Содержание
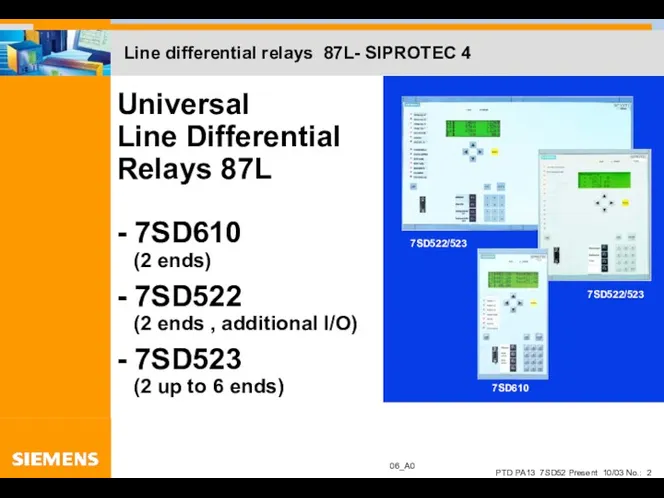
- 2. Line differential relays 87L- SIPROTEC 4 Universal Line Differential Relays 87L - 7SD610 (2 ends) -
- 3. Customer Benefits The protection applies its characteristic by itself. Adaptive measurement reduces the setting complexity and
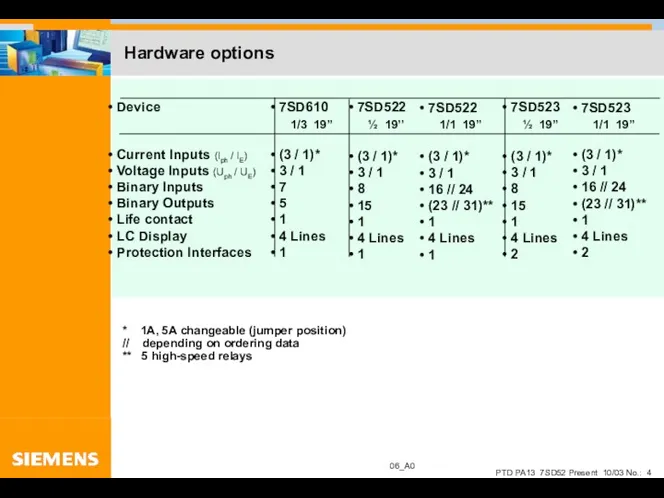
- 4. Hardware options 7SD610 1/3 19’’ (3 / 1)* 3 / 1 7 5 1 4 Lines
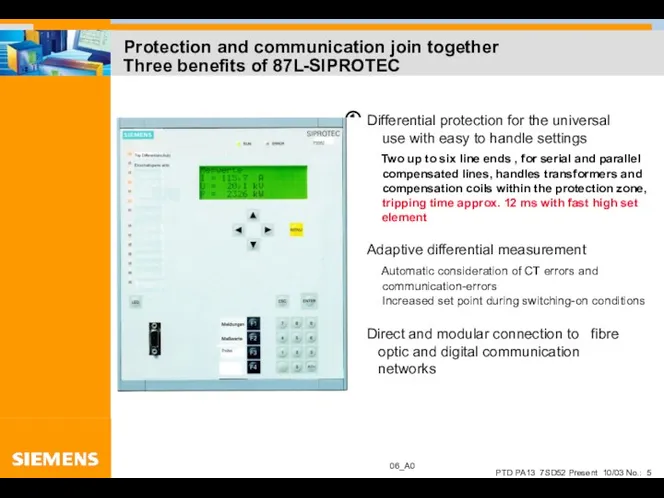
- 5. Protection and communication join together Three benefits of 87L-SIPROTEC
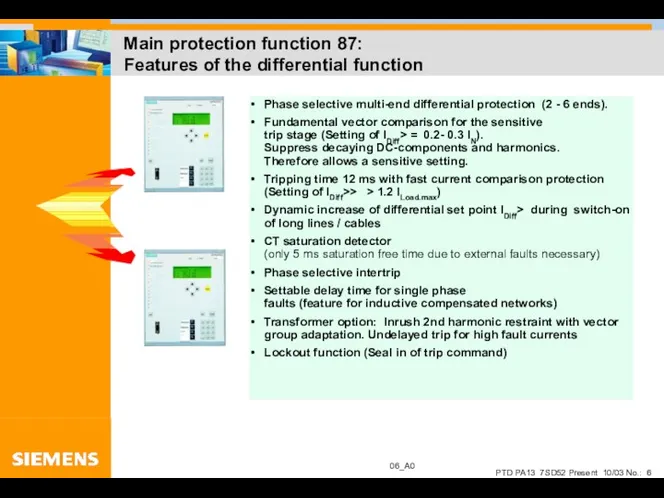
- 6. Main protection function 87: Features of the differential function
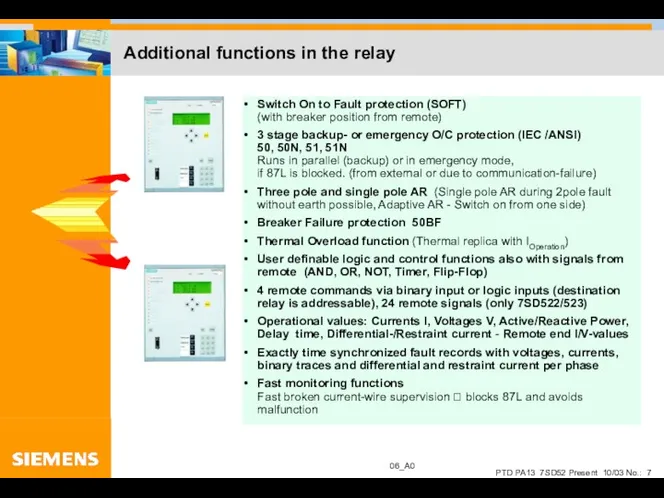
- 7. Additional functions in the relay
- 8. Communication features
- 9. IDiff>: Vector comparison
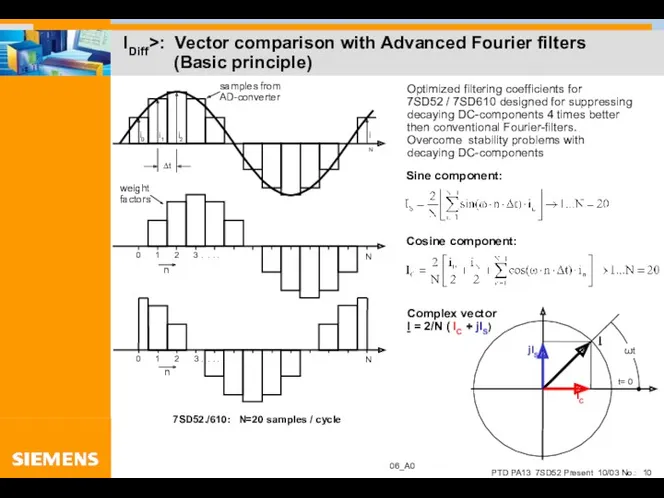
- 10. IDiff>: Vector comparison with Advanced Fourier filters (Basic principle)
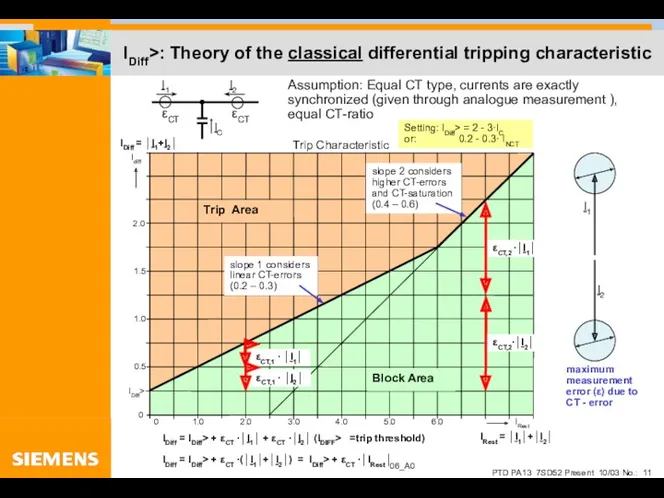
