Содержание
- 2. Chemical bonds Chemical bonds occur between atoms (identical or different) An atom= nucleus+electrons Nucleus = protons+neutrons
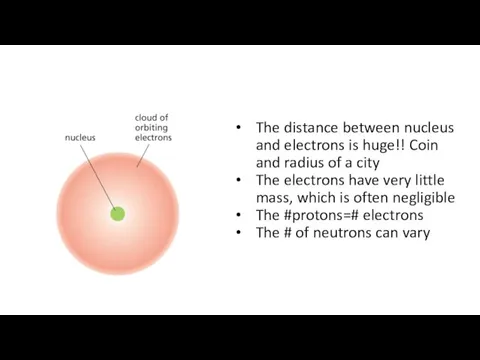
- 3. The distance between nucleus and electrons is huge!! Coin and radius of a city The electrons
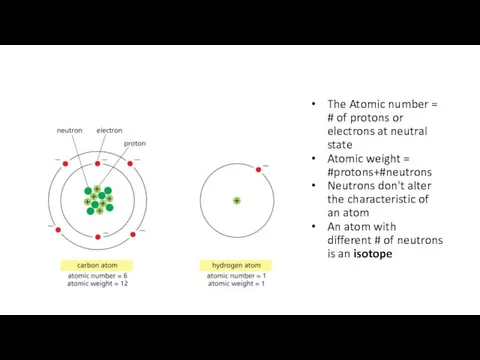
- 4. The Atomic number = # of protons or electrons at neutral state Atomic weight = #protons+#neutrons
- 5. Other properties of the atom Atomic weight/Molecular weight is defined in daltons . Atomic weight of
- 6. Molarity If we put 1 mole of glucose in 1 liter of water, we obtain 1
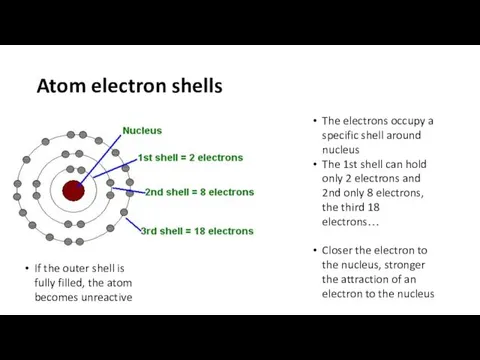
- 7. Atom electron shells The electrons occupy a specific shell around nucleus The 1st shell can hold
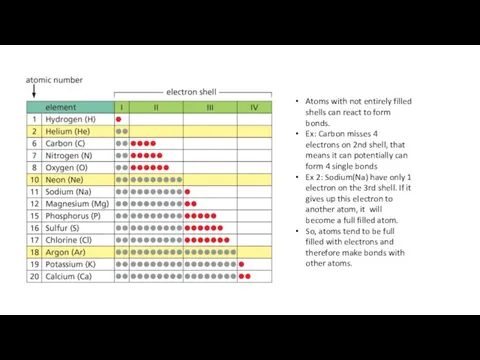
- 8. Atoms with not entirely filled shells can react to form bonds. Ex: Carbon misses 4 electrons
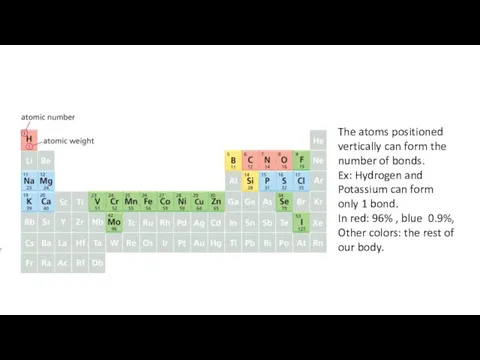
- 9. The atoms positioned vertically can form the number of bonds. Ex: Hydrogen and Potassium can form
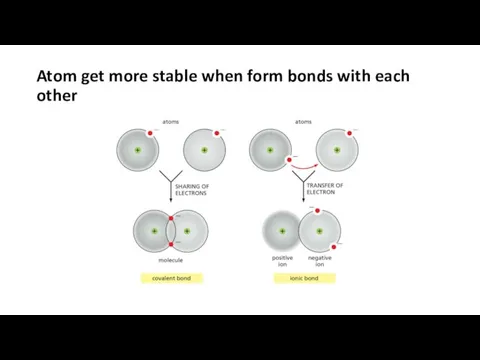
- 10. Atom get more stable when form bonds with each other
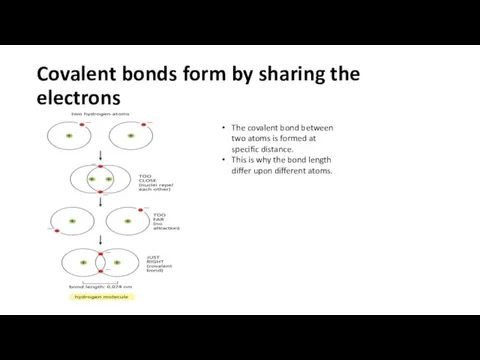
- 11. Covalent bonds form by sharing the electrons The covalent bond between two atoms is formed at
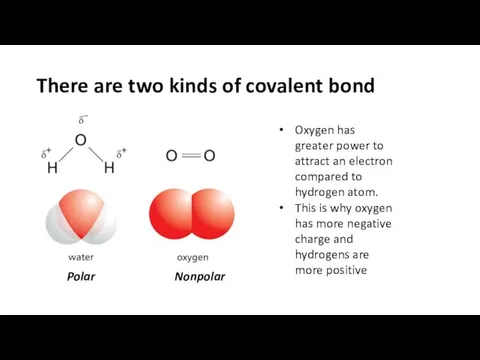
- 12. There are two kinds of covalent bond Oxygen has greater power to attract an electron compared
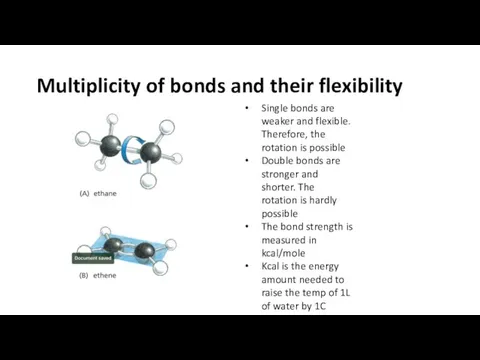
- 13. Multiplicity of bonds and their flexibility Single bonds are weaker and flexible. Therefore, the rotation is
