Cognitivism
Cognitive Approach:
- The cognitive approach is a broader perspective or orientation
within psychology and other fields.
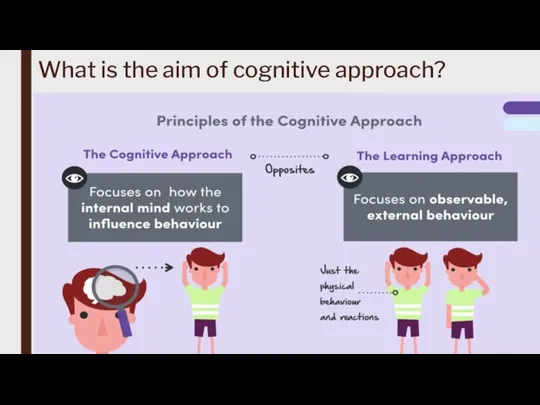
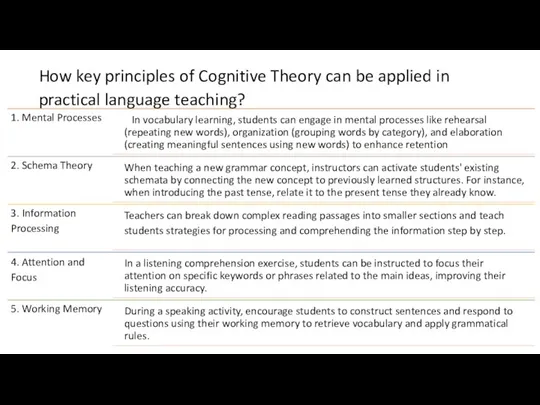
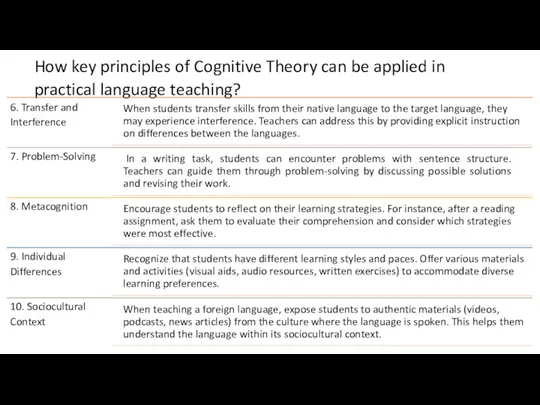
The cognitive approach emphasizes the study of internal mental representations, information processing, and how individuals perceive, organize, store, and use information.
It is not limited to a specific theory or school of thought but includes a range of theories, including cognitive psychology, cognitive neuroscience, cognitive development, and more.
The cognitive approach can be applied to various domains, including education, clinical psychology, artificial intelligence, and human- computer interaction.
Cognitivism:
Cognitivism is a specific theoretical perspective within the broader cognitive approach.
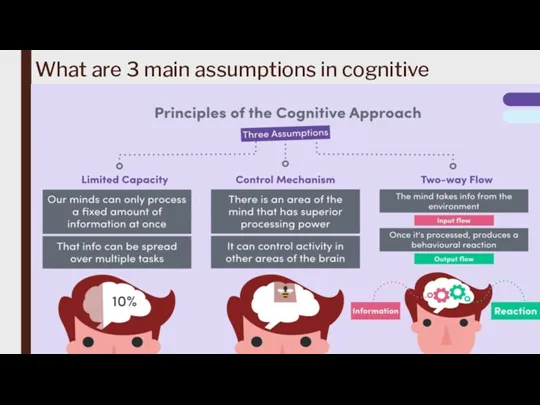
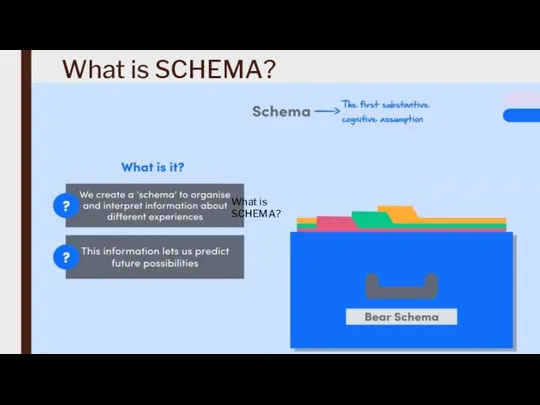
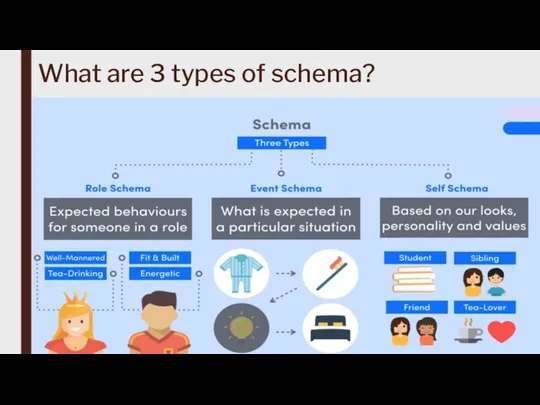
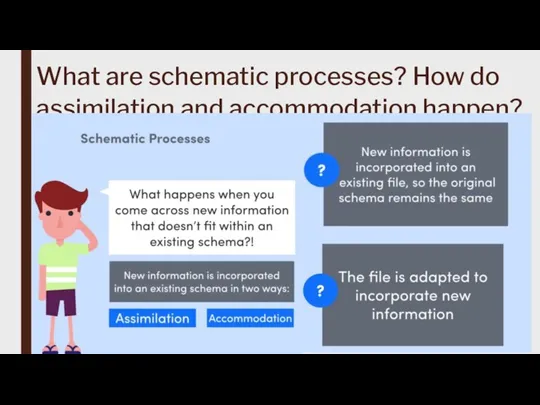
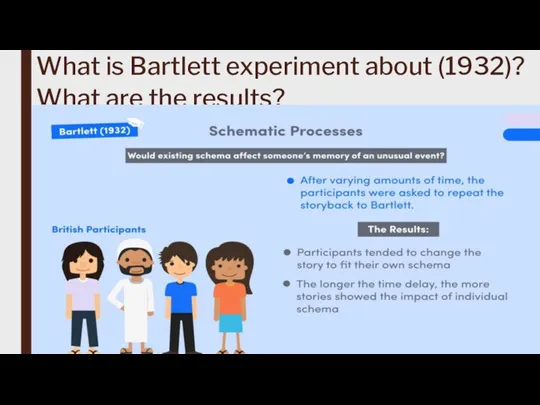
Cognitivism is often associated with key concepts such as schemas, memory systems, problem-solving strategies, and information encoding, retrieval, and manipulation.
It has had a significant impact on psychology, education, and related fields, leading to the development of cognitive psychology as a distinct subfield.
Cognitivism is primarily concerned with explaining how mental processes work and how they influence behavior and learning.









 Основные методы расчета транспортных систем
Основные методы расчета транспортных систем Развитие экскурсионной деятельности на примере Архангельской области
Развитие экскурсионной деятельности на примере Архангельской области Об обеспечении занятости граждан предпенсионного возраста
Об обеспечении занятости граждан предпенсионного возраста Розборка ноутбука Lenovo G570
Розборка ноутбука Lenovo G570 Полупроводниковые лазеры
Полупроводниковые лазеры Методы производства биотехнологических препаратов в современном мире
