Содержание
- 2. ozaikin@poczta.wwsi.edu.pl
- 3. ozaikin@poczta.wwsi.edu.pl
- 4. Ontological and Motivation aspects of competence-based learning process 21st International Conference on Knowledge Based and Intelligent
- 5. Background: open and distance learning (ODL) – new challenges and expectations Presentation plan 1 Competence-based larning
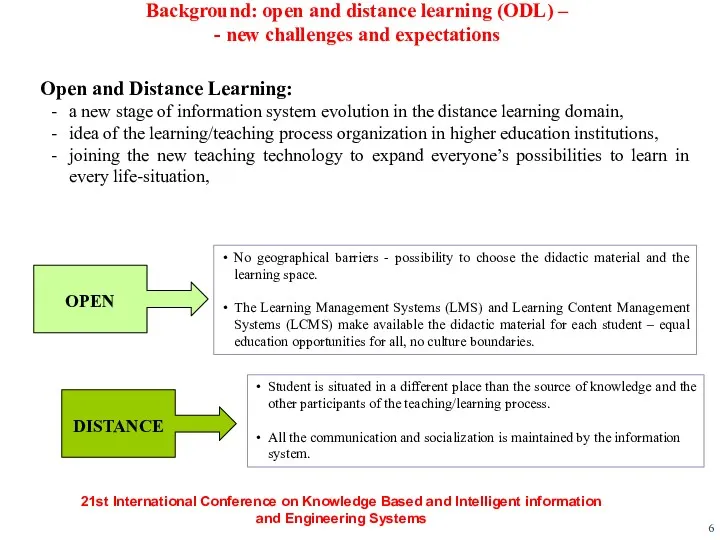
- 6. Background: open and distance learning (ODL) – - new challenges and expectations Open and Distance Learning:
- 7. ODL as a new way of learning The situation of higher education institutions in the world
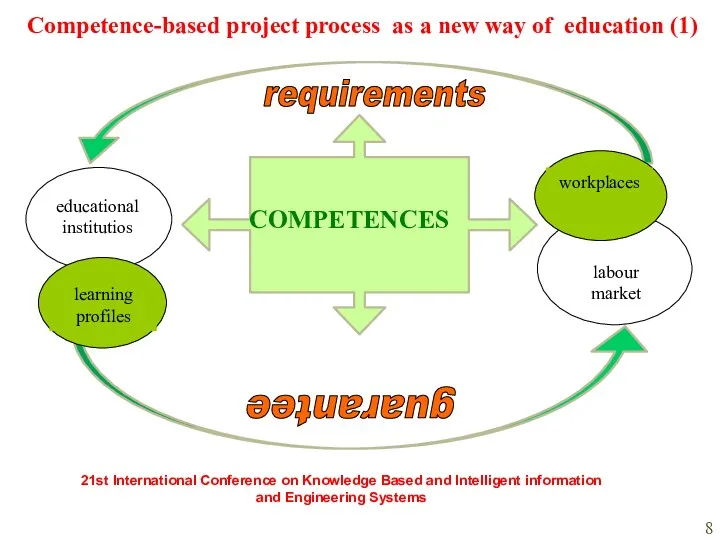
- 8. COMPETENCES guarantee requirements Competence-based project process as a new way of education (1) 21st International Conference
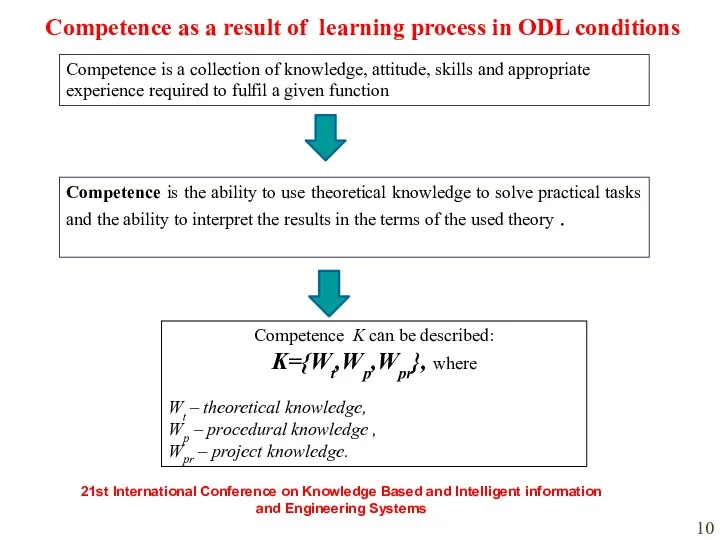
- 9. Competence as a result of learning process in ODL conditions Competence is a collection of knowledge,
- 10. Competence is the ability to use theoretical knowledge to solve practical tasks and the ability to
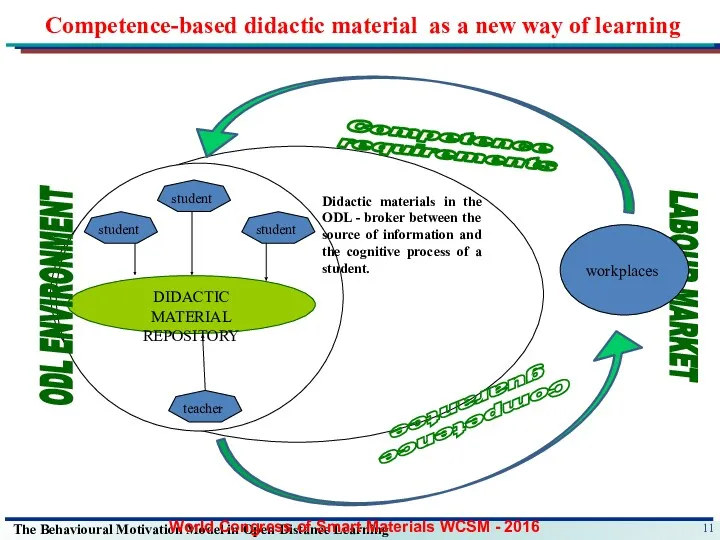
- 11. Competence guarantee Competence requirements student student student teacher DIDACTIC MATERIAL REPOSITORY ODL ENVIRONMENT LABOUR MARKET workplaces
