Содержание
- 2. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 9 E-Commerce: Digital Markets, Digital Goods What
- 3. STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES How has e-commerce affected business-to-business transactions? What is the role of m-commerce in
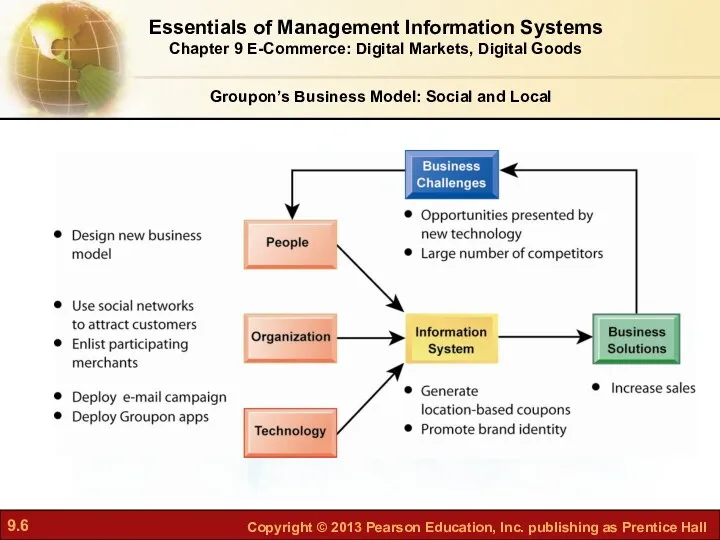
- 4. Groupon’s Business Model: Social and Local Problem: Competing with other business models utilizing social and local
- 5. Groupon offers subscribers daily deals from local merchants The catch: A group of 25 has to
- 6. Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 9 E-Commerce: Digital Markets, Digital Goods Groupon’s Business Model: Social
- 7. E-Commerce and the Internet E-Commerce Today E-commerce: use of the Internet and Web to transact business;
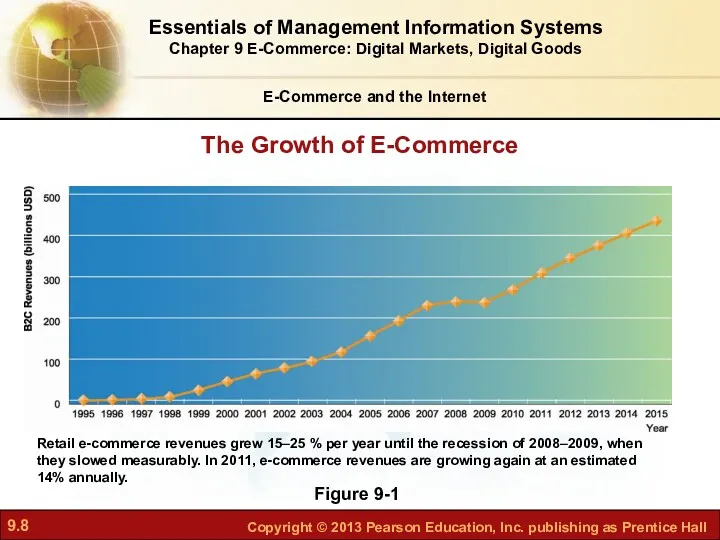
- 8. E-Commerce and the Internet Figure 9-1 The Growth of E-Commerce Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter
- 9. Why E-Commerce Is Different E-Commerce and the Internet Ubiquity Internet/Web technology available everywhere: work, home, and
- 10. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Global reach The technology reaches across national
- 11. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Universal standards One set of technology standards:
- 12. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Richness Supports video, audio, and text messages
- 13. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Interactivity The technology works through interaction with
