Содержание
- 2. * Queries (1 of 2) In JPA: SQL -> JP QL (Java Persistence Query Language) A
- 3. * Queries (2 of 2) A query can be issued at runtime by supplying the JP
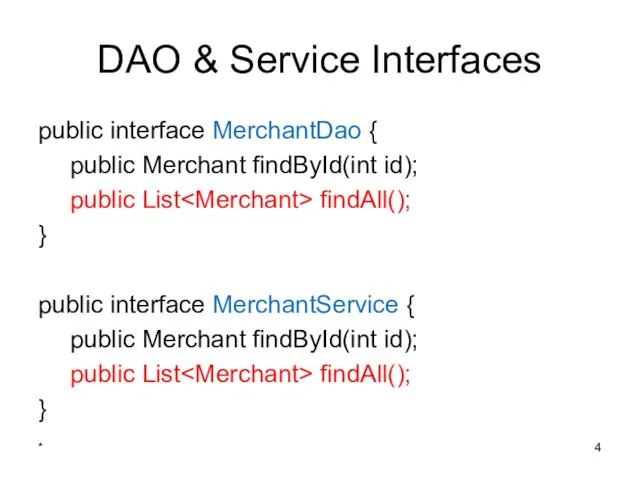
- 4. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao { public Merchant findById(int id); public List findAll(); }
- 5. MerchantDaoImpl Class @Repository public class MerchantDaoImpl implements MerchantDao{ @PersistenceContext private EntityManager em; . . . .
- 6. MerchantServiceImpl Class @Named public class MerchantServiceImpl implements MerchantService{ @Inject private MerchantDao merchantDao; . . . .
- 7. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); MerchantService merchantService
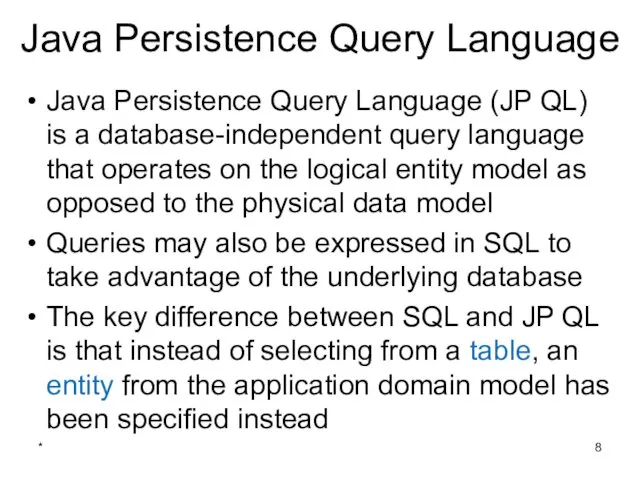
- 8. * Java Persistence Query Language Java Persistence Query Language (JP QL) is a database-independent query language
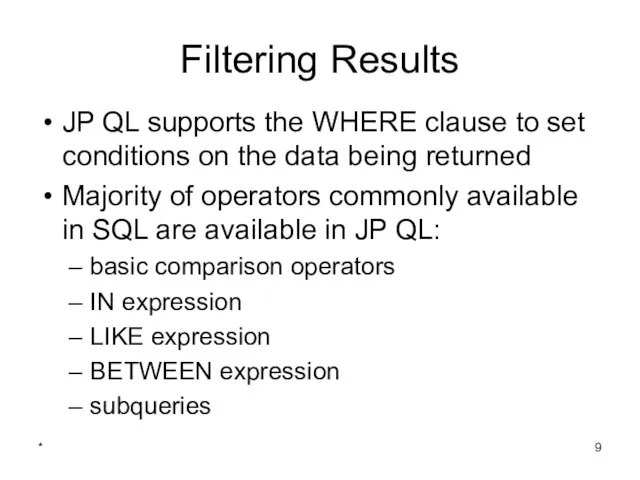
- 9. * Filtering Results JP QL supports the WHERE clause to set conditions on the data being
- 10. * Exercise: Find Payments Find all payments to the given merchant
- 11. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List findByMerchantId(int id); } public interface PaymentService
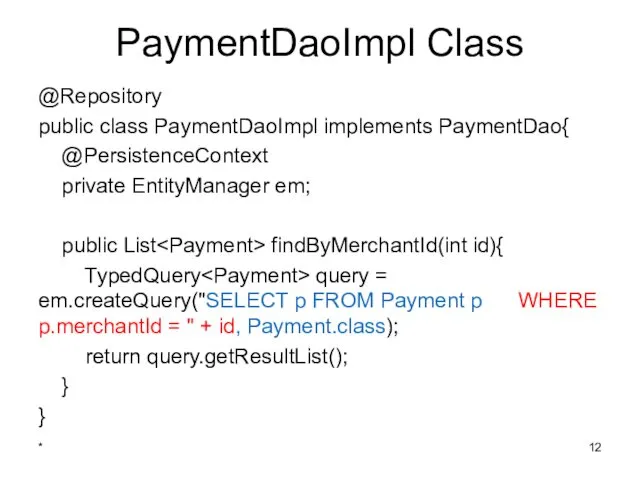
- 12. PaymentDaoImpl Class @Repository public class PaymentDaoImpl implements PaymentDao{ @PersistenceContext private EntityManager em; public List findByMerchantId(int id){
- 13. PaymentServiceImpl Class @Named public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService{ @Inject private PaymentDao paymentDao; public List findByMerchantId(int id){
- 14. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); PaymentService paymentService
- 15. * Exercise: Find Payments See P342PaymentsWhere project for the full text
- 16. * Joins Between Entities Just as with SQL and tables, if we want to navigate along
- 17. * Join Example Get names of customers who payed more then 500.0 by the time
- 18. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface CustomerDao { public Customer findById(int id); . . . .
- 19. CustomerDaoImpl Class public List getNames(double sumPayed){ String txt = "SELECT DISTINCT c.name FROM "; txt +=
- 20. CustomerServiceImpl Class public List getNames(double sumPayed){ return customerDao.getNames(sumPayed); } *
- 21. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); CustomerService customerService
- 22. * Join Example See P343PaymentJoin project for the full text
- 23. * Aggregate Queries There are five supported aggregate functions (AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX, SUM) Results may
- 24. * Aggregate Example Find the sum of all payments
- 25. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List findByMerchantId(int id); public double getPaymentSum(); }
- 26. PaymentDaoImpl Class public double getPaymentSum(){ TypedQuery query = em.createQuery ("SELECT SUM(p.sumPayed) FROM Payment p", Double.class); return
- 27. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); PaymentService paymentService
- 28. * Aggregate Example See P344Aggregation project for the full text
- 29. * Query Positional Parameters Parameters are indicated in the query string by a question mark followed
- 30. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao { public List findByMerchantId(int id); public double getPaymentSum(); public
- 31. PaymentDaoImpl Class public List getLargePayments(double limit){ TypedQuery query = em.createQuery ("SELECT p FROM Payment p WHERE
- 32. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); PaymentService paymentService
- 33. * Query Named Parameters Named parameters may also be used and are indicated in the query
- 34. PaymentDaoImpl Class public List getLargePayments(double limit){ TypedQuery query = em.createQuery ("SELECT p FROM Payment p WHERE
- 35. * Executing Queries The TypedQuery interface provides three different ways to execute a query: getSingleResult() -
- 36. * getResultList() Method Returns a collection containing the query results If the query did not return
- 37. * Exercise: Sort Merchants Create a project to sort merchants by the value of needToSend field
- 38. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao { public Merchant findById(int id); public List getSortedByNeedToPay(); }
- 39. MerchantDaoImpl Class public List getSortedByNeedToPay(){ String txt = "SELECT m FROM Merchant m ORDER BY m.needToSend";
- 40. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); MerchantService merchantService
- 41. * Exercise: Sort Merchants See P346Sort project for the full text
- 42. * getSingleResult() Method Instead of iterating to the first result in a collection, the object is
- 43. * Working with Query Results The result type of a query is determined by the expressions
- 44. * Constructor expressions (1/2) Provide developers with a way to map array of Object result types
- 45. * Constructor expressions (2/2) The argument to the NEW operator is the fully qualified name of
- 46. * Example: Grouping Payments Get general sum of charge for every merchant
- 47. * Class Result public class Result { private String name; private double sum; public Result(){ }
- 48. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao { public Merchant findById(int id); public List getSortedByNeedToPay(); public
- 49. MerchantDaoImpl Class public List getTotalReport(){ String txt = "SELECT new com.bionic.edu.Result (m.name, SUM(p.chargePayed)) "; txt +=
- 50. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); MerchantService merchantService
- 52. Скачать презентацию




