Содержание
- 2. План лекции 1 1. Современные требования к преподавателю ИЯ – составляющие профессиональной компетентности 2. Управленческая составляющая
- 3. John Dewey (1859-1952) the art of … giving shape to human powers and adapting them to
- 4. Современные требования к учителю ИЯ – составляющие профессиональной коммуникативной компетентности Компетентностный подход (причина возникновения, отличие от
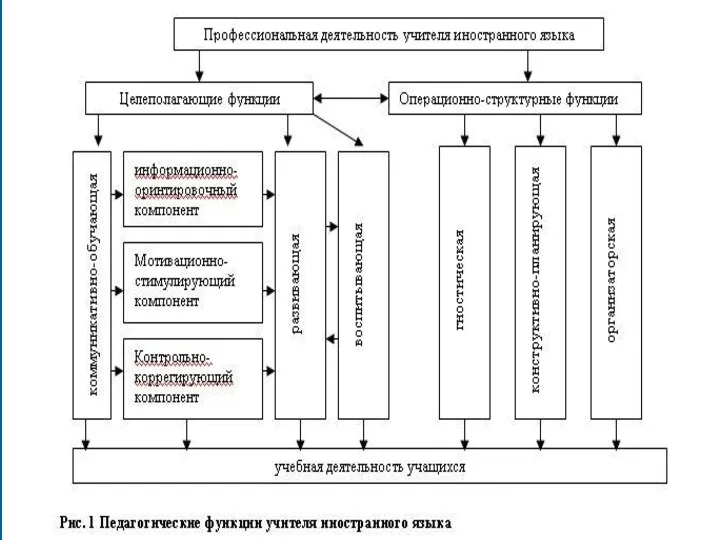
- 6. Управленческая составляющая профессиональной компетентности учителя ИЯ Составляющие ПК учителя Управленческая составляющая ПК учителя Управленческая компетентность учителя
- 7. Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента 3 позиции определения понятия «управление» Педагогическое управление Методическое управление Менеджмент
- 8. Основные понятия педагогического и методического менеджмента Принципы управления процессом обучения ИЯ Организация и управление Руководство и
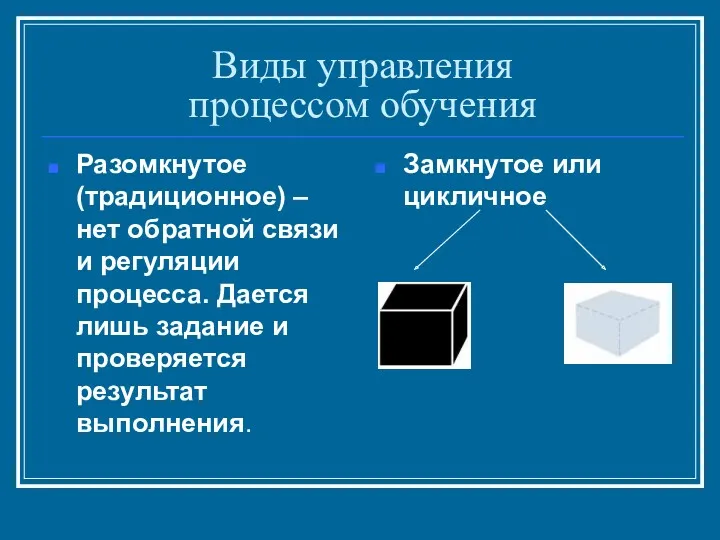
- 9. Виды управления процессом обучения Разомкнутое (традиционное) – нет обратной связи и регуляции процесса. Дается лишь задание
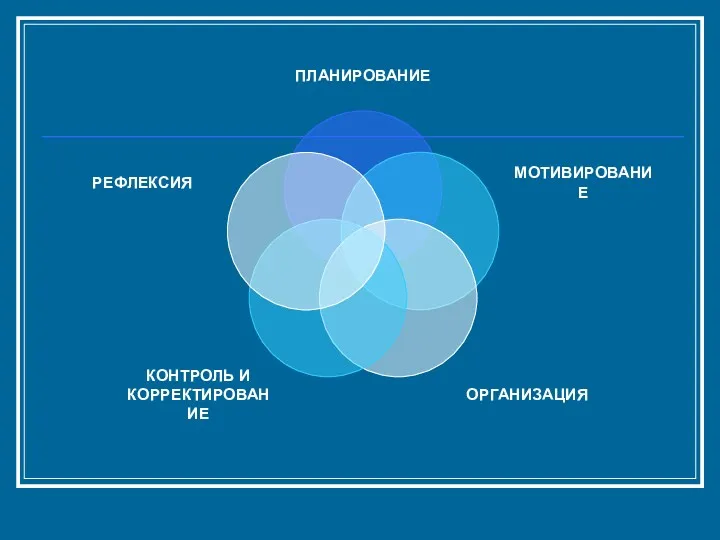
- 12. Planning Wording the aim: discussion, prioritizing, ranking, note-taking Thinking over ways of aim achievement and resources:
- 13. Motivating skills Formulation of problem Formulation of aim Interesting process of problem solving
- 14. Motivating techniques to help the teacher to formulate a problem Debates Discussion Problem Solving Questionnairing Quiz
- 15. Motivating techniques to help the teacher to formulate the aim Analysis Debates Illustration
- 16. Motivating techniques to help the teacher make the process interesting Decision making Discussion Extending ideas Problem
- 17. Organizing Group Work Skills Distribution of students into groups Distribution of roles and responsibilities Group uniting
- 18. Distributing students into groups techniques Grouping according to some idea Leader’s enrollment Expressing priorities
- 19. Distributing roles and responsibilities techniques Discussion Expressing priorities Listing Role-mapping Table filling
- 20. Group uniting techniques Teams competitions Groupmates learning activities
- 21. Organization of work with information skills Organizing students’ search of information Organizing students’ processing and selection
- 22. Organization of work with information techniques categorizing (grouping), comparing, compilation, description, discussion, information transfer, interview, linking,
- 23. Control and correction monitoring – careful watching some situation and checking if everything is being done
- 24. Principles of Monitoring continuous scientific purposeful prognostic norm-referencing
- 25. Feedback giving students information about what actions have led to the necessary level of work fulfillment
- 26. Formula of effective feedback (T. Russel) 1) give students the opportunity to see what they have
- 27. Self-control and self-correction the ability of a person to regulate his (her) own action the ability
- 28. The process of self-control development (M.E. Braigina) to learn to understand and accept the teacher’s control
- 29. Monitoring and self-correction techniques asking and answering questions table-filling observation interview comparing note-taking substitution reordering correction
- 30. Assessment The process of measuring, quantifying, and/or describing aspects related to the attributes covered by the
- 31. To provide assessment and self-assessment Comparing Level-determination Note-taking Observation Rating Table-filling
- 32. Correction Aim: to stimulate correction of mistakes in the usage of the English language (grammar, vocabulary,