- 11. IDiff>: Theory of the classical differential tripping characteristic
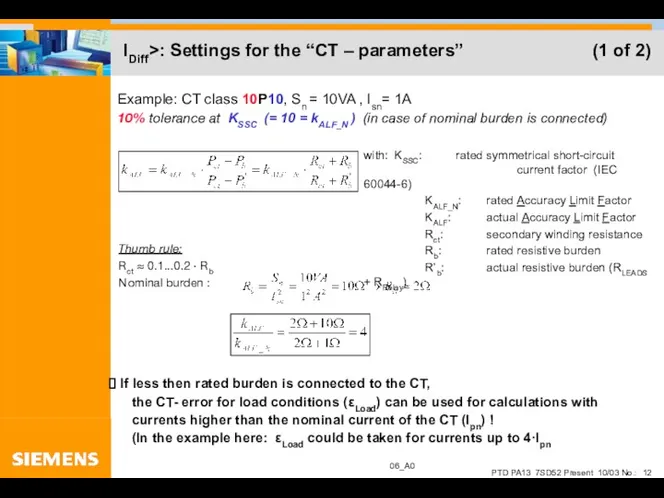
- 12. IDiff>: Settings for the “CT – parameters” (1 of 2)
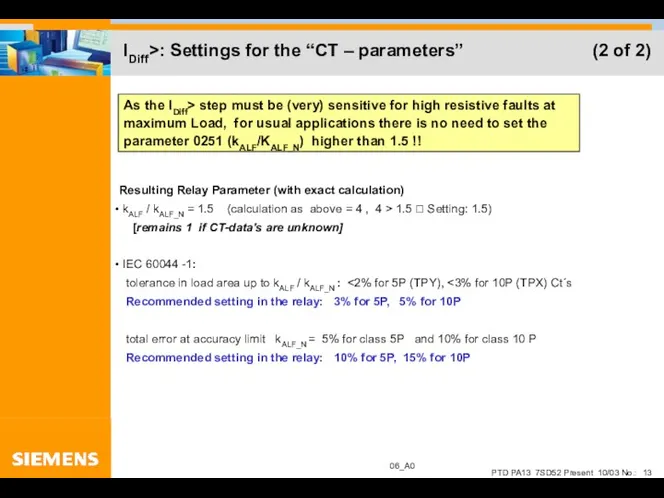
- 13. IDiff>: Settings for the “CT – parameters” (2 of 2)
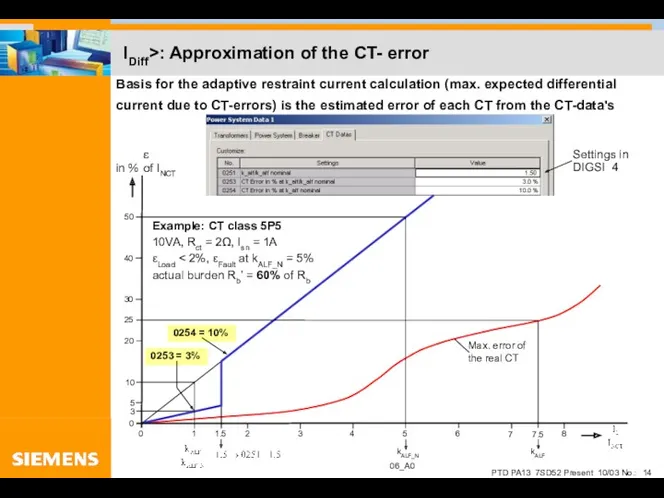
- 14. IDiff>: Approximation of the CT- error
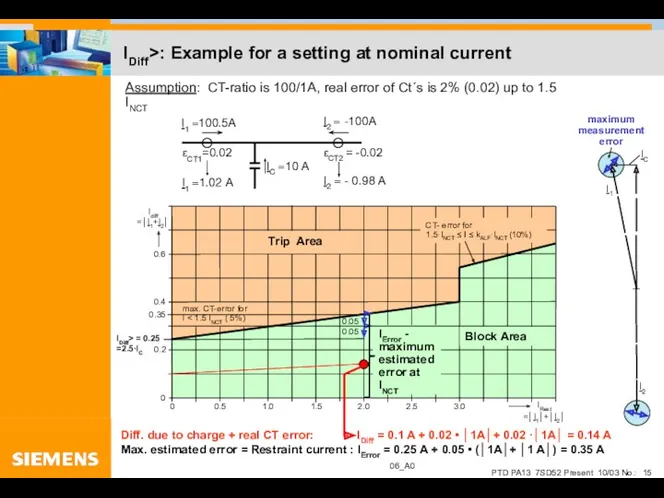
- 15. IDiff>: Example for a setting at nominal current
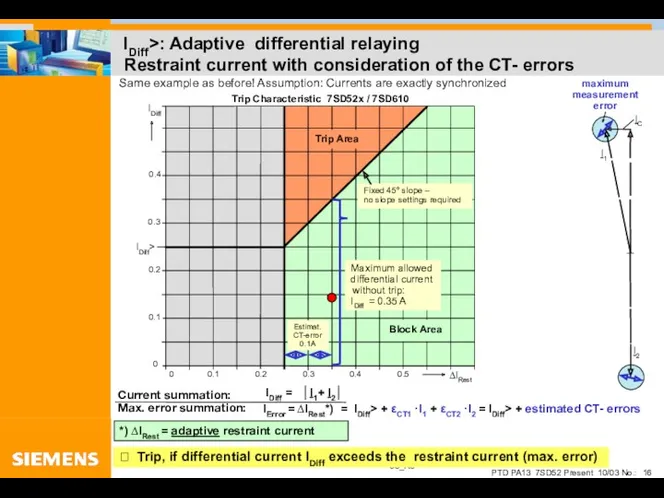
- 16. IDiff>: Adaptive differential relaying Restraint current with consideration of the CT- errors
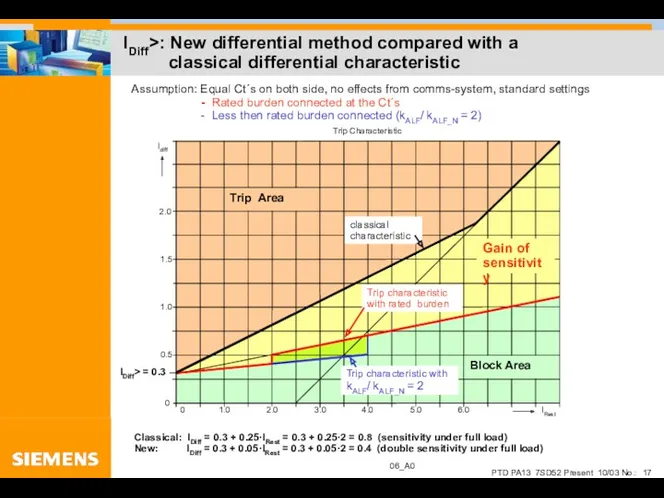
- 17. IDiff>: New differential method compared with a classical differential characteristic
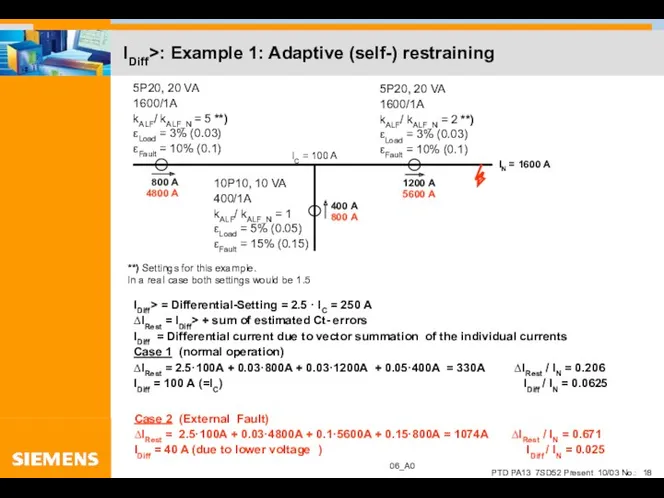
- 18. IDiff>: Example 1: Adaptive (self-) restraining
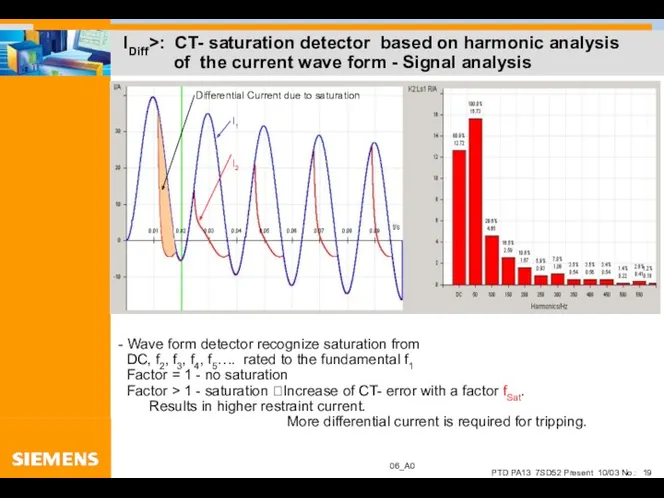
