Слайд 2
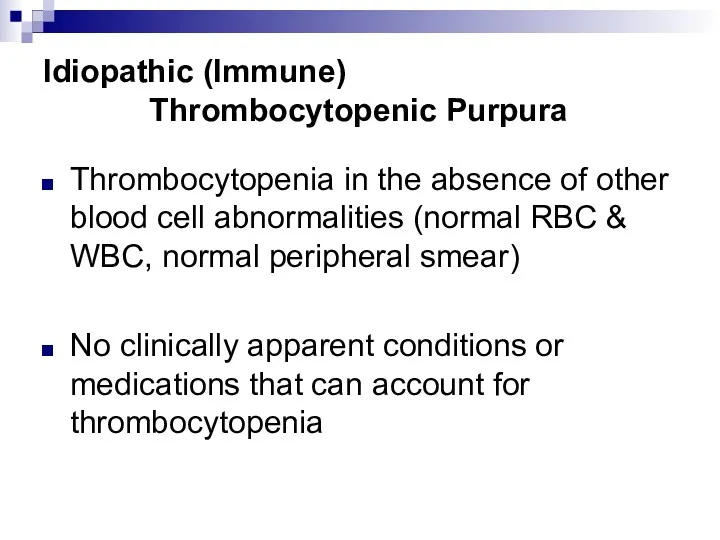
Idiopathic (Immune) Thrombocytopenic Purpura
Thrombocytopenia in the absence of other blood cell
abnormalities (normal RBC & WBC, normal peripheral smear)
No clinically apparent conditions or medications that can account for thrombocytopenia
Слайд 3

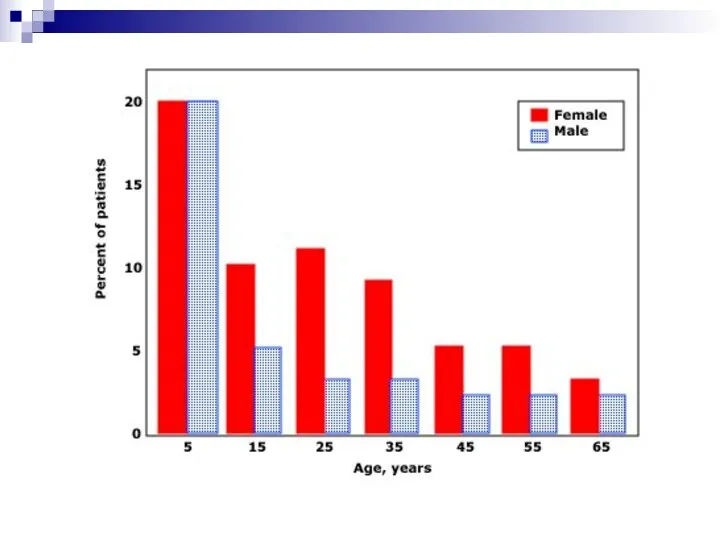
Statistics of ITP
Incidence of 22 million/year in one study
Prevalence greater as
often chronic
*Segal et al ?100 million/year
*age-adjusted prevalence 9.5/100,000
*1.9 :1 females / males
Слайд 4
Слайд 5

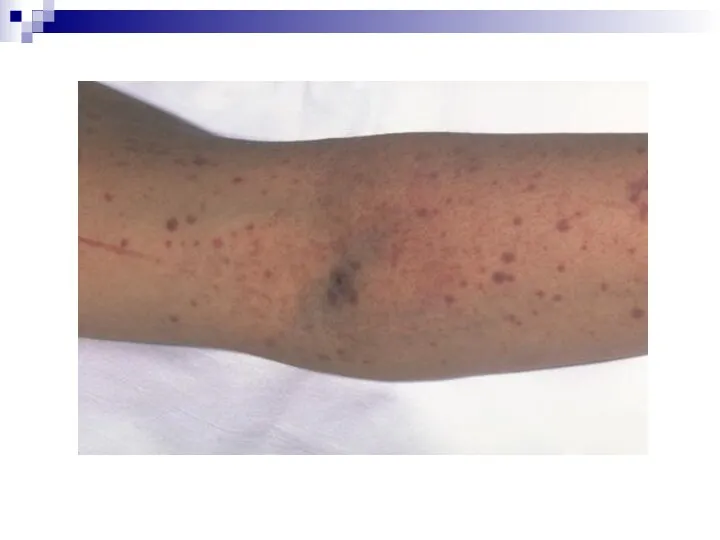
Clinical Manifestations
May be acute or insidious onset
Mucocutaneous Bleeding
*petechiae, purpura, ecchymosis
*epistaxis, gum bleeding
*menorrhagia
*GI bleed, CNS bleed = RARE
Слайд 6
Слайд 7

