Слайд 2

Muscle tissue satisfy requirement of the body in movement.
Слайд 3
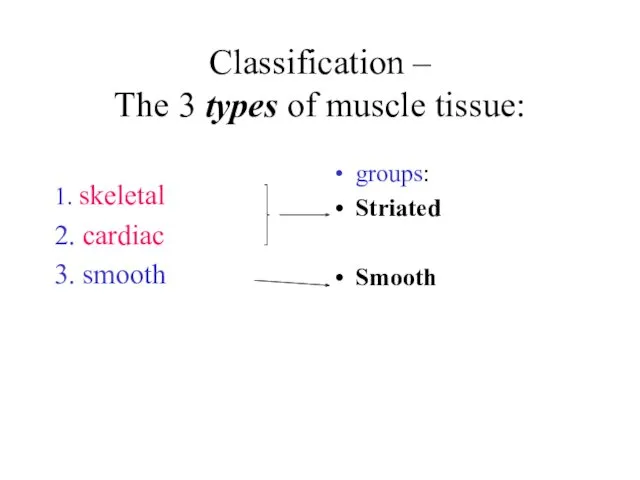
Classification –
The 3 types of muscle tissue:
1. skeletal
2. cardiac
3.
smooth
groups:
Striated
Smooth
Слайд 4

Why do muscles contract?
Muscle cells have contractile proteins -
actin and
myosin,
and some another .
The interaction of actin and myosin mediates the contraction of muscle cells.
Слайд 5

Why do muscles contract?
Actin and myosin form myofilaments:
Myosin - thick, dark
and Anisotropic (A)
Actin – thin, light and Isotropic (I)
Actin and myosin form special organelles – myofibrils, responsible for muscle contraction.
Слайд 6

Слайд 7

Locations: walls of visceral hollow organs
(stomach).
Functions: involuntary movement
--
(peristaltics)
(The innervation -- by autonomic nervous system)
Слайд 8
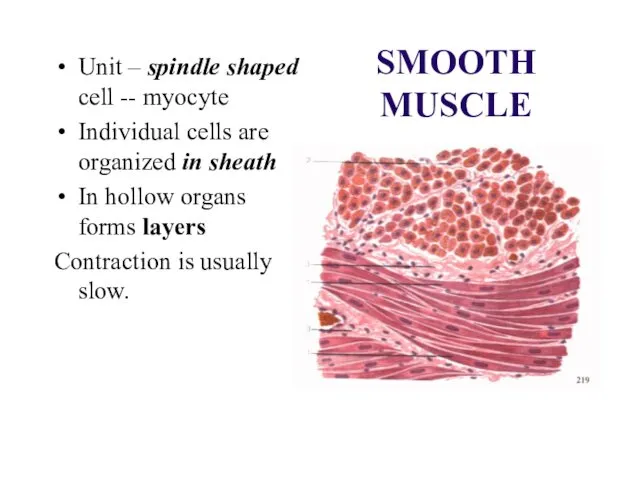
SMOOTH MUSCLE
Unit – spindle shaped cell -- myocyte
Individual cells are organized
in sheath
In hollow organs forms layers
Contraction is usually slow.
Слайд 9

Origin of smooth muscle
Smooth muscle cells arise from mesenchymal cells.
Слайд 10

Слайд 11

See: regular organization of the myofibrils gives rise to the cross-striation,
which characterises skeletal and cardiac muscle.
Слайд 12
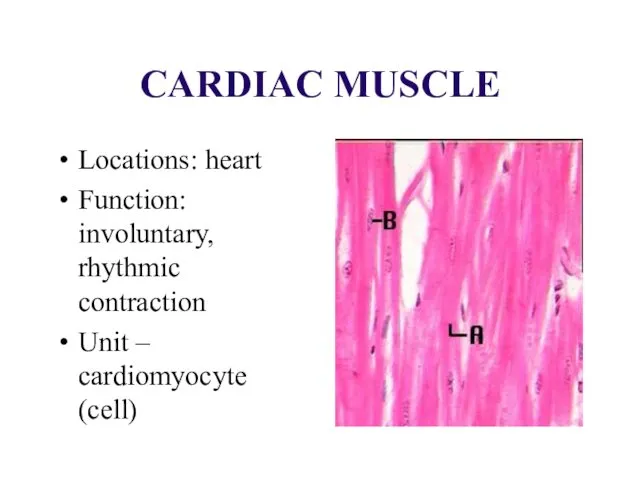
CARDIAC MUSCLE
Locations: heart
Function: involuntary, rhythmic contraction
Unit – cardiomyocyte (cell)
Слайд 13