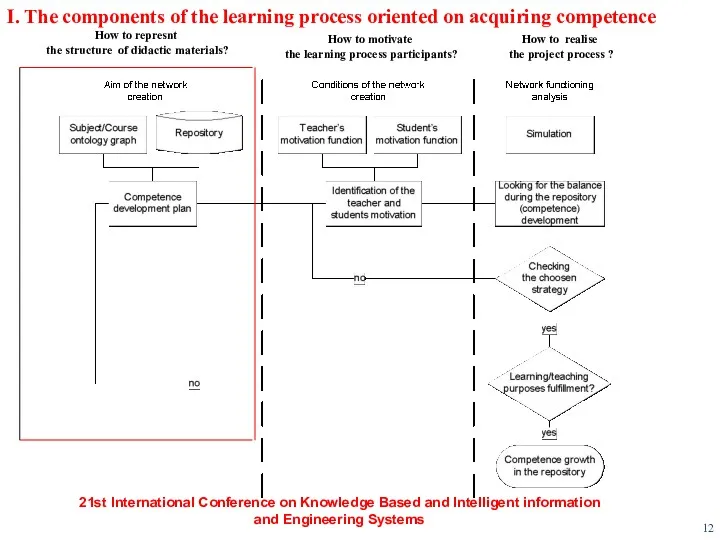
- 12. I. The components of the learning process oriented on acquiring competence How to represnt the structure
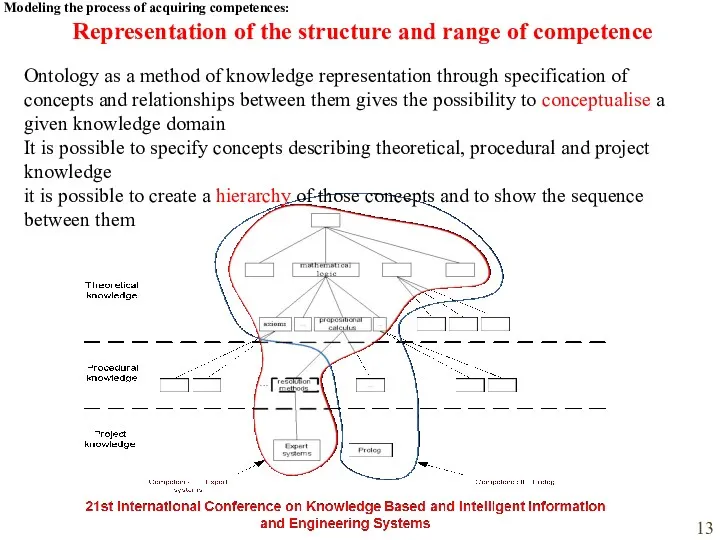
- 13. Representation of the structure and range of competence Modeling the process of acquiring competences: Ontology as
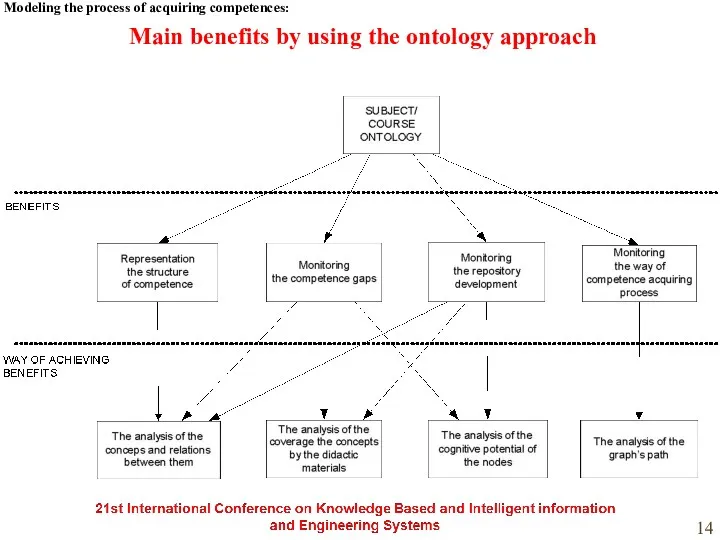
- 14. Main benefits by using the ontology approach Modeling the process of acquiring competences:
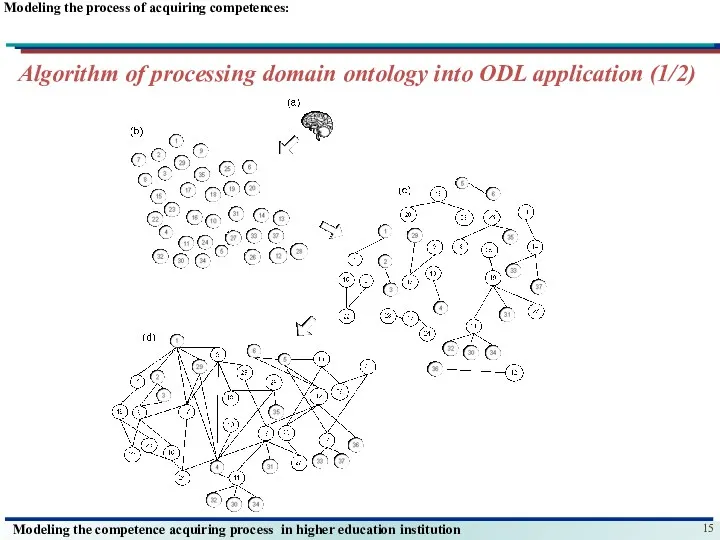
- 15. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: Algorithm of processing domain ontology into ODL application (1/2)
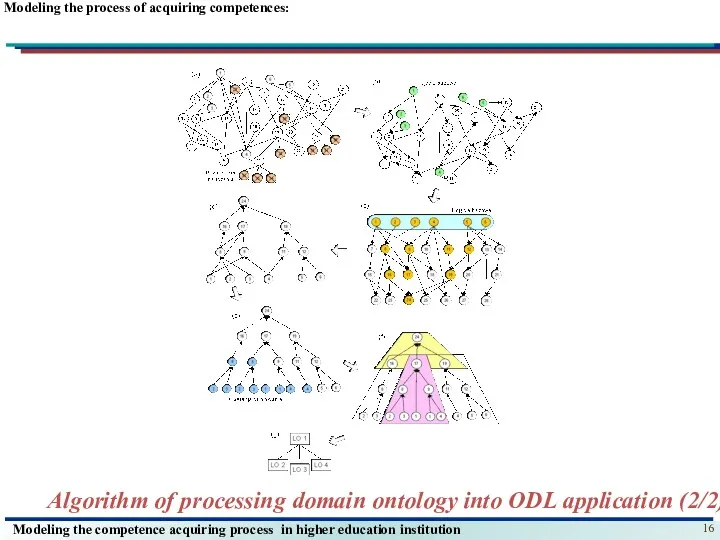
- 16. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: Algorithm of processing domain ontology into ODL application (2/2)
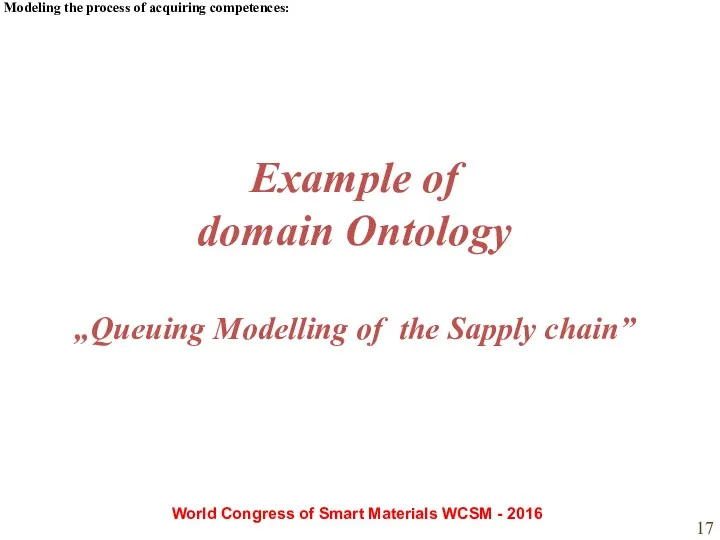
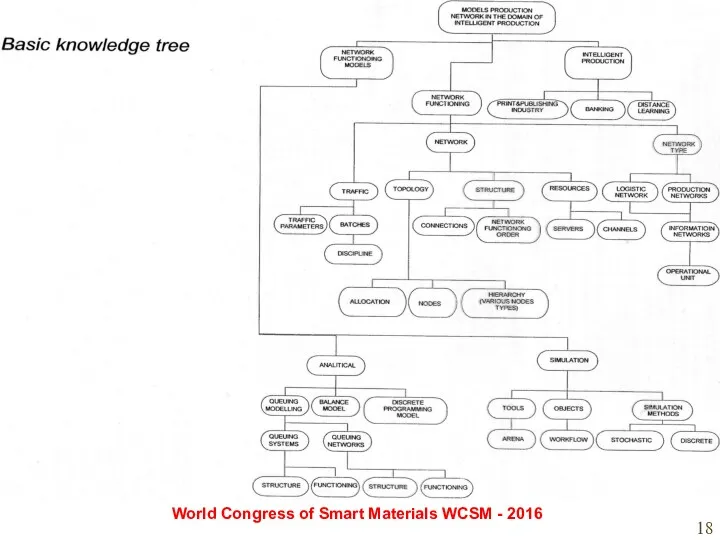
- 17. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 Example of
- 18. Main benefits by using the ontology approach Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of
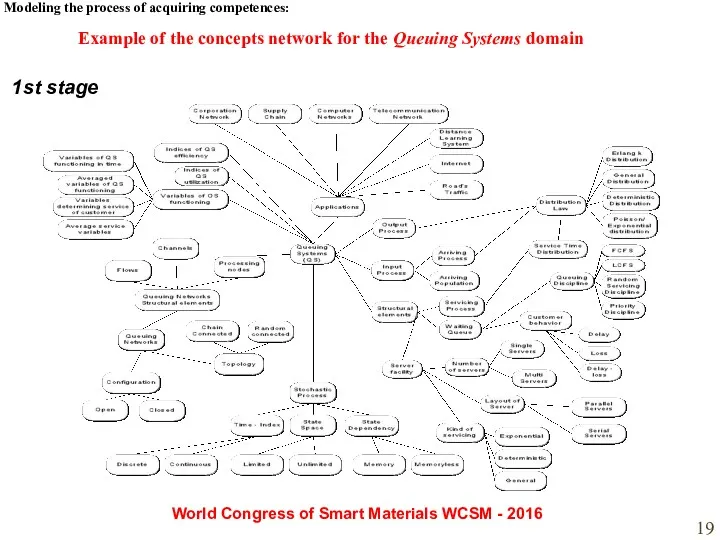
- 19. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 1st stage
