Содержание
- 2. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software What
- 3. What are the most important contemporary hardware and software trends? What are the principal issues in
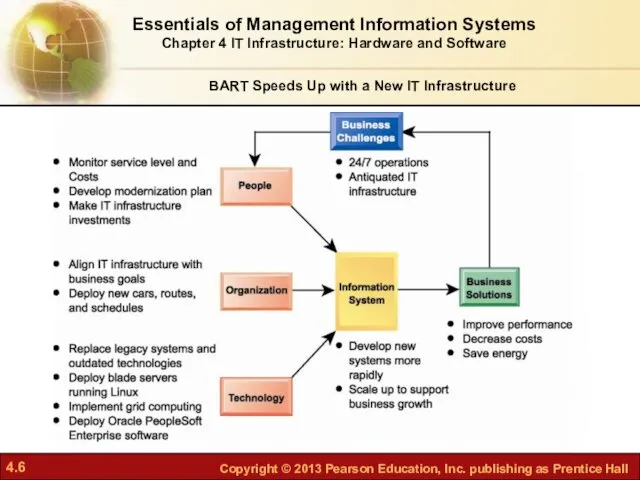
- 4. BART Speeds Up with a New IT Infrastructure Problem: Aging systems no longer able to provide
- 5. Oracle’s PeopleSoft Enterprise applications replaced legacy applications. Used blade servers, grid architecture, and virtualization, increasing server
- 6. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 4 IT Infrastructure: Hardware and Software BART Speeds Up with
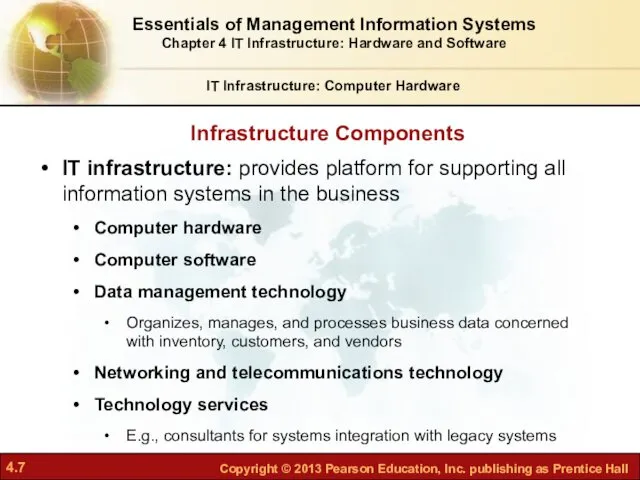
- 7. IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware IT infrastructure: provides platform for supporting all information systems in the business
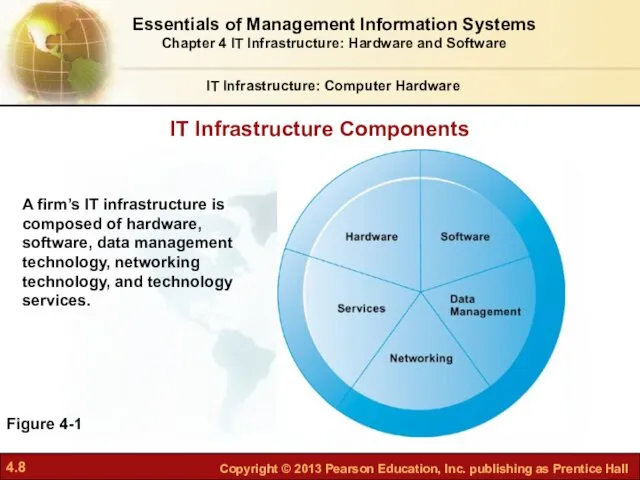
- 8. IT Infrastructure Components IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Figure 4-1 A firm’s IT infrastructure is composed of
- 9. Computers come in different sizes with varying capabilities for processing information Mobile devices PCs Workstations More
- 10. Servers: Support computer network, sharing files, and resources Provide hardware platform for e-commerce Mainframes: Large-capacity, high-performance
- 11. Supercomputer: More sophisticated computer used for tasks requiring extremely rapid and complex calculations with thousands of
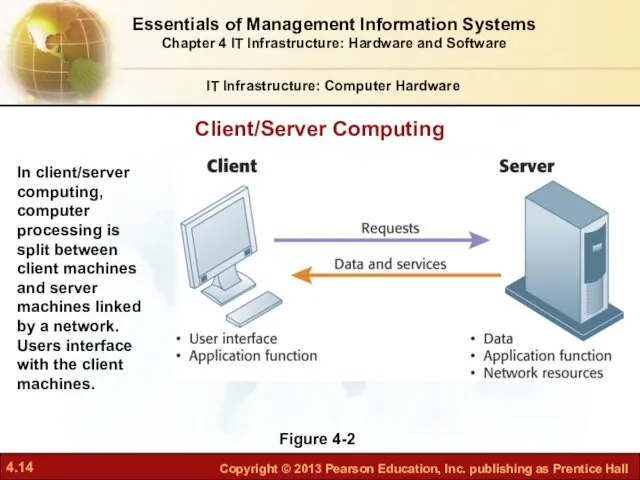
- 12. Client/server computing: Form of distributed computing Splits processing between “clients” and “servers” Clients: user point of
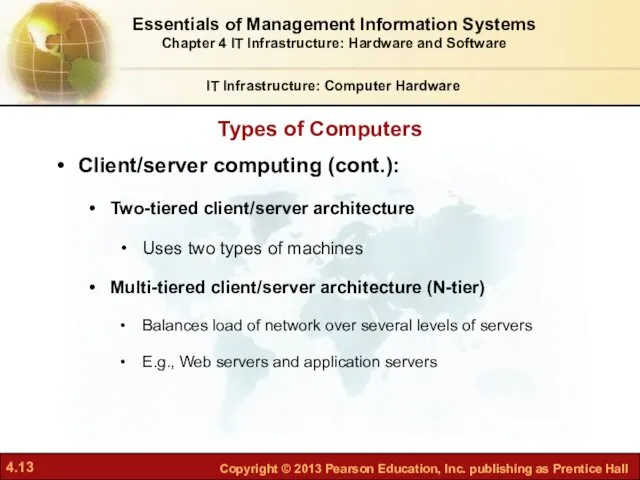
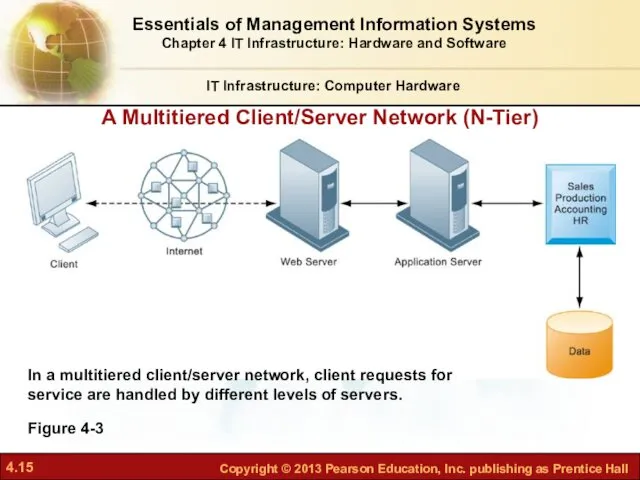
- 13. Client/server computing (cont.): Two-tiered client/server architecture Uses two types of machines Multi-tiered client/server architecture (N-tier) Balances
