Содержание
- 2. Educational video Students need to lead the classroom, not teachers . https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gzQhiB2EOVE REAL STORY OF A
- 3. Cognitive Psychology
- 4. Information Processing
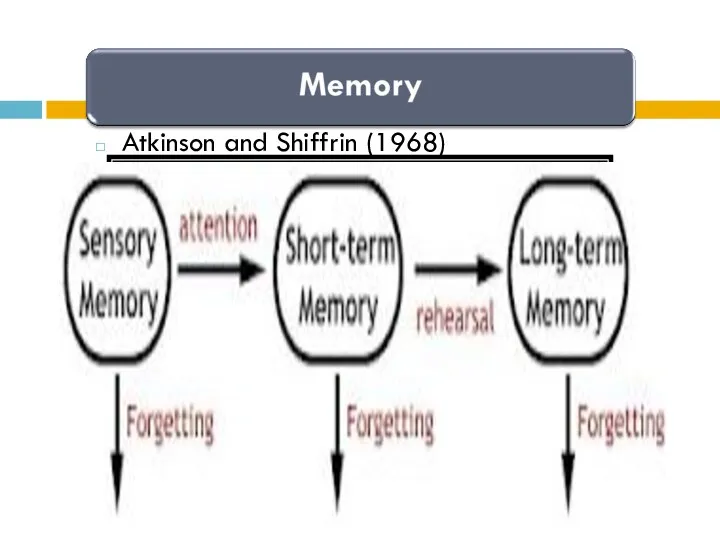
- 5. Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968)
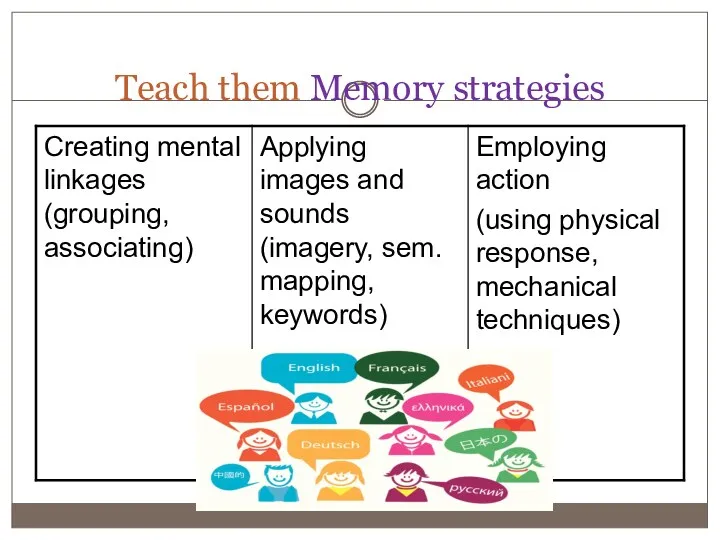
- 6. Teach them Memory strategies
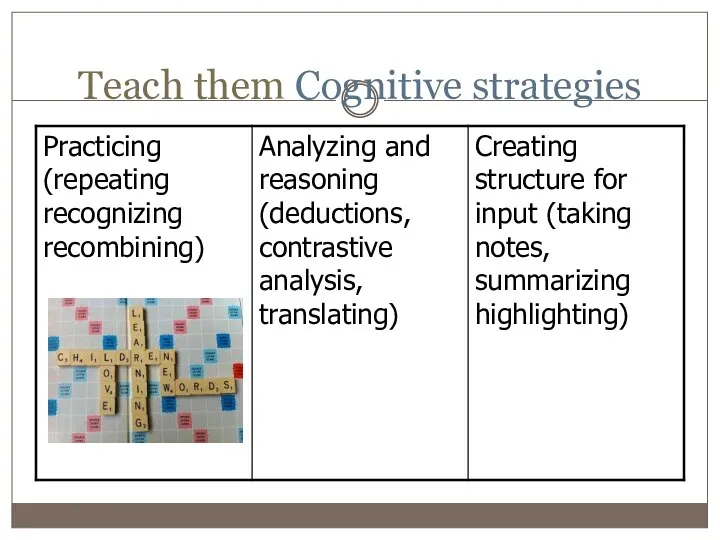
- 7. Teach them Cognitive strategies
- 9. Cognitivism or Cognitive Constructivism
- 10. Jerome Bruner
- 12. George Kelly
- 13. Piaget Piaget saw cognitive development as essentially a process of maturation. It is accomplished by the
- 14. Educational video: Use a Learning Theory: Cognitivism Watch a video and give examples of cognitivism in
- 15. Further School of Thought in Psychology:
- 17. HIS MAIN IDEAS : Learning occurs through social interactions within a social environment
- 18. PARENTS child
- 19. TEACHER STUDENT
- 20. STUDENT STUDENT
- 21. Mediation Helping learners to move into and through the next layer of knowledge and understanding. Who
- 22. Teacher Student
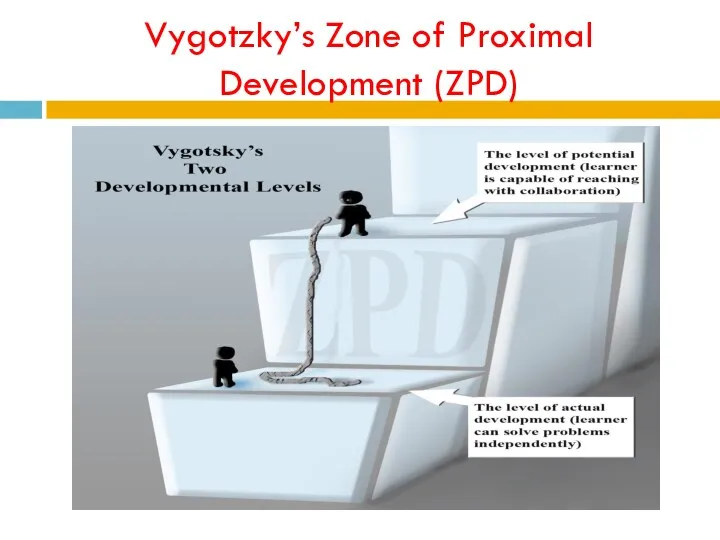
- 23. Vygotzky’s Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD)
- 24. The Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD). is Vygotsky’s term for the range of tasks that a
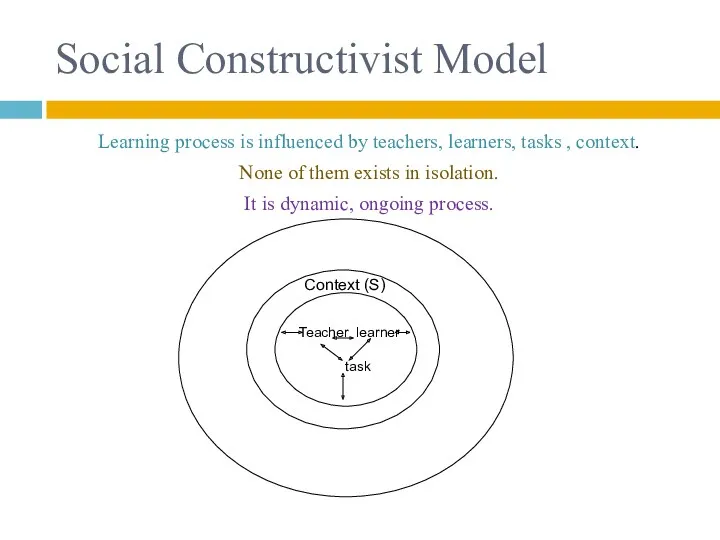
- 25. Social Constructivist Model Learning process is influenced by teachers, learners, tasks , context. None of them
- 26. Interpretation: Teachers select tasks which reflect their beliefs about teaching and learning. Learners interpret tasks in
- 27. French/German and Chinese/Korean departments To summarize the differences between cognitive and social interactionism approaches) Piaget vs
- 28. French/German Department Discuss the following questions: What are two features of the cognitive approach? What is
- 30. Скачать презентацию


















 Отрочество – особая пора в жизни. Урок 4
Отрочество – особая пора в жизни. Урок 4 Использование ресурсов памяти на уроках географии для эффективной подготовки к итоговой аттестации
Использование ресурсов памяти на уроках географии для эффективной подготовки к итоговой аттестации Презентация для релаксации.
Презентация для релаксации. Пізнавальна сфера людей похилого віку
