Содержание
- 2. Today’s objectives: Define electrode, anode, cathode, anion, cation, salt bridge/porous cup, electrolyte, and voltaic cell Predict
- 3. REMINDER: “Redox” Chemistry: Reduction and Oxidation reactions are all reactions that involve the change of an
- 4. Electrochemistry is the branch of science which deals with the relationship between chemical reaction and electricity.
- 5. Electrochemical Reaction: Redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions in which electrons are transferred from a donor (reducing agent) to
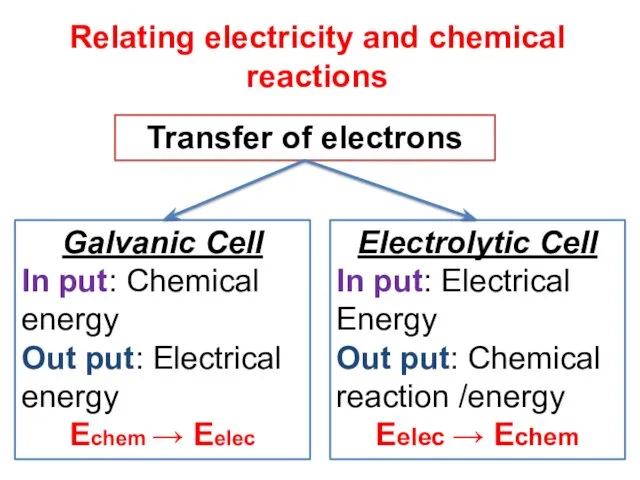
