x
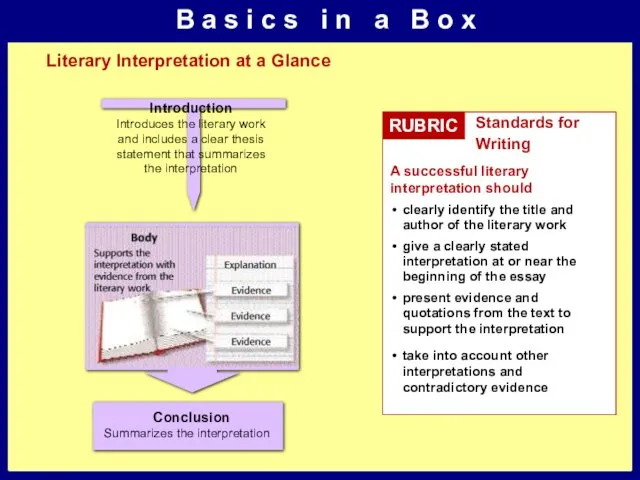
Literary Interpretation at a Glance
RUBRIC
Standards for Writing
A successful literary interpretation should
clearly identify the title and author of the literary work
give a clearly stated interpretation at or near the beginning of the essay
present evidence and quotations from the text to support the interpretation
take into account other interpretations and contradictory evidence
Introduces the literary work and includes a clear thesis statement that summarizes the interpretation
Introduction
Summarizes the interpretation
Conclusion









 Источник 1 (глаголь22.рф)
Источник 1 (глаголь22.рф) Область познания-экспериментирование
Область познания-экспериментирование Алгоритм решения генетических задач
Алгоритм решения генетических задач Көбіктер және оларды алу әдістері
Көбіктер және оларды алу әдістері Социально-педагогические технологии консультирования
Социально-педагогические технологии консультирования моя презентация
моя презентация Родительское собрание на тему ФГОСы
Родительское собрание на тему ФГОСы Наглядное пособие
Наглядное пособие Цифровые комбинационные устройства. Тема 4.2
Цифровые комбинационные устройства. Тема 4.2 Дети и война
Дети и война Морфологический анализ слова
Морфологический анализ слова Программы и фонды для мероприятия
Программы и фонды для мероприятия Обоснование параметров и разработка технических средств и технологии бурения направленных скважин из горных выработок
Обоснование параметров и разработка технических средств и технологии бурения направленных скважин из горных выработок Презентация к вводному занятию Волшебная страна бисера.
Презентация к вводному занятию Волшебная страна бисера. Самостійна робота учнів - засіб розвитку пізнавальної активності і творчого мислення
Самостійна робота учнів - засіб розвитку пізнавальної активності і творчого мислення Кәмпит бұл-қанттан
Кәмпит бұл-қанттан Сказка о том, как Лягушонок научился гудеть, как пароход. Постановка и автоматизация звука [Ы]
Сказка о том, как Лягушонок научился гудеть, как пароход. Постановка и автоматизация звука [Ы] What is Marketing Management?
What is Marketing Management? Реализация мероприятий в области информационных технологий
Реализация мероприятий в области информационных технологий Речевые игры для детей от 3-х лет.
Речевые игры для детей от 3-х лет. Виниловые обои
Виниловые обои презентация Службы района
презентация Службы района Keys_Poklevochka_1
Keys_Poklevochka_1 Синичкин день. Народный календарь.
Синичкин день. Народный календарь. Применение данных каротажа в процессе бурения с использованием комплексных приборов LWD121-2ННК-ГГКЛП и LWD172-2ННК-ГГКЛП-3Г
Применение данных каротажа в процессе бурения с использованием комплексных приборов LWD121-2ННК-ГГКЛП и LWD172-2ННК-ГГКЛП-3Г Страшный суд
Страшный суд Назначение и устройство токарно-винторезного станка ТВ-6
Назначение и устройство токарно-винторезного станка ТВ-6 Проблемы российского образования в современных условиях
Проблемы российского образования в современных условиях