Содержание
- 2. In hydroelectric power station potential and kinetic energy of stored water is converted into electric energy
- 3. 4% of the total hydel energy potential in world is in India. In India 25.32% of
- 5. PURPOSES OF MULTIPURPOSE HYDROPROJECT For irrigation of agricultural land. For navigation. For fisheries and tourism. For
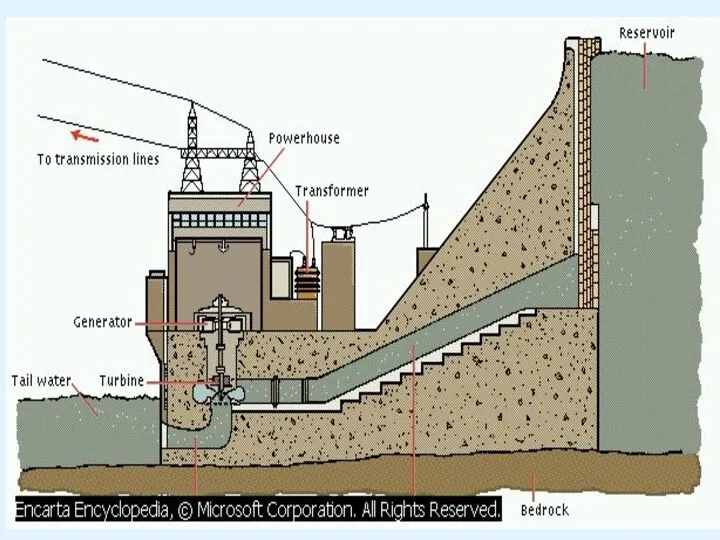
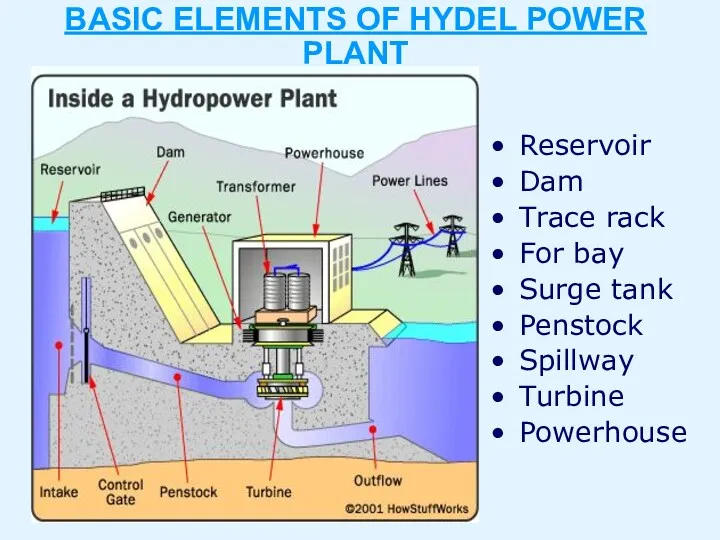
- 6. BASIC ELEMENTS OF HYDEL POWER PLANT Reservoir Dam Trace rack For bay Surge tank Penstock Spillway
- 7. CLASSIFICATION OF HYDEL POWER PLANT
- 8. According to availability of water:- a) Run of river plant without pondage b) Run-off river plant
- 9. According to plant capacity:- a) Microhydal plant (upto 5 MW ) b) Medium capacity plant (
- 10. WATER TURBINES USED IN HYDEL POWER PLANT PELTON TURBINE FRANCIS TURBINE KAPLAN TURBINE
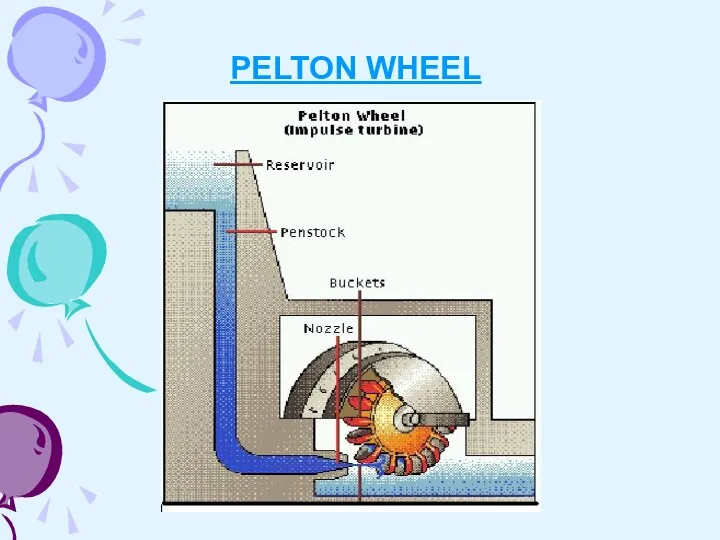
- 11. PELTON WHEEL
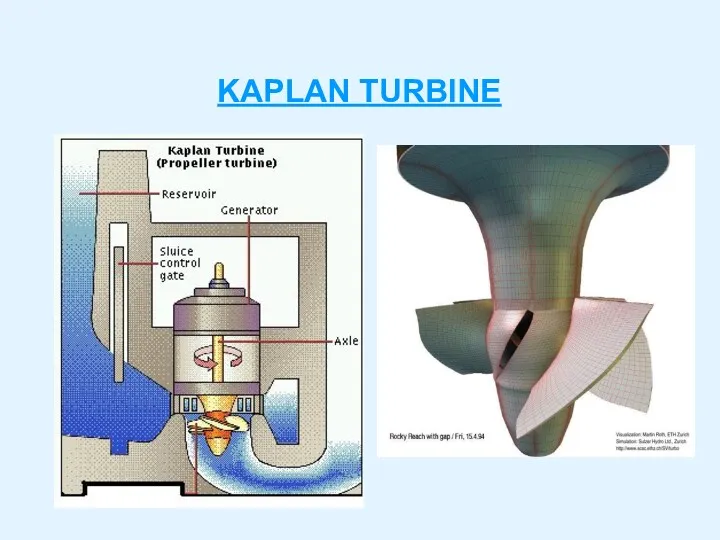
- 12. KAPLAN TURBINE
- 13. ADVANTAGES OF HYDEL POWER PLANT This plant is free from pollution. Its operation and maintenance cost
- 14. Disadvantages of hydel power plant Initial cost of dam and plant is high. The availability of
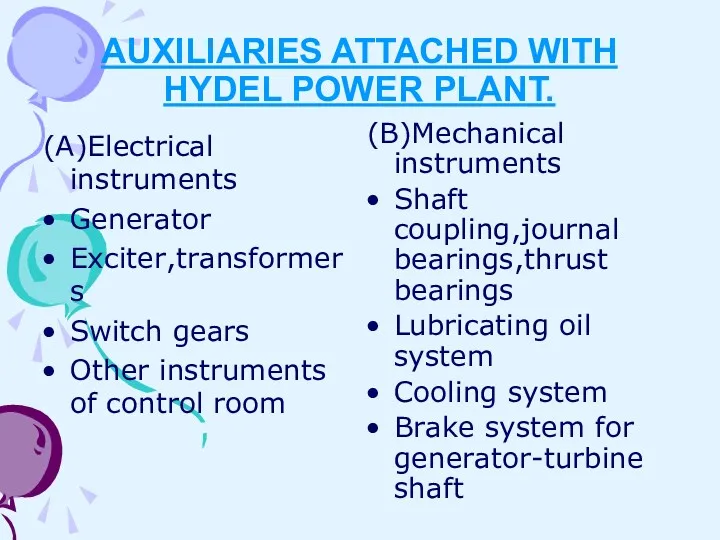
- 15. AUXILIARIES ATTACHED WITH HYDEL POWER PLANT. (A)Electrical instruments Generator Exciter,transformers Switch gears Other instruments of control
- 16. Lets see few of the International Hydel Power Plant Dam…
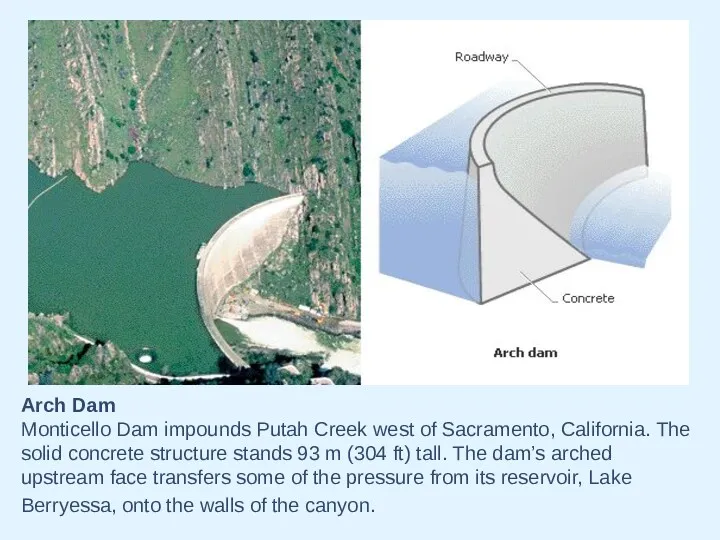
- 17. Arch Dam Monticello Dam impounds Putah Creek west of Sacramento, California. The solid concrete structure stands