- 6. Relating electricity and chemical reactions Transfer of electrons Galvanic Cell In put: Chemical energy Out put:
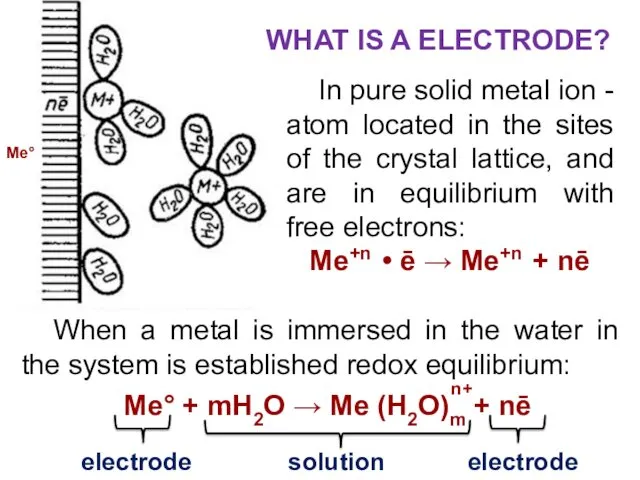
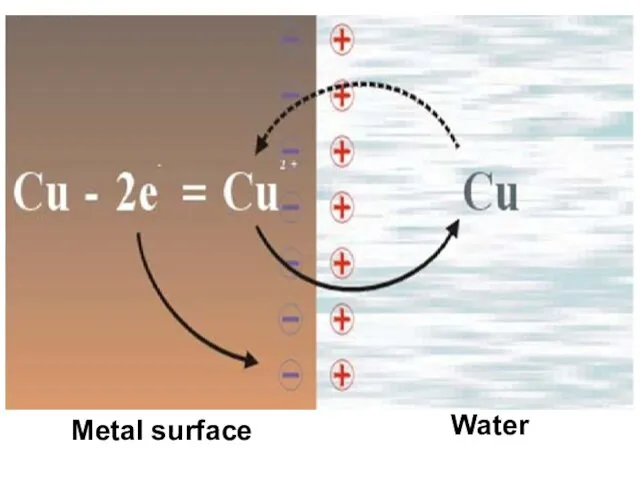
- 7. In pure solid metal ion - atom located in the sites of the crystal lattice, and
- 8. Metal surface Water
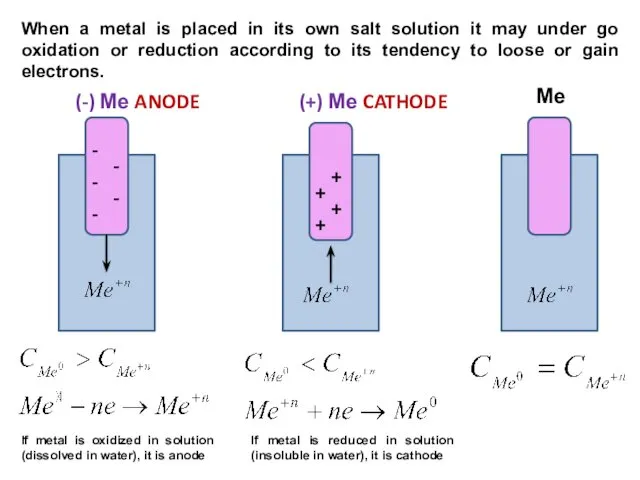
- 9. (-) Ме ANODE (+) Ме CATHODE Ме - - - - - + + + +
- 10. An electrode in an electrochemical cell is referred to as either an anode or a cathode
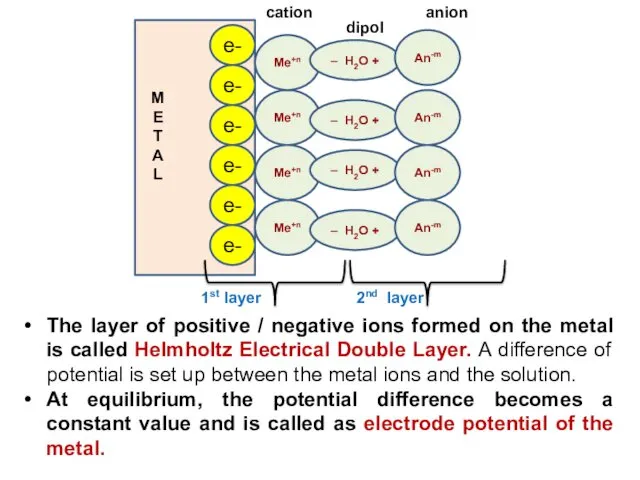
- 11. The layer of positive / negative ions formed on the metal is called Helmholtz Electrical Double
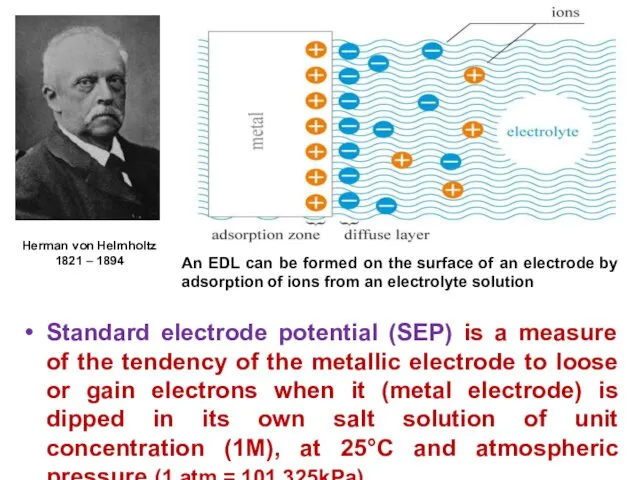