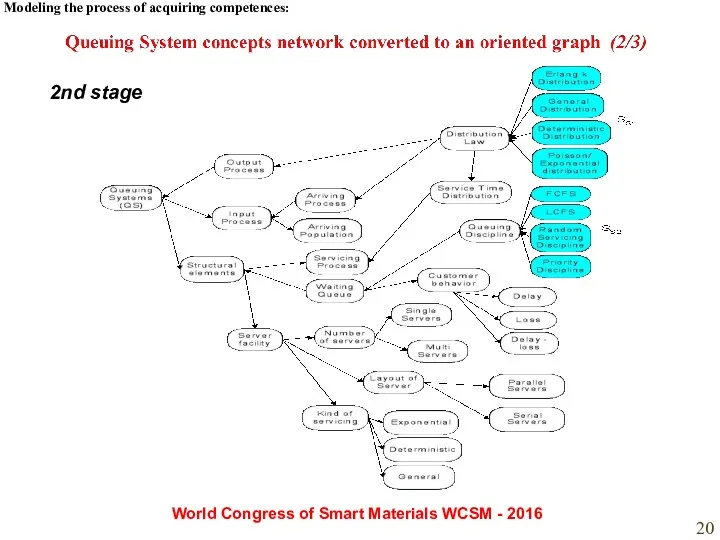
- 20. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 2nd stage
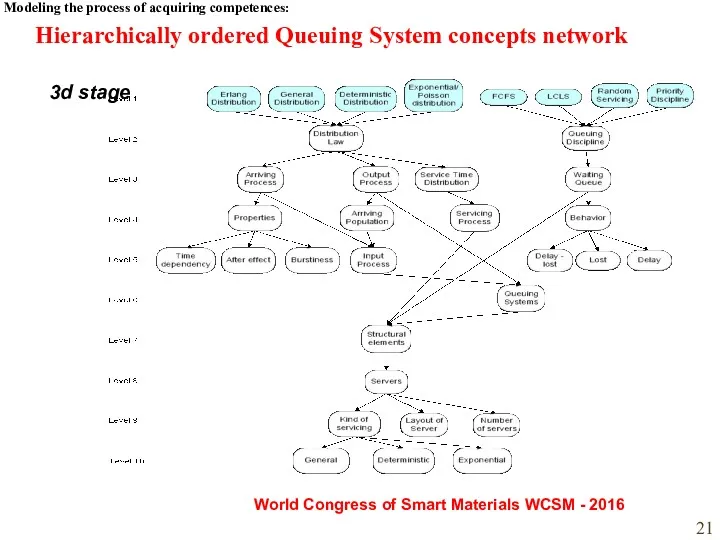
- 21. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 3d stage
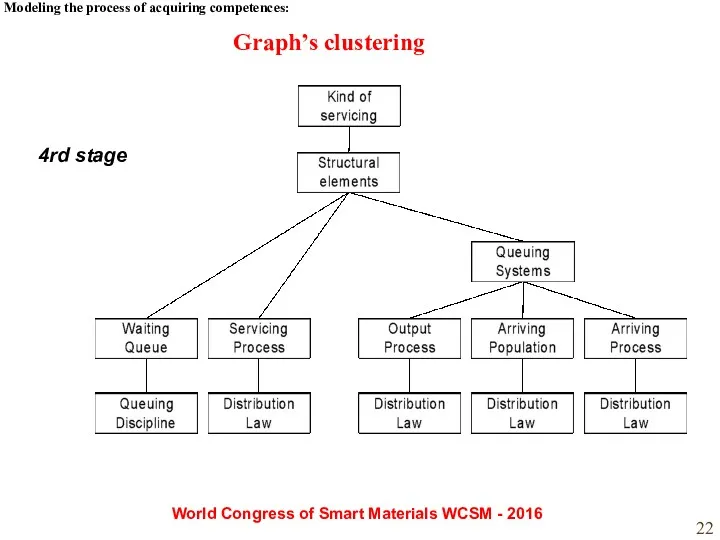
- 22. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 4rd stage
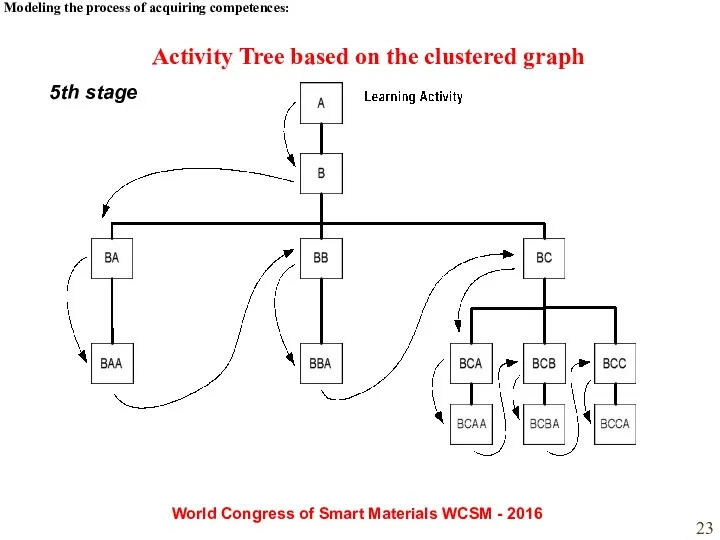
- 23. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 5th stage
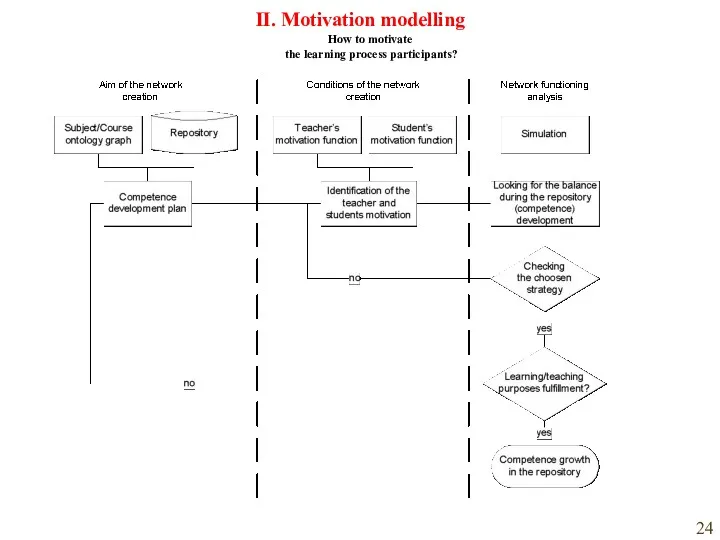
- 24. How to motivate the learning process participants? II. Motivation modelling
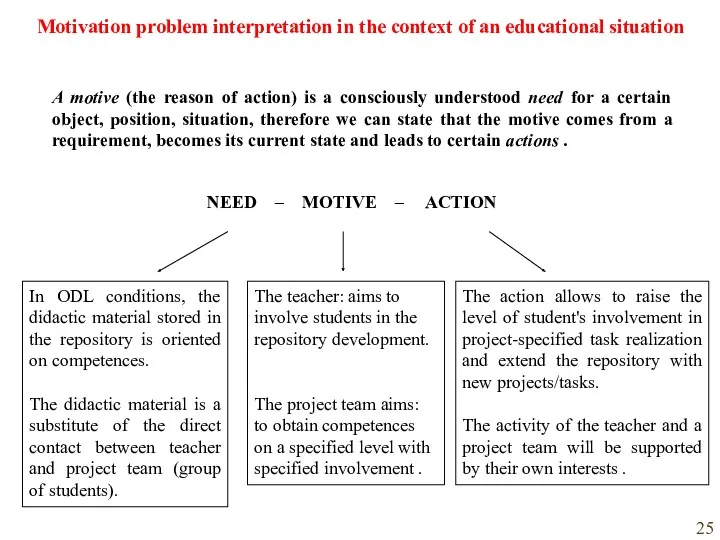
- 25. Motivation problem interpretation in the context of an educational situation A motive (the reason of action)
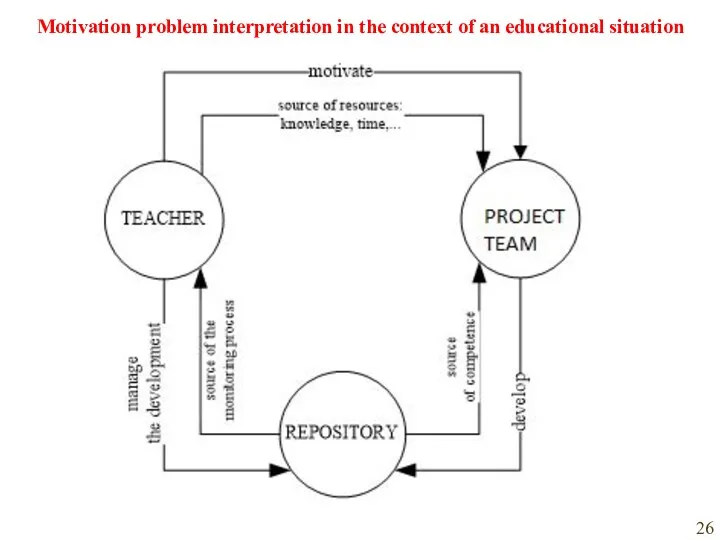
- 26. Motivation problem interpretation in the context of an educational situation
- 27. 1. The task of the teacher is not only to motivate the project team to learn,
- 28. The project process of acquiring competences is based on the following elements: a mechanism for representing
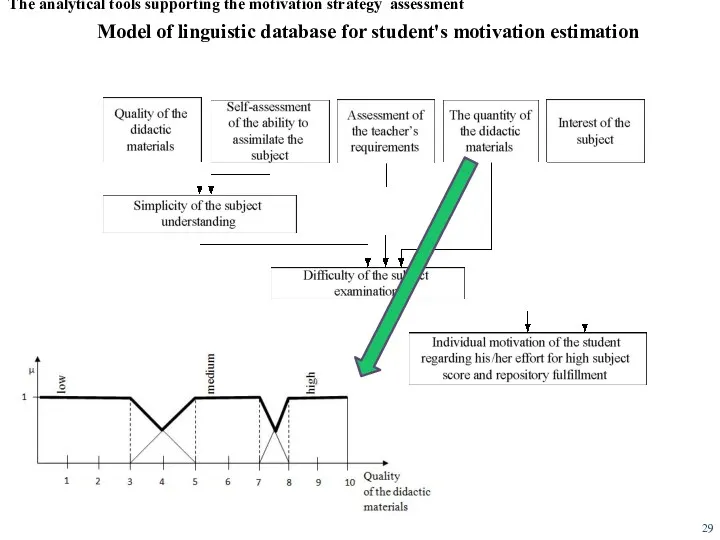
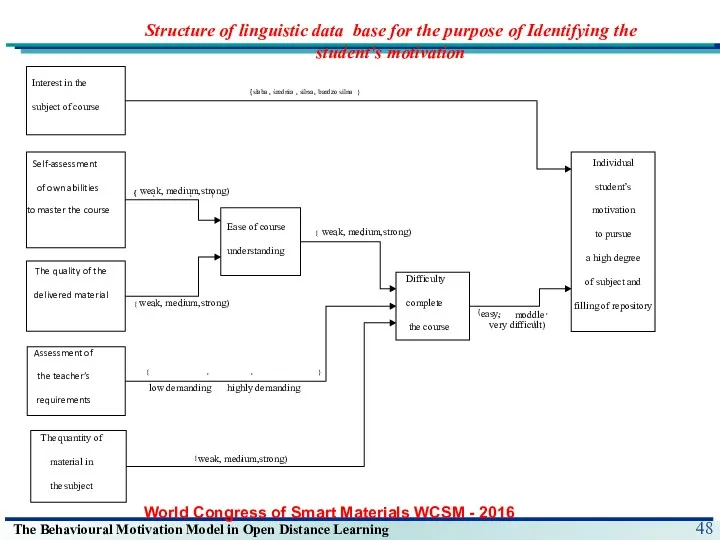
- 29. Model of linguistic database for student's motivation estimation The analytical tools supporting the motivation strategy assessment
