Содержание
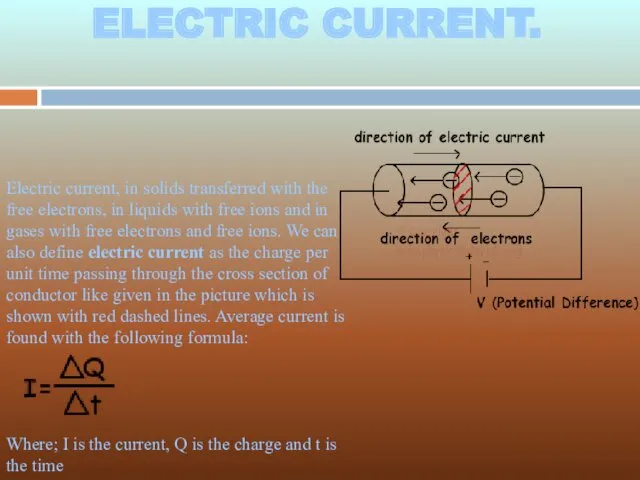
- 2. ELECTRIC CURRENT. ELECTRIC CURRENT. Electric current, in solids transferred with the free electrons, in liquids with
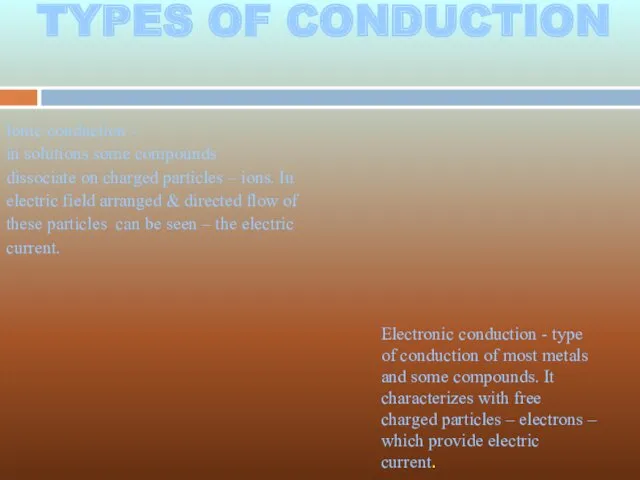
- 3. Ionic conduction - in solutions some compounds dissociate on charged particles – ions. In electric field
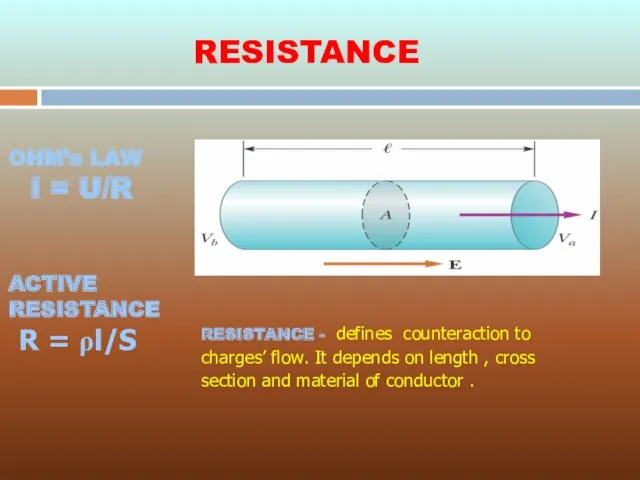
- 4. RESISTANCE - defines counteraction to charges’ flow. It depends on length , cross section and material
- 5. CAPACITY – defines potentials difference between two isolated bodies if they have charges of the same
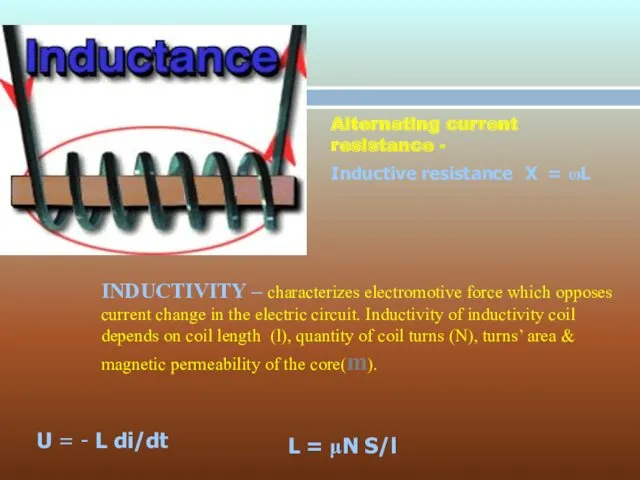