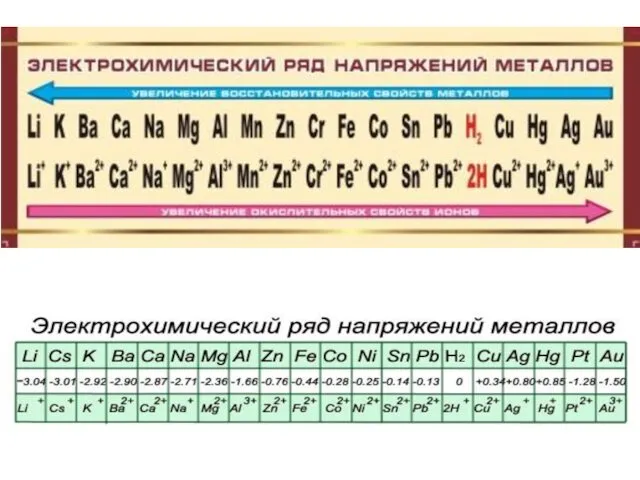
- 12. Standard electrode potential (SEP) is a measure of the tendency of the metallic electrode to loose
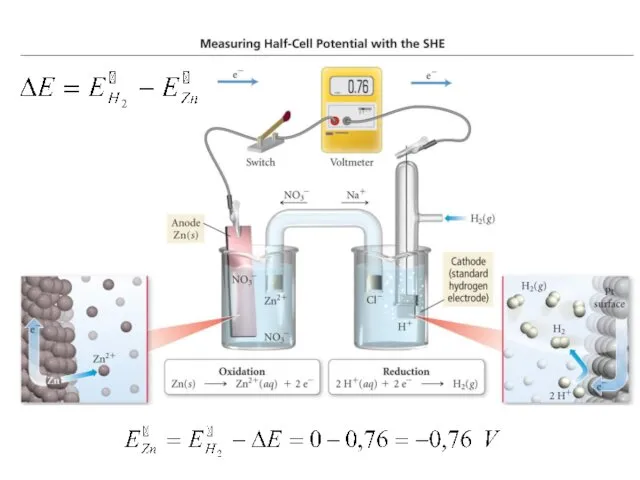
- 13. Measurement of SEP SEP cannot be measured directly. The electrode is coupled with a reference electrodes:
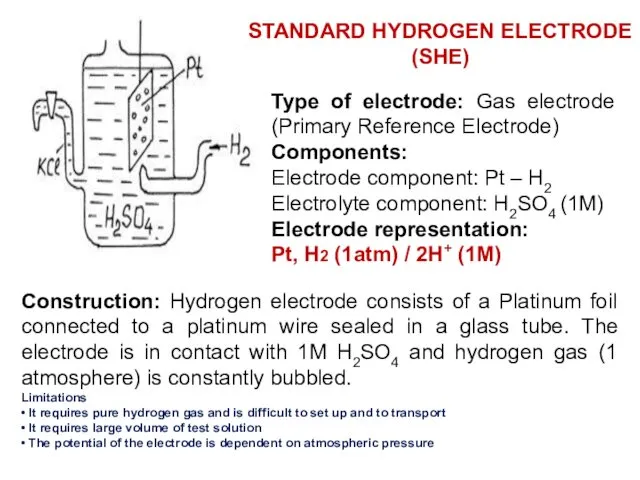
- 14. Type of electrode: Gas electrode (Primary Reference Electrode) Components: Electrode component: Pt – H2 Electrolyte component:
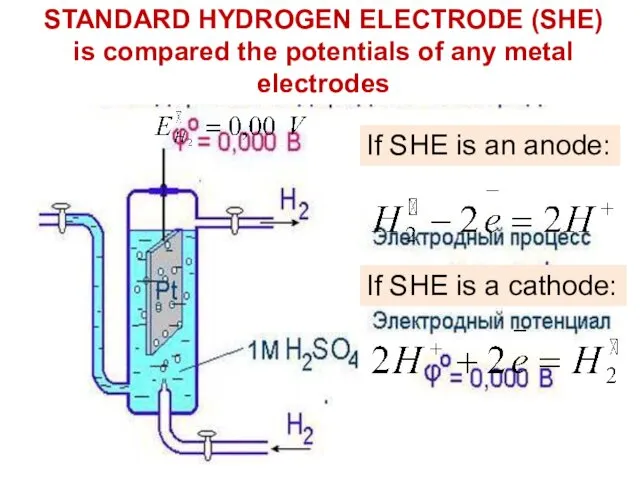
- 15. STANDARD HYDROGEN ELECTRODE (SHE) is compared the potentials of any metal electrodes If SHE is an