- 19. IDiff>: CT- saturation detector based on harmonic analysis of the current wave form - Signal analysis
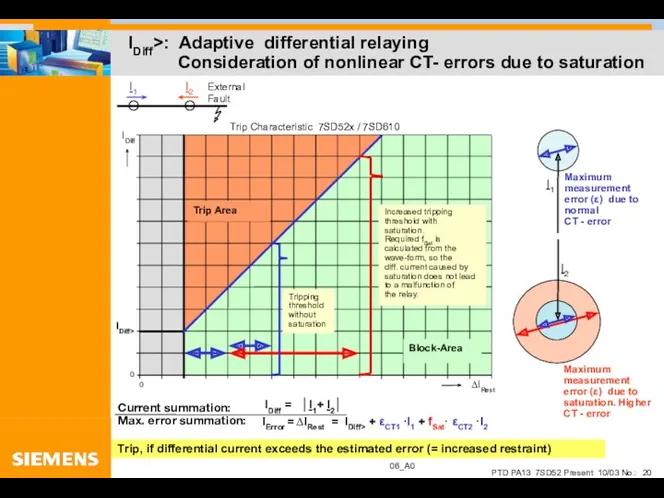
- 20. IDiff>: Adaptive differential relaying Consideration of nonlinear CT- errors due to saturation
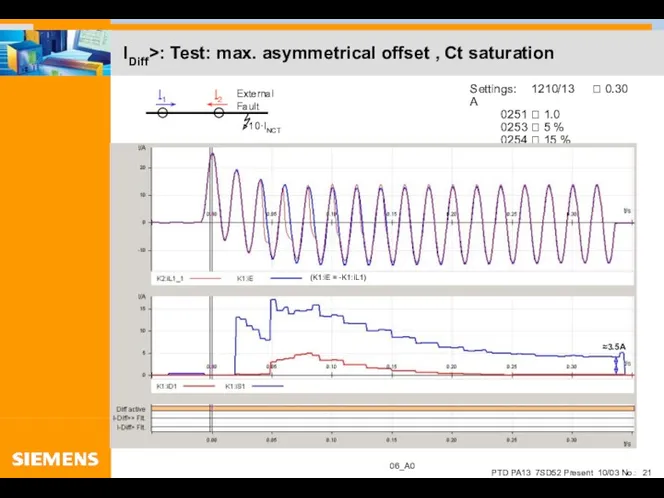
- 21. IDiff>: Test: max. asymmetrical offset , Ct saturation
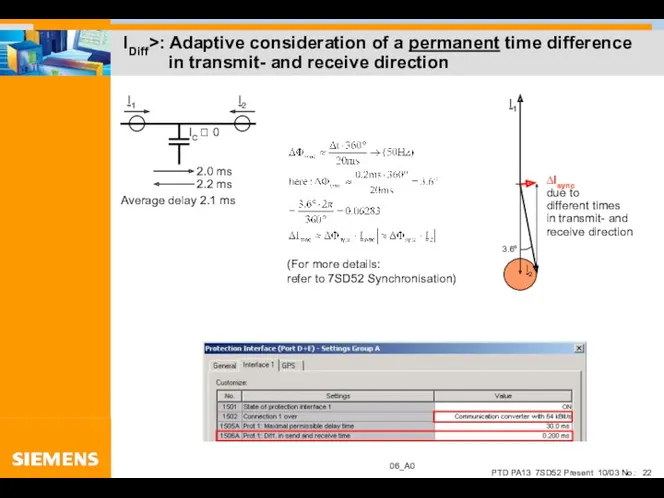
- 22. IDiff>: Adaptive consideration of a permanent time difference in transmit- and receive direction
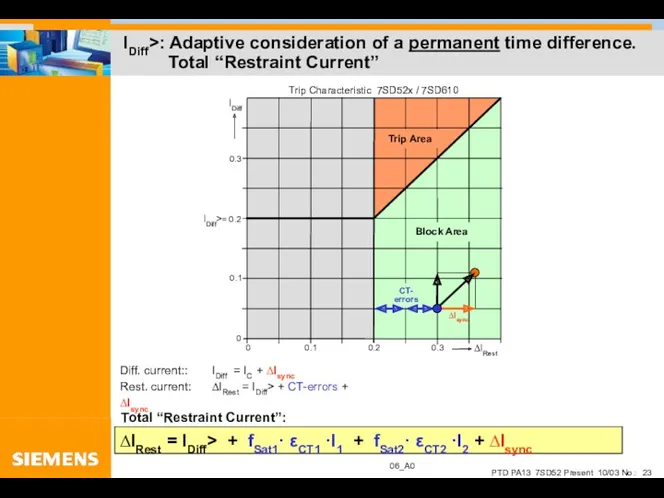
- 23. IDiff>: Adaptive consideration of a permanent time difference. Total “Restraint Current”
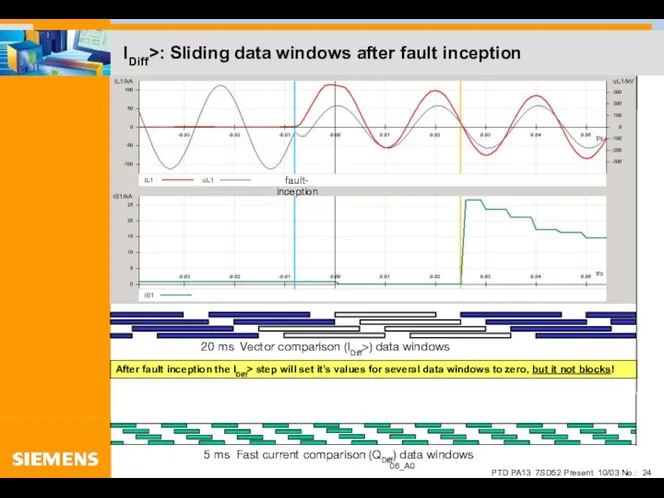
- 24. IDiff>: Sliding data windows after fault inception
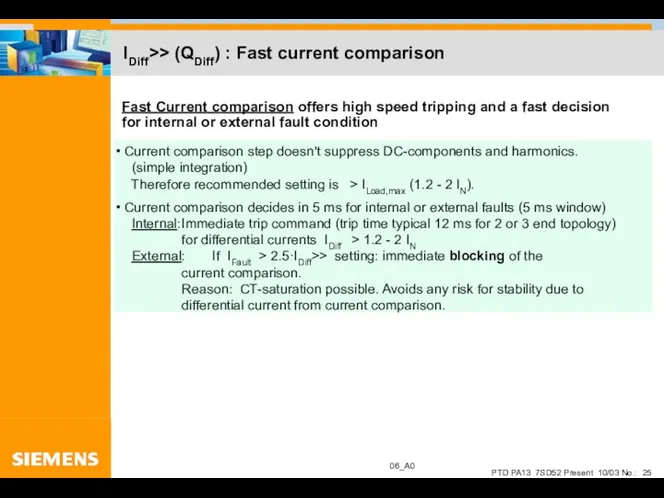
- 25. IDiff>> (QDiff) : Fast current comparison
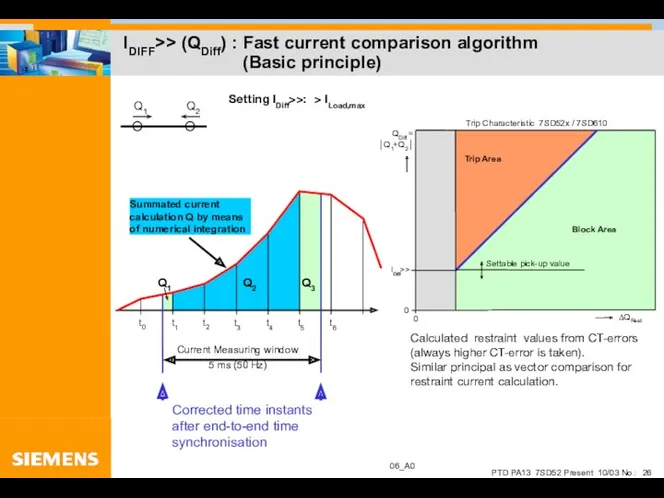
- 26. IDIFF>> (QDiff) : Fast current comparison algorithm (Basic principle)
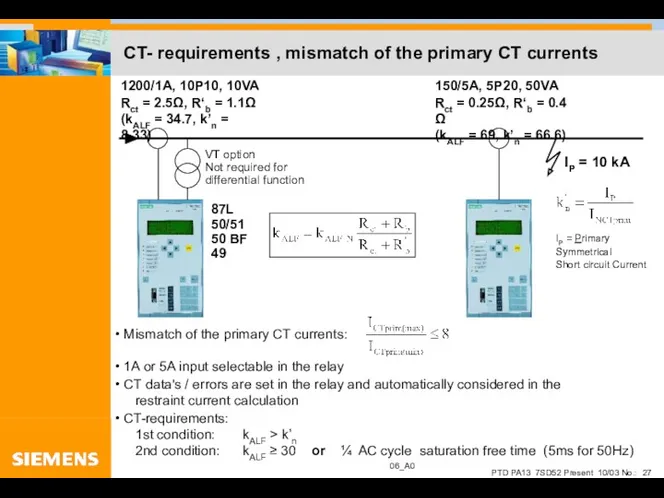