![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-6.jpg)



![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-13.jpg)






![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-20.jpg)





![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-26.jpg)




![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-31.jpg)







![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-39.jpg)









![Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/25949/slide-49.jpg)
 Ипотека для молодых учителей
Ипотека для молодых учителей Распад переохлажденного аустенита в углеродистых сталях при непрерывном охлаждении
Распад переохлажденного аустенита в углеродистых сталях при непрерывном охлаждении Модуль числа. Исследовательская работа по математике
Модуль числа. Исследовательская работа по математике Викторина Где эта улица, где этот дом...?
Викторина Где эта улица, где этот дом...? Презентация повар.
Презентация повар. Натюрморт. Типы натюрморта
Натюрморт. Типы натюрморта Витамины - наши друзья
Витамины - наши друзья Микроконтроллеры платформа Arduino UNO
Микроконтроллеры платформа Arduino UNO Организация процесса приготовления и приготовление сложных банкетных закусок
Организация процесса приготовления и приготовление сложных банкетных закусок Доклад Критическое мышление ПКФ
Доклад Критическое мышление ПКФ Автоматизация движения кабины и точная остановка лифта
Автоматизация движения кабины и точная остановка лифта С днем рождения
С днем рождения Организация погрузочно-разгрузочных, транспортных и складских работ
Организация погрузочно-разгрузочных, транспортных и складских работ Дорогие наши мамочки. Фотоальбом
Дорогие наши мамочки. Фотоальбом Михаил Афанасьевич Булгаков. Жизнь, творчество, личность (1891 – 1940). 9 класс
Михаил Афанасьевич Булгаков. Жизнь, творчество, личность (1891 – 1940). 9 класс Адаптация первоклассников к школьным условиям
Адаптация первоклассников к школьным условиям Рождество в приютах Тверской области
Рождество в приютах Тверской области Modern and efficient public transport system
Modern and efficient public transport system Болезни пародонта у детей
Болезни пародонта у детей Родительское собрание Детское воровство. Что делать? Кто виноват?
Родительское собрание Детское воровство. Что делать? Кто виноват? Храм - синтез искусств
Храм - синтез искусств История букв русского алфавита
История букв русского алфавита Щ.Анатол. Прабабушка
Щ.Анатол. Прабабушка Основы автоматизации технологических процессов ОМД
Основы автоматизации технологических процессов ОМД Теория надежности. Характеристика научно-технического направления, основные понятия, термины и определения. (Лекция 1)
Теория надежности. Характеристика научно-технического направления, основные понятия, термины и определения. (Лекция 1) Машинные стежки и строчки
Машинные стежки и строчки Factory Automation Solution
Factory Automation Solution Разработка технической документации на выбор комплекта оборудования для приема спутникового телевидения
Разработка технической документации на выбор комплекта оборудования для приема спутникового телевидения