- 14. Client/Server Computing IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Figure 4-2 In client/server computing, computer processing is split between
- 15. A Multitiered Client/Server Network (N-Tier) IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Figure 4-3 Essentials of Management Information Systems
- 16. Storage, Input, and Output Technology IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Primary secondary storage technologies Magnetic disk: Hard
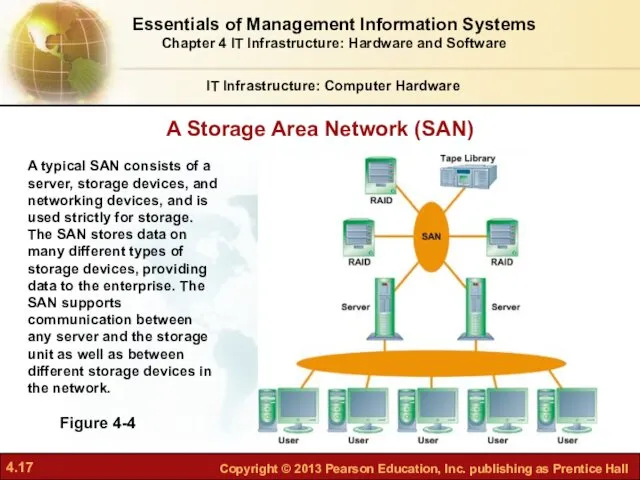
- 17. A Storage Area Network (SAN) IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Figure 4-4 A typical SAN consists of
- 18. Storage, Input, and Output Technology IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Input devices: Gather data and convert them
- 19. Storage, Input, and Output Technology IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Output devices: Display data after they have
- 20. Contemporary Hardware Trends IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware The emerging mobile digital platform Cell phones, smartphone Netbooks
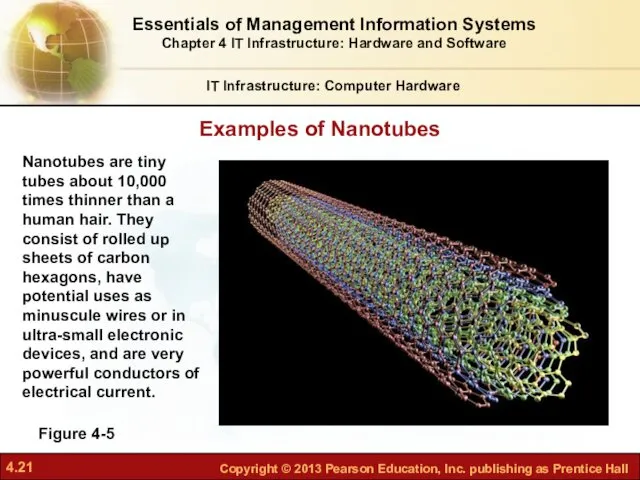
- 21. Examples of Nanotubes IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Figure 4-5 Nanotubes are tiny tubes about 10,000 times
- 22. Contemporary Hardware Trends IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Virtualization: Process of presenting a set of computing resources
- 23. Contemporary Hardware Trends IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Cloud Computing: A model of computing in which firms
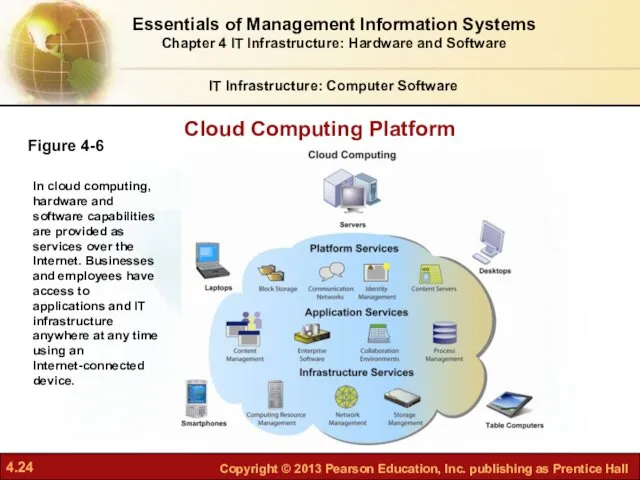
- 24. Cloud Computing Platform IT Infrastructure: Computer Software Figure 4-6 In cloud computing, hardware and software capabilities
- 25. Contemporary Hardware Trends IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Green computing Practices and technologies for designing, making, using,