Слайд 8
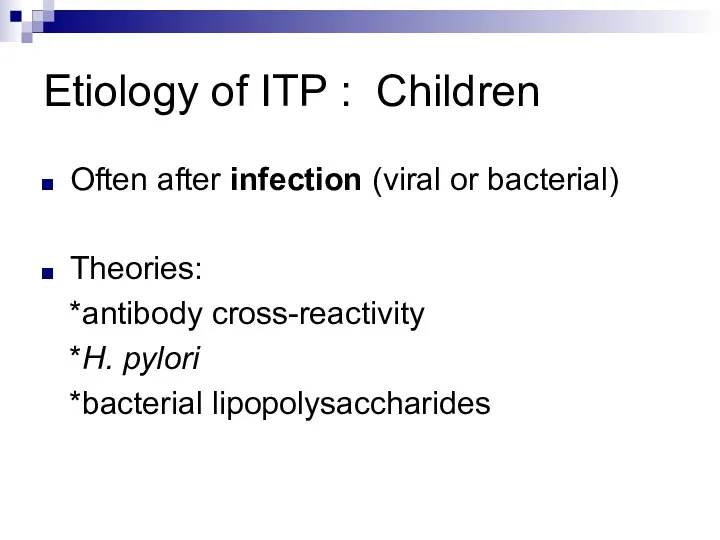
Etiology of ITP : Children
Often after infection (viral or bacterial)
Theories:
*antibody
cross-reactivity
*H. pylori
*bacterial lipopolysaccharides
Слайд 9

Diagnosis (of Exclusion)
Rule out other causes:
*lab error / PLT clumping
*drug / medication interaction
*infections (HIV, Hepatitis C)
*thyroid / autoimmune disease
*destructive / consumptive processes (TTP/HUS)
*bone marrow disease (leukemias, MDS)
Слайд 10

Diagnosis (of Exclusion)
Rule out other causes:
*lab error / PLT clumping
*drug / medication interaction
*infections (HIV, Hepatitis C)
*thyroid / autoimmune disease
*destructive / consumptive processes (TTP/HUS)
*bone marrow disease (leukemias, MDS)
Слайд 11
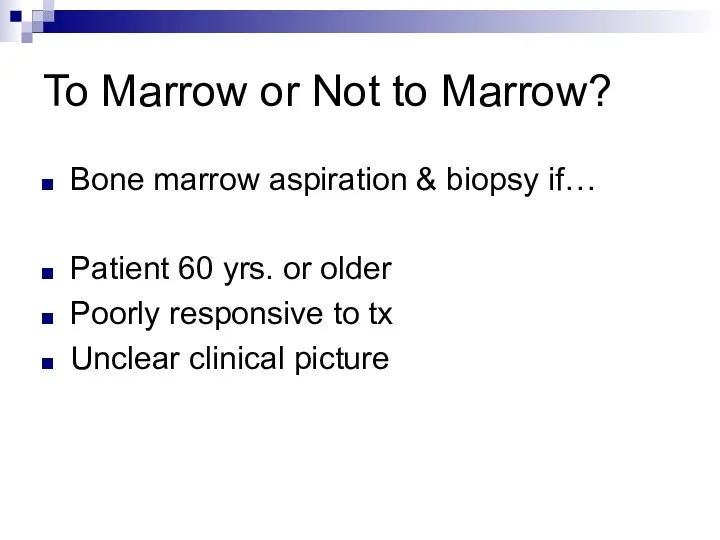
To Marrow or Not to Marrow?
Bone marrow aspiration & biopsy if…
Patient
60 yrs. or older
Poorly responsive to tx
Unclear clinical picture
Слайд 12