- 27. CT- requirements , mismatch of the primary CT currents
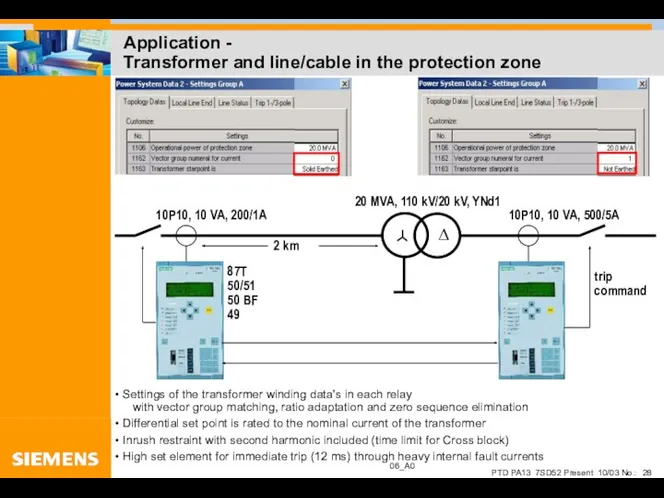
- 28. Application - Transformer and line/cable in the protection zone
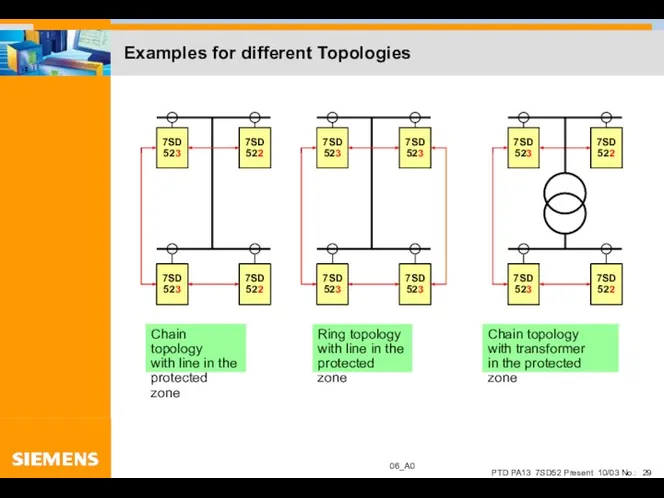
- 29. Examples for different Topologies
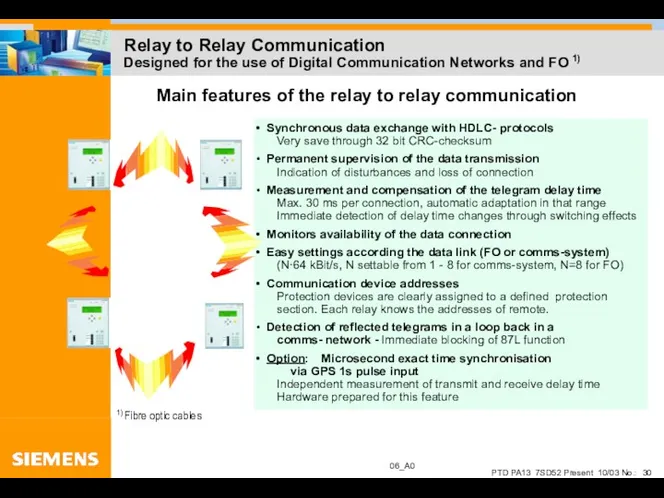
- 30. Relay to Relay Communication Designed for the use of Digital Communication Networks and FO 1) Main
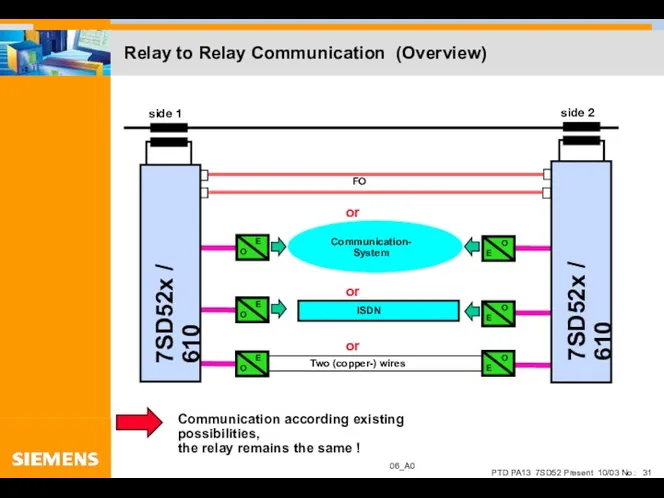
- 31. Relay to Relay Communication (Overview)
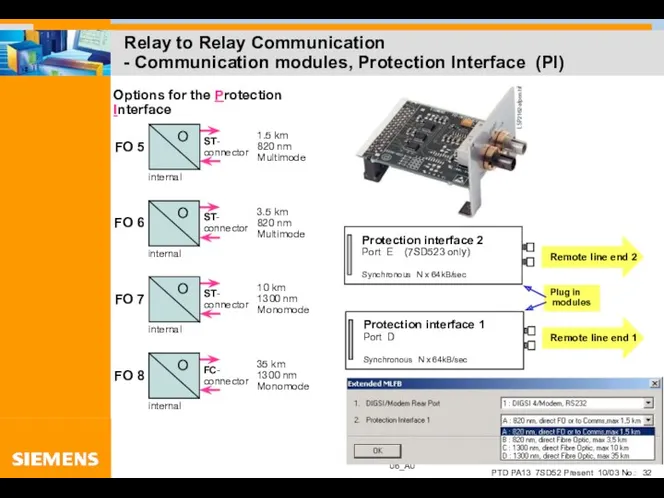
- 32. Relay to Relay Communication - Communication modules, Protection Interface (PI)
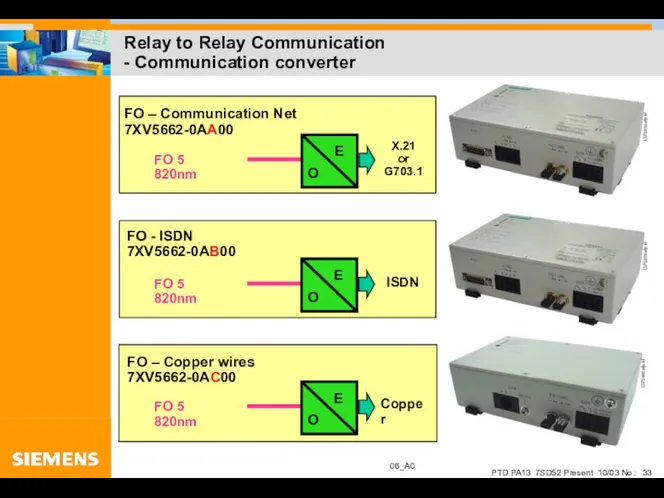
- 33. Relay to Relay Communication - Communication converter
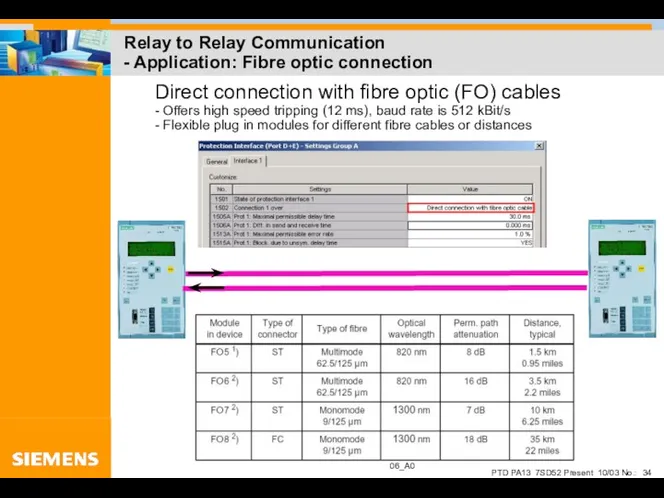
- 34. Relay to Relay Communication - Application: Fibre optic connection
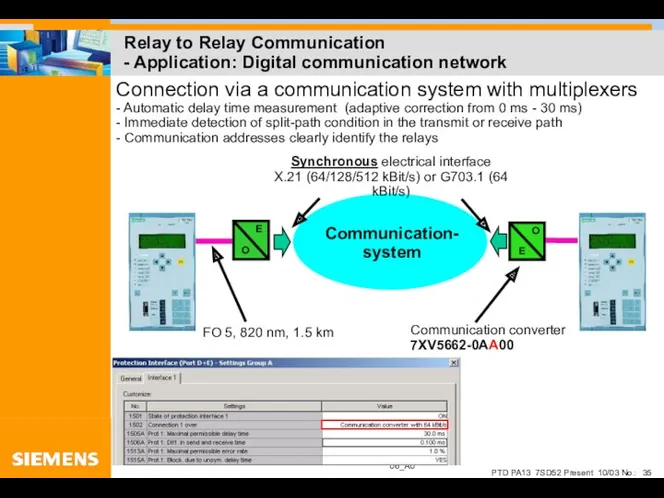
- 35. Relay to Relay Communication - Application: Digital communication network
