Содержание
- 2. Theory of Demand Theory of Supply Market Equilibrium Government Intervention in the Market Laws of market
- 3. Demand for a commodity Depends on size of the market (Industry Demand for the commodity) Summation
- 4. How are price and demand related for a good? (law of demand) Normal Goods Inferior Goods
- 5. Horizontal Summation of Individual Demand Curves Negatively sloped, why? Inverse relation between price and quantity QD=
- 6. Change in demand Change in quantity Demanded Market Demand
- 7. Monopolist WAPDA Perfect Competition No true example exists (Small scale farmers producing homogeneous wheat in USA)
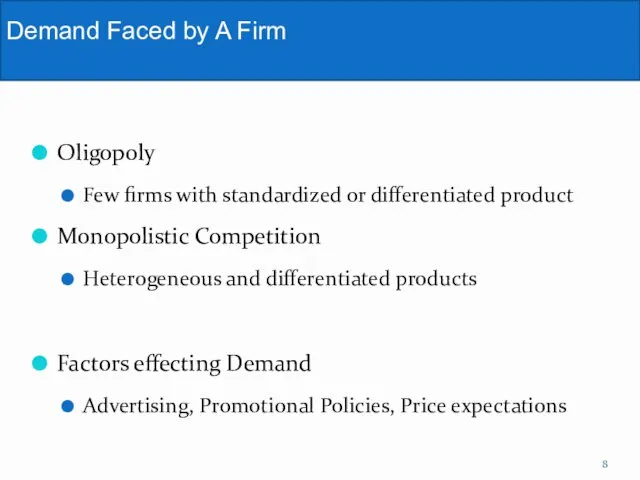
- 8. Oligopoly Few firms with standardized or differentiated product Monopolistic Competition Heterogeneous and differentiated products Factors effecting
- 9. Firms selling durable goods face more volatile & unstable demand Like automobiles, washing machines, water geezers
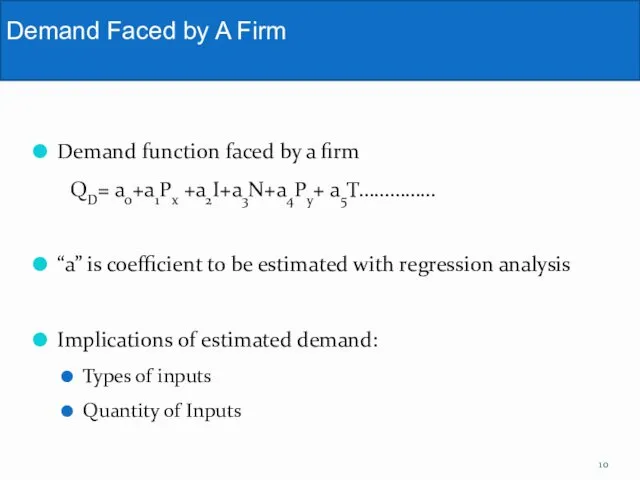
- 10. Demand function faced by a firm QD= a0+a1Px +a2I+a3N+a4Py+ a5T…………… “a” is coefficient to be estimated
- 11. Theory of Demand Theory of Supply Market Equilibrium Government Intervention in the Market Laws of market
- 12. The quantity sellers are willing to sell at a given price level Depends on: Price of
- 13. The higher the price, greater is the quantity sellers are willing to sell in the market
- 14. Horizontal Summation of Individual Supply Curves Positively sloped, why? Positive relation between price and quantity Market
- 15. Change in supply Change in quantity supplied Market Supply
- 16. Theory of Demand Theory of Supply Market Equilibrium Government Intervention in the Market Laws of market
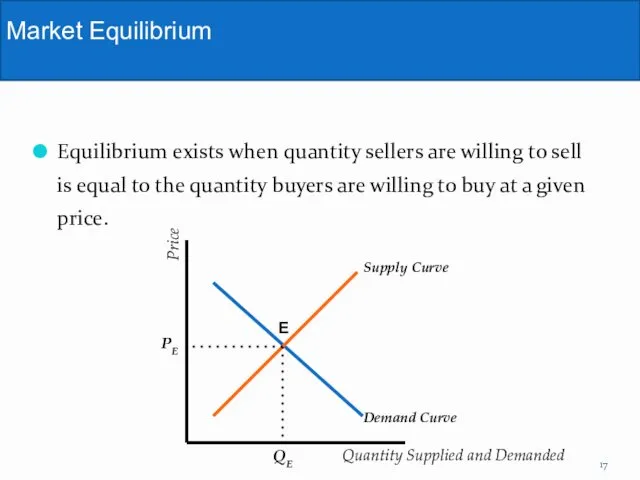
- 17. Equilibrium exists when quantity sellers are willing to sell is equal to the quantity buyers are
- 18. Surplus - Results in downward pressure on the price Shortage - Results in upward pressure on
- 19. Theory of Demand Theory of Supply Market Equilibrium Government Intervention in the Market Laws of market
- 20. Public Sector Services Monopolies Restrictions and Barriers to Entry Reducing Trade Barriers Vs Import Tariffs Taxation
- 22. Скачать презентацию















 Сумен қамтамасыздандыру жүйелері мен сұлбалары
Сумен қамтамасыздандыру жүйелері мен сұлбалары Вся Земля хвалу поёт лишь тебе, наш чудный Бог
Вся Земля хвалу поёт лишь тебе, наш чудный Бог Производство и промышленное использование ферментов
