Слайд 2
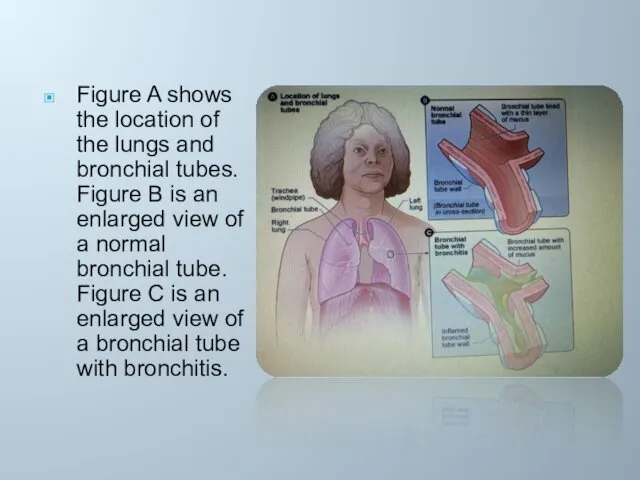
Figure A shows the location of the lungs and bronchial tubes.
Figure B is an enlarged view of a normal bronchial tube. Figure C is an enlarged view of a bronchial tube with bronchitis.
Слайд 3

Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs. Symptoms include
coughing upmucus, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort. Bronchitis is divided into two types: acute and chronic. Acute bronchitis is also known as a chest cold.
Слайд 4

Acute bronchitis usually has a cough that lasts around three weeks.In more
than 90% of cases the cause is a viral infection. These viruses may be spread through the air when people cough or by direct contact. Risk factors include exposure to tobacco smoke, dust, and other air pollution. A small number of cases are due to high levels of air pollution or bacteria such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae or Bordetella pertussis. Treatment of acute bronchitis typically involves rest,paracetamol (acetaminophen), and NSAIDs to help with the fever.
Слайд 5

Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that lasts for three months or
more per year for at least two years. Most people with chronic bronchitis have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Tobacco smoking is the most common cause, with a number of other factors such as air pollution and genetics playing a smaller role.Treatments includequitting smoking, vaccinations, rehabilitation, and often inhaled bronchodilators and steroids. Some people may benefit from long-term oxygen therapy or lung transplantation.
Слайд 6

Acute bronchitis is one of the most common diseases.About 5% of
adults are affected and about 6% of children have at least one episode a year. In 2010, COPD affects 329 million people or nearly 5% of the population. In 2013, it resulted in 2.9 million deaths up from 2.4 million deaths in 1990.
Слайд 7

Future in the Past
Like Simple Future, Future in the Past has two
different forms in English: "would" and "was going to." Although the two forms can sometimes be used interchangeably, they often express two different meanings.
Слайд 8
![FORM Would [would + VERB] Examples: I knew you would](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/37330/slide-7.jpg)
FORM Would
[would + VERB]
Examples:
I knew you would help him.
I knew you would not help him.
Слайд 9
![FORM Was/Were Going To [was/were + going to + VERB]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/37330/slide-8.jpg)
FORM Was/Were Going To
[was/were + going to + VERB]
Examples:
I knew you were
going to go to the party.
I knew you were not going to go to the party.






![FORM Would [would + VERB] Examples: I knew you would](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/37330/slide-7.jpg)
![FORM Was/Were Going To [was/were + going to + VERB]](/_ipx/f_webp&q_80&fit_contain&s_1440x1080/imagesDir/jpg/37330/slide-8.jpg)
 Геометрические задачи практического содержания в вариантах ГИА
Геометрические задачи практического содержания в вариантах ГИА Дискуссионные проблемы. Задание 25 по истории
Дискуссионные проблемы. Задание 25 по истории Формы и виды публичной коммуникации
Формы и виды публичной коммуникации Роль нефти и углеводородных газов в мировом и российском топливно-энергетическом балансах
Роль нефти и углеводородных газов в мировом и российском топливно-энергетическом балансах Розвиток металургii
Розвиток металургii Сетевые черви и защита от них
Сетевые черви и защита от них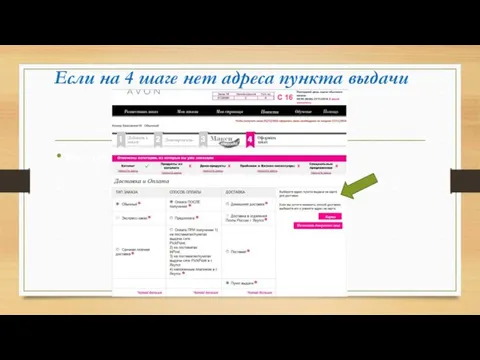 Отправка заказа Avon
Отправка заказа Avon транспорт
транспорт Театрально- интегрированная деятельность для детей старше-подготовительного возраста
Театрально- интегрированная деятельность для детей старше-подготовительного возраста Наш коллектив
Наш коллектив Урок в 8 классе Генетическая связь веществ
Урок в 8 классе Генетическая связь веществ Гипертоническая болезнь
Гипертоническая болезнь Презентация Я здесь живу, и край мне этот дорог.История развития поселка Первомайский
Презентация Я здесь живу, и край мне этот дорог.История развития поселка Первомайский Образование СССР. Внешняя политика СССР в 1921-1927 годах
Образование СССР. Внешняя политика СССР в 1921-1927 годах Получение гидролизатов из пивной дробины и изучение условий культивирования на них разных видов дрожжей
Получение гидролизатов из пивной дробины и изучение условий культивирования на них разных видов дрожжей Фруктовый сад-загадки
Фруктовый сад-загадки Иудаизм в культуре
Иудаизм в культуре Фундаментальные физические явления наноэлектроники
Фундаментальные физические явления наноэлектроники Роль супервайзера в достижении лидерства ТМ Nemiroff в рознице в г. Одесса
Роль супервайзера в достижении лидерства ТМ Nemiroff в рознице в г. Одесса Грозова енергетика
Грозова енергетика Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Здравствуй, Зимушка-зима
Презентация к внеклассному мероприятию Здравствуй, Зимушка-зима Мероприятия по раннему выявлению незаконного потребления наркотических средств и психотропных веществ
Мероприятия по раннему выявлению незаконного потребления наркотических средств и психотропных веществ e0ef78602e2a8994
e0ef78602e2a8994 Материаловедение. Технология конструкционных материалов. Материалы и материаловедение. (Тема 1)
Материаловедение. Технология конструкционных материалов. Материалы и материаловедение. (Тема 1) Оператор цикла For/Next
Оператор цикла For/Next Образ тургеневской девушки
Образ тургеневской девушки Интегрированное занятие Жили-были мама коза с козлятами
Интегрированное занятие Жили-были мама коза с козлятами Воспитательный процесс. Содержание воспитания
Воспитательный процесс. Содержание воспитания