Содержание
- 2. CONDITIONAL SENTENCES 201.016 IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All rights reserved.
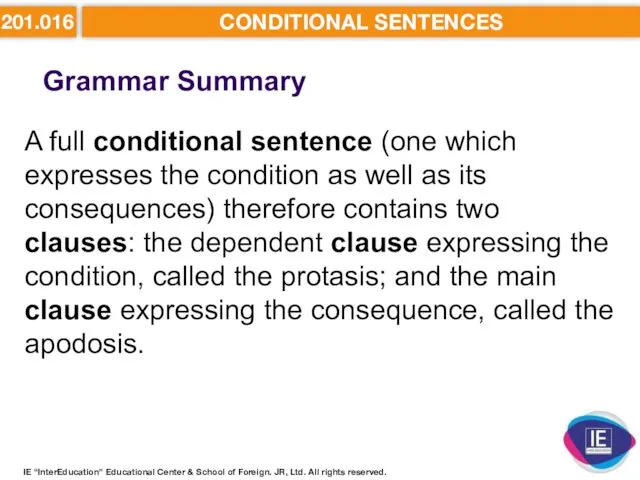
- 3. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Grammar Summary A full conditional sentence (one which expresses the condition as well
- 4. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Grammar Summary Conditional tenses are used to speculate about what could happen, what
- 5. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES THE ZERO CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd.
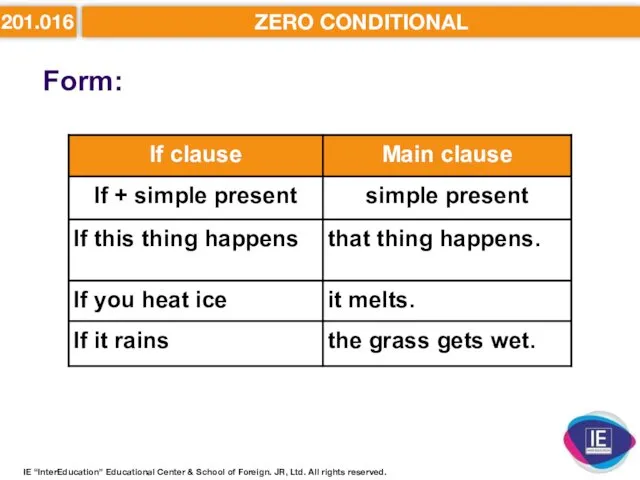
- 6. 201.016 ZERO CONDITIONAL Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All rights
- 7. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All rights
- 8. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 1: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 9. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 2: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
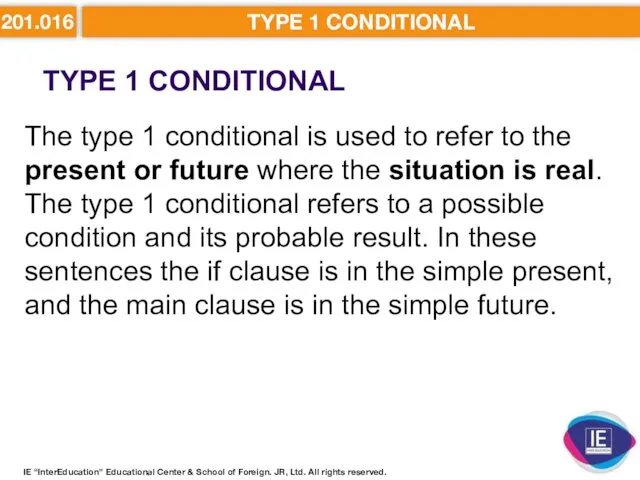
- 10. 201.016 TYPE 1 CONDITIONAL TYPE 1 CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
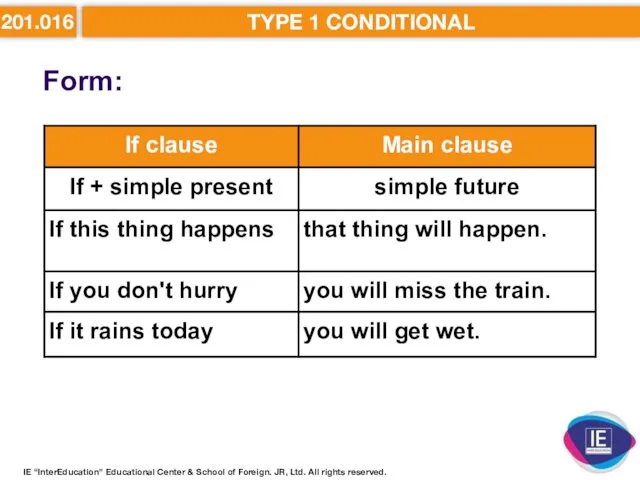
- 11. 201.016 TYPE 1 CONDITIONAL Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 12. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All rights
- 13. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 1: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 14. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 2: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 15. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Modals in Conditionals 1: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
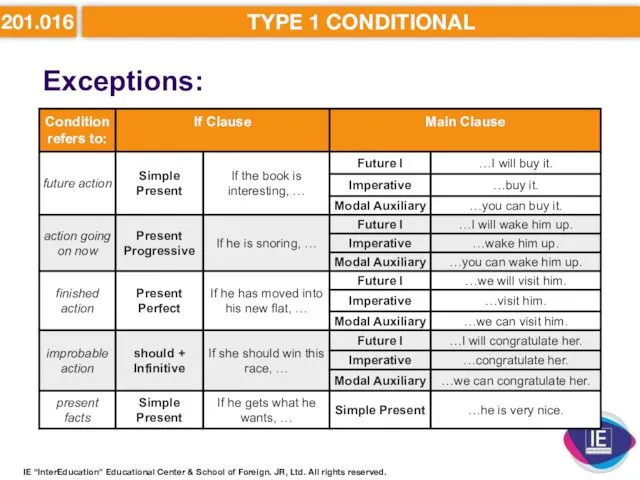
- 16. 201.016 TYPE 1 CONDITIONAL Exceptions: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 17. 201.016 TYPE 2 CONDITIONAL TYPE 2 CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
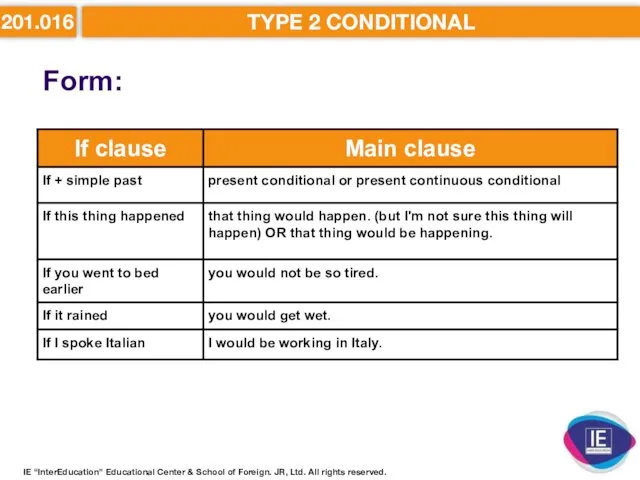