Cardiac muscle cells:
3 types:
Contractile,
Conducting
Secretory
Слайд 14
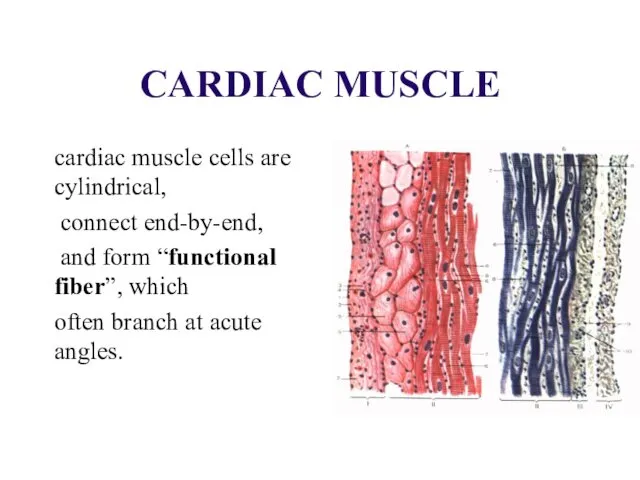
CARDIAC MUSCLE
cardiac muscle cells are cylindrical,
connect end-by-end,
and
form “functional fiber”, which
often branch at acute angles.
Слайд 15
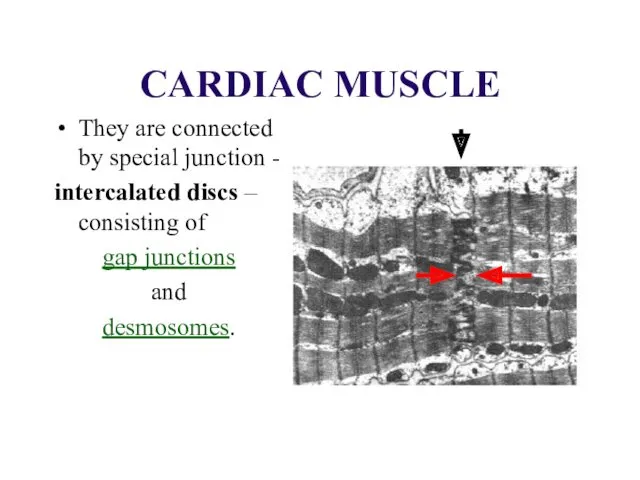
CARDIAC MUSCLE
They are connected by special junction -
intercalated discs
– consisting of
gap junctions
and
desmosomes.
Слайд 16
Слайд 17

Слайд 18
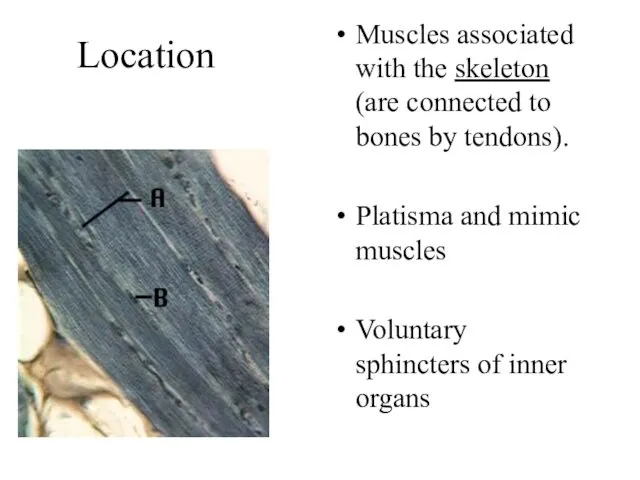
Location
Muscles associated with the skeleton (are connected to bones by tendons).
Platisma and mimic muscles
Voluntary sphincters of inner organs
Слайд 19

SKELETAL MUSCLE
--- is innervated by the somatic nervous system – voluntary!!
---- consists of very long tubular cells (also called muscle fibres).
Слайд 20

