Domino Effect Analysis and Assessment of Industrial Sites: A Review of Methodologies and Software Tools презентация
Содержание
- 2. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The "What-if" analysis is the simplest technique used to identify hazards. It
- 3. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure It is a brainstorming approach according to which a group of experienced
- 4. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Assembling an experienced, knowledgeable team is probably the single most important element
- 5. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The next most important step is gathering the needed information. The operation
- 6. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure If these documents are not available, the first recommendation for the review
- 7. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure If these documents are not available, the first recommendation for the review
- 8. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The great advantage of the "What-if" analysis is its flexibility. In essence
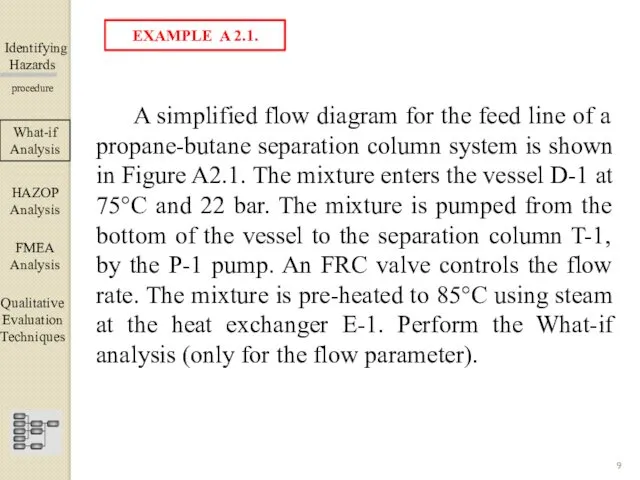
- 9. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure A simplified flow diagram for the feed line of a propane-butane separation
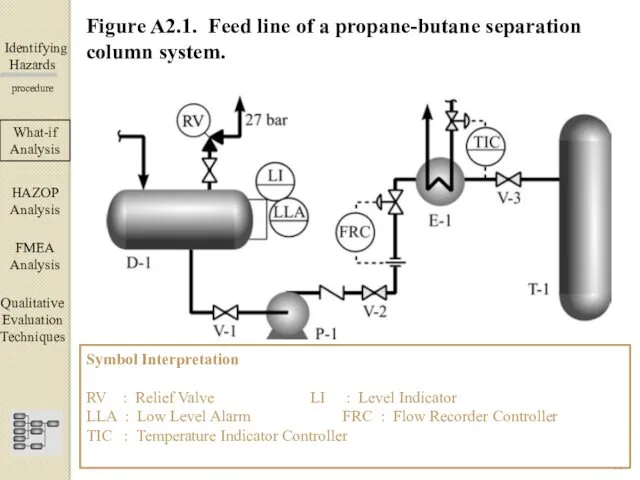
- 10. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Figure A2.1. Feed
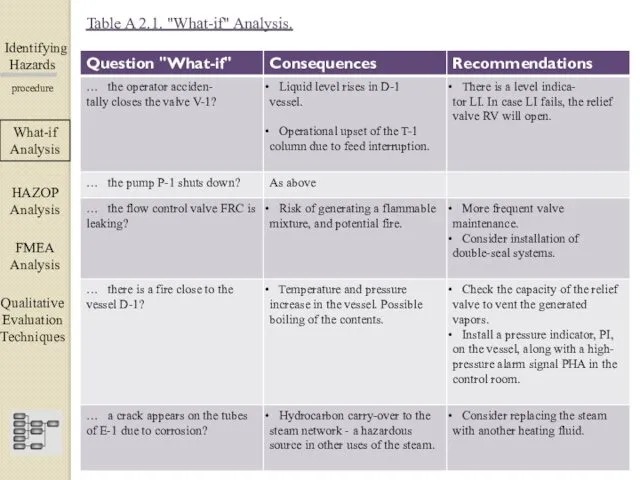
- 11. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure According to the aforementioned discussion, the analysis, the consequences and the recommendations
- 12. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Table A 2.1.