- 18. 201.016 TYPE 2 CONDITIONAL Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 19. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 1: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 20. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 1: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 21. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Modals in Conditionals 2: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
- 22. 201.016 PRESENT CONTINUOUS CONDITIONAL PRESENT CONTINUOUS CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
- 23. 201.016 PRESENT CONTINUOUS CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All rights
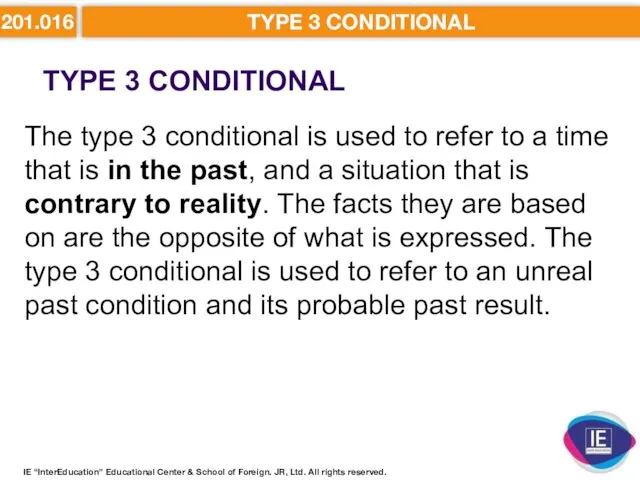
- 24. 201.016 TYPE 3 CONDITIONAL TYPE 3 CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
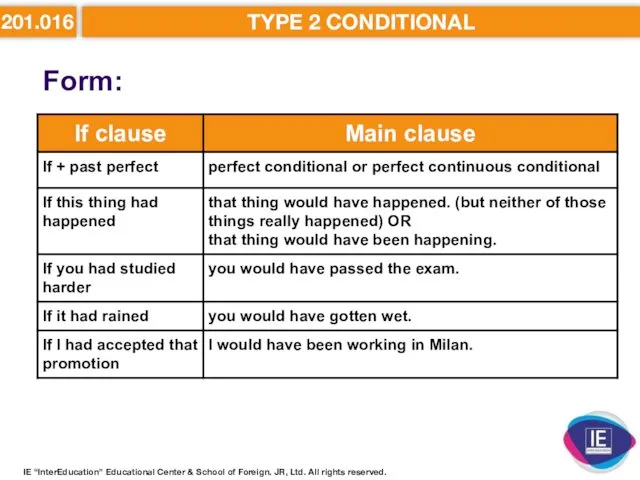
- 25. 201.016 TYPE 2 CONDITIONAL Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 26. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Function 1: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
- 27. 201.016 CONDITIONAL SENTENCES Modals in Conditionals 3: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
- 28. 201.016 PERFECT CONTINUOUS CONDITIONAL PERFECT CONTINUOUS CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
- 29. 201.016 MIXED TYPE CONDITIONAL TYPE 3 CONDITIONAL IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR,
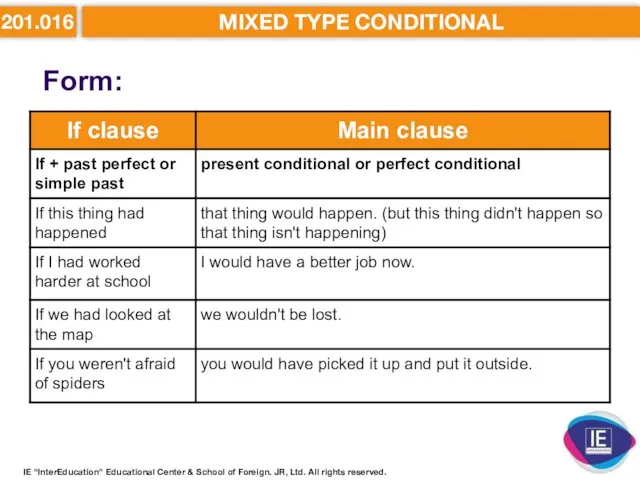
- 30. 201.016 MIXED TYPE CONDITIONAL Form: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign. JR, Ltd. All
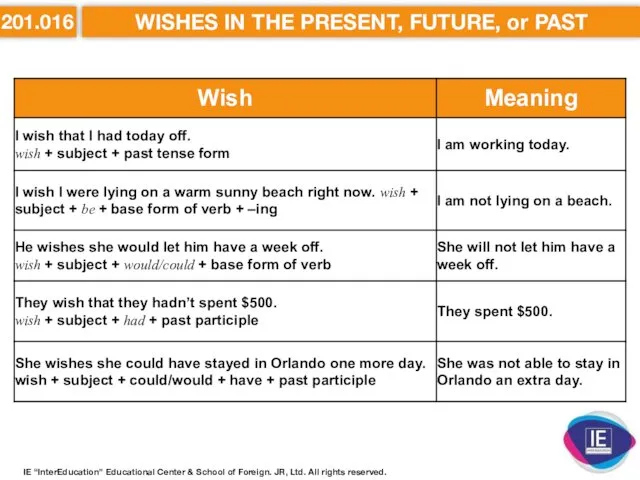
- 31. 201.016 WISHES IN THE PRESENT, FUTURE, or PAST Summary: IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of
- 32. 201.016 WISHES IN THE PRESENT, FUTURE, or PAST IE “InterEducation” Educational Center & School of Foreign.
- 34. Скачать презентацию




















 Правовое регулирование предпринимательской деятельности
Правовое регулирование предпринимательской деятельности Общие сведения о языке программирования Паскаль