- 14. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Information density Large increases in information density—the
- 15. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Personalization/Customization Technology permits modification of messages, goods
- 16. Unique Features of E-Commerce Technology E-Commerce and the Internet Social technology The technology promotes user content
- 17. Key Concepts: Digital Markets and Digital Goods E-Commerce and the Internet Digital market effects: Decreased information
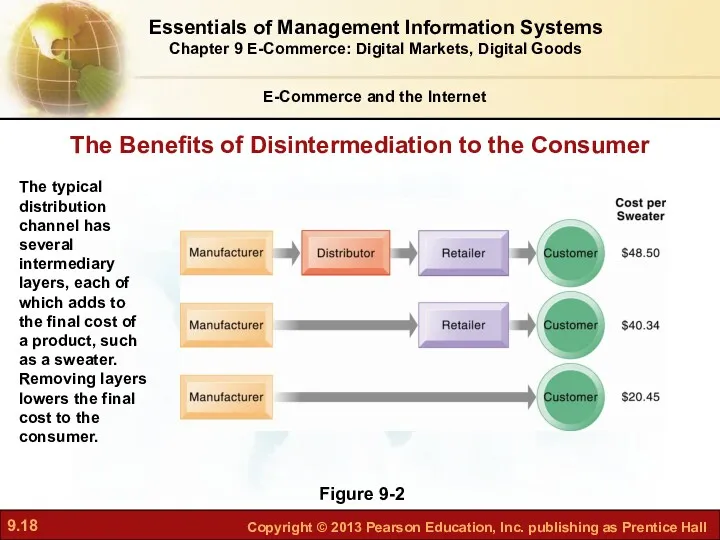
- 18. E-Commerce and the Internet Figure 9-2 The typical distribution channel has several intermediary layers, each of
- 19. E-Commerce and the Internet Digital goods Goods that can be delivered over a digital network E.g.,
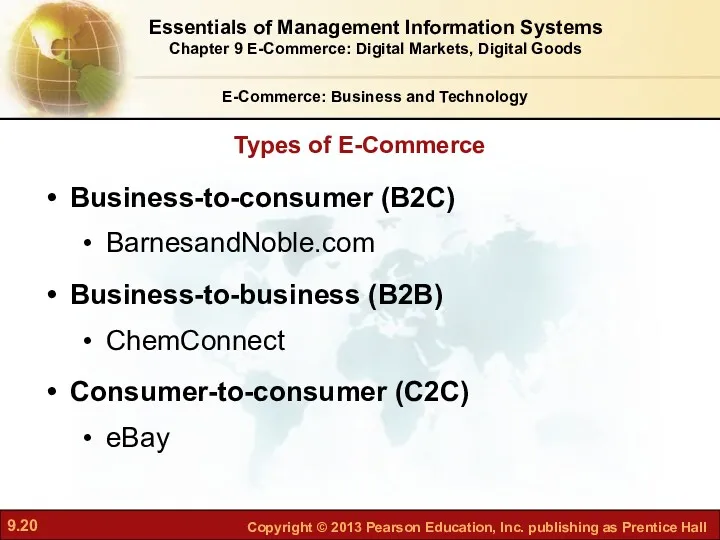
- 20. Types of E-Commerce E-Commerce: Business and Technology Business-to-consumer (B2C) BarnesandNoble.com Business-to-business (B2B) ChemConnect Consumer-to-consumer (C2C) eBay
- 21. E-Commerce Business Models E-Commerce: Business and Technology E-tailer Content provider Transaction broker Market creator Service provider
- 22. Interactive Session: Organizations Walmart, Amazon, and eBay: Who Will Dominate Internet Retailing? Read the Interactive Session
- 23. E-Commerce Revenue Models E-Commerce: Business and Technology Advertising Sales Subscription Free/Freemium Transaction fee Affiliate Essentials of
