Содержание
- 2. King’s Interhigh Logo
- 3. Electricity – Fundamentals Explore 1: Analogies for Electricity
- 4. Objectives
- 5. Starter Watch the clip. Explain how it could be a model for an electrical circuit. Try
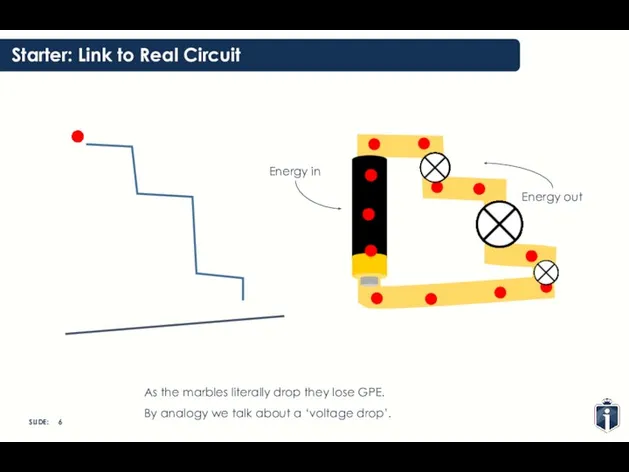
- 6. Starter: Link to Real Circuit As the marbles literally drop they lose GPE. By analogy we
- 7. Waterfall Sim This is a bit more complicated than the penguins. Sign up required. Explain the
- 8. Chain How is a bicycle chain like a circuit. How is better than the water analogy?
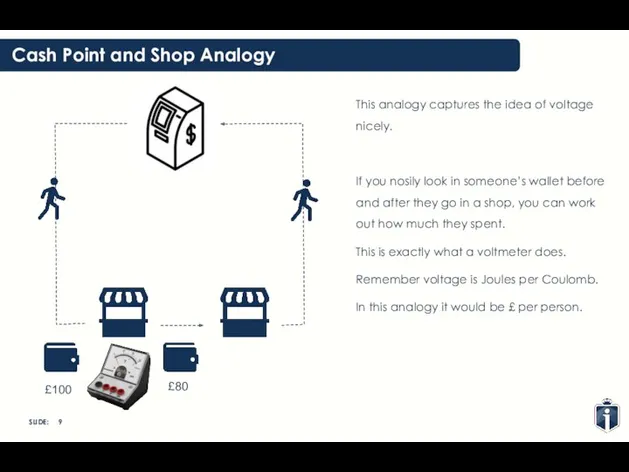
- 9. Cash Point and Shop Analogy This analogy captures the idea of voltage nicely. If you nosily
- 10. Analogy Summary All of the analogies we have looked at have pros and cons. Try and
- 11. Calculation 1 What is resistance if current is 68.3 mA and Voltage is 4.1 kV?
- 12. Calculation 2 What is current if time is 3 days and charge is 23.6 kC?
- 13. Calculation 3 7.8 C does 8,800 J of work. What must the voltage have been?
- 14. Voltage vs Voltage Across
- 15. Plenary Try and write your own summary for the topic so far.