SKELETAL MUSCLE
Skeletal muscle fibers run the full length of a muscle.
The average length of skeletal muscle cells in humans is about 3 cm (sartorius muscle up to 30 cm, stapedius muscle only about 1 mm). Their diameters vary from 10 to 100 µm.
Слайд 21
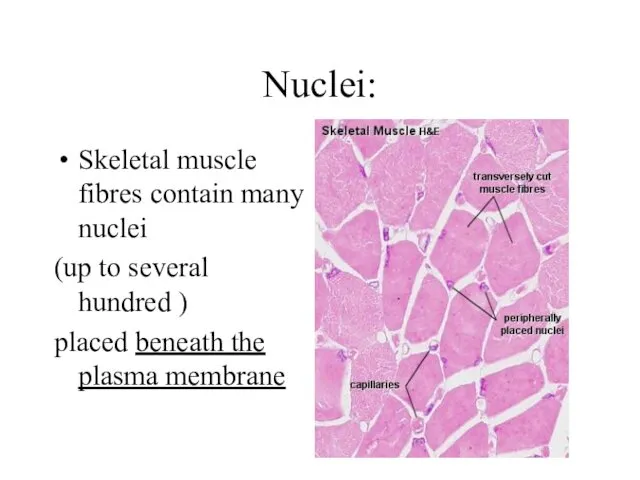
Nuclei:
Skeletal muscle fibres contain many nuclei
(up to several hundred )
placed
beneath the plasma membrane
Слайд 22
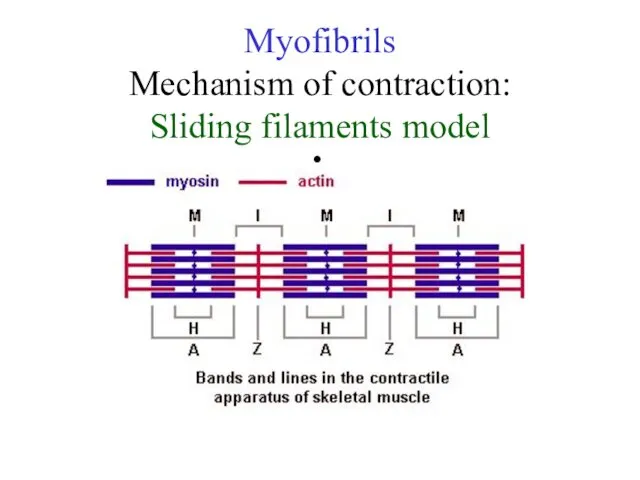
Myofibrils
Mechanism of contraction:
Sliding filaments model
Слайд 23

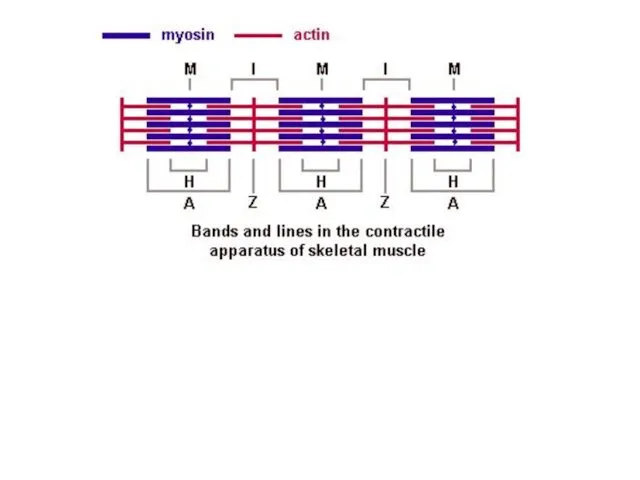
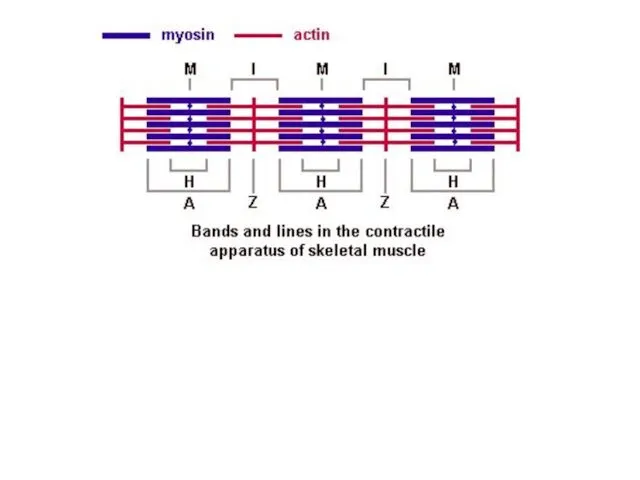
Myofibrils has some bands and lines depending on the distribution and
interconnection of myofilaments -- :
I-band - actin filaments only,
A-band - myosin filaments which may overlap with actin filaments
T or Z-line -- band of connections between actin filaments; zone of apposition of actin filaments belonging to two neighboring sarcomeres;
M-line - band of connections between myosin filaments.
H-band - zone of myosin filaments only (no overlap with actin filaments) within the A-band
Слайд 24
Слайд 25
Слайд 26