- 24. Web 2.0, Social Networking and the Wisdom of Crowds E-Commerce: Business and Technology Most popular Web
- 25. E-Commerce Marketing Internet provides marketers with new ways of identifying and communicating with customers Long tail
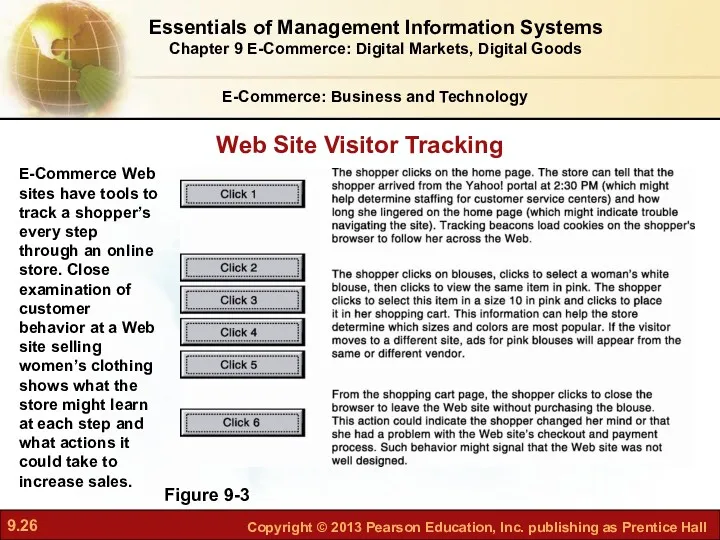
- 26. E-Commerce: Business and Technology Figure 9-3 E-Commerce Web sites have tools to track a shopper’s every
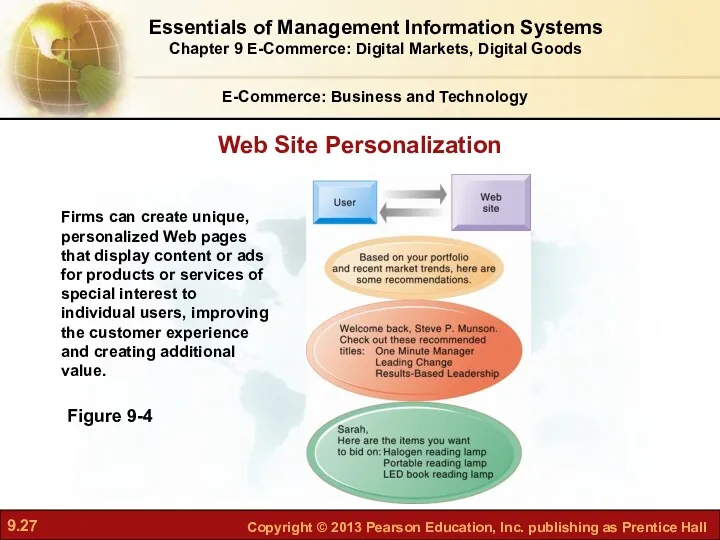
- 27. E-Commerce: Business and Technology Figure 9-4 Firms can create unique, personalized Web pages that display content
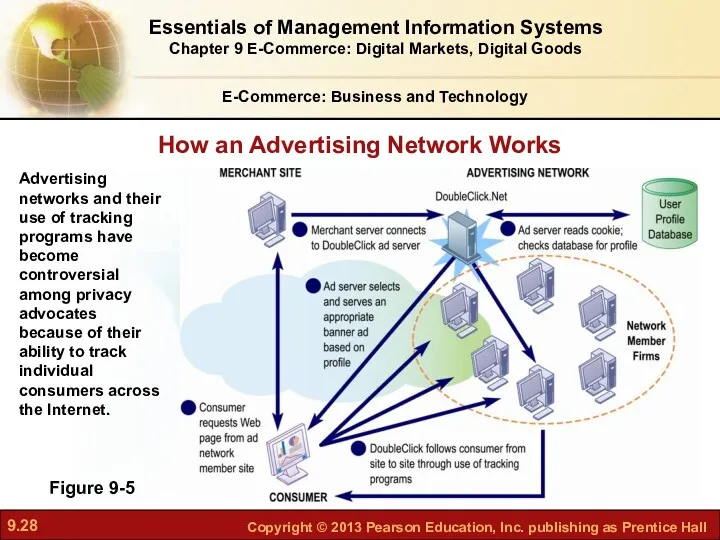
- 28. E-Commerce: Business and Technology Figure 9-5 How an Advertising Network Works Essentials of Management Information Systems
- 29. Social E-Commerce and Social Network Marketing Social e-commerce: Based on digital social graph Mapping of all
- 30. Social E-Commerce and Social Network Marketing Social media: Fastest growing media for branding and marketing Social
- 31. Interactive Session: People Social Commerce Creates New Customer Relationships Read the Interactive Session and then discuss
- 32. B2B E-Commerce: New Efficiencies and Relationships E-Commerce: Business and Technology Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter
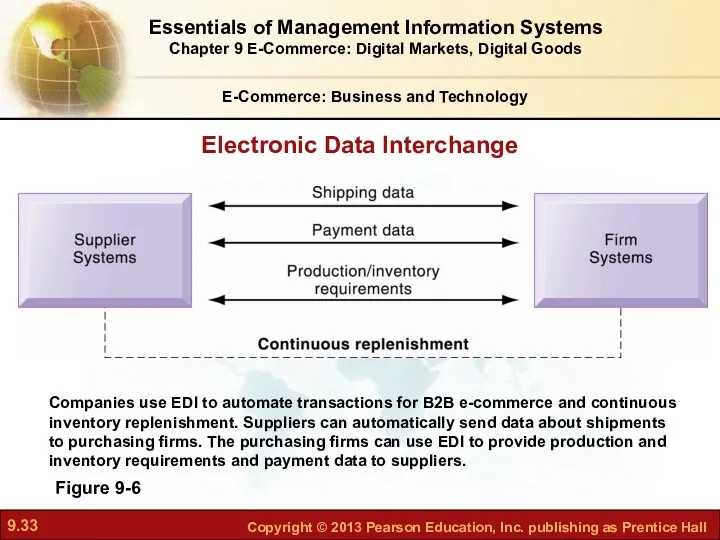
- 33. E-Commerce: Business and Technology Figure 9-6 Companies use EDI to automate transactions for B2B e-commerce and
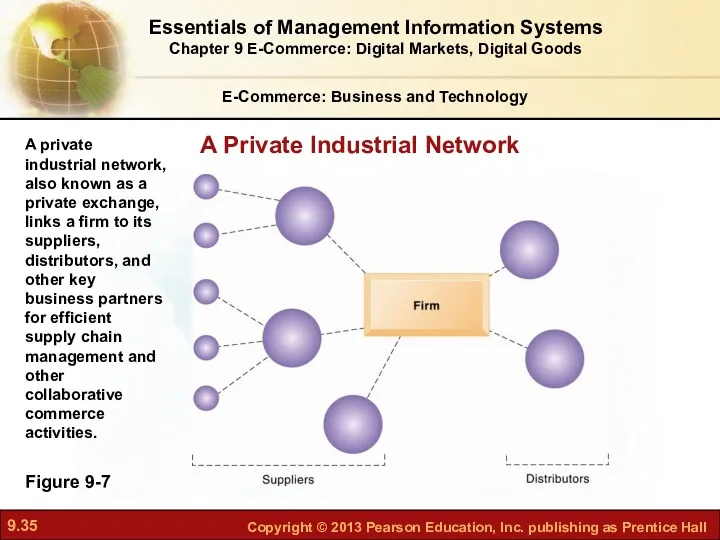