- 26. Read the Interactive Session and then discuss the following questions: What business and social problems does
- 27. Contemporary Hardware Trends IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware High-performance and power-saving processors Multicore processor: Integrated circuit with
- 28. Contemporary Hardware Trends IT Infrastructure: Computer Hardware Autonomic computing: Development of systems that can configure themselves,
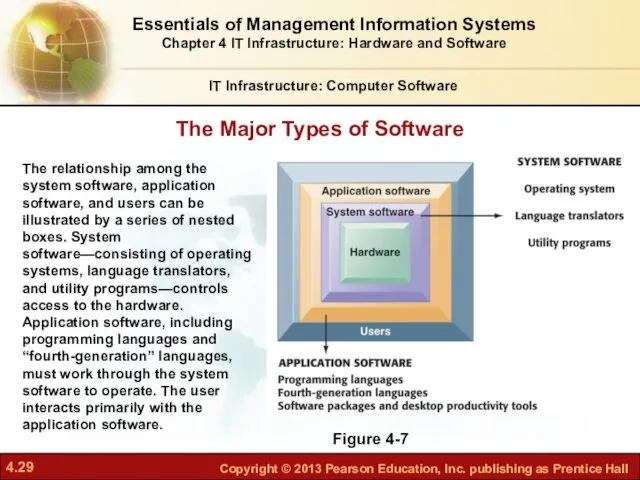
- 29. The Major Types of Software IT Infrastructure: Computer Software Figure 4-7 The relationship among the system
- 30. The software that controls computer activities GUIs and multitouch PC operating systems Windows (Windows 8) Mac
- 31. Application Software and Desktop Productivity Tools Application programming languages for business COBOL C, C++ Visual Basic:
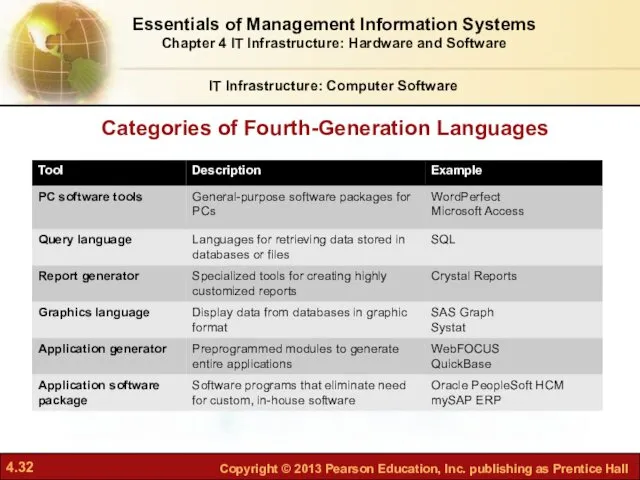
- 32. Categories of Fourth-Generation Languages IT Infrastructure: Computer Software Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 4 IT
- 33. Application Software and Desktop Productivity Tools Software packages and desktop productivity tools Word processing software Spreadsheet
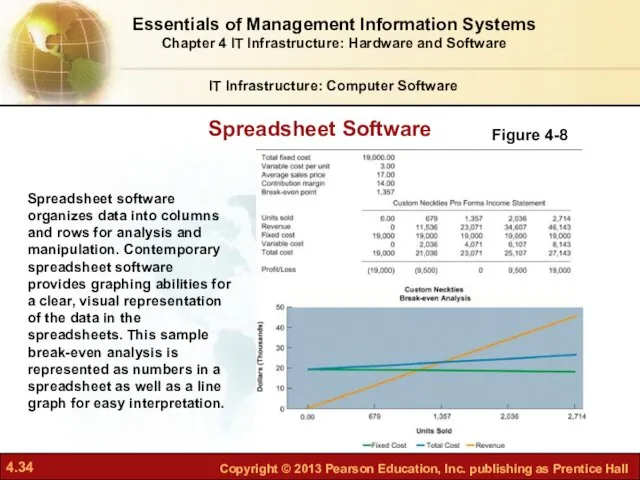
- 34. Spreadsheet Software IT Infrastructure: Computer Software Figure 4-8 Spreadsheet software organizes data into columns and rows
- 35. Java: Operating system-independent, processor-independent, object-oriented programming language Hypertext markup language (HTML): Page description language for specifying
- 36. Web services: Software components that exchange information with one another using universal Web communication standards and
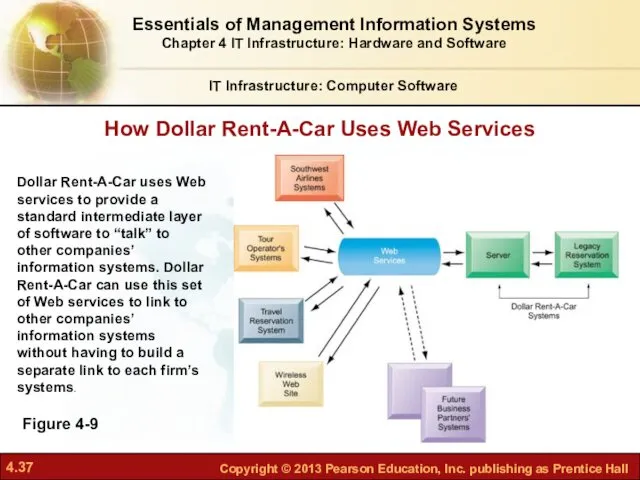