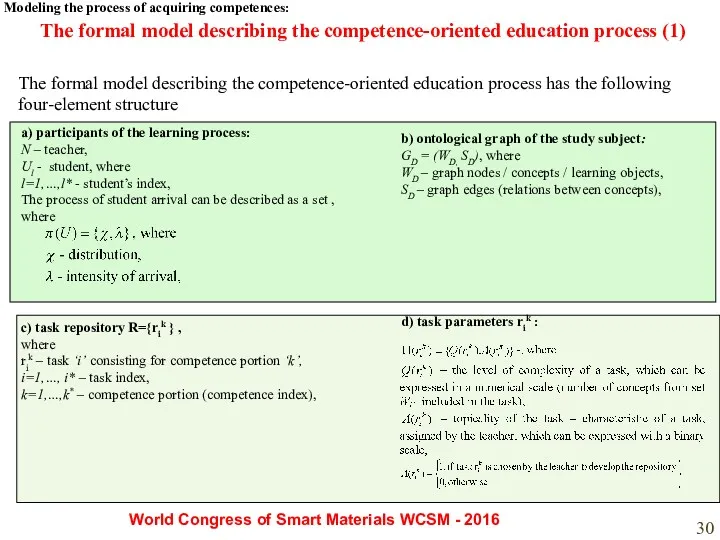
- 30. The formal model describing the competence-oriented education process (1) a) participants of the learning process: N
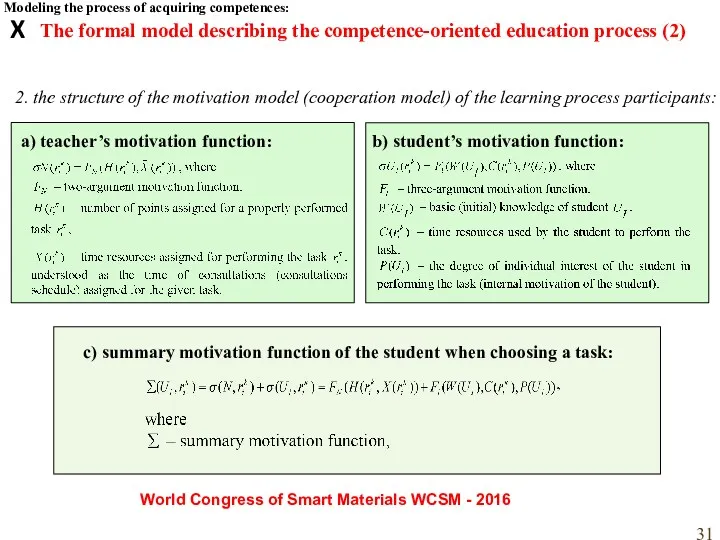
- 31. The formal model describing the competence-oriented education process (2) 2. the structure of the motivation model
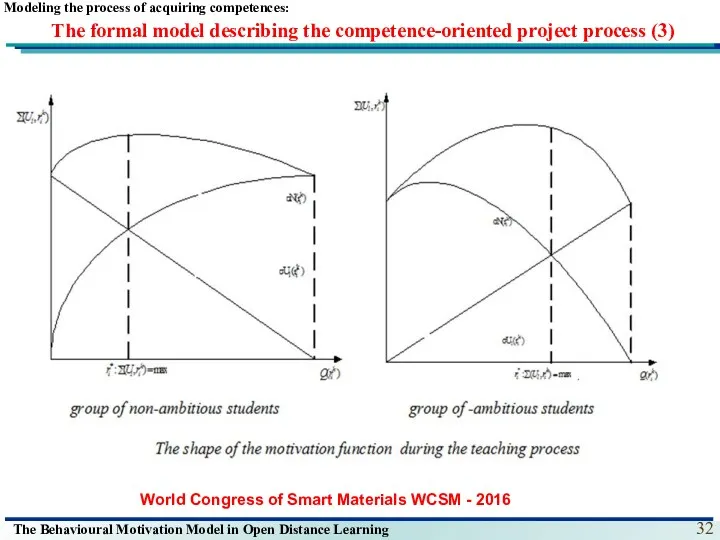
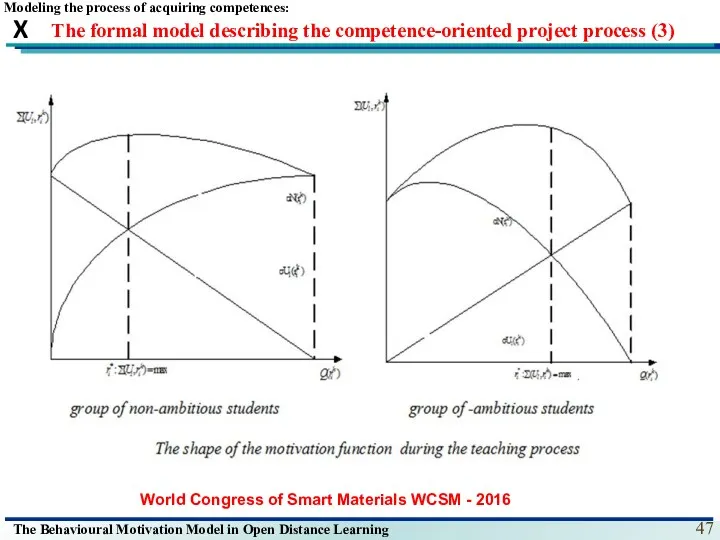
- 32. The formal model describing the competence-oriented project process (3) Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World
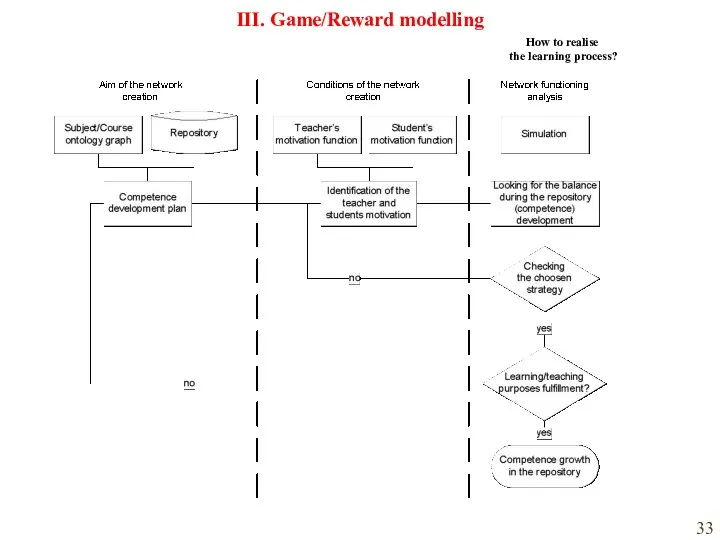
- 33. How to realise the learning process? III. Game/Reward modelling
- 34. The formulated model is consistent to a multi-agent two-layer insentive system which consists of one centre
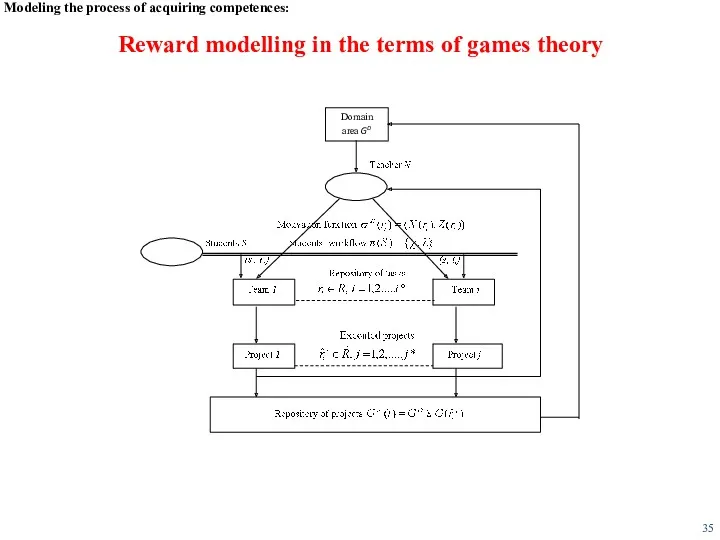
- 35. Modeling the process of acquiring competences: Reward modelling in the terms of games theory
- 36. The formal model describing the competence-oriented project process (3) Modeling the process of acquiring competences: The
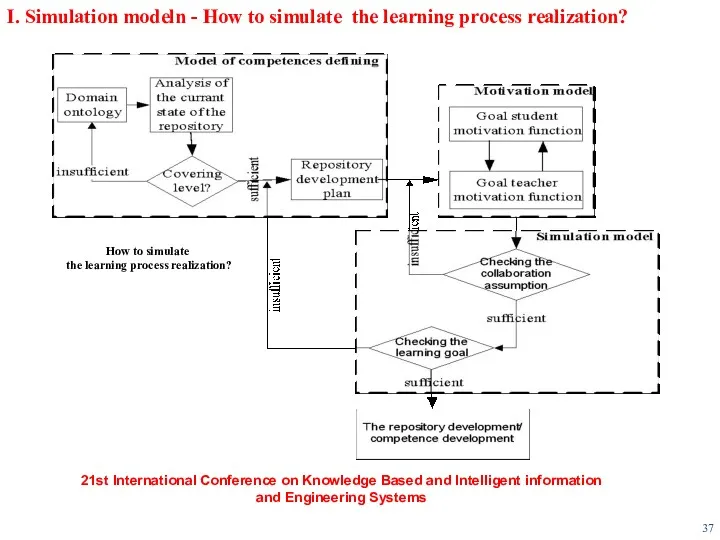