- 34. B2B E-Commerce: New Efficiencies and Relationships Private industrial network (private exchange) Large firm using extranet to
- 35. E-Commerce: Business and Technology Figure 9-7 A private industrial network, also known as a private exchange,
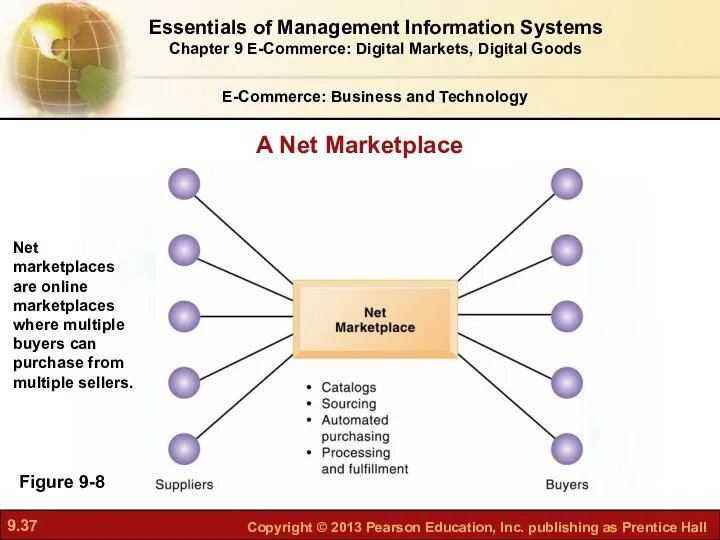
- 36. Net marketplaces (e-hubs) Single market for many buyers and sellers Industry-owned or owned by independent intermediary
- 37. E-Commerce: Business and Technology Figure 9-8 Net marketplaces are online marketplaces where multiple buyers can purchase
- 38. Exchanges Independently owned third-party Net marketplaces Connect thousands of suppliers and buyers for spot purchasing Typically
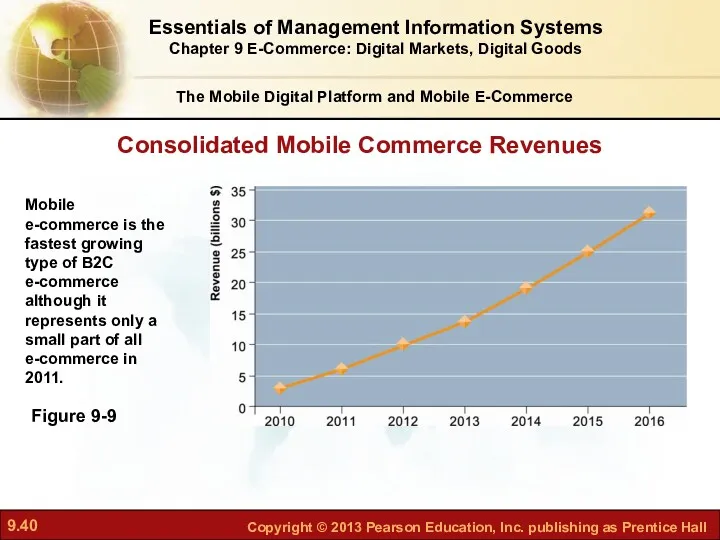
- 39. M-Commerce Services and Applications The Mobile Digital Platform and Mobile E-Commerce Although m-commerce represents a small
- 40. The Mobile Digital Platform and Mobile E-Commerce Figure 9-9 Consolidated Mobile Commerce Revenues Essentials of Management
- 41. Pieces of the Site-Building Puzzle Building an E-Commerce Web Site Assembling a team with the skills
- 42. Business Objectives, System Functionality, and Information Requirements Building an E-Commerce Web Site Business decisions drive the
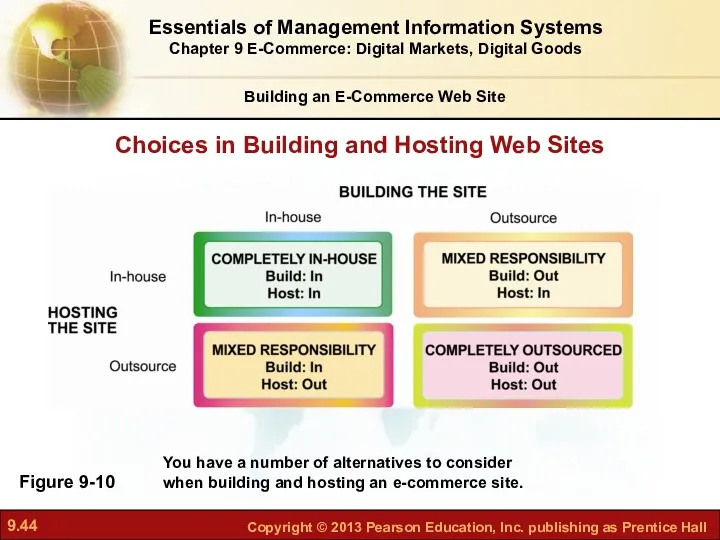
- 43. Building the Web Site: In-House versus Outsourcing Building an E-Commerce Web Site Alternatives in building the
- 44. Figure 9-10 Choices in Building and Hosting Web Sites Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 9
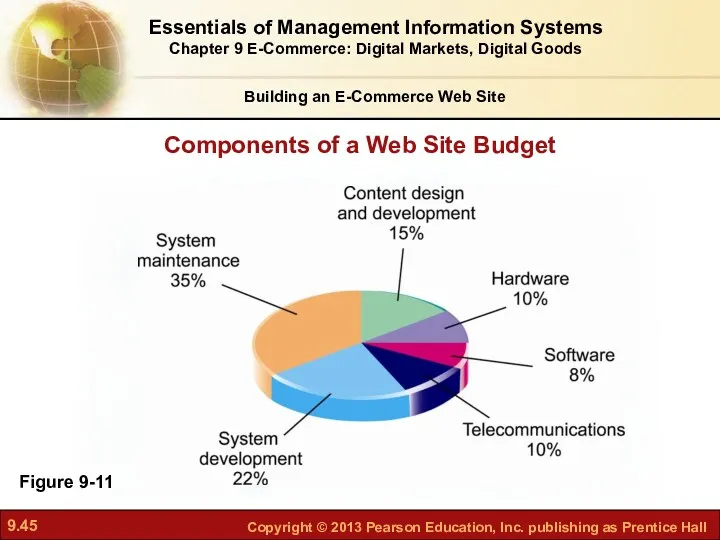