Anti-Platelet Antibody Testing
NOT recommended by ASH Practice Guidelines
Poor positive/negative predictive values,
poor sensitivity with all current testing methods…
…and doesn’t change the management!
Слайд 13

Management of ITP
Goal = prevention of bleeding, NOT cure!
Слайд 14

General Principles of Therapy
Major bleeding rare if PLT > 10,000
Goal =
get PLT count to safe level to prevent bleeding…
…not to specifically cure the ITP!
Слайд 15

“Safe” Platelet Counts
“moderately” t-penic = 30-50,000
Probably safe if asymptomatic
Caution with elderly
(CNS bleeds)
Слайд 16

When Planning Therapy…
Tailor therapy and decision to treat to the individual
patient
Weigh bleeding vs. therapy risks
Слайд 17

Initial Therapy
Prednisone 1 mg/kg/day
*usually response within 2 weeks
Taper off after
PLT response
Duration of use = controversial
Слайд 18

Second-Line Therapy
IV Immune Globulin (IVIg)
1 gram/kg/day x 2 days
WinRho (anti-D)
– if pt is Rh+
50-75 mcg/kg/day
Слайд 19
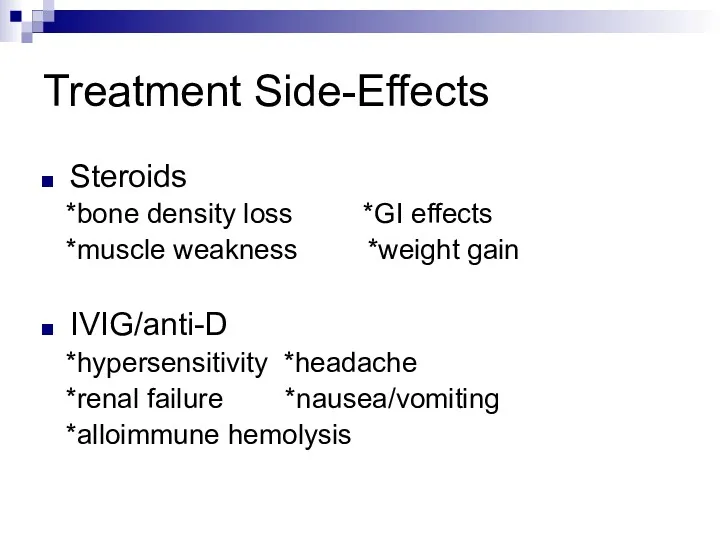
Treatment Side-Effects
Steroids
*bone density loss *GI effects
*muscle weakness *weight gain
IVIG/anti-D
*hypersensitivity *headache
*renal failure *nausea/vomiting
*alloimmune hemolysis
Слайд 20