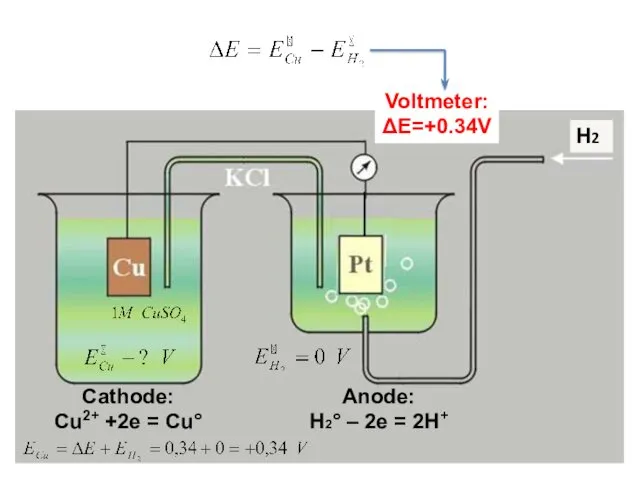
- 16. Cathode: Cu2+ +2e = Cu° Anode: H2° – 2e = 2H+ Н2 Voltmeter: ΔE=+0.34V
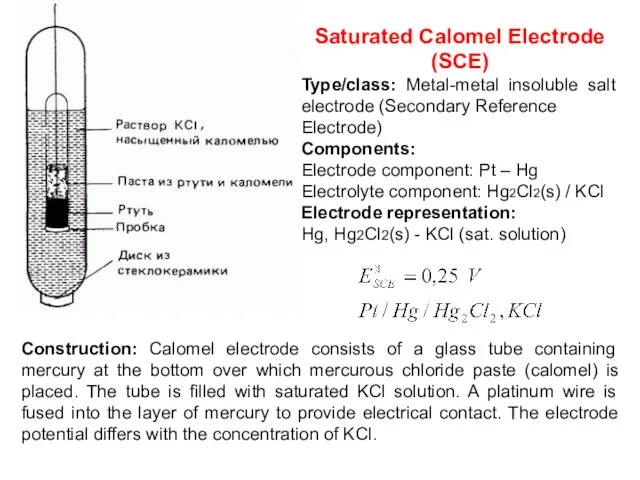
- 18. Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE) Type/class: Metal-metal insoluble salt electrode (Secondary Reference Electrode) Components: Electrode component: Pt
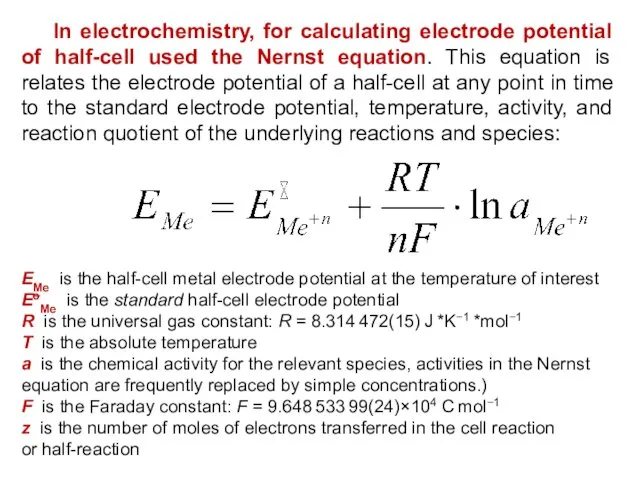
- 20. In electrochemistry, for calculating electrode potential of half-cell used the Nernst equation. This equation is relates
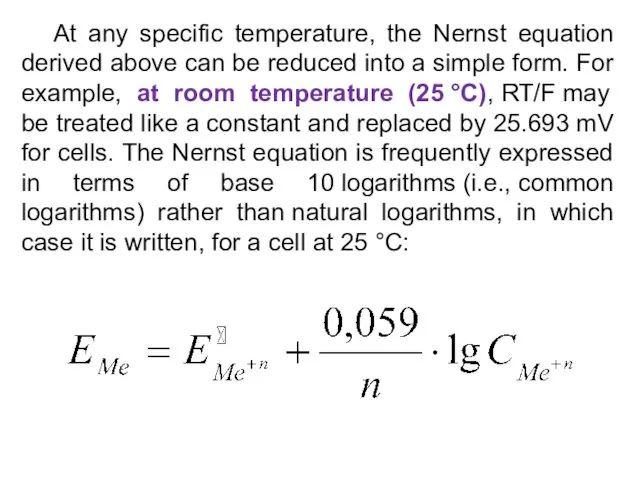
- 21. At any specific temperature, the Nernst equation derived above can be reduced into a simple form.