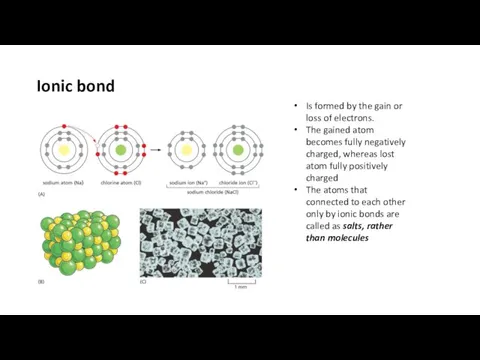
- 14. Ionic bond Is formed by the gain or loss of electrons. The gained atom becomes fully
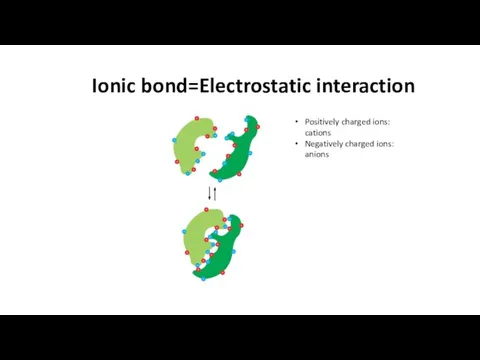
- 15. Ionic bond=Electrostatic interaction Positively charged ions: cations Negatively charged ions: anions
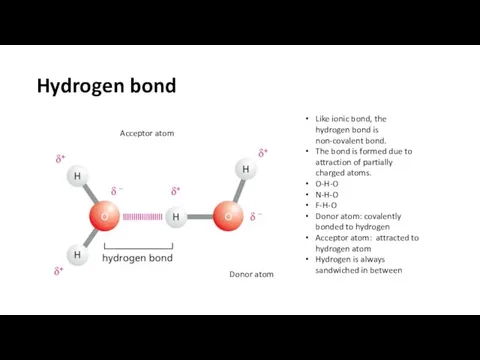
- 16. Hydrogen bond Like ionic bond, the hydrogen bond is non-covalent bond. The bond is formed due
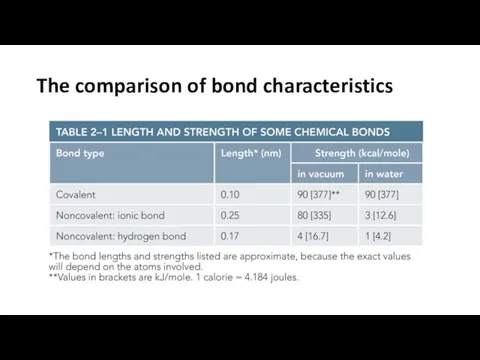
- 17. The comparison of bond characteristics
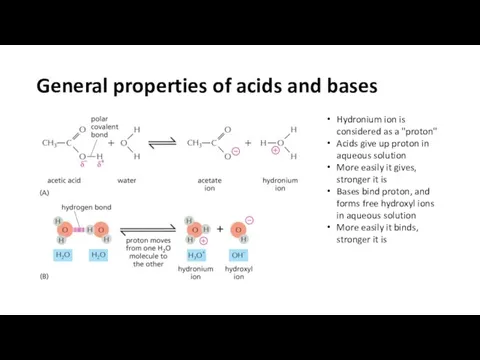
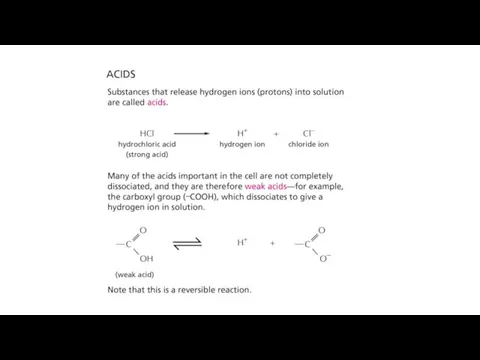
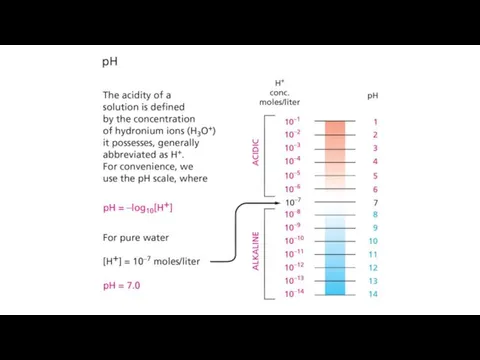
- 18. General properties of acids and bases Hydronium ion is considered as a "proton" Acids give up
- 24. Скачать презентацию





 Титульные листы
Титульные листы Модель Окамура-Хата
Модель Окамура-Хата Кто нас защищает. МЧС России
Кто нас защищает. МЧС России Мешочек для новогоднего подарка
Мешочек для новогоднего подарка Итоговое родительское собрание в 4Б классе.2012 -2013 уч.год.Презентация.
Итоговое родительское собрание в 4Б классе.2012 -2013 уч.год.Презентация. Схемы электровоза 2ЭС4К
Схемы электровоза 2ЭС4К Лучшие фотографии вторая половина 20 века
Лучшие фотографии вторая половина 20 века Применение распределительного свойства умножения
Применение распределительного свойства умножения Презентация к уроку труда Сердце, полное роз
Презентация к уроку труда Сердце, полное роз Наказание и поощрение в воспитании ребёнка
Наказание и поощрение в воспитании ребёнка Карен Хорни: социокультурная теория личности