- 6. INDUCTIVITY – characterizes electromotive force which opposes current change in the electric circuit. Inductivity of inductivity
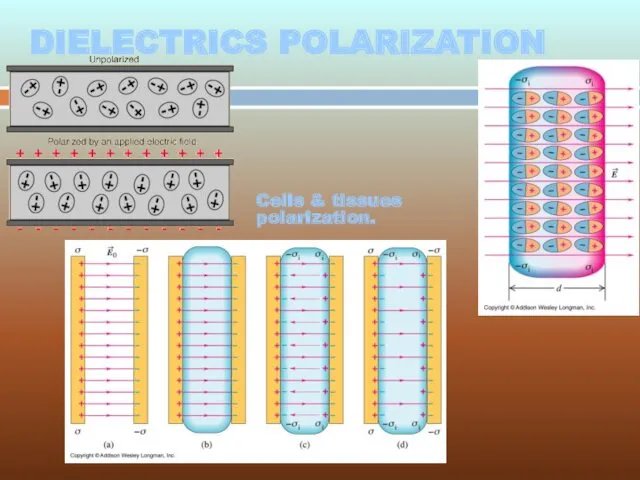
- 7. DIELECTRICS POLARIZATION Cells & tissues polarization.
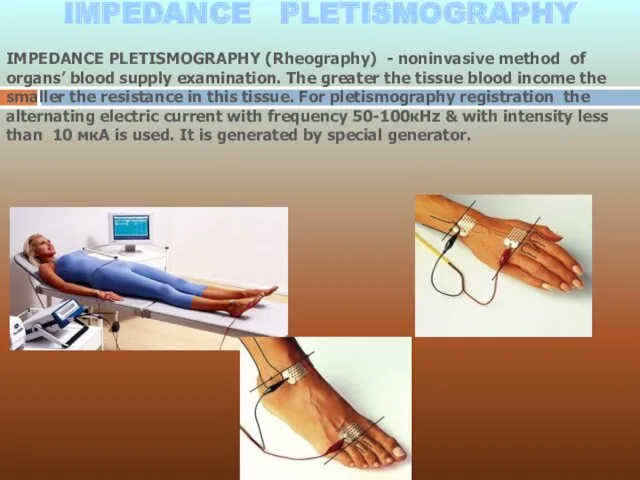
- 8. IMPEDANCE PLETISMOGRAPHY (Rheography) - noninvasive method of organs’ blood supply examination. The greater the tissue blood
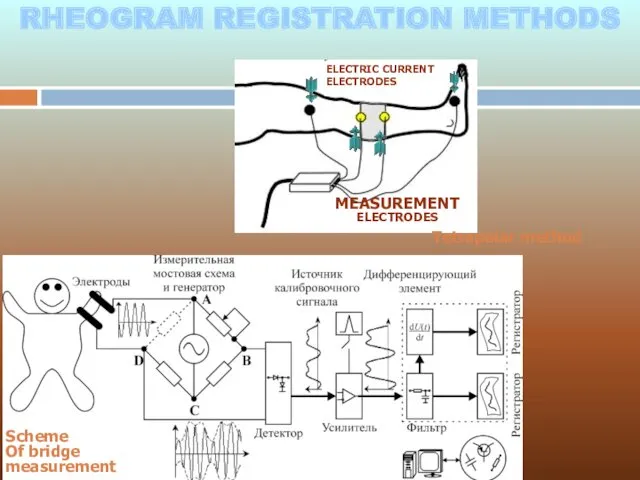
- 9. RHEOGRAM REGISTRATION METHODS ELECTRIC CURRENT ELECTRODES MEASUREMENT ELECTRODES Tetrapolar method Scheme Of bridge measurement
- 11. Скачать презентацию

 Восстание под руководством Емельяна Пугачёва (1773 – 1775 гг.)