Пізнавальна сфера людей похилого віку Теория иерархии потребностей А. Маслоу
Теория иерархии потребностей А. Маслоу научение и учение
научение и учение Психические процессы
Психические процессы Психология как наука. Предмет психологии, ее задачи
Психология как наука. Предмет психологии, ее задачи Басқарудағы шешім қабылдау процестеріне психологиялық талдау
Басқарудағы шешім қабылдау процестеріне психологиялық талдау Психологическое здоровье школьника. Семинар по психологии
Психологическое здоровье школьника. Семинар по психологии Современные методы диагностики по выявлению детей и подростков, склонных к асоциальному поведению
Современные методы диагностики по выявлению детей и подростков, склонных к асоциальному поведению Методика Е.А. Климова Определение типа будущей профессии
Методика Е.А. Климова Определение типа будущей профессии Personality theories
Personality theories Психологические особенности подросткового возраста
Психологические особенности подросткового возраста Место социальной психологии в системе научного знания. Предмет и задачи социальной психологии
Место социальной психологии в системе научного знания. Предмет и задачи социальной психологии Қарым-қатынас психологиясы
Қарым-қатынас психологиясы Обучение и морально-психологическая подготовка населения поведению в чрезвычайных ситуациях
Обучение и морально-психологическая подготовка населения поведению в чрезвычайных ситуациях Виртуальная беседа Выбери жизнь
Виртуальная беседа Выбери жизнь Комплексный подход к достижению и оценке предметных и метапредметных результатов в системе Л.В. Занкова
Комплексный подход к достижению и оценке предметных и метапредметных результатов в системе Л.В. Занкова Постановка целей
Постановка целей Что такое любовь
Что такое любовь Урок психологического развития. 3 класс.
Урок психологического развития. 3 класс. Структура родительского комитета
Структура родительского комитета Современные дети. Какие они?
Современные дети. Какие они? Визитная карточка часть 1
Визитная карточка часть 1 О революции знаний в психологии раннего детства
О революции знаний в психологии раннего детства Игровая социально-реабилитационная технология Мозартика
Игровая социально-реабилитационная технология Мозартика Аналіз симптому в різних психосоматичних концепціях
Аналіз симптому в різних психосоматичних концепціях