Содержание
- 2. Aim To separate and identify some common cations present in an inorganic mixture of salts by
- 3. Materials and Tools Required Test tubes Boiling tubes Test tube holder Test tube stand Flame Reagents
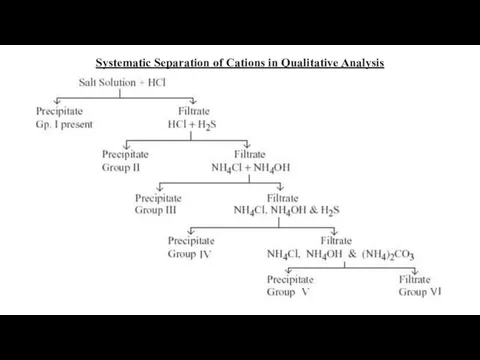
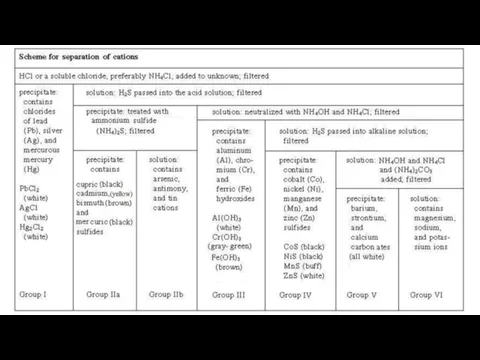
- 4. Group I Cations (Ag+, Hg22+ and Pb2+) Reagent : dil. HCl Cations form insoluble chlorides with
- 5. Group II Cations IIA: (Hg2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, Bi3+) IIB: (As3+, Sb3+ and As5+) Reagent : dil.
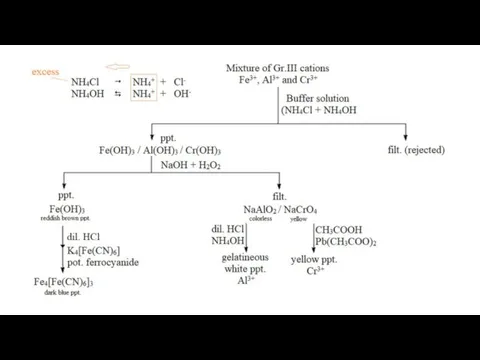
- 6. Group III Cations (Al3+, Fe3+, Fe2+ and Cr3+) Reagent : (NH4Cl + NH4OH) = Buffer solution
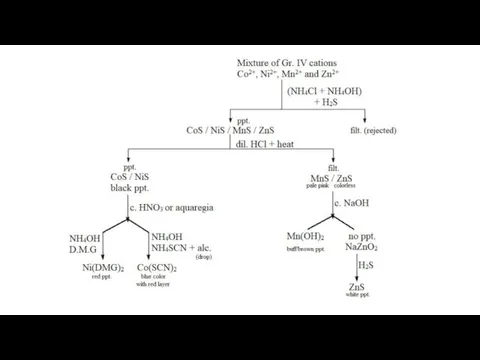
- 7. Group IV Cations (Co2+, Ni2+, Zn2+ and Mn2+) Reagent : (NH4Cl + NH4OH) + H2S After
- 8. Group V Cations (Ca2+ Sr2+ and Ba2+) Reagent : (NH4Cl + NH4OH) + (NH4)2CO3 These three
- 9. Group VI Cations (NH4+, Mg2+, K+ and Na+) No specific reagent None of the cations in
- 11. Systematic Separation of Cations in Qualitative Analysis
- 22. Скачать презентацию















 Анализ анекдотов на тему работы системы здравоохранения
Анализ анекдотов на тему работы системы здравоохранения Новый порядок заключения контрактов по результатам электронных процедур в соответствии со статьей 83.2 Закона № 44-ФЗ
Новый порядок заключения контрактов по результатам электронных процедур в соответствии со статьей 83.2 Закона № 44-ФЗ Сварочные материалы применяемые для сварки
Сварочные материалы применяемые для сварки Культура детско-родительских отношений в роду
Культура детско-родительских отношений в роду Сестринское сопровождение детей первого года жизни
Сестринское сопровождение детей первого года жизни Страхование ответственности за загрязнение окружающей среды (экологическое страхование) в России и за рубежом
Страхование ответственности за загрязнение окружающей среды (экологическое страхование) в России и за рубежом Толеран – очищувальний крем-гель
Толеран – очищувальний крем-гель Экономика и государство
Экономика и государство Влияние пищевых добавок на организм человека
Влияние пищевых добавок на организм человека Летите голуби, летите . Кроссворд
Летите голуби, летите . Кроссворд Путешествие в сказочную страну
Путешествие в сказочную страну Технология и конструкции подвески хвостовика
Технология и конструкции подвески хвостовика Паронимы. Разграничение паронимов и омонимов
Паронимы. Разграничение паронимов и омонимов Восстановление энергии из органических отходов путем газификации
Восстановление энергии из органических отходов путем газификации Спутниковая связь
Спутниковая связь Гранд Макет Россия
Гранд Макет Россия Блюда из нерыбных продуктов моря
Блюда из нерыбных продуктов моря Салют Победы. Урок рисования. Практическая работа
Салют Победы. Урок рисования. Практическая работа Коррупция
Коррупция Знатоки флоры Приморского края. Интерактивная игра.
Знатоки флоры Приморского края. Интерактивная игра. Цветы
Цветы Электрические машины переменного тока
Электрические машины переменного тока Романтизм
Романтизм Наречие как часть речи (урок русского языка в 7 классе)
Наречие как часть речи (урок русского языка в 7 классе) Работа с бумагой и картоном. Светофор.
Работа с бумагой и картоном. Светофор. Предварительное расследование. Уголовный процесс
Предварительное расследование. Уголовный процесс Предохранительные устройства 1-го контура (ИПУ КД)
Предохранительные устройства 1-го контура (ИПУ КД) Презентация2
Презентация2