- 37. How Dollar Rent-A-Car Uses Web Services IT Infrastructure: Computer Software Figure 4-9 Dollar Rent-A-Car uses Web
- 38. Open source software Linux, Apache Cloud-based software and tools SaaS (software as a service) Google Docs
- 39. Managing Hardware and Software Technology Capacity planning Process of predicting when hardware system becomes saturated Ensuring
- 40. Managing Hardware and Software Technology Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) model Used to analyze direct and
- 41. Managing Hardware and Software Technology Using technology service providers Outsourcing Using external provider to: Run networks
- 42. Managing Hardware and Software Technology Using cloud services Small businesses “rent” infrastructure from another firm to
- 43. Managing Hardware and Software Technology Managing software localization for global business Local language interfaces English not
- 44. Interactive Session: People Should You Use Your iPhone for Work? IT Infrastructure: Computer Software Read the
- 46. Скачать презентацию




























 Сложноподчинённое предложение. Типы придаточных предложений
Сложноподчинённое предложение. Типы придаточных предложений Инновационные технологии и технические средства для реализации проекта ВСЖМ 1
Инновационные технологии и технические средства для реализации проекта ВСЖМ 1 Презентация.Знакомство детей с элементами национальной культуры народов, проживающих на территории Крутинского района
Презентация.Знакомство детей с элементами национальной культуры народов, проживающих на территории Крутинского района Александр II: начало правления. Крестьянская реформа 1861 г
Александр II: начало правления. Крестьянская реформа 1861 г Презентация к уроку ПДД Сигналы светофора и регулировщика№
Презентация к уроку ПДД Сигналы светофора и регулировщика№ Аква - фитнес. Плавание и другие формы доходов в бассейне