Splenectomy
Usually reserved for treatment failure
Consider risk of bleeding, pt lifestyle
RISKS
*surgical
procedure
*loss of immune function ? vaccinations
Слайд 21
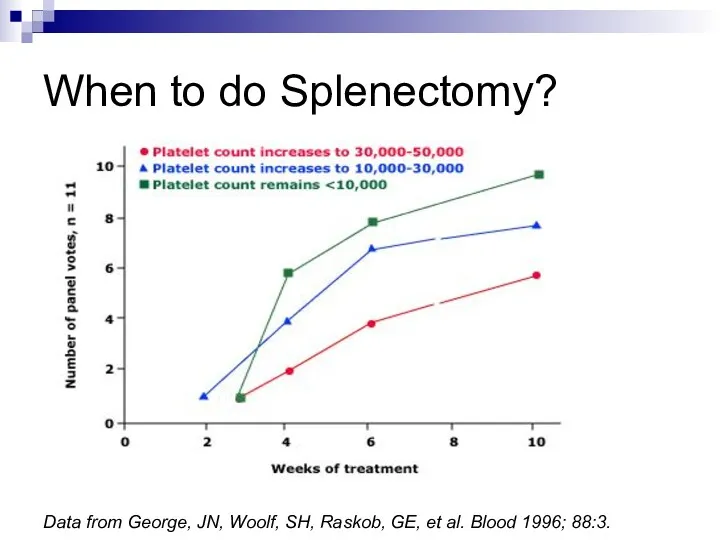
Data from George, JN, Woolf, SH, Raskob, GE, et al. Blood
1996; 88:3.
When to do Splenectomy?
Слайд 22
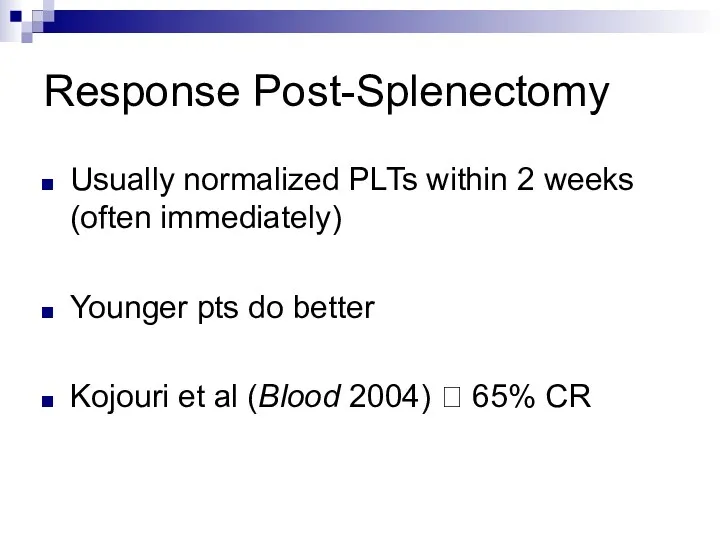
Response Post-Splenectomy
Usually normalized PLTs within 2 weeks (often immediately)
Younger pts do
better
Kojouri et al (Blood 2004) ? 65% CR
Слайд 23
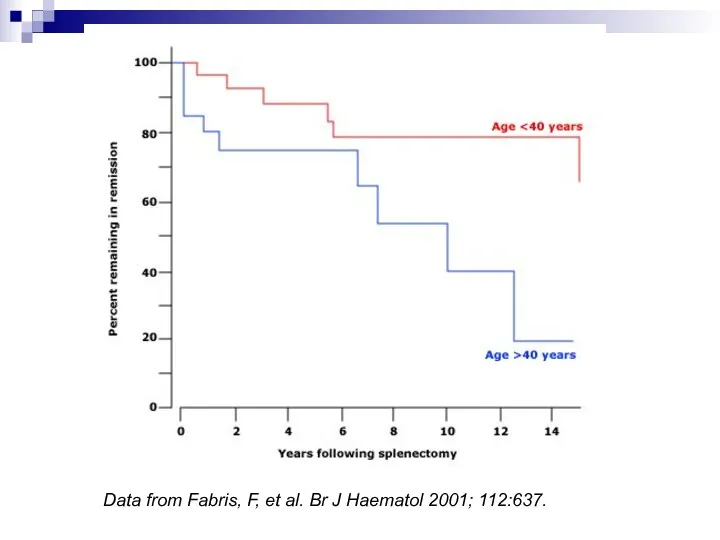
Data from Fabris, F, et al. Br J Haematol 2001; 112:637.
Слайд 24
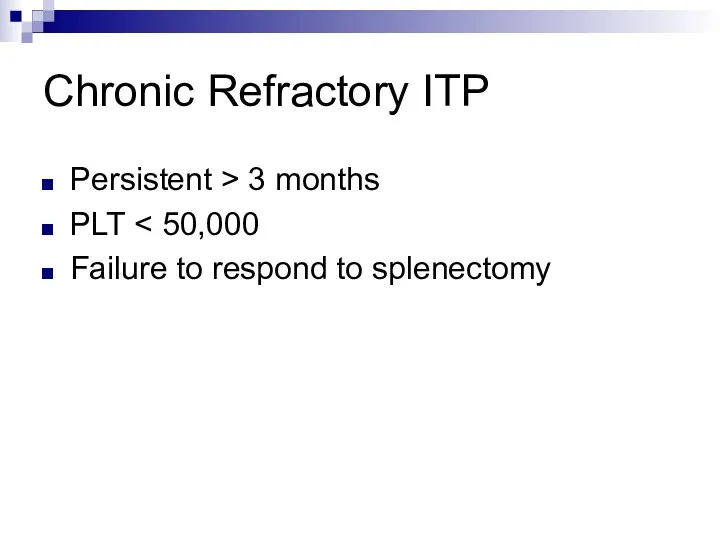
Chronic Refractory ITP
Persistent > 3 months
PLT < 50,000
Failure to respond to
splenectomy
Слайд 25