- 13. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The HAzard and OPerability study, HAZOP was originally developed by engineers in
- 14. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The HAZOP analysis can be applied to all processes. It is based
- 15. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The primary purpose of the HAZOP analysis is the identification of possible
- 16. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure On the other hand, to carry out a HAZOP we need a
- 17. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure HAZOP studies may also be used more extensively, including: What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ
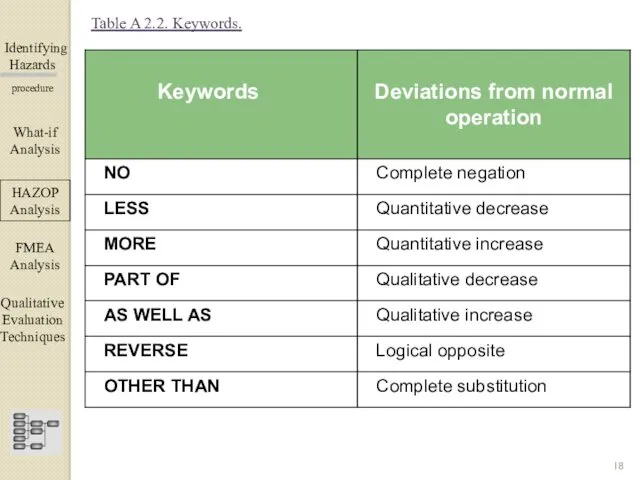
- 18. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Table A 2.2. Keywords. What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation
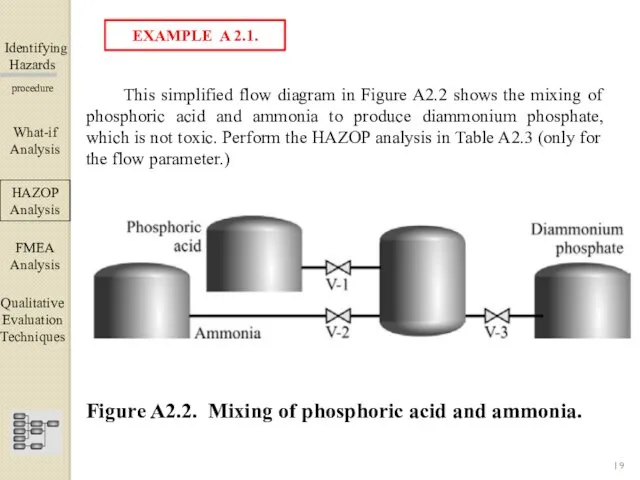
- 19. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure This simplified flow diagram in Figure A2.2 shows the mixing of phosphoric
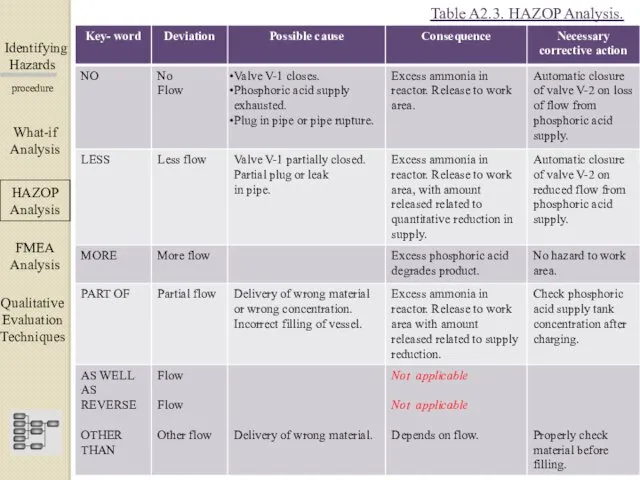
- 20. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Table A2.3. HAZOP
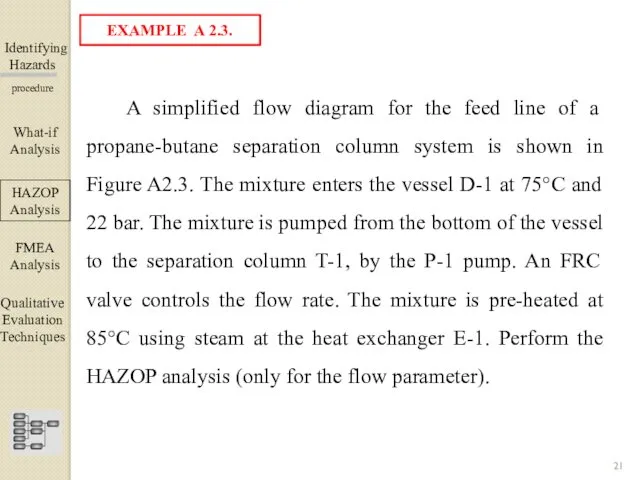
- 21. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure A simplified flow diagram for the feed line of a propane-butane separation
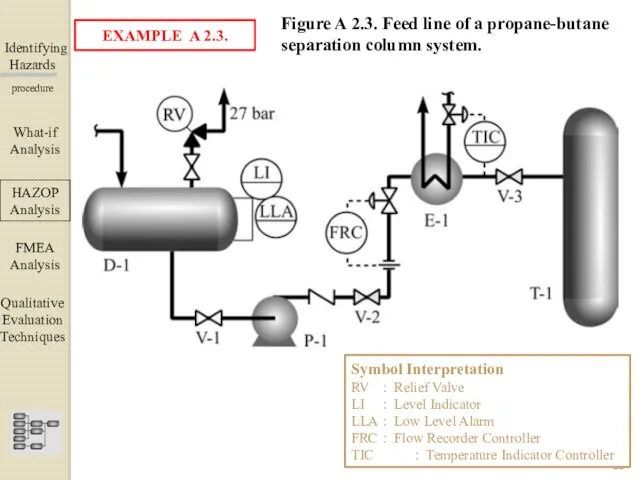
- 22. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques EXAMPLE A 2.3.