- 18. Kariba Arch Dam The Kariba Dam lies along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe. The facility
- 19. G and P Corrigan/Robert Harding Picture Library Hoover Dam The Hoover Dam is an arch-gravity dam
- 20. Lake Mead Lake Mead, a vast artificial lake, straddles the border between Arizona and Nevada. The
- 21. Flat Slab Buttress Dam Lake Tahoe Dam impounds the Truckee River in northern California. Like all
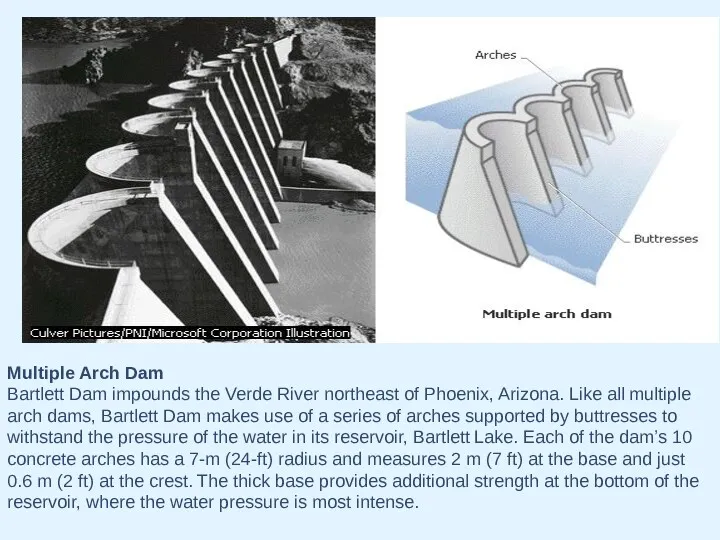
- 22. Multiple Arch Dam Bartlett Dam impounds the Verde River northeast of Phoenix, Arizona. Like all multiple
- 23. Concrete Gravity Dam Shasta Dam impounds the Sacramento River in northern California. Like all concrete gravity
- 24. Grand Dixence Dam With a height of 285 m (935 ft), the Grand Dixence Dam in
- 26. Скачать презентацию















 Презентация Путешествие в страну Здоровья
Презентация Путешествие в страну Здоровья Физиология внешней нервной деятельности. Торможение условных рефлексов. Типы ВНД
Физиология внешней нервной деятельности. Торможение условных рефлексов. Типы ВНД Инженерно-геологические изыскания
Инженерно-геологические изыскания Программа СОЦИАЛЬНО - ПЕДАГОГИЧЕСКАЯ ПОДДЕРЖКА УЧАЩИХСЯ В ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОМ УЧРЕЖДЕНИИ
Программа СОЦИАЛЬНО - ПЕДАГОГИЧЕСКАЯ ПОДДЕРЖКА УЧАЩИХСЯ В ОБРАЗОВАТЕЛЬНОМ УЧРЕЖДЕНИИ Инструкция по работе с дилерскими подсайтами
Инструкция по работе с дилерскими подсайтами Презентация От благодарных читателей
Презентация От благодарных читателей Кредитная и банковская системы