- 16. Objectives
- 17. Electricity – Fundamentals Explore 2: Exam Practice
- 18. Objectives
- 19. Why was the Coulomb invented? Because electrons are ridiculously small and therefore awkwardly numerous. Starter
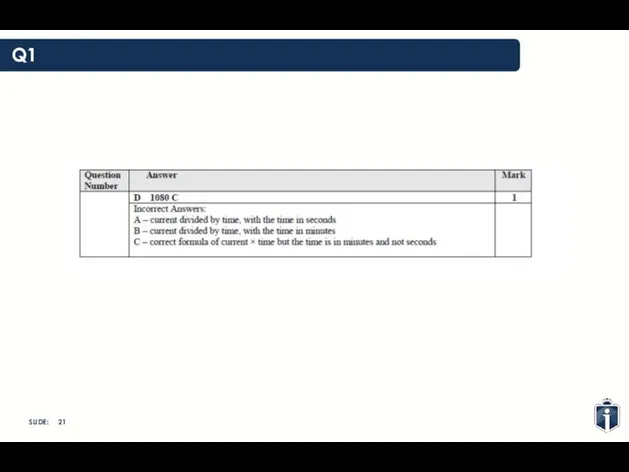
- 20. Q1 A 0.03 C B 2 C C 18 C D 1080 C
- 21. Q1
- 22. Q2
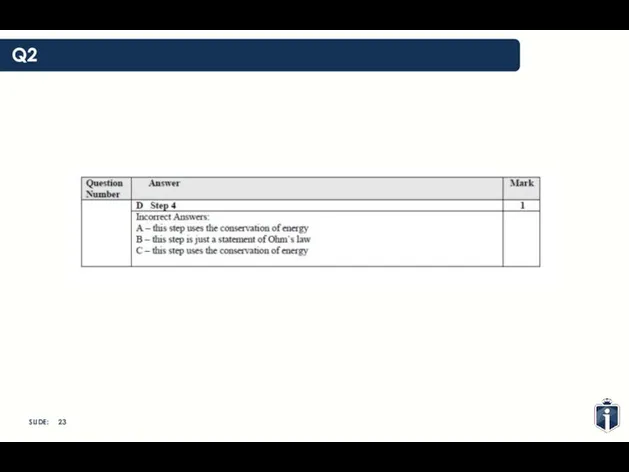
- 23. Q2
- 24. Q3 A 0.75 C B 45 C C 750 C D 45,000 C
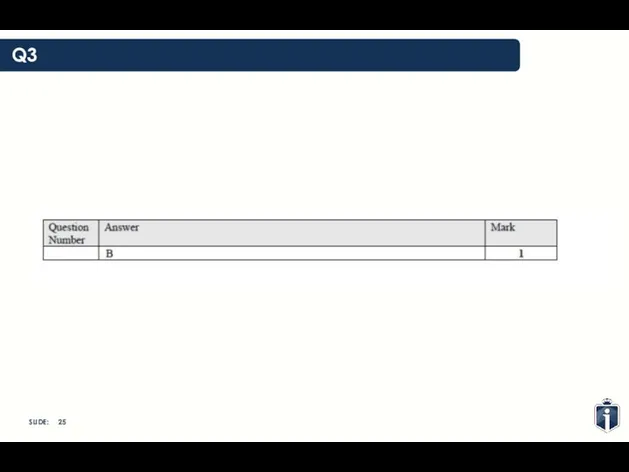
- 25. Q3
- 26. Q4
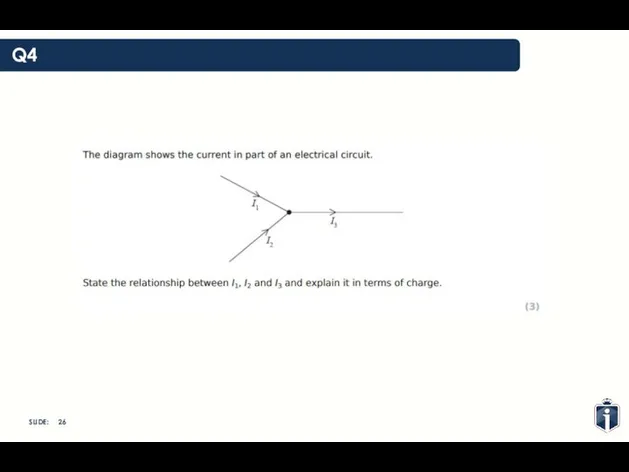
- 27. Q4
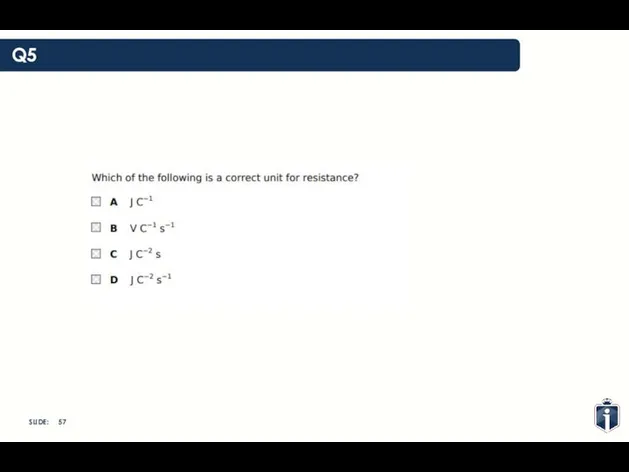
- 28. Q5
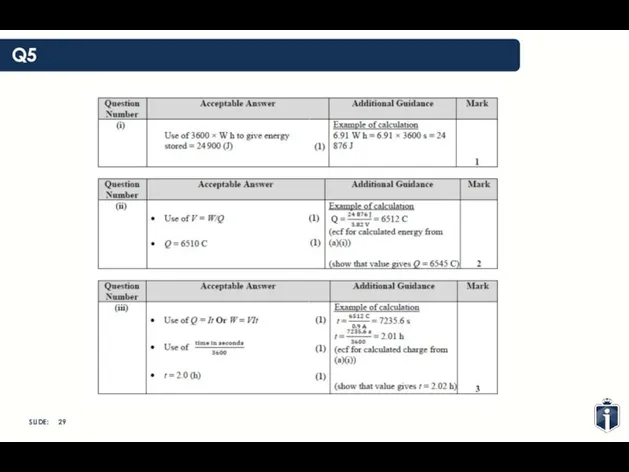
- 29. Q5
- 30. Q6
- 31. Q6
- 32. Plenary: Taboo Play Taboo with any word from the learning objectives. Describe the word without using
- 33. Objectives
- 34. Electricity – Fundamentals Explore 3: Practical
- 35. Objectives
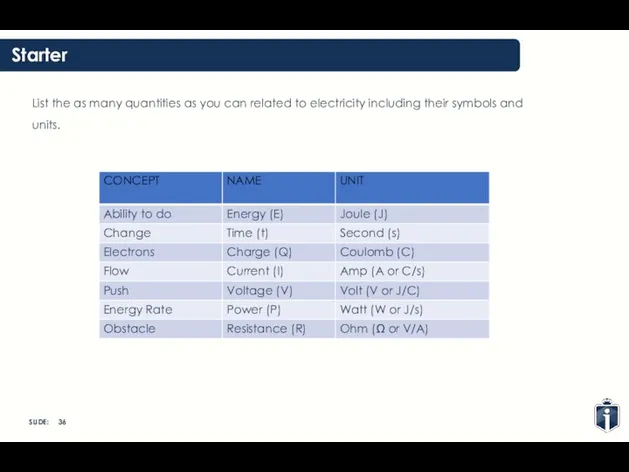
- 36. Starter List the as many quantities as you can related to electricity including their symbols and
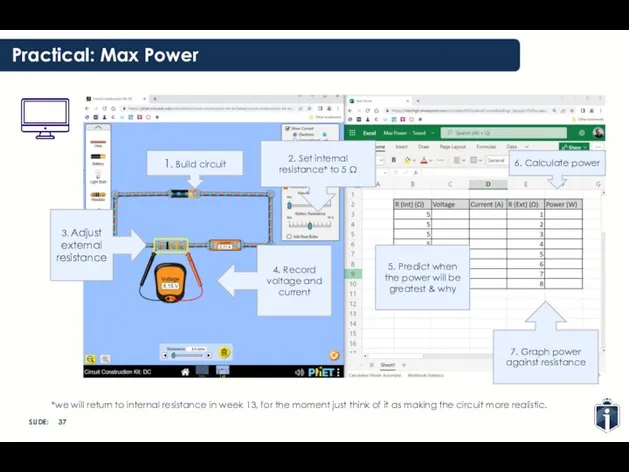
- 37. Practical: Max Power 2. Set internal resistance* to 5 Ω 1. Build circuit 3. Adjust external
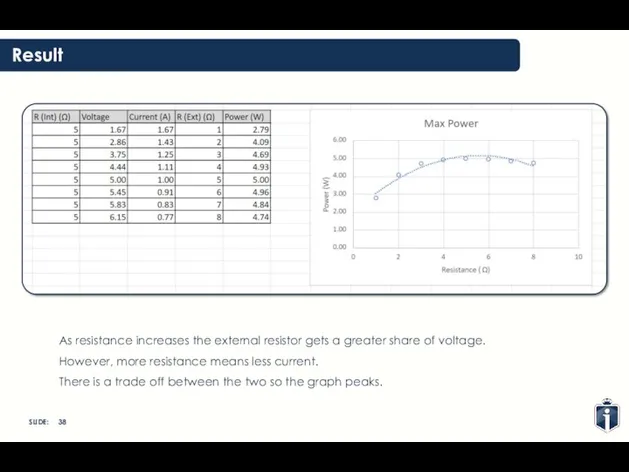