- 45. Figure 9-11 Components of a Web Site Budget Essentials of Management Information Systems Chapter 9 E-Commerce:
- 47. Скачать презентацию































 класс. ЛР №5
класс. ЛР №5 Презентация к выступлению на научно-практической конференции Диск
Презентация к выступлению на научно-практической конференции Диск Анимация. Живые рисунки на компьютере
Анимация. Живые рисунки на компьютере Сысоев
Сысоев Обучение грамматической стороне иноязычной речи
Обучение грамматической стороне иноязычной речи Искусство воспитания. Рекомендательный список литературы для родителей
Искусство воспитания. Рекомендательный список литературы для родителей психология общения
психология общения тыва дылга кичээл Темачангыс аймак кежигуннерлиг состер 7класс презентация
тыва дылга кичээл Темачангыс аймак кежигуннерлиг состер 7класс презентация Профотбор. Проблема отбора
Профотбор. Проблема отбора Система автоматизированного расчета и проектирования механического оборудования и конструкций
Система автоматизированного расчета и проектирования механического оборудования и конструкций Балет. История возникновения
Балет. История возникновения Интегрированный урок русского и английского языка по теме Сослагательное наклонение в языках агглютинативных и флективных.
Интегрированный урок русского и английского языка по теме Сослагательное наклонение в языках агглютинативных и флективных. История Древнего Египта
История Древнего Египта Развитие выносливости у подростков 13-14 лет в школьной секции общей физической подготовки