- 22. Problem: Calculate the electrode potential of zinc if it was dipped in 0,01M ZnSO4 solution Using
- 23. We know that reduction (gaining electrons) can’t happen without an oxidation to provide the electrons. When
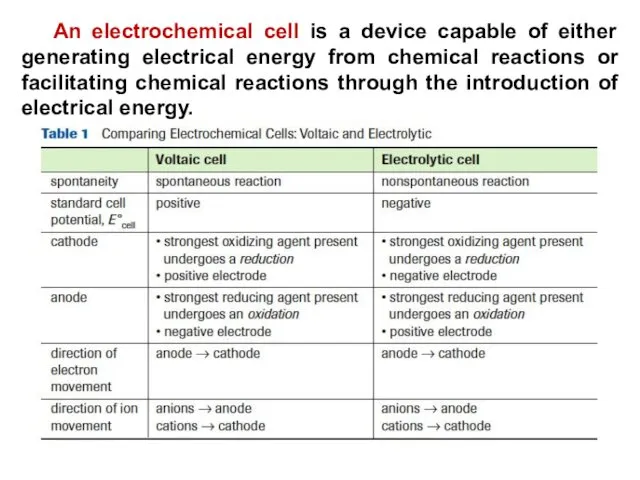
- 24. An electrochemical cell is a device capable of either generating electrical energy from chemical reactions or
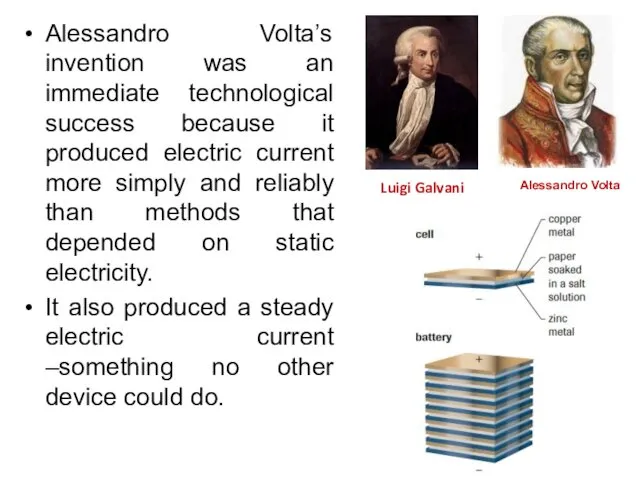
- 25. An electrichemical cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy Alessandro Volta invented the first electric cell
- 26. Alessandro Volta’s invention was an immediate technological success because it produced electric current more simply and
- 27. A galvanic cell, or voltaic cell, named after Luigi Galvani, or Alessandro Volta respectively, is an
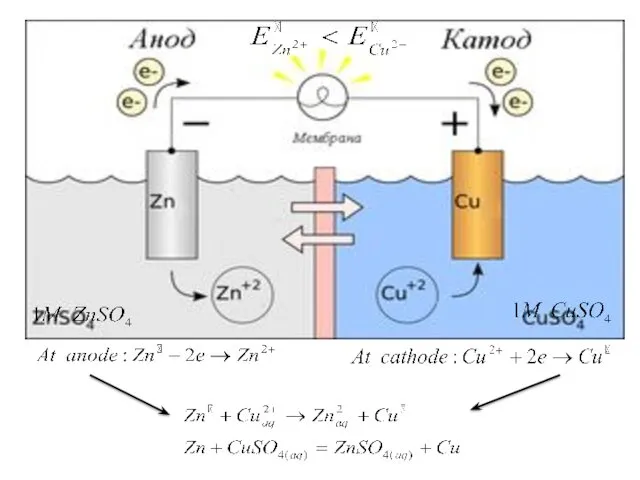
- 28. Galvanic cell composed of two half-cells; which each consist of a metal rod or strip immersed
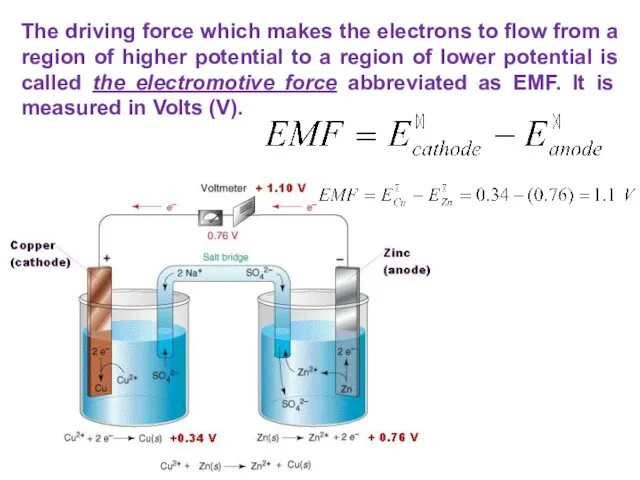
- 29. The driving force which makes the electrons to flow from a region of higher potential to
- 30. If the ΔE>0, it is positive, the reaction occurring is spontaneous. If the ΔE THE ELECTROMOTIVE
- 32. Representation of a galvanic cell Galvanic cell consists of two electrodes, anode and cathode The anode