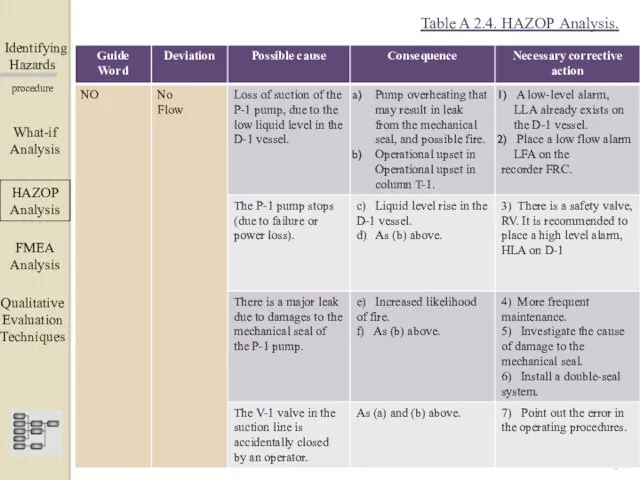
- 23. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The analysis, consequences and recommendations for this particular example are shown in
- 24. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Table A 2.4.
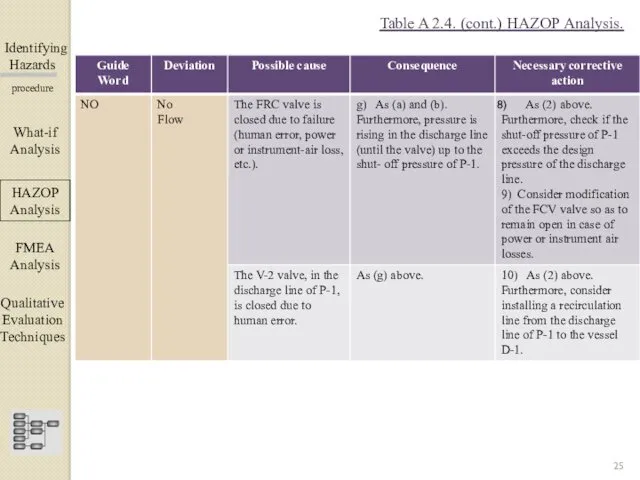
- 25. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Table A 2.4.
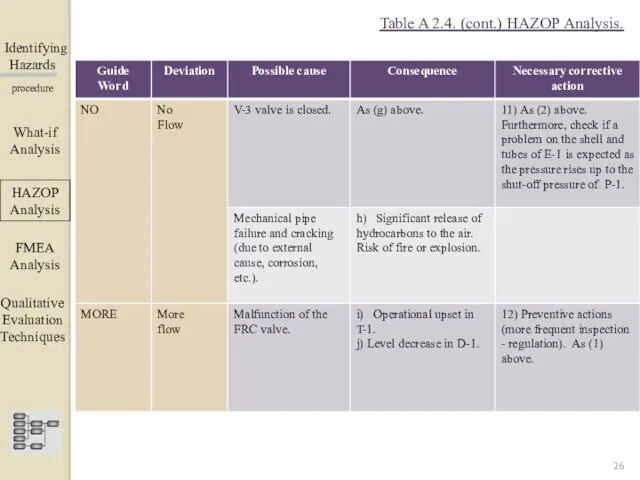
- 26. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Table A 2.4.
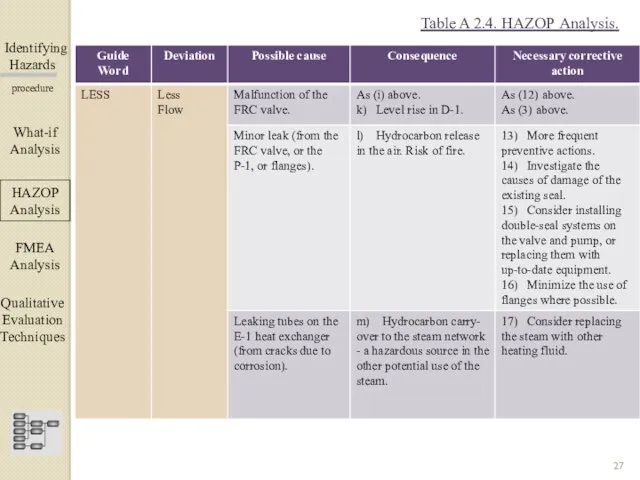
- 27. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure What-if Analysis ΗΑΖΟΡ Analysis FMEA Analysis Qualitative Evaluation Techniques Table A 2.4.