Карен Хорни: социокультурная теория личности Где живут слоны?
Где живут слоны? Зеленый уголок. Ландшафтный дизайн
Зеленый уголок. Ландшафтный дизайн Использование дождевых и талых вод в водоснабжении промышленных объектов
Использование дождевых и талых вод в водоснабжении промышленных объектов 20231031_problema_antigeroya_v_literature._urok_-lektsiya
20231031_problema_antigeroya_v_literature._urok_-lektsiya Бартоломео Франческо Растрелли (Варфоломей Варфоломеевич Растрелли) 1700 - 1771
Бартоломео Франческо Растрелли (Варфоломей Варфоломеевич Растрелли) 1700 - 1771 Заболевания носа и придаточных пазух. Методы исследования. Ожоги наружного носа
Заболевания носа и придаточных пазух. Методы исследования. Ожоги наружного носа Правительство Самарской области
Правительство Самарской области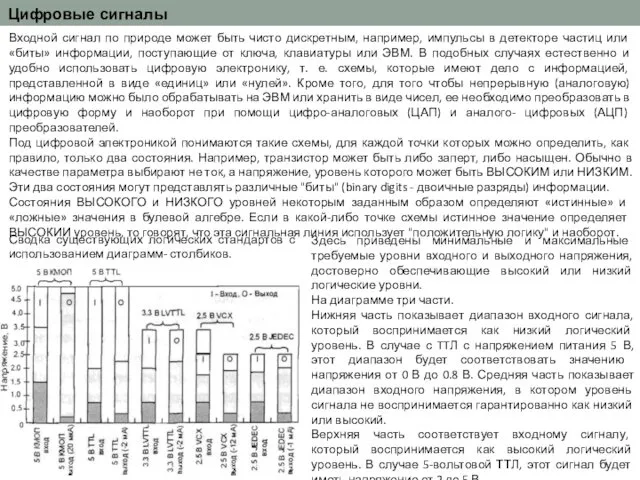 Цифровая схемотехника. Цифровые сигналы. 1
Цифровая схемотехника. Цифровые сигналы. 1 Дворцовые перевороты
Дворцовые перевороты Социальные гарантии для сотрудников уголовно-исполнительной системы
Социальные гарантии для сотрудников уголовно-исполнительной системы Постоянные магниты. Магнитное поле Земли
Постоянные магниты. Магнитное поле Земли Терроризм. Основные типы терроризма
Терроризм. Основные типы терроризма Абсолютизм в Западной Европе. Тридцатилетняя война 1618-1648года
Абсолютизм в Западной Европе. Тридцатилетняя война 1618-1648года День Земли
День Земли Анатомия и физиология мужской репродуктивной системы
Анатомия и физиология мужской репродуктивной системы Снятие мерок
Снятие мерок В мире книг Альберта Лиханова
В мире книг Альберта Лиханова