- 33. Many natural phenomena are based on electrochemical processes, such as the corrosion of metals, the ability
- 35. Скачать презентацию












 Визитная карточка педагога дополнительного образования (хореографа) Даниловой Елены Валерьевны Диск
Визитная карточка педагога дополнительного образования (хореографа) Даниловой Елены Валерьевны Диск Мастер класс Пинетки
Мастер класс Пинетки Презентация Социальный партнер
Презентация Социальный партнер Метаболизм липидов. Липолиз. Окисление жирных кислот и глицерола
Метаболизм липидов. Липолиз. Окисление жирных кислот и глицерола Император Карл Великий (768 – 814 гг.)
Император Карл Великий (768 – 814 гг.) Правление Павла I. Общественно-экономические реформы в начале XIX века. Александр I и Николай I. (Тема 9)
Правление Павла I. Общественно-экономические реформы в начале XIX века. Александр I и Николай I. (Тема 9) Глагол to be
Глагол to be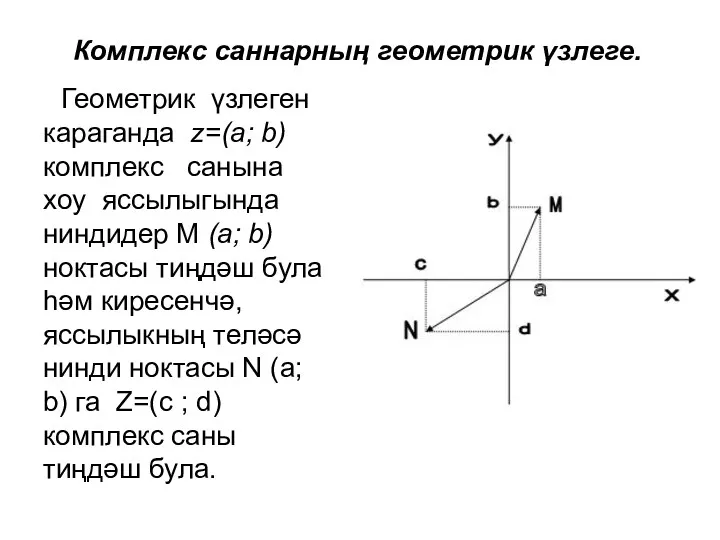 Комплекс саннар
Комплекс саннар Методы освоения подземных пространств
Методы освоения подземных пространств Место духовно-нравственного воспитания по ФГОС
Место духовно-нравственного воспитания по ФГОС Проведение динамометрирования
Проведение динамометрирования Подбери по образцу.