Развитие выносливости у подростков 13-14 лет в школьной секции общей физической подготовки Презентация внеклассного занятия по теме Мы за безопасность! для учащихся 3 классов
Презентация внеклассного занятия по теме Мы за безопасность! для учащихся 3 классов Энтеральные вирусные гепатиты А и Е
Энтеральные вирусные гепатиты А и Е Озон. Строение молекулы озона
Озон. Строение молекулы озона Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Я здоровье сберегу - сам себе я помогу!
Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Я здоровье сберегу - сам себе я помогу! Пристрої компютера. Фотоальбом
Пристрої компютера. Фотоальбом Проблемы электроэнергетики в трудах ученых САМГТУ. Виртуальная выставка
Проблемы электроэнергетики в трудах ученых САМГТУ. Виртуальная выставка Микроконтроллеры. Модули АЦП и ЦАП
Микроконтроллеры. Модули АЦП и ЦАП Аргоновый, водородный, азотный баллон, описание устройства, их назначения и правила эксплуатации
Аргоновый, водородный, азотный баллон, описание устройства, их назначения и правила эксплуатации Древний Ближний Восток. Семинар 2
Древний Ближний Восток. Семинар 2 Формирование сознательного чтения у учащихся начальных классов
Формирование сознательного чтения у учащихся начальных классов Презентация Дети-герои
Презентация Дети-герои Минеральная вода
Минеральная вода Полезные ископаемые, 5 кл
Полезные ископаемые, 5 кл Гироскопы. Применение в технике
Гироскопы. Применение в технике