Производство и промышленное использование ферментов Создания в классе развивающей среды как условия повышения образовательного потенциала обучающихся
Создания в классе развивающей среды как условия повышения образовательного потенциала обучающихся Основы теории обогатительных процессов. Общие представления о моделировании
Основы теории обогатительных процессов. Общие представления о моделировании Введение в психологию. Психология как наука
Введение в психологию. Психология как наука Mercedes Benz Smart Key Programming
Mercedes Benz Smart Key Programming КАЭС – первая атомная электростанция России
КАЭС – первая атомная электростанция России Обновленная навигация на сайте Oriflame
Обновленная навигация на сайте Oriflame Система финансирования дополнительных занятий
Система финансирования дополнительных занятий Естественное право. Позитивное право. Живое право
Естественное право. Позитивное право. Живое право Задание 9 ЕГЭ. Правописание приставок (теория)
Задание 9 ЕГЭ. Правописание приставок (теория) Викторина – путешествие по произведениям С.Я. Маршака
Викторина – путешествие по произведениям С.Я. Маршака Литература Русского Зарубежья
Литература Русского Зарубежья Мастер - класс. Деловая игра как способ развития социальной компетентности у учащихся на уроках географии.
Мастер - класс. Деловая игра как способ развития социальной компетентности у учащихся на уроках географии. Методика поэтапного формирования коммуникативной компетенции в письменной речи.
Методика поэтапного формирования коммуникативной компетенции в письменной речи. Наземные датчики Surface Sensors
Наземные датчики Surface Sensors Культура города Омска
Культура города Омска Моделирование юбки
Моделирование юбки Презентация к 8 Марта
Презентация к 8 Марта Презентация к уроку на тему: Основания
Презентация к уроку на тему: Основания Мы помним! День солидарности в борьбе с терроризмом. День памяти жертв Беслана
Мы помним! День солидарности в борьбе с терроризмом. День памяти жертв Беслана 20230208_prezentatsiya_burina_shk_37
20230208_prezentatsiya_burina_shk_37 Молодежное представительство Беспокойные сердца
Молодежное представительство Беспокойные сердца Влияние вибрационного массажа на физическое развитие и двигательную подготовленность студентов - легкоатлетов
Влияние вибрационного массажа на физическое развитие и двигательную подготовленность студентов - легкоатлетов Компания ОООЦМС (ЦентрМеталлСнаб)
Компания ОООЦМС (ЦентрМеталлСнаб) CASE-технологии
CASE-технологии 20231106_reshenie_zadaniy_ege_po_fizike_vysokogo_urovnya
20231106_reshenie_zadaniy_ege_po_fizike_vysokogo_urovnya