Подбери по образцу. Ет және сүйек пастасын өндіру жабдығын орнату,іске қосу және пайдалану
Ет және сүйек пастасын өндіру жабдығын орнату,іске қосу және пайдалану Анализ опасных технологических процессов в производстве мармелада
Анализ опасных технологических процессов в производстве мармелада Утренник Мы теперь не просто дети, мы теперь ученики
Утренник Мы теперь не просто дети, мы теперь ученики Паллиативная помощь
Паллиативная помощь Saving Energy at Home
Saving Energy at Home Крестики - нолики
Крестики - нолики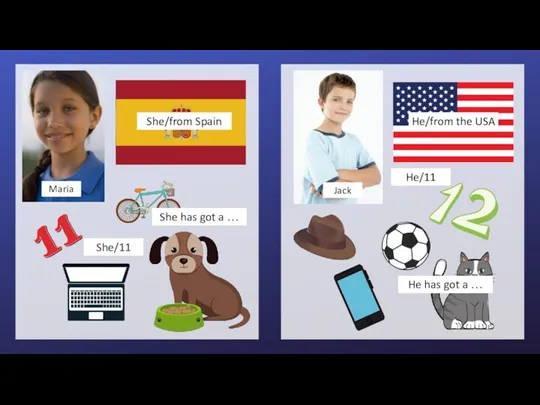 She/from. He/from
She/from. He/from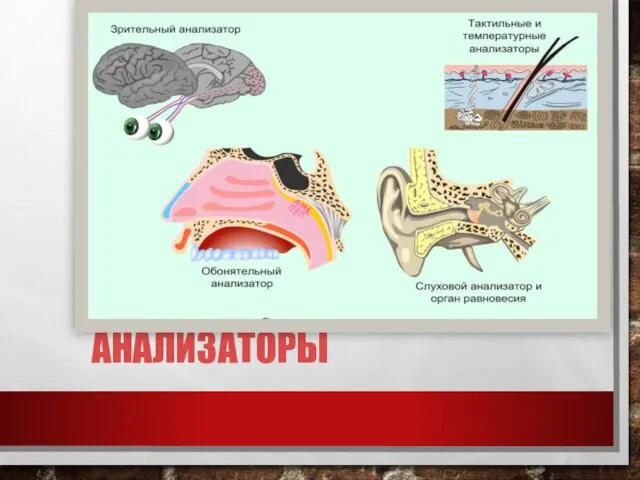 Анализаторы
Анализаторы Презентация Игра по сказкам А.С.Пушкина
Презентация Игра по сказкам А.С.Пушкина Исследовательская практика младших школьников
Исследовательская практика младших школьников Технология ремонта секционных радиаторов отопительного прибора
Технология ремонта секционных радиаторов отопительного прибора Особенности определения инструментальной составляющей погрешности измерений. Лекция 11
Особенности определения инструментальной составляющей погрешности измерений. Лекция 11 Методи та оцінка ризику при проведені комп’ютерного аудиту
Методи та оцінка ризику при проведені комп’ютерного аудиту Презентация по дисциплине: Документационное обеспечение управления
Презентация по дисциплине: Документационное обеспечение управления Тема 6. Геология. Минералы
Тема 6. Геология. Минералы Строительные работы и процессы
Строительные работы и процессы