- 38. Result As resistance increases the external resistor gets a greater share of voltage. However, more resistance
- 39. Plenary Which statement(s) are correct? Voltage is proportional to resistance Voltage is inversely proportional to current
- 40. Objectives
- 41. Electricity – Fundamentals Explore 4: Exam Practice
- 42. Explore 4 Objective
- 43. Starter Calculate the mass of electrons in the human body. Assume Mass of 70 kg To
- 44. Q1
- 45. Q1
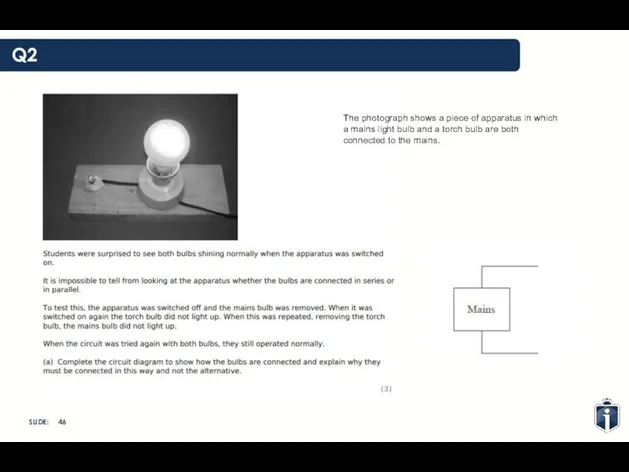
- 46. Q2 The photograph shows a piece of apparatus in which a mains light bulb and a
- 47. Q2
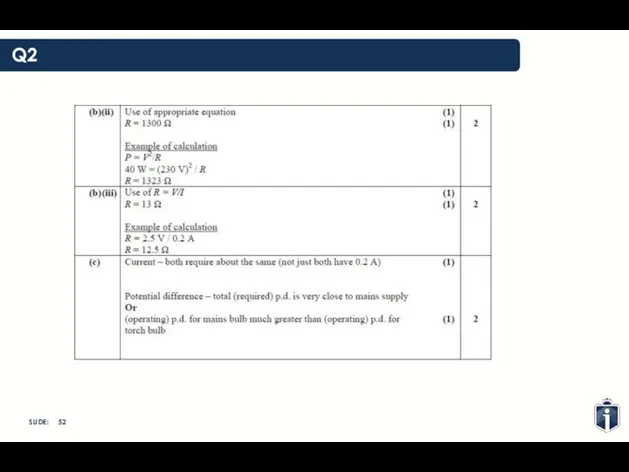
- 48. Q2
- 49. Q2
- 50. Q2
- 51. Q2
- 52. Q2
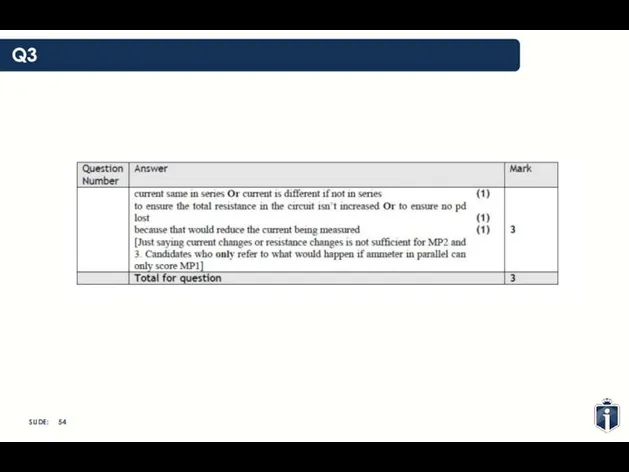
- 53. Q3
- 54. Q3
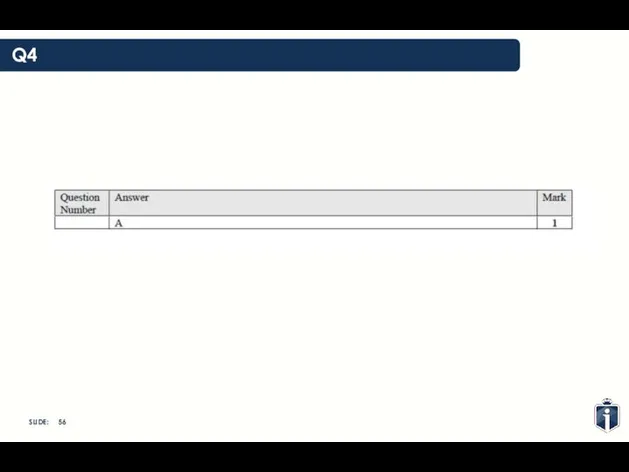
- 55. Q4
- 56. Q4
- 57. Q5
- 58. Q5
- 59. Plenary Taboo Play Taboo with any word from the learning objectives. Describe the word without using
- 61. Скачать презентацию









































 Теплофикационная установка (ТФУ)
Теплофикационная установка (ТФУ) Приносит ли вред сладкая газированная вода детскому организму
Приносит ли вред сладкая газированная вода детскому организму Краткосрочный проект Ёлочка, живи!