- 37. I. Simulation modeln - How to simulate the learning process realization? How to simulate the learning
- 38. 21st International Conference on Knowledge Based and Intelligent information and Engineering Systems
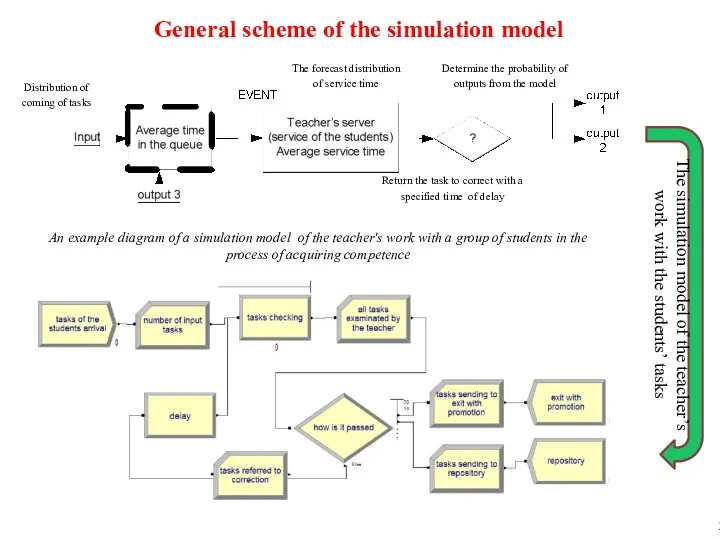
- 39. General scheme of the simulation model The simulation model of the teacher’s work with the students’
- 40. Conditions of the simulation experiment The collaboration process between students and teacher can be interpretated as
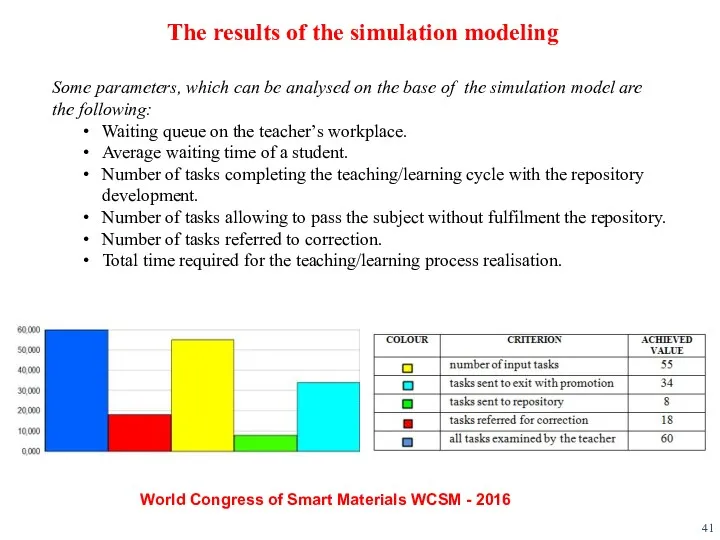
- 41. Some parameters, which can be analysed on the base of the simulation model are the following:
- 42. Summary The learning process requires analysis from the competence modelling perspective. The changing requirements and conditions
- 43. Thank you for your attention
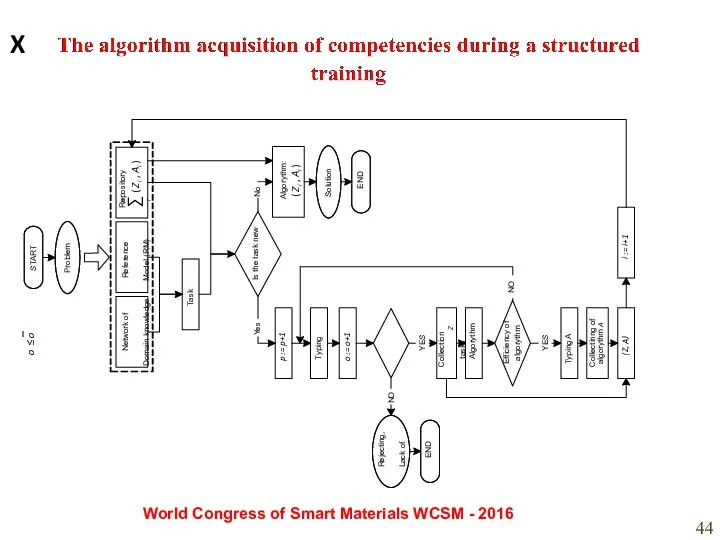
- 44. World Congress of Smart Materials WCSM - 2016 X
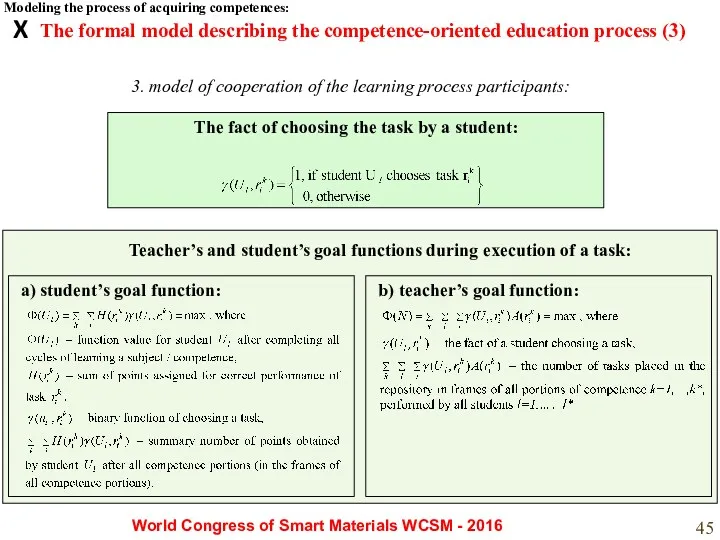
- 45. The fact of choosing the task by a student: The formal model describing the competence-oriented education
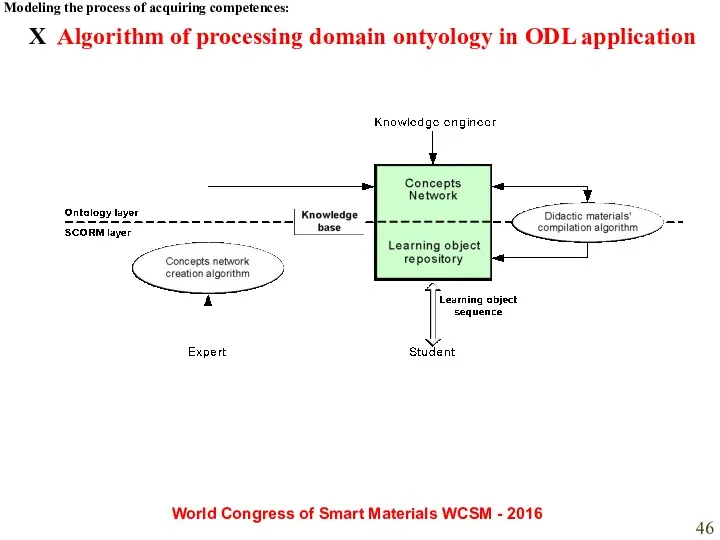
- 46. X Algorithm of processing domain ontyology in ODL application Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World