Восстание под руководством Емельяна Пугачёва (1773 – 1775 гг.) ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К МЕРОПРИЯТИЮ ДЛЯ ДЕТЕЙ ПОДГОТОВИТЕЛЬНОЙ ГРУППЫ Я — ПЕРВОКЛАССНИК Диск
ПРЕЗЕНТАЦИЯ К МЕРОПРИЯТИЮ ДЛЯ ДЕТЕЙ ПОДГОТОВИТЕЛЬНОЙ ГРУППЫ Я — ПЕРВОКЛАССНИК Диск Washington is the capital of the United States of America
Washington is the capital of the United States of America ВВЭР (водо-водяной энергетический реактор)
ВВЭР (водо-водяной энергетический реактор) Презентация Парад Победы
Презентация Парад Победы Организация свадебного торжества
Организация свадебного торжества Християнська етика. Щедрість і захланність
Християнська етика. Щедрість і захланність Современные средства поражения
Современные средства поражения prezetantsia
prezetantsia Презентация Проектная технология в начальной школе
Презентация Проектная технология в начальной школе Коротковой Юлии, юс1-11
Коротковой Юлии, юс1-11 past simple
past simple Классификация веществ. Приготовление растворов. Расчёт массовой доли растворённого вещества
Классификация веществ. Приготовление растворов. Расчёт массовой доли растворённого вещества Пізня зрілість (Е. Еріксон)
Пізня зрілість (Е. Еріксон) Проект Вместе лучше. Концепция воспитательной работы в классе.
Проект Вместе лучше. Концепция воспитательной работы в классе. Информационные технологии. Структура технологической системы
Информационные технологии. Структура технологической системы Детская игровая комната
Детская игровая комната Эпоха Просвещения
Эпоха Просвещения Реконструкция и реновация особняков России
Реконструкция и реновация особняков России Presentation Zilubag for customers
Presentation Zilubag for customers Асфиксия – жизнеугрожающее состояние, связанное с нарушением газообмена
Асфиксия – жизнеугрожающее состояние, связанное с нарушением газообмена Предмет органической химии
Предмет органической химии Автозаправочные станции
Автозаправочные станции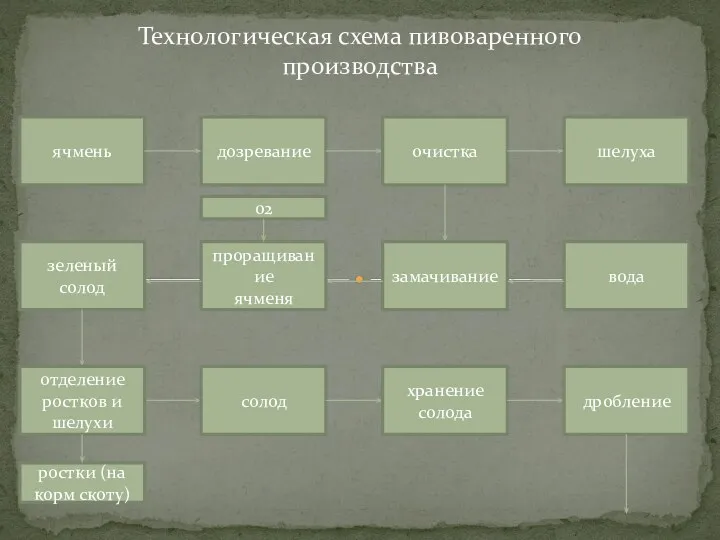 Технология производства пива
Технология производства пива Артикли в английском языке
Артикли в английском языке Сушка
Сушка урок по технологии обработки древесины на деревообрабатывающих станках
урок по технологии обработки древесины на деревообрабатывающих станках Овощи (большой - маленький). Уроки логопеда
Овощи (большой - маленький). Уроки логопеда