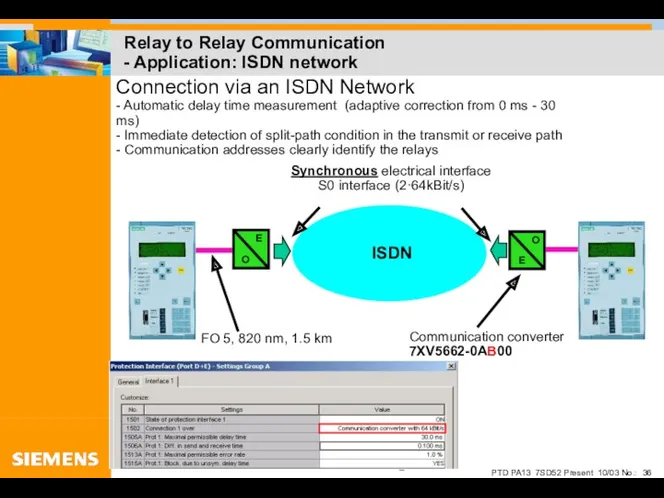
- 36. Relay to Relay Communication - Application: ISDN network
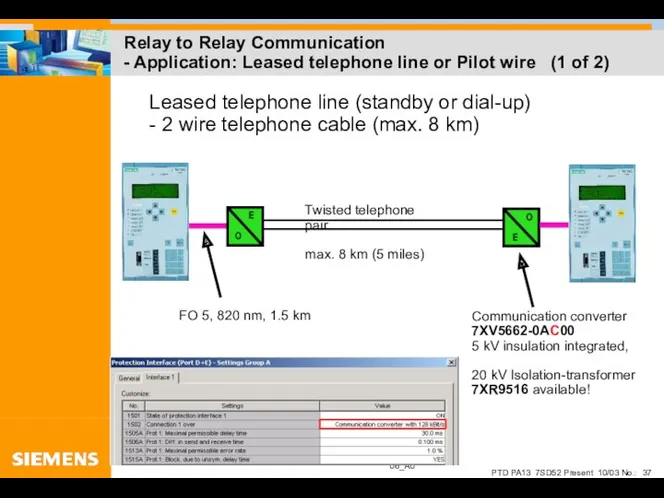
- 37. Relay to Relay Communication - Application: Leased telephone line or Pilot wire (1 of 2)
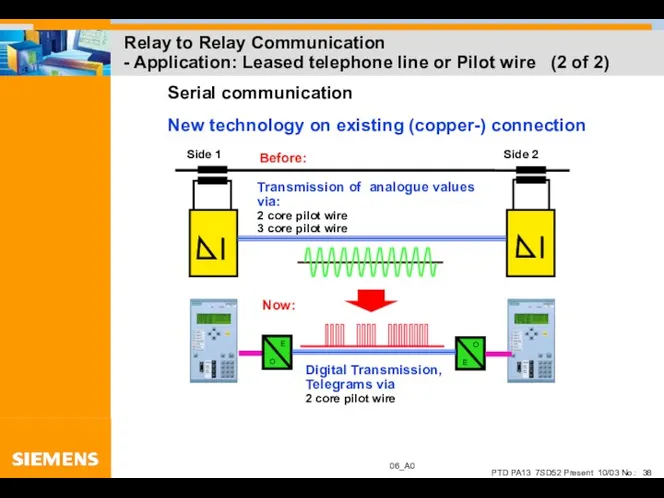
- 38. Relay to Relay Communication - Application: Leased telephone line or Pilot wire (2 of 2)
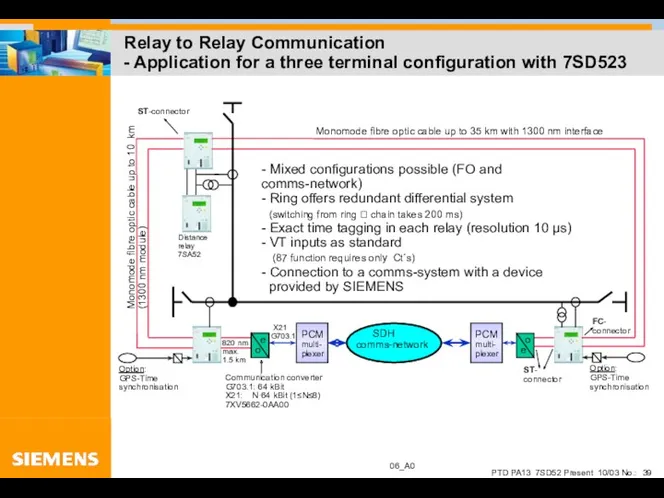
- 39. Relay to Relay Communication - Application for a three terminal configuration with 7SD523
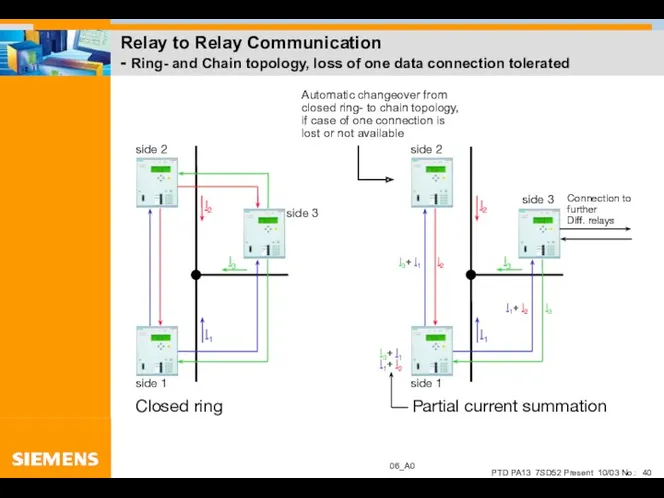
- 40. Relay to Relay Communication - Ring- and Chain topology, loss of one data connection tolerated
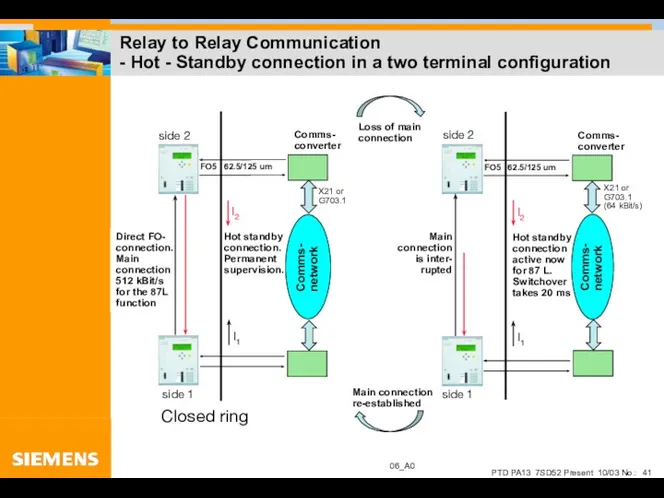
- 41. Relay to Relay Communication - Hot - Standby connection in a two terminal configuration
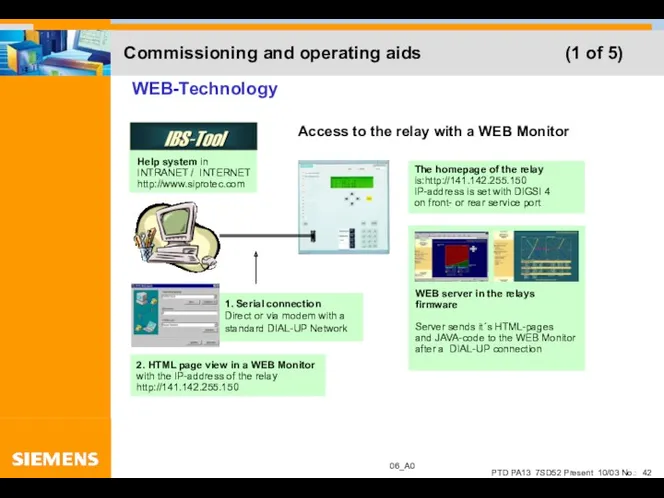
- 42. Commissioning and operating aids (1 of 5)
