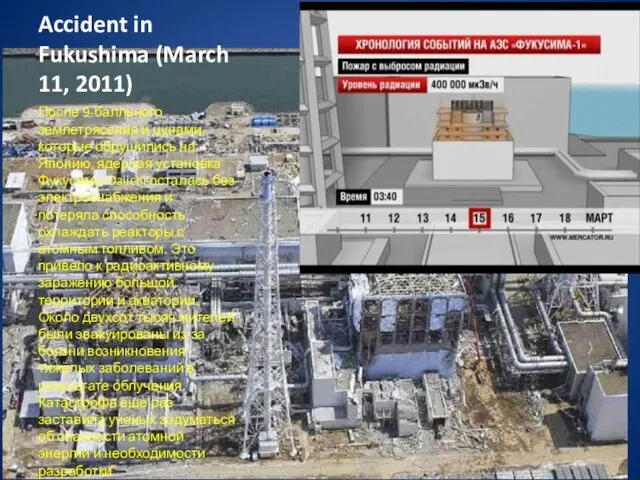
- 19. Accident in Fukushima (March 11, 2011) После 9-балльного землетрясения и цунами, которые обрушились на Японию, ядерная
- 21. Скачать презентацию
















 Лекция по дисциплине Начальная профессиональная подготовка специальность Пожарная безопасность
Лекция по дисциплине Начальная профессиональная подготовка специальность Пожарная безопасность Аварийно-спасательные и другие неотложные работы
Аварийно-спасательные и другие неотложные работы Квест-игра по правилам дорожного движения в подготовительной группе Путешествие по улицам города
Квест-игра по правилам дорожного движения в подготовительной группе Путешествие по улицам города Прогнозирование обстановки при чрезвычайных ситуациях
Прогнозирование обстановки при чрезвычайных ситуациях Анализ и оценка условий труда на производстве
Анализ и оценка условий труда на производстве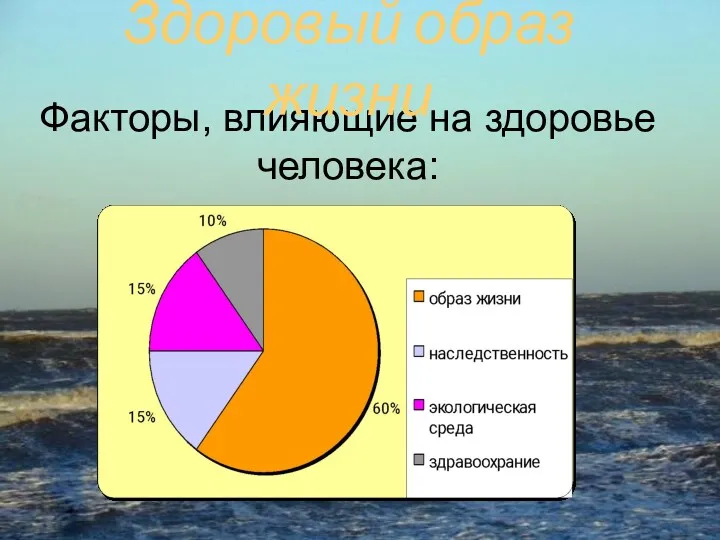 Факторы, влияющие на здоровье человека
Факторы, влияющие на здоровье человека Автоматическая пожарная сигнализация на предприятиях
Автоматическая пожарная сигнализация на предприятиях Hygiene of nutrition
Hygiene of nutrition Техногенні небезпеки та їх вражаючі фактори
Техногенні небезпеки та їх вражаючі фактори Вред табакокурения
Вред табакокурения Охрана труда
Охрана труда Основы военной службы. Тесты по ОБЖ для 11 классов
Основы военной службы. Тесты по ОБЖ для 11 классов Защита территории от чрезвичайных ситуаций. Организация аварийно – спасательных работ в зоне чрезвычайной ситуации
Защита территории от чрезвичайных ситуаций. Организация аварийно – спасательных работ в зоне чрезвычайной ситуации Обеспечение пожарной безопасности производственных и бытовых объектов
Обеспечение пожарной безопасности производственных и бытовых объектов Влияние насвая на здоровье подростков
Влияние насвая на здоровье подростков Опасные ситуации и меры предосторожности в местах большого скопления людей
Опасные ситуации и меры предосторожности в местах большого скопления людей Урок Обеспечение человека в природной среде при автономном существование
Урок Обеспечение человека в природной среде при автономном существование Наводнения
Наводнения Путешествие без опасности. 4 класс
Путешествие без опасности. 4 класс Средства защиты работающих
Средства защиты работающих ТИПЫ КОСТРОВ
ТИПЫ КОСТРОВ Принципы, методы и средства обеспечения безопасности деятельности. Основы управления безопасностью деятельности
Принципы, методы и средства обеспечения безопасности деятельности. Основы управления безопасностью деятельности Ліквідація наслідків хімічно небезпечних НС. Тема 1.5
Ліквідація наслідків хімічно небезпечних НС. Тема 1.5 Помоги Незнайке. Дидактическая игра по правилам пожарной безопасности
Помоги Незнайке. Дидактическая игра по правилам пожарной безопасности Международный терроризм
Международный терроризм Организация работ по наряд-допуску
Организация работ по наряд-допуску 20231024_biologicheskoe_oruzhie
20231024_biologicheskoe_oruzhie ПДД и правила безопасности для всех
ПДД и правила безопасности для всех