Методы производства биотехнологических препаратов в современном мире Учение об инфекции
Учение об инфекции Транспорт Беларуси (инфографика). Авиационный, автомобильный, железнодорожный, водный
Транспорт Беларуси (инфографика). Авиационный, автомобильный, железнодорожный, водный Коммутационные аппараты до 1000 В
Коммутационные аппараты до 1000 В Классный час Что такое толерантность?
Классный час Что такое толерантность? Клиническая симптоматология гастритов и язвенной болезни
Клиническая симптоматология гастритов и язвенной болезни Су ресурстарын тазарту әдістері
Су ресурстарын тазарту әдістері Современный урок: шаг к успеху
Современный урок: шаг к успеху Построение изображений в линзах
Построение изображений в линзах Презентация Обучение чтению детей
Презентация Обучение чтению детей Плоские железобетонные перекрытия (монолитное перекрытие)
Плоские железобетонные перекрытия (монолитное перекрытие) Гендерные проблемы белорусского общества
Гендерные проблемы белорусского общества Качество товаров
Качество товаров презентация Фронтовая тетрадь- песенник Трифонова С.И.
презентация Фронтовая тетрадь- песенник Трифонова С.И. Аккумуляторные батареи
Аккумуляторные батареи Квест- игра В поисках Антарктиды для старшей группы (формирование элементарных математических представлений)
Квест- игра В поисках Антарктиды для старшей группы (формирование элементарных математических представлений) Презентация Все профессии нужны, все профессии важны!
Презентация Все профессии нужны, все профессии важны! ЕГЭ по русскому языку: выполнение тестовых заданий
ЕГЭ по русскому языку: выполнение тестовых заданий Системы двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными
Системы двух линейных уравнений с двумя переменными Презентация по теме Технология проблемного обучения
Презентация по теме Технология проблемного обучения Линолиум. Основы знания товара
Линолиум. Основы знания товара внеклассное занятие на тему Дружбой нужно дорожить
внеклассное занятие на тему Дружбой нужно дорожить Планирование производственной программы Основные понятия
Планирование производственной программы Основные понятия