- 33. Reflexive analysis Analysis – a careful examination of some object in order to understand it better
- 34. ORGANIZING REFLEXIVE ANALYSIS SKILLS To organize the process of recollection of main actions in the whole
- 35. Organizing Reflexive Analysis Techniques discussion, individual interview, individual report, listing, predicting, project documents studying, questionnairing, ranking,
- 37. Скачать презентацию































 Календарный учебный график на 2019-2020 учебный год
Календарный учебный график на 2019-2020 учебный год Конвенция о правах ребенка
Конвенция о правах ребенка Формирование правильного произношения у детей
Формирование правильного произношения у детей Отчет о проведении третьего этапа краевой акции Экологический марафон. День птиц в старшей группе Пчелки
Отчет о проведении третьего этапа краевой акции Экологический марафон. День птиц в старшей группе Пчелки Коррекция слоговой структуры слова у детей с нарушением интеллекта
Коррекция слоговой структуры слова у детей с нарушением интеллекта Методы и формы обучения
Методы и формы обучения Проблемы преемственности. ДОУ и начальная школа
Проблемы преемственности. ДОУ и начальная школа 5 настольных игр своими руками
5 настольных игр своими руками Медико-социально-педагогический патронаж и ранняя комплексная помощь детям группы риска. (раздел 3, тема 9)
Медико-социально-педагогический патронаж и ранняя комплексная помощь детям группы риска. (раздел 3, тема 9) Идеальный учитель
Идеальный учитель Презентация Образовательная среда как условие сохранения здоровья школьников с ОВЗ
Презентация Образовательная среда как условие сохранения здоровья школьников с ОВЗ Н.П. Осинин - детский сибирский писатель
Н.П. Осинин - детский сибирский писатель И муза вечная со мной
И муза вечная со мной Үштік одақ : ата-ана, мұғалім, оқушы арасындағы қарым қатынасты жақсарту
Үштік одақ : ата-ана, мұғалім, оқушы арасындағы қарым қатынасты жақсарту ПРЕЕМСТВЕННОСТЬ ДОШКОЛЬНОГО И НАЧАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ В РАМКАХ РЕАЛИЗАЦИИ ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОГО ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОГО СТАНДАРТА НАЧАЛЬНОГО ОБЩЕГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
ПРЕЕМСТВЕННОСТЬ ДОШКОЛЬНОГО И НАЧАЛЬНОГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ В РАМКАХ РЕАЛИЗАЦИИ ФЕДЕРАЛЬНОГО ГОСУДАРСТВЕННОГО СТАНДАРТА НАЧАЛЬНОГО ОБЩЕГО ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ Презентация для классного часа в 11 классе.Тема: Гражданская позиция школьников: что это значит?
Презентация для классного часа в 11 классе.Тема: Гражданская позиция школьников: что это значит? Зачем нужны автомобили, поезда
Зачем нужны автомобили, поезда Эмоции
Эмоции Профорієнтаційна робота з учнями 9-11 класів
Профорієнтаційна робота з учнями 9-11 класів Научно-исследовательская работа Тайна школьного портфеля
Научно-исследовательская работа Тайна школьного портфеля Роль информационных технологий, в духовно-нравственном воспитании обучающихся
Роль информационных технологий, в духовно-нравственном воспитании обучающихся Здоровьесберегающие технологии на уроках в начальной школе
Здоровьесберегающие технологии на уроках в начальной школе Портфолио - 5-а класса
Портфолио - 5-а класса Творческий проект Шкатулка из газетных трубочек с использованием техники декупаж
Творческий проект Шкатулка из газетных трубочек с использованием техники декупаж Мое любимое число 7
Мое любимое число 7 Презентация Веселые старты на коньках
Презентация Веселые старты на коньках классный час Олимпийский старт Кубани
классный час Олимпийский старт Кубани Игры мира. Студия настольных спортивных игр. Выездные мероприятия
Игры мира. Студия настольных спортивных игр. Выездные мероприятия