Кредитная и банковская системы Роль иероглифов в китайской культуре
Роль иероглифов в китайской культуре Вымирание горбатых китов
Вымирание горбатых китов Отчет по неделе игры и игрушки (подготовительная группа)
Отчет по неделе игры и игрушки (подготовительная группа) Отчет о работе НОУ 2014/15
Отчет о работе НОУ 2014/15 Аналитический отчёт
Аналитический отчёт Презентации учащихся 4 класса о космосе к дням науки
Презентации учащихся 4 класса о космосе к дням науки Электродвигатели постоянного тока
Электродвигатели постоянного тока Конституционное право
Конституционное право Теория фотоэффекта
Теория фотоэффекта Надзор прокурора за исполнением судебных решений о применении принудительных мер медицинского характера
Надзор прокурора за исполнением судебных решений о применении принудительных мер медицинского характера Презентация1
Презентация1 Презентация Принципы построения предметно-развивающей среды
Презентация Принципы построения предметно-развивающей среды 8 Марта
8 Марта Представления
Представления Презентация к уроку по теме Алкены
Презентация к уроку по теме Алкены Курорт на черном море город Анапа
Курорт на черном море город Анапа Классный уголок
Классный уголок Средства физического воспитания
Средства физического воспитания Интеллектуальная игра по географии Путешествие по странам и континентам
Интеллектуальная игра по географии Путешествие по странам и континентам Все вокруг-геометрия! Мастер-класс. Элементы Пентамино
Все вокруг-геометрия! Мастер-класс. Элементы Пентамино Системный анализ. (Лекция 2)
Системный анализ. (Лекция 2)