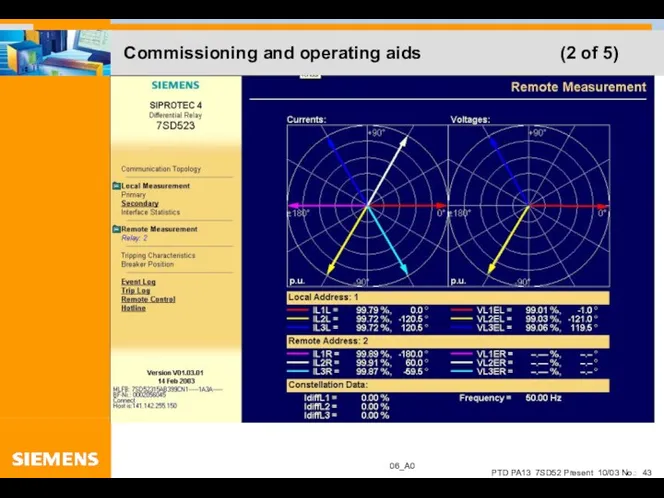
- 43. Commissioning and operating aids (2 of 5)
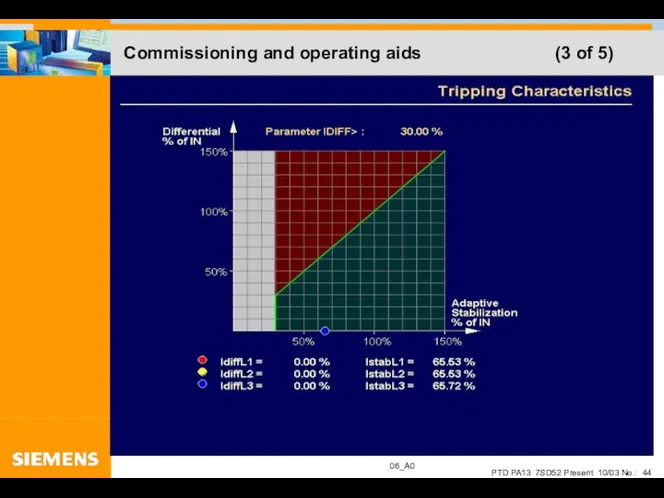
- 44. Commissioning and operating aids (3 of 5)
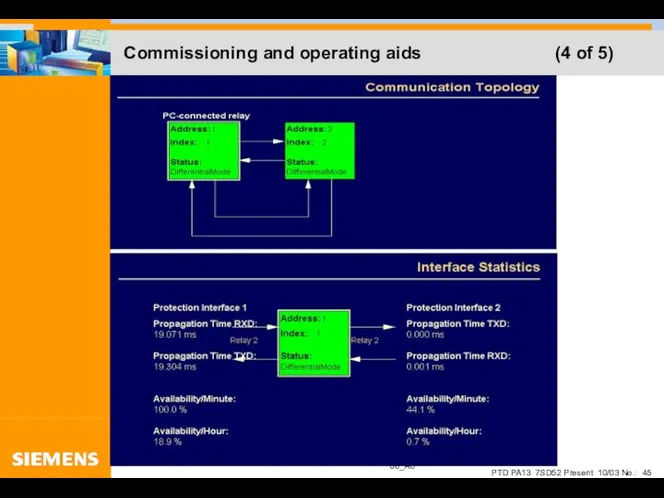
- 45. Commissioning and operating aids (4 of 5)
- 47. Скачать презентацию


 ОВПФ классификация ГОСТ
ОВПФ классификация ГОСТ Действия солдата в обороне. Выбор, оборудование и занятие места (окопа) для стрельбы. Тема 5,3
Действия солдата в обороне. Выбор, оборудование и занятие места (окопа) для стрельбы. Тема 5,3 Образование славянских государств
Образование славянских государств Школы здоровья. Концепция. Цели, направления работы
Школы здоровья. Концепция. Цели, направления работы Оптимизация системы водоснабжения г. Шахтерск
Оптимизация системы водоснабжения г. Шахтерск Mechanical engineering in Kazakhstan
Mechanical engineering in Kazakhstan Цифровой диктант