When all else fails…
Steroids
IVIg / anti-D
Rituximab (anti-CD20)
Cyclophosphamide
Danazol
Accessory splenectomy
H. pylori eradication
Слайд 26

Wrapping it up…
ITP is often a chronic disease in adults
Multiple therapies
may be needed over time
Goal = prevention of complications
Therapy needs to be tailored to the individual patient
Слайд 27



























 Художники-пейзажисты
Художники-пейзажисты Технологии рефлексии в педагогическом процессе
Технологии рефлексии в педагогическом процессе Послідовне з’єднання провідників
Послідовне з’єднання провідників Мавзу. Жамият тараккиётининг гоя ва Мафкура Билан ўзаро богликлиги
Мавзу. Жамият тараккиётининг гоя ва Мафкура Билан ўзаро богликлиги Алюминий
Алюминий Каталог дидактическ игр по нравственно- патриотическому воспитанию детей дошкольного возраста
Каталог дидактическ игр по нравственно- патриотическому воспитанию детей дошкольного возраста Коммунальные ресурсы на общедомовые нужды
Коммунальные ресурсы на общедомовые нужды How to Introduce Yourself in English. Как рассказать о себе на англ.языке
How to Introduce Yourself in English. Как рассказать о себе на англ.языке FinFactor. Решение кейса от Changellenge
FinFactor. Решение кейса от Changellenge Урок Периодический закон Д.И. Менделеева 9 класс.
Урок Периодический закон Д.И. Менделеева 9 класс. Первая оценка и как к ней относится
Первая оценка и как к ней относится Презентация Одаренные дети
Презентация Одаренные дети Презентация Познавательно - исследовательская деятельность детей старшего дошкольного возраста
Презентация Познавательно - исследовательская деятельность детей старшего дошкольного возраста Хирургическая анатомия суставов
Хирургическая анатомия суставов ВКР: Имидж гостиничного предприятия (планирование, формирование, продвижение)
ВКР: Имидж гостиничного предприятия (планирование, формирование, продвижение) Музыкально - дидактическая игра Угадай, на чём играю?
Музыкально - дидактическая игра Угадай, на чём играю? Матрицы. Свойства операций над матрицами. Теорема о ранге матрицы
Матрицы. Свойства операций над матрицами. Теорема о ранге матрицы Применение смазочно-охлаждающих жидкостей (СОЖ)
Применение смазочно-охлаждающих жидкостей (СОЖ) Логопедическое занятие-игра. Драматизация сказки Репка Тема: Слоговой анализ и синтез
Логопедическое занятие-игра. Драматизация сказки Репка Тема: Слоговой анализ и синтез  Внеурочная и проектная деятельность учащихся
Внеурочная и проектная деятельность учащихся Часть 2. Фотоотчёт. Дорогою Добра.Летний городской лагерь.
Часть 2. Фотоотчёт. Дорогою Добра.Летний городской лагерь. Герб Санкт-Петербурга
Герб Санкт-Петербурга 20231022_dif._podhod
20231022_dif._podhod История туризма и гостеприимства
История туризма и гостеприимства Модернизация устройства РЗиА на электрической подстанции 110/35/10 кВ
Модернизация устройства РЗиА на электрической подстанции 110/35/10 кВ Ясли-это серьезно!
Ясли-это серьезно! Пристрої компютера. Фотоальбом
Пристрої компютера. Фотоальбом Роль религии в жизни общества
Роль религии в жизни общества