- 28. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The Failure Modes and Effects Analysis, FMEA, evaluates the ways in which
- 29. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The FMEA analysis is usually applied to systems, subsystems, components, procedures, interfaces
- 30. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure In order to determine and define priorities, usually the following three criteria
- 31. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure These three criteria define the Risk Priority Number, RPN, as What-if Analysis
- 32. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The principles of an FMEA analysis are easy to understand and to
- 33. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Qualitative evaluation techniques are normally applied to identify any potential hazard as
- 34. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The Safety Review, also known as Process Safety Review, or Design Safety
- 35. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Safety Reviews intend to identify those operating procedures or plant conditions that
- 36. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The Safety Review Team must have a lot of experience in applying
- 37. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Checklist Analysis uses a written list of objects or procedural steps that
- 38. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure As a minimum, a Checklist Analysis can be employed to ensure that
- 39. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Preliminary Hazard Analysis refers to the effort to identify possible hazards from
- 40. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The Preliminary Hazard Analysis is not a discrete technique, but it depends
- 41. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Criticality Analysis ranks the damage potential of system elements according to a
- 42. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Change Analysis is based upon the examination of possible changes of a
- 43. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure In this case, the full understanding of the physical principles governing the
- 44. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure The Critical Incident Technique is based upon the critical evaluation of previous
- 45. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Energy Analysis refers to the identification of all energy sources within a
- 46. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Worst-Case Analysis technique examines all possible failures that could occur and focus
- 47. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Network Logic Analysis describes the system operation as a network of logic
- 48. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Scenario Analysis is based upon the examination of possible scenarios proposed by
- 49. Identifying Hazards ▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀ procedure Systematic Inspection uses checklists, codes, regulations, industrial standards and guidelines, prior mishap
- 51. Скачать презентацию































 Россия в 1992-2007 годах
Россия в 1992-2007 годах Разработка и обоснование нового туристского маршрута: Тверская область, Торжок
Разработка и обоснование нового туристского маршрута: Тверская область, Торжок Задание №24 ЕГЭ по истории. Алгоритм выполнения
Задание №24 ЕГЭ по истории. Алгоритм выполнения 20231107_narodnye_promysly_i_remesla_rossii_beresta
20231107_narodnye_promysly_i_remesla_rossii_beresta Как обнаружили электричество
Как обнаружили электричество Нормативно-правовая база инклюзивного образования в России
Нормативно-правовая база инклюзивного образования в России Использование ИКТ при организации образовательной деятельности дошкольников
Использование ИКТ при организации образовательной деятельности дошкольников Приготовление пищи в походе
Приготовление пищи в походе 20231013_volgodonskoy_pedagogicheskiy_kolledzh_gbpou_ro_vpk
20231013_volgodonskoy_pedagogicheskiy_kolledzh_gbpou_ro_vpk Физическая работоспособность спортсмена
Физическая работоспособность спортсмена Ақсай мұнай газ кен орны
Ақсай мұнай газ кен орны Детям о Рождестве
Детям о Рождестве Наглядное пособие по теоретической механике
Наглядное пособие по теоретической механике Метод интервалов для непрерывных функций
Метод интервалов для непрерывных функций История наушников
История наушников When i'm ill!
When i'm ill! Рослинний світ
Рослинний світ Казанское ханство
Казанское ханство Презентация к занятию Движение пешеходов, их права и обязанности. Диск
Презентация к занятию Движение пешеходов, их права и обязанности. Диск Социальный проект:Наш двор
Социальный проект:Наш двор Мистика и тайны загадочного числа пи
Мистика и тайны загадочного числа пи Презентация по географии на тему:География как наука
Презентация по географии на тему:География как наука Серная кислота
Серная кислота Особенности развития связной речи у детей 4-5 лет
Особенности развития связной речи у детей 4-5 лет Организация работы со способными и одарёнными детьми на уроках биологии и во внеурочной деятельности
Организация работы со способными и одарёнными детьми на уроках биологии и во внеурочной деятельности Химико-термическая обработка стали
Химико-термическая обработка стали Ісіктер туралы жалпы ілім. Органоспецификалық емес эпителиальды ісіктер
Ісіктер туралы жалпы ілім. Органоспецификалық емес эпителиальды ісіктер Решение комбинаторных задач. Приложение к уроку №1
Решение комбинаторных задач. Приложение к уроку №1