Цифровой диктант Родовые понятия и методологические основания социологии Эмиля Дюркгейма в цитатах
Родовые понятия и методологические основания социологии Эмиля Дюркгейма в цитатах Гостиная. Спальня. Лоджии. Прихожая
Гостиная. Спальня. Лоджии. Прихожая Борьба с коррупцией в истории России
Борьба с коррупцией в истории России Применение технологии развития критического мышления на уроках английского языка
Применение технологии развития критического мышления на уроках английского языка класный час Что?Где?Когда?
класный час Что?Где?Когда? Видимое движение планет
Видимое движение планет Основные законы в химии
Основные законы в химии Презентация дидактических игр к НОД Семена и условия их прорастания
Презентация дидактических игр к НОД Семена и условия их прорастания Анатомически и клинически узкий таз у женщины
Анатомически и клинически узкий таз у женщины Патология терморегуляции
Патология терморегуляции Телеконтакт. Мы делаем всё, что вы когда - либо слышали про контакт - центры!
Телеконтакт. Мы делаем всё, что вы когда - либо слышали про контакт - центры! Веб-сервис для анализа сигналов на основе вейвлет-нейронной сети
Веб-сервис для анализа сигналов на основе вейвлет-нейронной сети Памятка родителю от ребёнка
Памятка родителю от ребёнка Аппликация Птица - весна
Аппликация Птица - весна Эволюция концепций управления. Периодизация этапов развития управленческой мысли
Эволюция концепций управления. Периодизация этапов развития управленческой мысли Вазоконстрикторы и антигипотензивные средства
Вазоконстрикторы и антигипотензивные средства Обеспечение успешной адаптации учащихся 5 класса
Обеспечение успешной адаптации учащихся 5 класса Россия в Первой мировой войне
Россия в Первой мировой войне Всё обо мне
Всё обо мне Занятие 4. Массивы
Занятие 4. Массивы Презентация к занятию История создания сотового телефона
Презентация к занятию История создания сотового телефона