Sarcomeres --
are parts, smallest contractile units of myofibrils.
Sarcomere formula:
S =
½ I + A + ½ I
Слайд 27

Sarcomere formula after contraction
S = A
(- ½ I, - ½ I,
- H)
Слайд 28

Слайд 29

Origin of skeletal muscle
The myoblasts of all skeletal muscle fibres originate
from the paraxial mesoderm - myotome.
Слайд 30

1. Myoblasts undergo frequent divisions and coalesce with the formation of
a multinucleated, syncytial muscle fibre or myotube. The nuclei of the myotube are still located centrally in the muscle fibre.
2. In the course of the synthesis of the myofilaments and myofibrils, the nuclei are gradually displaced to the periphery of the cell.





























 Красота в искусстве и жизни
Красота в искусстве и жизни Пп Егoр
Пп Егoр 10 важных навыков для работы будущего
10 важных навыков для работы будущего Синтетические противомикробные средства
Синтетические противомикробные средства Физико-математические аспекты нефтегазового дела
Физико-математические аспекты нефтегазового дела Презентация День Победы
Презентация День Победы 20231025_prezentatsiya_po_obshchestvoznaniyu_na_temu_chelovek_i_ego_deyatelnost_6_klass
20231025_prezentatsiya_po_obshchestvoznaniyu_na_temu_chelovek_i_ego_deyatelnost_6_klass Говорящие фамилии в произведениях
Говорящие фамилии в произведениях Тобольский гений России.- презентация
Тобольский гений России.- презентация Сварочные материалы
Сварочные материалы Танцы народов мира.
Танцы народов мира. Модерн в архитектуре
Модерн в архитектуре Измеряй на свой аршин.
Измеряй на свой аршин. 20200108_prezentatsiya_k_zanyatiyu
20200108_prezentatsiya_k_zanyatiyu Проектирование и эксплуатация газонефтепроводов (часть 1)
Проектирование и эксплуатация газонефтепроводов (часть 1) Программирование на языке Паскаль. Символьные строки
Программирование на языке Паскаль. Символьные строки Государственные скрининговые программы по раннему выявлению онкопатологии репродуктивной системы
Государственные скрининговые программы по раннему выявлению онкопатологии репродуктивной системы Traditions of America
Traditions of America Камины и печи. Балконы, эркеры. Окна, двери
Камины и печи. Балконы, эркеры. Окна, двери Всемирный день борьбы со СПИДом
Всемирный день борьбы со СПИДом Class Lobosa – amoebas, amibes Order
Class Lobosa – amoebas, amibes Order Сверление. Механизированное и ручное оборудование для сверления
Сверление. Механизированное и ручное оборудование для сверления Технологическое производство и методы получение белково-витаминных концентратов
Технологическое производство и методы получение белково-витаминных концентратов презентация для самообразования учителей о Кембриджской Программе внедрения семи модулей, как Новых подходах в воспитании и обучении детей.
презентация для самообразования учителей о Кембриджской Программе внедрения семи модулей, как Новых подходах в воспитании и обучении детей. Тульская городская игрушка
Тульская городская игрушка Презентация ДЕТИ ГОВОРЯТ ТЕЛЕФОНУ ДОВЕРИЯ ДА! май 2014
Презентация ДЕТИ ГОВОРЯТ ТЕЛЕФОНУ ДОВЕРИЯ ДА! май 2014 Обобщение опыта работы по социально-коммуникативному развитию дошкольников.
Обобщение опыта работы по социально-коммуникативному развитию дошкольников. Внутренняя политика Александра III (1981-1894)
Внутренняя политика Александра III (1981-1894)