Общие сведения о языке программирования Паскаль Урок решения задач по теме Файл и файловая система
Урок решения задач по теме Файл и файловая система МОЯ-ЮГРА-МОЯ ПЛАНЕТА!.ИГРЫ НАРОДОВ СЕВЕРА.
МОЯ-ЮГРА-МОЯ ПЛАНЕТА!.ИГРЫ НАРОДОВ СЕВЕРА. Урок по теме Минеральные воды
Урок по теме Минеральные воды Формирование общих речевых навыков у детей дошкольного возраста
Формирование общих речевых навыков у детей дошкольного возраста Русский футуризм. Поэзия
Русский футуризм. Поэзия Магниторезонансная томография
Магниторезонансная томография Отопление дома
Отопление дома ООО Телерадиокомпания 2х2
ООО Телерадиокомпания 2х2 Разработка конструкторско - технической документации для изготовление платья из трикотажа на женщину средней возрастной группы
Разработка конструкторско - технической документации для изготовление платья из трикотажа на женщину средней возрастной группы Подготовка к сочинению по тексту в формате ЕГЭ
Подготовка к сочинению по тексту в формате ЕГЭ Дуденков - (Ем) - лиц.77 - презентация
Дуденков - (Ем) - лиц.77 - презентация Расчет ПГУ с АБХМ
Расчет ПГУ с АБХМ Социальная эпистемология
Социальная эпистемология Непредельные углеводороды .Алкены 10 класс
Непредельные углеводороды .Алкены 10 класс Зарядка для непослушного язычка
Зарядка для непослушного язычка Угольная промышленность
Угольная промышленность Популяція біології. Вплив вітамінів на організм людини
Популяція біології. Вплив вітамінів на організм людини Экономика Тюменской области
Экономика Тюменской области Многоатомные спирты
Многоатомные спирты Городской транспортный комплекс
Городской транспортный комплекс Шубарши кентінің жастары. Қазақ күресі
Шубарши кентінің жастары. Қазақ күресі Викторина Здорово быть здоровым!
Викторина Здорово быть здоровым! Холодная листовая штамповка
Холодная листовая штамповка Расчет количества профнастила на крышу: рекомендации мастеров
Расчет количества профнастила на крышу: рекомендации мастеров Общий обзор организма человека
Общий обзор организма человека Русская печатная кириллическая книга
Русская печатная кириллическая книга