- 47. The formal model describing the competence-oriented project process (3) Modeling the process of acquiring competences: World
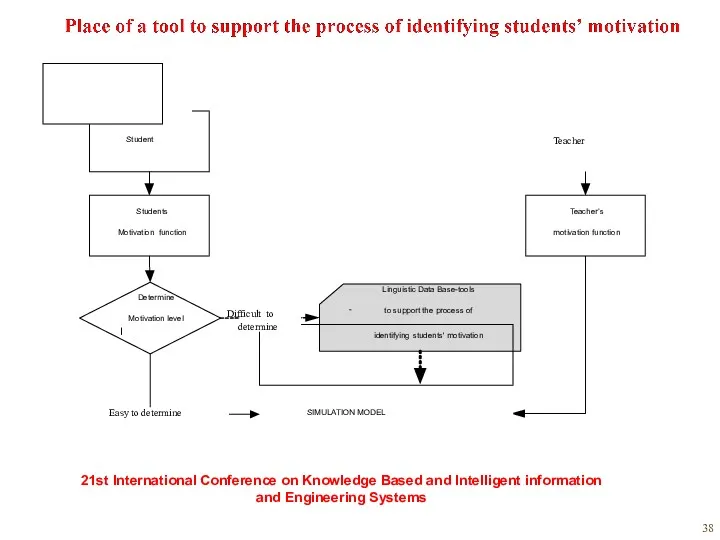
- 48. Structure of linguistic data base for the purpose of Identifying the student's motivation World Congress of
- 50. Скачать презентацию













 Практическая работа по окружающему миру
Практическая работа по окружающему миру Классный час :Александр Владимирович Попов – известный российский пловец четырёхкратный олимпийский чемпион.
Классный час :Александр Владимирович Попов – известный российский пловец четырёхкратный олимпийский чемпион. Новогодний КВИЗ
Новогодний КВИЗ Зянятие. 15 мая — Международный День семьи
Зянятие. 15 мая — Международный День семьи Презентация выступления на педагогическом совете Организация индивидуальной работы с учащимися
Презентация выступления на педагогическом совете Организация индивидуальной работы с учащимися Презентация Үзебез ияләштергән җан ияләре өчен үзебез җаваплы
Презентация Үзебез ияләштергән җан ияләре өчен үзебез җаваплы Калимуллина Румия Мустафиевна - учитель русского языка и литературы МБОУ СОШ № 7 г. Азнакаево