Аква - фитнес. Плавание и другие формы доходов в бассейне Доклад на педагогическом совете от 25.03.2015
Доклад на педагогическом совете от 25.03.2015 Обучение детей чтению.
Обучение детей чтению. Пишем сочинение на ОГЭ
Пишем сочинение на ОГЭ Фольклор Колыбельные песни
Фольклор Колыбельные песни Альдегиды и кетоны
Альдегиды и кетоны Поздравляю с 23 февраля
Поздравляю с 23 февраля Элементы математической логики
Элементы математической логики Духовная сфера в жизни общества
Духовная сфера в жизни общества Результат усвоения систематизированных знаний, умений и навыков
Результат усвоения систематизированных знаний, умений и навыков Я люблю собак
Я люблю собак Ақсу аудандандық ветеринариялық зертханасы
Ақсу аудандандық ветеринариялық зертханасы Зима
Зима Работа телеметриста
Работа телеметриста Гуманизм педагогической системы Яна Амоса Коменского (1592-1670)
Гуманизм педагогической системы Яна Амоса Коменского (1592-1670) Технология производства аминокислот кормового назначения
Технология производства аминокислот кормового назначения Медицинская паразитология. Экологические связи в подцарстве Простейшие
Медицинская паразитология. Экологические связи в подцарстве Простейшие Презентация Загадки об осени
Презентация Загадки об осени Меры нетарифного регулирования, как составная часть системы внешнеторговых запретов и ограничений
Меры нетарифного регулирования, как составная часть системы внешнеторговых запретов и ограничений Информация и информационные процессы. Представление информации
Информация и информационные процессы. Представление информации СССР в годы перестройки. Л.17
СССР в годы перестройки. Л.17 Edukacja Zdrowotna Dr Hanka Delbani
Edukacja Zdrowotna Dr Hanka Delbani Невротикалық бұзылулардың психогигенасы мен психопрофилактикасы
Невротикалық бұзылулардың психогигенасы мен психопрофилактикасы