Краткосрочный проект Ёлочка, живи! Открытый урок по математике в 5 классе.
Открытый урок по математике в 5 классе. Готовность ребёнка к школе
Готовность ребёнка к школе Куклы, в которые играем
Куклы, в которые играем Цифровые комбинационные устройства. Тема 4.2
Цифровые комбинационные устройства. Тема 4.2 Проект Мир музыки, ритмики и танцев
Проект Мир музыки, ритмики и танцев Стратегическое управление стоматологической клиникой на основе сбалансированной системы показателей эффективности. Часть 1
Стратегическое управление стоматологической клиникой на основе сбалансированной системы показателей эффективности. Часть 1 Открытые горные работы
Открытые горные работы Классы string и stringBilder. Регулярные выражения. (Лекция 10)
Классы string и stringBilder. Регулярные выражения. (Лекция 10) проект Искатели здоровья
проект Искатели здоровья Гастро-эзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь
Гастро-эзофагеальная рефлюксная болезнь Программа дополнительного образования Волшебная иголочка для детей 5 - 7 лет.
Программа дополнительного образования Волшебная иголочка для детей 5 - 7 лет. презентация
презентация Состав и характеристики АРЭК самолета Су-27
Состав и характеристики АРЭК самолета Су-27 Презентация по технологии _Игрушка из зубочисток_, 4 класс
Презентация по технологии _Игрушка из зубочисток_, 4 класс Генеральная совокупность и выборка. Дискретные и интервальные вариационные ряды
Генеральная совокупность и выборка. Дискретные и интервальные вариационные ряды raskar Mocap
raskar Mocap Интерактивная игра Своя игра. ОРКСЭ. Основы православной культуры.
Интерактивная игра Своя игра. ОРКСЭ. Основы православной культуры. Витаминная азбука
Витаминная азбука Схемотехника цифровых устройств. Лабораторные занятия
Схемотехника цифровых устройств. Лабораторные занятия Способы разделения смесей
Способы разделения смесей Правила поведения в воде и возле водоёмов
Правила поведения в воде и возле водоёмов магатова_презентация
магатова_презентация Семеновская матрешка
Семеновская матрешка Участник конкурса Лучшее территориальное общественное самоуправление ТОС Мегрегские карелы
Участник конкурса Лучшее территориальное общественное самоуправление ТОС Мегрегские карелы Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений
Двойное оплодотворение у цветковых растений