Калимуллина Румия Мустафиевна - учитель русского языка и литературы МБОУ СОШ № 7 г. Азнакаево Моя майбутня професія - програміст
Моя майбутня професія - програміст Игра ко дню Учителя Где логика?
Игра ко дню Учителя Где логика? Творческая работа Дмитрий Ярошенко - югорский спортсмен
Творческая работа Дмитрий Ярошенко - югорский спортсмен ЗОЖ
ЗОЖ Публичная презентация на конкурс Лучших учителей-2014
Публичная презентация на конкурс Лучших учителей-2014 Теорія і методика фізичного виховання
Теорія і методика фізичного виховання Творческо-инновационная деятельность учителя как ресурс реализации ФГОС нового поколения(презентация)
Творческо-инновационная деятельность учителя как ресурс реализации ФГОС нового поколения(презентация) Интерактивный тренажёр Гусенице помогаем, слоги мы считаем.
Интерактивный тренажёр Гусенице помогаем, слоги мы считаем. Профессия моих родителей: начальник карьера Подлесный
Профессия моих родителей: начальник карьера Подлесный Формирование жизненной компетентности учащихся с ОВЗ на уроках швейного дела
Формирование жизненной компетентности учащихся с ОВЗ на уроках швейного дела Классный час Профессия - спасатель. (2 класс, дети с УУО)
Классный час Профессия - спасатель. (2 класс, дети с УУО) Рекомендации по составлению индивидуальной образовательной программы
Рекомендации по составлению индивидуальной образовательной программы Стиль педагога в межличностном общении со студентами
Стиль педагога в межличностном общении со студентами Генезис форм обучения
Генезис форм обучения Профессиональное развитие педагога. Особенности профессиональной педагогической деятельности
Профессиональное развитие педагога. Особенности профессиональной педагогической деятельности Доклад на педагогическом совете по теме: Развитие коммуникативных умений и навыков у учащихся на уроках биологии. Часть 2.
Доклад на педагогическом совете по теме: Развитие коммуникативных умений и навыков у учащихся на уроках биологии. Часть 2. Профессия дизайнер
Профессия дизайнер Использование здоровьесберегающих технологий
Использование здоровьесберегающих технологий Работа родительского комитета
Работа родительского комитета Мероприятие День открытых дверей
Мероприятие День открытых дверей Презентация - приложение к интеллектуально - познавательной игре Что? Где? Когда? ( на материале немецкого языка )
Презентация - приложение к интеллектуально - познавательной игре Что? Где? Когда? ( на материале немецкого языка )